A Simple in Syringe Low Density Solvent-Dispersive Liquid Liquid Microextraction for Enrichment of Some Metal Ions Prior to Their Determination by High Performance Liquid Chromatography in Food Samples
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Separation of Metal–PDC Complexes by HPLC
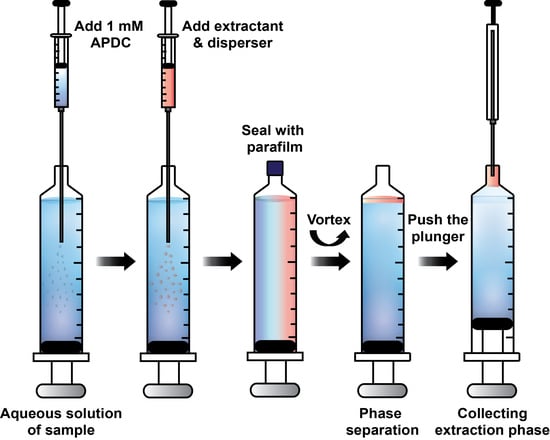
2.2. In Syringe Low Density Solvent-Dispersive Liquid Liquid Microextraction (ISLD-DLLME)
2.2.1. The Effect of pH
2.2.2. Effect of Types and Volume of the Extraction Solvent
2.2.3. Effect of Types and Volume of the Dispersive Solvent
2.2.4. Effect of Salt Addition
2.2.5. Effect of Vortex Time
2.2.6. Analytical Features
2.2.7. Interference Studies
2.2.8. Analysis of Samples
3. Experimental
3.1. Chemicals and Solutions
3.2. Instrumentations
3.3. In Syringe Low Density Solvent-Dispersive Liquid Liquid Microextraction (ISLD-DLLME)
3.4. Liquid Chromatography
3.5. Sample Preparation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tchounwou, P.B.; Yedjou, C.G.; Patlolla, A.K.; Sutton, D.J. Heavy Metal Toxicity and the Environment. Natl. Inst. Health 2012, 101, 133–164. [Google Scholar]
- Shrivas, K.; Dewangan, K.; Ahmed, A. Surfactant-based dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction for the determination of zinc in environmental water samples using flame atomic absorption spectrometry. Anal. Methods 2016, 8, 5519–5525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakanupongkul, A.; Sananmuang, R.; Udnan, Y.; Ampiah-Bonney, R.J.; Chaiyasith, W.C. Speciation of mercury in water and freshwater fish samples by a two-step solidified floating organic drop microextraction with electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry. Food Chem. 2019, 277, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikuła, B.; Puzio, B. Determination of trace metals by ICP-OES in plant materials after preconcentration of 1,10-phenanthroline complexes on activated carbon. Talanta 2007, 71, 136–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çelik, I.; Kara, D.; Karadaş, C.; Fisher, A.; Hill, S.J. A novel ligand less-dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction method for matrix elimination and the preconcentration of rare earth elements from natural waters. Talanta 2015, 134, 476–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, S.; Zhu, F.; Zhao, X.; Yang, H.; Chen, X. A reusable P, N-doped carbon quantum dot fluorescent sensor for cobalt ion. Sens. Actuator B: Chem. 2018, 260, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, Z.; Wang, L.; Gao, H.; Xue, Y.; Lou, X. Task-specific ionic liquid-enabled mercury sensor for sensitive detection of total mercury in food digestion solution. Sens. Actuator B: Chem. 2019, 285, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gettar, R.T.; Garavaglia, R.N.; Gautier, E.A.; Batistoni, D.A. Determination of inorganic and organic anionic arsenic species in water by ion chromatography coupled to hydride generation–inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2000, 884, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassileva, E.; Becker, A.; Broekaert, J.A.C. Determination of arsenic and selenium species in groundwater and soil extracts by ion chromatography coupled to inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2001, 441, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proch, J.; Niedzielski, P. In–spray chamber hydride generation by multi–mode sample introduction system (MSIS) as an interface in the hyphenated system of high performance liquid chromatography and inductivity coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry (HPLC/HG–ICP–OES) in arsenic species determination. Talanta 2020, 208, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Bezerra, M.A.; dos Santos, W.N.L.; Lemos, V.A.; Korn, M.d.G.A.; Ferreira, S.L.C. On-line system for preconcentration and determination of metals in vegetables by inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 148, 334–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozdemir, S.; Kilinc, E.; Oner, E.T. Preconcentrations and determinations of copper, nickel and lead in baby food samples employing Coprinus silvaticus immobilized multi-walled carbon nanotube as solid phase sorbent. Food Chem. 2019, 276, 174–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (ATSDR). Toxicological Profile for Cobalt. Public Health Service. Available online: https://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/toxprofiles/tp.asp?id=373&tid=64 (accessed on 27 April 2004).
- Guertin, J.; Jacobs, J.A.; Avakian, C.P. Overview of chromium(VI) in the environment: Background and history. In Chromium (VI) Handbook; CRC Press Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, America, 2005; pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Jarüp, L. Hazards of heavy metal contamination. Br. Med. Bull. 2003, 68, 167–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- USDA Foreign Agricultural Service, China, Peoples Republic of FAIRS Product Specific. Maximum Levels of Contaminants in Foods. Available online: https://apps.fas.usda.gov/gainfiles/200608/146208660.pdf (accessed on 12 November 2014).
- Coulibaly, M.; Bamba, D.; Yao, N.A.; Zoro, E.G.; El Rhazi, M. Some aspects of speciation and reactivity of mercury in various matrices. Comptes. Rendus. Chim. 2016, 19, 832–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization GEMS/Food-EURO second workshop on reliable evaluation of low-level contamination of food. Available online: http://www.who.int/foodsafety/publications/chem/en/lowlevel_may1995.pdf (accessed on 26 May 1995).
- Ryu, K.Y.; Lee, S.Y.; Park, D.Y.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, C. A novel colorimetric chemosensor for detection of Co2+ and S2− in an aqueous environment. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 242, 792–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocúrová, L.; Balogh, I.S.; Nagy, L.; Billes, F.; Simon, A.; Andruch, V. Application of a bisindocarbocyanine reagent for dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction of silver with subsequent spectrophotometric determination. Microchem. J. 2011, 99, 514–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajid, M. Dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction coupled with derivatization: A review of different modes, applications, and green aspects. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 106, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaiyamate, P.; Seebunrueng, K.; Srijaranai, S. Vortex-assisted low density solvent and surfactant based dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction for sensitive spectrophotometric determination of cobalt. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 7243–7251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Werner, J. Ionic liquid ultrasound-assisted dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction based on solidification of the aqueous phase for preconcentration of heavy metals ions prior to determination by LC-UV. Talanta 2018, 182, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalbani, N.; Soylak, M. Separation-preconcentration of nickel and lead in food samples by a combination of solid-liquid-solid dispersive extraction using SiO2 nanoparticles, ionic liquid-based dispersive liquid-liquid micro-extraction. Talanta 2015, 131, 361–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Ma, X. Speciation analysis of mercury in water samples using dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction combined with high-performance liquid chromatography. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 702, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Płotka-Wasylka, J.; Rutkowska, M.; Owczarek, K.; Tobiszewski, M.; Namieśnik, J. Extraction with environmentally friendly solvents. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2017, 91, 12–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadfarnia, S.; Shabani, A.M.H. Recent development in liquid phase microextraction for determination of trace level concentration of metals—A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 658, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Shahawi, M.S.; Al-Saidi, H.M. Dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction for chemical speciation and determination of ultra-trace concentrations of metal ions. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2013, 44, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seebunrueng, K.; Dejchaiwatana, C.; Santaladchaiyakit, Y.; Srijaranai, S. Development of supramolecular solvent based microextraction prior to high performance liquid chromatography for simultaneous determination of phenols in environmental water. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 50143–50149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seebunrueng, K.; Santaladchaiyakit, Y.; Srijaranai, S. Vortex-assisted low density solvent liquid–liquid microextraction and salt-induced demulsification coupled to high performance liquid chromatography for the determination of five organophosphorus pesticide residues in fruits. Talanta 2015, 132, 769–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakhaei, J.M.; Jamali, M.R.; Sohrabnezhad, S.; Rahnama, R. In-syringe solvent-assisted dispersive solid phase extraction followed by flame atomic absorption spectrometry for determination of nickel in water and food samples. Microchem. J. 2019, 144, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Cheng, M.; Guo, F.; Wang, X.; Cheng, J. In-syringe demulsified dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction and high performance liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry for the determination of trace fungicides in environmental water samples. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 724, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngaosi, N.; Seebunrueng, K.; Srijaranai, S. In-syringe reversed dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction coupled to high performance liquid chromatography for the determination of sulfonylurea herbicide residues in cereal samples. Anal. Methods 2016, 8, 4254–4262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreto, J.A.; Dos Santos de Assis, R.; Cassella, R.J.; Lemos, V.A. A novel strategy based on in-syringe dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction for the determination of nickel in chocolate samples. Talanta 2019, 193, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilli, S.; Tong, P. Liquid chromatography of metal chelates: Chromatographic studies of homologous dialkyldithiocarbamates. Anal. Chim. Acta 1999, 395, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Den Boeff, G.; Poppa, H. Differential spectrophotometry of nickel as its pyridine-2,6-dicarboxylic acid complex. Talanta 1968, 15, 1058–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, B.; Shen, Y.; Gao, Z.; Zhou, M.; Ma, Y.; Zhao, S. Determination of total iron in water and foods by dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction coupled with microvolume UV–vis spectrophotometry. Food Chem. 2015, 176, 288–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butwong, N.; Burakham, R.; Srijaranai, S. Use of surfactant as mobile phase additive in LC for simultaneous determination of metal-pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate chelates. Chromatographia 2010, 71, 639–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shijo, Y.; Takada, K.; Uehara, N. Determination of metal ions by high-performance liquid chromatographic separation of their pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate complexes after solvent extraction. Anal. Sci. 1993, 9, 315–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- AOAC Official Method 973.35. Lead in Evaporated Milk. Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometric Method. Available online: http://www.wdfxw.net/doc11928282.htm (accessed on 16 June 2017).
- Liška, O.; Lehotay, J.; Brandšteterová, E. Liquid chromatography of metal complexes of N-disubstituted dithiocarbanic acids. J. Chromatogr. 1979, 172, 384–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bone, K.M.; Hibbert, W.D. Solvent extraction with ammonium pyrrolidinedithiocarbamate and 2,6-dimethyl-4-heptanone for the determination of trace metals in effluents and natural waters. Anal. Chim. Acta 1979, 107, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaee, M.; Assadi, Y.; Milani Hosseini, M.-R.; Aghaee, E.; Ahmadi, F.; Berijani, S. Determination of organic compounds in water using dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction. J. Chromatogr. A 2006, 1116, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somsubsin, S.; Seebunrueng, K.; Boonchiangma, S.; Srijaranai, S. A simple solvent based microextraction for high performance liquid chromatographic analysis of aflatoxins in rice samples. Talanta 2018, 176, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, J. Determination of metal ions in tea samples using task-specific ionic liquid-based ultrasound-assisted dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction coupled to liquid chromatography with ultraviolet detection: Liquid Chromatography. J. Sep. Sci. 2016, 39, 1411–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-M.; Zhang, F.-P.; Jiao, B.-Y.; Rao, J.-Y.; Leng, G. Automated dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction coupled to high performance liquid chromatography-cold vapour atomic fluorescence spectroscopy for the determination of mercury species in natural water samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1493, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.-L.; Wang, J.-Q.; Zheng, Z.-X.; Xiao, P. Cloud point extraction combined with high-performance liquid chromatography for speciation of chromium(III) and chromium(VI) in environmental sediment samples. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 177, 114–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not from the authors. |






| Analyte | Linear Range (μg L−1) | Linear Equation | R2 | LOD (μg L−1) | LOQ (μg L−1) | EF | %RSD * | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intra-Day (n = 5) | Inter-Day (n = 3 × 5) | |||||||
| Ni2+ | 0.05–5 (5–500) a | y = 2.681x + 4.493 (y = 0.042x − 1.654) | 0.9952 (0.9951) | 0.014 (1.6) | 0.050 (5.7) | 64 | 7.1 (5.1) | 8.9 (7.9) |
| Cr2O72− | 0.05–5 (10–500) | y = 19.59x − 0.626 (y = 0.155x − 1.186) | 0.9964 (0.9960) | 0.011 (3.1) | 0.049 (10) | 126 | 5.6 (4.4) | 7.0 (6.1) |
| Hg2+ Co2+ | 5–200 (500–1000) 0.05–5 (20–500) | y = 2.301x + 17.35 (y = 0.010x − 3.081) y = 34.09x + 4.304 (y = 0.167x − 2.411) | 0.9979 (0.9942) 0.9945 (0.9956) | 2.0 (120) 0.011 (5.8) | 5.0 (460) 0.047 (18) | 230 204 | 5.8 (2.8) 6.3 (2.7) | 8.1 (4.9) 7.2 (5.2) |
| Method (Chelating Agent) | Sample (Metal Ions Studied) | Extraction Solvent (Dispersive Solvent) | Extractant Volume (Disperser Volume) | Extraction Time (min) a | LOD (µg L−1) | EF | RSDs (%) | Analytical Technique | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solvent extraction (APDC) | NR (Pb2+, Ni2+, Co2+, Cu2+, Bi3+, In3+) | Re-extraction by acetonitrile | 2 mL | 21 | 0.023–0.21 | NR | ≤9.2 | HPLC-UV | [39] |
| UA-DLLME-SAP (APDC) | Water (Ni2+, Co2+, Cd2+, Cu2+, Pb2+) | Cyphos IL 104 | 10 μL | 66 | 0.02–0.03 | 207–211 | ≤7 | HPLC-UV | [23] |
| UA-DLLME (TOMATS) | Tea (Cd2+, Co2+, Pb2+) | TOMATS IL | 10 μL | 17 | 2–13 | 200 | ≤12 | HPLC-UV | [45] |
| Automated DLLME (2-ME) | Water (Hg2+, MeHg+, EtHg+) | [C6MIM][PF6] (acetone) | 30 μL (800 μL) | 2 | 0.0015–0.003 | 41–47 | ≤5.1 | HPLC-CVAFS | [46] |
| Cloud point extraction (TAN) | Water (Cr3+, Cr6+) | 1.25% Triton X-114 | NR | 45 | 3.5–7.5 | 40–45 | ≤4.7 | HPLC-UV | [47] |
| ISLD-DLLME (APDC) | Fish, shrimp, shellfish (Ni2+, Cr2O72−, Co2+, Hg2+) | 1-octanol (Methanol) | 50 μL (250 μL) | 1 | 0.01–2 | 64–230 | ≤8.9 | HPLC-UV | This work |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Laosuwan, M.; Mukdasai, S.; Srijaranai, S. A Simple in Syringe Low Density Solvent-Dispersive Liquid Liquid Microextraction for Enrichment of Some Metal Ions Prior to Their Determination by High Performance Liquid Chromatography in Food Samples. Molecules 2020, 25, 552. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25030552
Laosuwan M, Mukdasai S, Srijaranai S. A Simple in Syringe Low Density Solvent-Dispersive Liquid Liquid Microextraction for Enrichment of Some Metal Ions Prior to Their Determination by High Performance Liquid Chromatography in Food Samples. Molecules. 2020; 25(3):552. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25030552
Chicago/Turabian StyleLaosuwan, Melasinee, Siriboon Mukdasai, and Supalax Srijaranai. 2020. "A Simple in Syringe Low Density Solvent-Dispersive Liquid Liquid Microextraction for Enrichment of Some Metal Ions Prior to Their Determination by High Performance Liquid Chromatography in Food Samples" Molecules 25, no. 3: 552. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25030552
APA StyleLaosuwan, M., Mukdasai, S., & Srijaranai, S. (2020). A Simple in Syringe Low Density Solvent-Dispersive Liquid Liquid Microextraction for Enrichment of Some Metal Ions Prior to Their Determination by High Performance Liquid Chromatography in Food Samples. Molecules, 25(3), 552. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25030552