Harnessing Ionic Interactions and Hydrogen Bonding for Nucleophilic Fluorination
Abstract
:1. Introduction
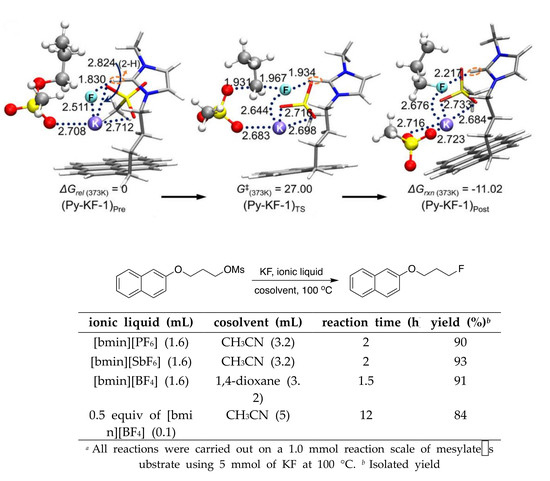
2. SN2 Fluorination in Ionic Liquids
3. SNAr Fluorination of Diaryliodonium Salts
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vaillancourt, F.H.; Yeh, E.; Vosburg, D.A.; Garneau-Tsodikova, S.; Walsh, C.T. Nature’s inventory of halogenation catalysts: Oxidative strategies predominate. Chem. Rev. 2006, 106, 3364–3378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Champagne, P.A.; Desroches, J.; Hamel, J.D.; Vandamme, M.; Paquin, J.F. Monofluorination of Organic Compounds: 10 Years of Innovation. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 9073–9174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mascaretti, O.A. Modern methods for the monofluorination of aliphatic organic compounds. Aldrichim. Acta 1993, 26, 47–58. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.W.; Oliveira, M.T.; Jang, H.B.; Lee, S.; Chi, D.Y.; Kim, D.W.; Song, C.E. Hydrogen-bond promoted nucleophilic fluorination: Concept, mechanism and applications in positron emission tomography. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 4638–4650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, T.; Neumann, C.N.; Ritter, T. Introduction of fluorine and fluorine-containing functional groups. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 8214–8264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, X.; Wu, T.; Phipps, R.J.; Toste, F.D. Advances in catalytic enantioselective fluorination, mono-, di-, and trifluoromethylation, and trifluoromethylthiolation reactions. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 826–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, L.; Ploessl, K.; Kung, H.F. Expanding the scope of fluorine tags for PET imaging. Science 2013, 342, 429–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preshlock, S.; Tredwell, M.; Gouverneur, V. 18F-Labeling of Arenes and Heteroarenes for Applications in Positron Emission Tomography. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 719–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phelps, M.E. Positron emission tomography provides molecular imaging of biological processes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 9226–9233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sheldon, R. Paul Olivier. Catalytic reactions in ionic liquids. Chem. Commun. 2001, 2399–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasserscheid, P.; Keim, W. Ionic Liquids—New “Solutions” for Transition Metal Catalysis. Angew. Chem. 2000, 39, 3772–3789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welton, T. Room-Temperature Ionic Liquids. Solvents for Synthesis and Catalysis. Chem. Rev. 1999, 99, 2071–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dupont, J.; De Souza, R.F.; Suarez, P.A.Z. Ionic liquid (molten salt) phase organometallic catalysis. Chem. Rev. 2002, 102, 3667–3692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupont, J.; Suarez, P.A.Z. Physico-chemical processes in imidazolium ionic liquids. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2006, 8, 2441–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binnemans, K. Ionic liquid crystals. Chem. Rev. 2005, 105, 4148–4204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, W.; Tak, H.C. Ionic-liquid-supported synthesis: A novel liquid-phase strategy for organic synthesis. Acc. Chem. Res. 2006, 39, 897–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Z.; Chen, B.; Li, C.; Liu, H. Predictive molecular thermodynamic models for liquid solvents, solid salts, polymers, and ionic liquids. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 1419–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallett, J.P.; Welton, T. Room-temperature ionic liquids: Solvents for synthesis and catalysis. 2. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 3508–3576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.E. Methodologies in Asymmetric Catalysis. ACS Symp. Ser. 2004, 880. [Google Scholar]
- Vekariya, R.L. A review of ionic liquids: Applications towards catalytic organic transformations. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 227, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, S.-M.; Chen, K.-H.; Fu, H.-C.; He, L.-N. Ionic Liquids Catalysis for Carbon Dioxide Conversion With Nucleophiles. Front. Chem. 2018, 6, 462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oh, Y.H.; Jang, H.B.; Im, S.; Song, M.J.; Kim, S.Y.; Park, S.W.; Chi, D.Y.; Song, C.E.; Lee, S. SN2 Fluorination reactions in ionic liquids: A mechanistic study towards solvent engineering. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2011, 9, 418–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.W.; Song, C.E.; Chi, D.Y. New method of fluorination using potassium fluoride in ionic liquid: Significantly enhanced reactivity of fluoride and improved selectivity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 10278–10279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, B.K.; Lee, S.S.; Kang, S.M.; Kim, J.; Kim, D.W.; Lee, S. Mechanism of Nucleophilic Fluorination Facilitated by a Pyrene-tagged Ionic Liquids: Synergistic Effects of Pyrene–Metal Cation π-Interactions. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2018, 39, 1047–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Kim, D.W. Sustainable Catalysis in Ionic liquids; Lozano, P., Ed.; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.W.; Shin, J.Y.; Chun, Y.S.; Jang, H.B.; Song, C.E.; Lee, S.G. Toward understanding the origin of positive effects of ionic liquids on catalysis: Formation of more reactive catalysts and stabilization of reactive intermediates and transition states in ionic liquids. Acc. Chem. Res. 2010, 43, 985–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newington, I.; Perez-Arlandis, J.M.; Welton, T. Ionic liquids as designer solvents for nucleophilic aromatic substitutions. Org. Lett. 2007, 9, 5247–5250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadhav, V.H.; Jang, S.H.; Jeong, H.J.; Lim, S.T.; Sohn, M.H.; Kim, J.Y.; Lee, S.; Lee, J.W.; Song, C.E.; Kim, D.W. Oligoethylene glycols as highly efficient mutifunctional promoters for nucleophilic-substitution reactions. Chem. A Eur. J. 2012, 18, 3918–3924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, T.; Sethi, A.; Welton, T.; Woolf, J. Diels-Alder Reactions in Room-Temperature Ionic Liquids. Tetrahedron Lett. 1999, 2–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauchot, V.; Schmitzer, A.R. Asymmetric aldol reaction catalyzed by the anion of an ionic liquid. J. Org. Chem. 2012, 77, 4917–4923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Chen, W.; Xiao, J. Heck reaction in ionic liquids and the in situ identification of N-heterocyclic carbene complexes of palladium. Organometallics 2000, 19, 1123–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Chen, W.; Ross, J.; Xiao, J. Palladium-catalyzed regioselective arylation of an electron-rich olefin by aryl halides in ionic liquids. Org. Lett. 2001, 3, 295–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Böhm, V.P.W.; Herrmann, W.A. Nonaqueous ionic liquids: Superior reaction media for the catalytic Heck-Vinylation of chloroarenes. Chem. A Eur. J. 2000, 6, 1017–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranu, B.C.; Banerjee, S. Ionic liquid as catalyst and reaction medium. The dramatic influence of a task-specific ionic liquid, [bmIm]OH, in Michael addition of active methylene compounds to conjugated ketones, carboxylic esters, and nitriles. Org. Lett. 2005, 7, 3049–3052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.W.; Song, C.E.; Chi, D.Y. Significantly enhanced reactivities of the nucleophilic substitution reactions in ionic liquid. J. Org. Chem. 2003, 68, 4281–4285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.W.; Yan, H.; Jang, H.B.; Kim, H.K.; Park, S.W.; Lee, S.; Chi, D.Y.; Song, C.E. Bis-terminal hydroxy polyethers as all-purpose, multifunctional organic promoters: A mechanistic investigation and applications. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 7683–7686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.W.; Ahn, D.-S.; Oh, Y.-H.; Lee, S.; Kil, H.S.; Oh, S.J.; Lee, S.J.; Kim, J.S.; Ryu, J.S.; Moon, D.H.; et al. A new class of S<inf>N</inf>2 reactions catalyzed by protic solvents: Facile fluorination for isotopic labeling of diagnostic molecules. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.W.; Jeong, H.J.; Lim, S.T.; Sohn, M.-H.; Katzenellenbogen, J.A.; Chi, D.Y. Facile nucleophilic fluorination reactions using tert-alcohols as a reaction medium: Significantly enhanced reactivity of alkali metal fluorides and improved selectivity. J. Org. Chem. 2008, 73, 957–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinde, S.S.; Khonde, N.S.; Kumar, P. Tri-tert-Butanolamine as an Organic Promoter in Nucleophilic Fluorination. ChemistrySelect 2017, 2, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouvet, S.; Pégot, B.; Marrot, J.; Magnier, E. Solvent free nucleophilic introduction of fluorine with [bmim][F]. Tetrahedron Lett. 2014, 55, 826–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.; Lee, S. Mechanistic study of SN2 reactions in [Bmim]F. (Unpublished).
- Han, H.J.; Lee, S.-S.; Kang, S.M.; Kim, Y.; Park, C.; Yoo, S.; Kim, C.H.; Oh, Y.-H.; Lee, S.; Kim., D.W. Effects of Structural Modifications of Bis-tert-Alcohol-Functionalized Crwon-Calix [4]arenes as Nucleophilic Fluorination Promotors and Relations with Computational Predictions. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2020, 2020, 728–735, Accepted Manuscript. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Lu, G.-p.; Cai, C. Facile aromatic nucleophilic substitution(SNAr) reactions in ionic liquids: An electrophile-nucleophile dual activation by [Omim]Br for the reaction. Green Chem. 2016, 18, 5580. [Google Scholar]
- Jadhav, V.H.; Kim, J.Y.; Chi, D.Y.; Lee, S.; Kim, D.W. Organocatalysis of nucleophilic substitution reactions by the combined effects of two promoters fused in a molecule: Oligoethylene glycol substituted imidazolium salts. Tetrahedron 2014, 70, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taher, A.; Lee, K.C.; Han, H.J.; Kim, D.W. Pyrene-Tagged Ionic Liquids: Separable Organic Catalysts for SN2 Fluorination. Org. Lett. 2017, 19, 3342–3345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pretze, M.; Wängler, C.; Wängler, B. 6-[18F]fluoro-L-DOPA: A well-established neurotracer with expanding application spectrum and strongly improved radiosyntheses. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 674063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shah, A.; Pike, V.W.; Widdowson, D.A. The synthesis of [18F]fluoroarenes from the reaction of cyclotron-produced [18F]fluoride ion with diaryliodonium salts. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1998, 1, 2043–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pike, V.W.; Aigbirhio, F.I. Reactions of cyclotron-produced [18F]fluoride with diaryliodonium salts—A novel single-step route to no-carrier-added [18F]fluoroarenes. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1995, 2215–2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, T.L.; Ermert, J.; Hocke, C.; Coenen, H.H. Nucleophilic 18F-fluorination of heteroaromatic iodonium salts with no-carrier-added [18F]fluoride. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 8018–8025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tredwell, M.; Gouverneur, V. 18F labeling of arenes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 11426–11437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Qin, L.; Neumann, K.D.; Uppaluri, S.; Cerny, R.L.; DiMagno, S.G. Improved arene fluorination methodology for I(III) salts. Org. Lett. 2010, 12, 3352–3355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuan, Z.; Cheng, R.; Chen, P.; Liu, G.; Liang, S.H. Efficient Pathway for the Preparation of Aryl(isoquinoline)iodonium(III) Salts and Synthesis of Radiofluorinated Isoquinolines. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 11882–11886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zlatopolskiy, B.D.; Zischler, J.; Krapf, P.; Zarrad, F.; Urusova, E.A.; Kordys, E.; Endepols, H.; Neumaier, B. Copper-mediated aromatic radiofluorination revisited: Efficient production of PET tracers on a preparative scale. Chem. A Eur. J. 2015, 21, 5972–5979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichiishi, N.; Canty, A.J.; Yates, B.F.; Sanford, M.S. Cu-catalyzed fluorination of diaryliodonium salts with KF. Org. Lett. 2013, 15, 5134–5137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ichiishi, N.; Brooks, A.F.; Topczewski, J.J.; Rodnick, M.E.; Sanford, M.S.; Scott, P.J.H. Copper-catalyzed [18F]fluorination of (Mesityl)(aryl)iodonium salts. Org. Lett. 2014, 16, 3224–3227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ichiishi, N.; Canty, A.J.; Yates, B.F.; Sanford, M.S. Mechanistic investigations of Cu-catalyzed fluorination of diaryliodonium salts: Elaborating the CuI/CuIII manifold in copper catalysis. Organometallics 2014, 33, 5525–5534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Seidl, T.L.; Sundalam, S.K.; McCullough, B.; Stuart, D.R. Unsymmetrical Aryl(2,4,6-trimethoxyphenyl)iodonium Salts: One-Pot Synthesis, Scope, Stability, and Synthetic Studies. J. Org. Chem. 2016, 81, 1998–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, Y.D.; Son, J.; Chun, J.H. Chemoselective Radiosyntheses of Electron-Rich [18F]Fluoroarenes from Aryl(2,4,6-trimethoxyphenyl)iodonium Tosylates. J. Org. Chem. 2019, 84, 3678–3686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, K.S. Nucleophilic Aromatic [18F]Fluorination of Electron Rich Aromatic Systems via Diaryliodonium Salts. Ph.D Thesis, Inha University, Incheon, Korea, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Berry, C.R.; Garg, P.K.; Zalutsky, M.R.; Coleman, R.E.; DeGrado, T.R. Uptake and retention kinetics of para-fluorine-18-fluorobenzylguanidine in isolated rat heart. J. Nucl. Med. 1996, 37, 2011–2016. [Google Scholar]
- Garg, P.K.; Garg, S.; Zalutsky, M.R. Synthesis and preliminary evaluation of para- and meta-[18F]fluorobenzylguanidine. Nucl. Med. Biol. 1994, 21, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, Y.W.; Jang, K.S.; Gu, G.; Koeppe, R.A.; Sherman, P.S.; Quesada, C.A.; Raffel, D.M. Fluoro-Hydroxyphenethylguanidines: Efficient Synthesis and Comparison of Two Structural Isomers as Radiotracers of Cardiac Sympathetic Innervation. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2017, 8, 1530–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higuchi, T.; Yousefi, B.H.; Kaiser, F.; Gärtner, F.; Rischpler, C.; Reder, S.; Yu, M.; Robinson, S.; Schwaiger, M.; Nekolla, S.G. Assessment of the 18F-Labeled PET tracer LMI1195 for imaging norepinephrine handling in rat hearts. J. Nucl. Med. 2013, 54, 1142–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, B.C.; Paik, J.Y.; Chi, D.Y.; Lee, K.H.; Choe, Y.S. Potential and Practical Adrenomedullary PET Radiopharmaceuticals as an Alternative to m-Iodobenzylguanidine: M-(ω[18F]Fluoroalkyl)benzylguanidines. Bioconjugate Chem. 2004, 15, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raffel, D.; Loc, C.; Mardon, K.; Mazi, B.; Syrota, A. Bromobenzylguanidine in Isolated Working Rat Heart A-l. Nucl. Med. Biol. 1998, 25, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaidyanathan, G.; Affleck, D.J.; Zalutsky, M.R. (4-[18F]Fluoro-3-iodobenzyl)guanidine, a Potential MIBG Analogue for Positron Emission Tomography. J. Med. Chem. 1994, 37, 3655–3662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaidyanathan, C.; Affleck, D.J.; Zalutsky, M.R. Validation of 4-[fluorine-18]fluoro-3-iodobenzylguanidine as a positron- emitting analog of MIBG. J. Nucl. Med. 1995, 36, 644–650. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vaidyanathan, G.; McDougald, D.; Koumarianou, E.; Choi, J.; Hens, M.; Zalutsky, M.R. Synthesis and evaluation of 4-[18F]fluoropropoxy-3-iodobenzylguanidine ([18F]FPOIBG): A novel 18F-labeled analogue of MIBG. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2015, 42, 673–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, M.; Bozek, J.; Lamoy, M.; Guaraldi, M.; Silva, P.; Kagan, M.; Yalamanchili, P.; Onthank, D.; Mistry, M.; Lazewatsky, J.; et al. Evaluation of LMI1195, a novel 18F-labeled cardiac neuronal PET imaging agent, in cells and animal models. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2011, 4, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Huang, R.; Pillarsetty, N.; Thorek, D.L.; Vaidyanathan, G.; Serganova, I.; Blasberg, R.G.; Lewis, J.S. Synthesis and evaluation of 18F-labeled benzylguanidine analogs for targeting the human norepinephrine transporter. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2014, 41, 322–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jang, K.S.; Lee, S.S.; Oh, Y.H.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, S.E.; Kim, D.W.; Lee, B.C.; Lee, S.; Raffel, D.M. Control of reactivity and selectivity of guanidinyliodonium salts toward 18F-Labeling by monitoring of protecting groups: Experiment and theory. J. Fluor. Chem. 2019, 227, 109387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, R.; Westwell, A.D.; Daniels, S.; Wirth, T. Convenient synthesis of diaryliodonium salts for the production of [18F]F-DOPA. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2015, 2015, 625–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zlatopolskiy, B.D.; Zischler, J.; Urusova, E.A.; Endepols, H.; Kordys, E.; Frauendorf, H.; Mottaghy, F.M.; Neumaier, B. A Practical One-Pot Synthesis of Positron Emission Tomography (PET) Tracers via Nickel-Mediated Radiofluorination. ChemistryOpen 2015, 4, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, E.; Hooker, J.M.; Ritter, T. Nickel-mediated oxidative fluorination for PET with aqueous [18F] fluoride. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 17456–17458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oh, Y.-H.; Choi, H.; Lee, S.-S.; Lee, S. Toward the Robust Synthesis of [18F]F-DOPA: Quantum Chemical Analysis of SNAr Cold Fluorination of Diaryl Iodonium Salt by 19F. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2020, (in press). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maisonial-Besset, A.; Serre, A.; Ouadi, A.; Schmitt, S.; Canitrot, D.; Léal, F.; Miot-Noirault, E.; Brasse, D.; Marchand, P.; Chezal, J.M. Base/Cryptand/Metal-Free Automated Nucleophilic Radiofluorination of [18F]FDOPA from Iodonium Salts: Importance of Hydrogen Carbonate Counterion. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2018, 2018, 7058–7065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]















| Ionic Liquid (mL) | Cosolvent (mL) | Reaction Time (h) | Yield (%) b |
|---|---|---|---|
| [bmin][PF6] (1.6) | CH3CN (3.2) | 2 | 90 |
| [bmin][SbF6] (1.6) | CH3CN (3.2) | 2 | 93 |
| [bmin][BF4] (1.6) | 1,4-dioxane (3.2) | 1.5 | 91 |
| 0.5 equiv of [bmin][BF4] (0.1) | CH3CN (5) | 12 | 84 |

| Entry | Time (min) | Temperature (°C) | BMIMF (Equiv) | Yield a (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 30 | 80 | 1 | 49 |
| 2 | 30 | 80 | 2 | 84 |
| 3 | 30 | 80 | 3 | 95 (85) b |

| Entry | Substrate | Radio TLC Yield | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 min | 10 min | 15 min | 30 min | ||
| 1 | 1a | 37.27 | 38.54 | 39.84 | 40.99 |
| 2 | 1b | 15.68 | 23.28 | 24.53 | 18.50 |
| 3 | 1c | 25.62 | 25.99 | 34.00 | 34.41 |
| 4 | 1d | 65.12 | 68.12 | 68.33 | 68.35 |
| 5 | 1e | 28.21 | 30.14 | 30.55 | 31.79 |
| 6 | 1f | 20.47 | 20.86 | 18.35 | 30.05 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oh, Y.-H.; Choi, H.; Park, C.; Kim, D.W.; Lee, S. Harnessing Ionic Interactions and Hydrogen Bonding for Nucleophilic Fluorination. Molecules 2020, 25, 721. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25030721
Oh Y-H, Choi H, Park C, Kim DW, Lee S. Harnessing Ionic Interactions and Hydrogen Bonding for Nucleophilic Fluorination. Molecules. 2020; 25(3):721. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25030721
Chicago/Turabian StyleOh, Young-Ho, Hyoju Choi, Chanho Park, Dong Wook Kim, and Sungyul Lee. 2020. "Harnessing Ionic Interactions and Hydrogen Bonding for Nucleophilic Fluorination" Molecules 25, no. 3: 721. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25030721
APA StyleOh, Y. -H., Choi, H., Park, C., Kim, D. W., & Lee, S. (2020). Harnessing Ionic Interactions and Hydrogen Bonding for Nucleophilic Fluorination. Molecules, 25(3), 721. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25030721