Pyrazoles as Key Scaffolds for the Development of Fluorine-18-Labeled Radiotracers for Positron Emission Tomography (PET)
Abstract
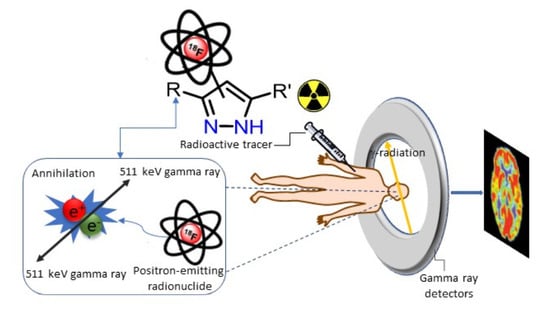
:1. Introduction
2. Pyrazoles
2.1. Pyrazoles as Probes for PET Imaging
2.1.1. Adenosine Receptors Ligands
2.1.2. Cannabinoid Receptors Ligands
2.1.3. Cyclooxygenase Inhibitors
2.1.4. Dopamine Receptors Ligands
2.1.5. Glucocorticoid Receptor Ligands
2.1.6. Insulin-Like Growth Factor-1 Receptor Ligands
2.1.7. Phosphodiester-10A Enzyme Inhibitors
2.1.8. Translocator Protein Receptor Ligands
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Z.; Conti, P.S. Radiopharmaceutical chemistry for positron emission tomography. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2010, 62, 1031–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damont, A.; Roeda, D.; Dollé, F. The potential of carbon-11 and fluorine-18 chemistry: Illustration through the development of positron emission tomography radioligands targeting the translocator protein 18 kDa. J. Label. Compd. Radiopharm. 2013, 56, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coleman, R.E. Clinical PET in oncology. Clin. Positron Imaging 1998, 1, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, C.J.; Bulte, J.W.M.; Chen, K.; Chen, X.; Khaw, B.-A.; Shokeen, M.; Wooley, K.L.; VanBrocklin, H.F. Design of targeted cardiovascular molecular imaging probes. J. Nucl. Med. 2010, 51, 3S–17S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiong, K.L.; Yang, Q.W.; Gong, S.G.; Zhang, W.G. The role of positron emission tomography imaging of β-amyloid in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Nucl. Med. Commun. 2010, 31, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, P.S.; McCarthy, T.J.; Dzik-Jurasz, A.S.K. The role of clinical imaging in oncological drug development. Br. J. Radiol. 2008, 81, 685–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazzato, R.L.; Garnon, J.; Shaygi, B.; Koch, G.; Tsoumakidou, G.; Caudrelier, J.; Addeo, P.; Bachellier, P.; Namer, I.J.; Gangi, A. PET/CT-guided interventions: Indications, advantages, disadvantages and the state of the art. Minim. Invasive Ther. Allied Technol. 2018, 27, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, K.A.; Hoskin, P.J.; Saunders, M.I. Positron emission tomography in oncology: A review. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 19, 237–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, V.L.M.; Silva, A.M.S.; Pinto, D.C.G.A.; Jagerovic, N.; Callado, L.F.; Cavaleiro, J.A.S.; Elguero, J. Synthesis and pharmacological evaluation of chlorinated N-alkyl-3- and -5-(2-hydroxyphenyl)pyrazoles as CB1 cannabinoid ligands. Monatsh. Chem. 2007, 138, 797–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, V.L.M.; Silva, A.M.S.; Pinto, D.C.G.A.; Cavaleiro, J.A.S.; Elguero, J. Synthesis of (E)- and (Z)-3(5)-(2-hydroxyphenyl)-4-styrylpyrazoles. Monatsh. Chem. 2009, 140, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, V.L.M.; Silva, A.M.S.; Pinto, D.C.G.A.; Rodríguez, P.; Gómez, M.; Jagerovic, N.; Callado, L.F.; Cavaleiro, J.A.S.; Elguero, J.; Fernández-Ruiz, J. Synthesis and pharmacological evaluation of new (E)- and (Z)-3-aryl-4-styryl-1H-pyrazoles as potential cannabinoid ligands. Arkivoc 2010, 226–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marques, J.; Silva, V.L.M.; Silva, A.M.S.; Marques, M.P.M.; Braga, S.S. Ru(II) trithiacyclononane 3-(2-hydroxyphenyl)-5-(4-methoxystyryl)pyrazole, a complex with facile synthesis and high cytotoxicity against PC-3 and MDA-MB-231 cells. Complex Metals 2014, 1, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soengas, R.G.; Silva, V.L.M.; Ide, D.; Kato, A.; Cardoso, S.M.; Almeida Paz, F.A.; Silva, A.M.S. Synthesis of 3-(2-nitrovinyl)-4H-chromones: Useful scaffolds for the construction of biologically relevant 3-(pyrazol-5-yl)chromones. Tetrahedron 2016, 72, 3198–3203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carreira, A.R.F.; Pereira, D.M.; Andrade, P.B.; Valentão, P.; Silva, A.M.S.; Braga, S.S.; Silva, V.L.M. Novel styrylpyrazole-glucosides and their unexpected dioxolo-bridged doppelgangers: Synthesis and cytotoxicity. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 8299–8310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrigach, F.; Touzani, R. Pyrazole derivatives with NCN junction and their biological activity: A review. Med. Chem. 2016, 6, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suri, M.; Jousseaume, T.; Neumann, J.J.; Glorius, F. An efficient copper-catalyzed formation of highly substituted pyrazoles using molecular oxygen as the oxidant. Green Chem. 2012, 14, 2193–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Kaur, K.; Gupta, G.K.; Sharma, A.K. Pyrazole containing natural products: Synthetic preview and biological significance. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 69, 735–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, V.L.M.; Elguero, J.; Silva, A.M.S. Current progress on antioxidants incorporating the pyrazole core. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 15, 394–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Maksoud, M.S.; El-Gamal, M.I.; Gamal El-Din, M.M.; Oh, C.H. Design, synthesis, in vitro anticancer evaluation, kinase inhibitory effects, and pharmacokinetic profile of new 1,3,4-triarylpyrazole derivatives possessing terminal sulfonamide moiety. J. Enz. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2019, 34, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chowdary, B.N.; Umashankara, M.; Dinesh, B.; Girish, K.; Baba, A.R. Development of 5-(aryl)-3-phenyl-1H-pyrazole derivatives as potent antimicrobial compounds. Asian J. Chem. 2019, 31, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secci, D.; Bolasco, A.; Chimenti, P.; Carradori, S. The state of the art of pyrazole derivatives as monoamine oxidase inhibitors and antidepressant/anticonvulsant agents. Curr. Med. Chem. 2011, 18, 5114–5144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.J.; Zhang, H.; Sun, J.; Wang, Z.C.; Yang, Y.S.; Li, D.D.; Zhang, F.; Gong, H.B.; Zhu, H.L. Synthesis, biological evaluation of novel 4,5-dihydro-2H-pyrazole 2-hydroxyphenyl derivatives as BRAF inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2012, 20, 6089–6096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanitame, A.; Oyamada, Y.; Ofuji, K.; Fujimoto, M.; Iwai, N.; Hiyama, Y.; Suzuki, K.; Ito, H.; Terauchi, H.; Kawasaki, M.; et al. Synthesis and antibacterial activity of a novel series of potent DNA gyrase inhibitors. Pyrazole derivatives. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 3693–3696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansari, A.; Ali, A.; Asif, M.; Shamsuzzaman, S. Review: Biologically active pyrazole derivatives. New J. Chem. 2016, 41, 16–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.-J.; Zhao, M.-Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, X.; Zhu, H.-L. Pyrazole derivatives as antitumor, anti-inflammatory and antibacterial agents. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2013, 13, 1957–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Küçükgüzel, S.G.; Senkardes, S. Recent advances in bioactive pyrazoles. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 97, 786–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, C.M.M.; Silva, V.L.M.; Silva, A.M.S. Synthesis of chromone-related pyrazole compounds. Molecules 2017, 22, 1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Faria, J.V.; Vegi, P.F.; Miguita, A.G.C.; dos Santos, M.S.; Boechat, N.; Bernardino, A.M.R. Recently reported biological activities of pyrazole compounds. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2017, 25, 5891–5903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Fernandez, R.; Goya, P.; Elguero, J. A review of recent progress (2002–2012) on the biological activities of pyrazoles. Arkivoc 2014, 233–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhu, V.V.; Kannan, N.; Guruvayoorappan, C. 1,2-Diazole prevents cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in experimental rats. Pharmacol. Reports 2013, 65, 980–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borea, P.A.; Gessi, S.; Merighi, S.; Vincenzi, F.; Varani, K. Pharmacology of adenosine receptors: The state of the art. Physiol. Rev. 2018, 98, 1591–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khanapur, S.; Paul, S.; Shah, A.; Vatakuti, S.; Koole, M.J.B.; Zijlma, R.; Dierckx, R.A.J.O.; Luurtsema, G.; Garg, P.; van Waarde, A.; et al. Development of [18F]-labelled pyrazolo[4,3-e]-1,2,4-triazolo[1,5-c]pyrimidine (SCH442416) analogs for the imaging of cerebral adenosine A2A receptors with positron emission tomography. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 6765–6780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khanapur, S.; van Waarde, A.; Dierckx, R.A.J.O.; Elsinga, P.H.; Koole, M.J.B. Preclinical evaluation and quantification of 18F-fluoroethyl and 18F-fluoropropyl analogs of SCH442416 as radioligands for PET imaging of the adenosine A2A receptor in rat brain. J. Nucl. Med. 2017, 58, 466–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Daughters, R.S.; Bullis, C.; Bengiamin, R.; Stucky, M.W.; Brennan, J.; Simone, D.A. The cannabinoid receptor agonist WIN 55,212-2 mesylate blocks the development of hyperalgesia produced by capsaicin in rats. Pain 1999, 81, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Rosales, F.; Walsh, D. Intractable nausea and vomiting due to gastrointestinal mucosal metastases relieved by tetrahydrocannabinol (Dronabinol). J. Pain Symptom Manag. 1997, 14, 311–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, C.M.; Kirkham, T.C. Anandamide induces overeating: Mediation by central cannabinoid (CB1) receptors. Psychopharmacology 1999, 143, 315–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathews, W.B.; Scheffel, U.; Finley, P.; Ravert, H.T.; Frank, R.A.; Rinaldi-Carmona, M.; Barth, F.; Dannals, R.F. Biodistribution of [18F]SR144385 and [18F]SR147963: Selective radioligands for positron emission tomographic studies of brain cannabinoid receptors. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2000, 27, 757–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horti, A.G.; Fan, H.; Kuwabara, H.; Hilton, J.; Ravert, H.T.; Holt, D.P.; Alexander, M.; Kumar, A.; Rahmim, A.; Scheffel, U.; et al. 11C-JHU75528: A radiotracer for PET imaging of CB1 cannabinoid receptors. J. Nucl. Med. 2006, 47, 1689–1696. [Google Scholar]
- Rinaldi-Carmona, M.; Barth, F.; Héaulme, M.; Shire, D.; Calandra, B.; Congy, C.; Martinez, S.; Maruani, J.; Néliat, G.; Caput, D.; et al. SR141716A, a potent and selective antagonist of the brain cannabinoid receptor. FEBS Lett. 1994, 350, 240–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moreira, F.A.; Crippa, J.A.S. The psychiatric side-effects of rimonabant. Braz. J. Psychiatry 2009, 31, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mathews, W.B.; Ravert, H.T.; Musachio, J.L.; Frank, R.A.; Rinaldi-Carmona, M.; Barth, F.; Dannals, R.F. Synthesis of [18F]SR144385: A selective radioligand for positron emission tomography studies of brain cannabinoid receptors. J. Label. Compd. Radiopharm. 1999, 42, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoch-Rouse, R.; Horti, A.G. Synthesis of N-(piperidin-1-yl)-5-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1-(2-chlorophenyl)-4-[18F]fluoro-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxamide by nucleophilic [18F] fluorination: A PET radiotracer for studying CB1 cannabinoid receptors. J. Label. Compd. Radiopharm. 2003, 46, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nojiri, Y.; Ishiwata, K.; Qinggeletu; Tobiishi, S.; Sasada, T.; Yamamoto, F.; Mukai, T.; Maeda, M. Radiosynthesis and biodistribution in mice of a 18F-labelled analog of O-1302 for use in cerebral CB1 cannabinoid receptor imaging. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2008, 31, 1274–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.; Gifford, A.; Liu, Q.; Thotapally, R.; Ding, Y.-S.; Makriyannis, A.; Gatley, S.J. Candidate PET radioligands for cannabinoid CB1 receptors: [18F]AM5144 and related pyrazole compounds. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2005, 32, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatley, S.J.; Lan, R.; Volkow, N.D.; Pappas, N.; King, P.; Wong, C.T.; Gifford, A.N.; Pyatt, B.; Dewey, S.L.; Makriyannis, A. Imaging the brain marijuana receptor: Development of a radioligand that binds to cannabinoid CB1 receptors in vivo. J. Neurochem. 1998, 70, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, C.-P.; Huang, H.-L.; Huang, J.-K.; Hung, M.-S.; Wu, C.-H.; Song, J.-S.; Lee, C.-J.; Yub, C.-S.; Shia, K.-S. Fluorine-18 isotope labeling for positron emission tomography imaging. Direct evidence for DBPR211 as a peripherally restricted CB1 inverse agonist. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2019, 27, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taketo, M.M. Cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors in tumorigenesis (Part II). J. Natl. Can. Inst. 1998, 90, 1529–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Minghetti, L. Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) in inflammatory and degenerative brain diseases. J. Neuropath. Exp. Neur. 2004, 63, 901–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uddin, M.J.; Crews, B.C.; Ghebreselasie, K.; Huda, I.; Kingsley, P.J.; Ansari, M.S.; Tantawy, M.N.; Reese, J.J.; Marnett, L.J. Fluorinated COX-2 inhibitors as agents in PET imaging of inflammation and cancer. Cancer Prev. Res. 2011, 4, 1536–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lebedev, A.; Jiao, J.; Lee, J.; Yang, F.; Allison, N.; Herschman, H.; Sadeghi, S. Radiochemistry on electrodes: Synthesis of an 18F-labelled and in vivo stable COX-2 inhibitor. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, T.J.; Sheriff, A.U.; Graneto, M.J.; Talley, J.J.; Welch, M.J. Radiosynthesis, in vitro validation, and in vivo evaluation of 18F-labeled COX-1 and COX-2 inhibitors. J. Nucl. Med. 2002, 43, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Prante, O.; Tietze, R.; Hocke, C.; Löber, S.; Hübner, H.; Kuwert, T.; Gmeiner, P. Synthesis, radiofluorination, and in vitro evaluation of pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyridine-based dopamine D4-receptor ligands: Discovery of an inverse agonist radioligand for PET. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 1800–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stöβel, A.; Box, R.; Purkayastha, N.; Hübner, H.; Hocke, C.; Prante, O.; Gmeiner, P. Development of molecular tools based on the dopamine D3 receptor ligand FAUC 329 showing inhibiting effects on drug and food maintained behavior. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2017, 25, 3491–3499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyte, R.M.; Labaree, D.C.; Fede, J.-M.; Harris, C.; Hochberg, R.B. Iodinated and fluorinated steroid 2′-aryl-[3,2-c] pyrazoles as potential glucocorticoid receptor imaging agents. Steroids 1998, 63, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Würst, F.; Kniess, T.; Kretzschmar, M.; Bergmann, R. Synthesis and radiopharmacological evaluation of 2′-(4-fluorophenyl)-21-[18F]fluoro-20-oxo-11β,17α-dihydroxypregn-4-eno[3,2-c]pyrazole as potential glucocorticoid receptor ligand for positron emission tomography (PET). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2005, 15, 1303–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majo, V.J.; Arango, V.; Simpson, N.R.; Prabhakaran, J.; Kassir, S.A.; Underwood, M.D.; Bakalian, M.; Canoll, P.; Mann, J.J.; Dileep Kumar, J.S. Synthesis and in vitro evaluation of [18F]BMS-754807: A potential PET ligand for IGF-1R. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 4191–4194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tu, Z.; Xu, J.; Jones, L.A.; Li, S.; Mach, R.H. Carbon-11 labelled papaverine as a PET tracer for imaging PDE10A: Radiosynthesis, in vitro and in vivo evaluation. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2010, 37, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Celen, S.; Koole, M.; De Angelis, M.; Sannen, I.; Chitneni, S.K.; Alcazar, J.; Dedeurwaerdere, S.; Moechars, D.; Schmidt, M.; Verbruggen, A.; et al. Preclinical evaluation of 18F-JNJ41510417 as a radioligand for PET imaging of phosphodiesterase-10A in the brain. J. Nucl. Med. 2010, 51, 1584–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andres, J.-I.; De Angelis, M.; Alcazar, J.; Iturrino, L.; Langlois, X.; Dedeurwaerdere, S.; Lenaerts, I.; Vanhoof, G.; Celen, S.; Bormans, G. Synthesis, in vivo occupancy, and radiolabeling of potent phosphodiesterase subtype-10 inhibitors as candidates for positron emission tomography imaging. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 5820–5835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laere, K.V.; Ahmad, R.U.; Hudyana, H.; Celen, S.; Dubois, K.; Schmidt, M.E.; Bormans, G.; Koole, M. Human biodistribution and dosimetry of 18F-JNJ42259152, a radioligand for phosphodiesterase 10A imaging. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2013, 40, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laere, K.V.; Ahmad, R.U.; Hudyana, H.; Dubois, K.; Schmidt, M.E.; Celen, S.; Bormans, G.; Koole, M. Quantification of 18F-JNJ-42259152, a novel phosphodiesterase 10A PET tracer: Kinetic modelling and test-retest study in human brain. J. Nucl. Med. 2013, 54, 1285–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ooms, M.; Altili, B.; Celen, S.; Koole, M.; Verbruggen, A.; Laere, K.V.; Bormans, G. [18F]JNJ-42259152 binding to phosphodiesterase 10A, a key regulator of medium spiny neuron excitability, is altered in the presence of cyclic AMP. J. Neurochem. 2016, 139, 897–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stepanov, V.; Takano, A.; Nakao, R.; Amini, N.; Miura, S.; Kimura, H.; Taniguchi, T.; Halldin, C. Development of two fluorine-18 labeled PET radioligands targeting PDE10A and in vivo PET evaluation in nonhuman primates. Nucl. Med Biol. 2018, 57, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, D.; McKinley, E.T.; Hight, M.R.; Uddin, M.I.; Harp, J.M.; Fu, A.; Nickels, M.L.; Buck, J.R.; Manning, H.C. Synthesis and structure-activity relationships of 5,6,7-substituted pyrazolopyrimidines: Discovery of a novel TSPO PET ligand for cancer imaging. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 3429–3433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, J.; Winkeler, A.; Peyronneau, M.A.; Dollé, F.; Boisgard, R. Evaluation of PET imaging performance of the TSPO radioligand [18F]DPA-714 in mouse and rat models of cancer and inflammation. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2016, 18, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hagens, M.H.J.; Golla, S.V.; Wijburg, M.T.; Yaqub, M.; Heijtel, D.; Steenwijk, M.D.; Schober, P.; Brevé, J.J.P.; Schuit, R.C.; Reekie, T.A.; et al. In vivo assessment of neuroinflammation in progressive multiple sclerosis: A proof of concept study with [18F]DPA714 PET. J. Neuroinflammation 2018, 15, 314–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lavisse, S.; Inoue, K.; Jan, C.; Peyronneau, M.A.; Petit, F.; Goutal, S.; Dauguet, J.; Guillermier, M.; Dollé, F.; Rbah-Vidal, L.; et al. [18F]DPA-714 PET imaging of translocator protein TSPO (18 kDa) in the normal and excitotoxically-lesioned nonhuman primate brain. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2015, 42, 478–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, T.; López-Picón, F.R.; Krzyczmonik, A.; Forsback, S.; Kirjavainen, A.K.; Takkinen, J.S.; Alzghool, O.; Rajander, J.; Teperi, S.; Cacheux, F.; et al. [18F]F-DPA for the detection of activated microglia in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2018, 67, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gungor, H.; Saleem, A.; Babar, S.; Dina, R.; El-Bahrawy, M.A.; Curry, E.; Rama, N.; Chen, M.; Pickford, E.; Agarwal, R.; et al. Dose-finding quantitative 18F-FDG PET imaging study with the oral Pan-AKT inhibitor GSK2141795 in patients with gynecologic malignancies. J. Nucl. Med. 2015, 56, 1828–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Inoue, O.; Yamasaki, T.; Hashimoto, K.; Kojima, M. Evaluation of 3H-PK11195 as a radioligand for the in vivo study of peripheral benzodiazepine receptor. Kaku Igaku. 1985, 22, 1385–1389. [Google Scholar]
- Camsonne, R.; Moulin, M.A.; Crouzel, C.; Syrota, A.; Maziere, M.; Comar, D. Carbon-11 labelling of PK11195 and visualization of benzodiazepine peripheral receptors using positron emission tomography. J. Pharmacol. 1986, 17, 383. [Google Scholar]
- Damont, A.; Médran-Navarrete, V.; Cacheux, F.; Kuhnast, B.; Pottier, G.; Bernards, N.; Marquet, F.; Puech, F.; Boisgard, R.; Dollé, F. Novel pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidines as translocator protein 18 kDa (TSPO) ligands: Synthesis, in vitro biological evaluation, [18F]-labeling, and in vivo neuroinflammation PET images. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 7449–7464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fookes, C.J.R.; Pham, T.Q.; Mattner, F.; Greguric, I.; Loc’h, C.; Liu, X.; Berghofer, P.; Shepherd, R.; Gregoire, M.-C.; Katsifis, A. Synthesis and biological evaluation of substituted [18F]imidazo[1,2-a]pyridines and [18F]pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidines for the study of the peripheral benzodiazepine receptor using positron emission tomography. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 3700–3712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chauveau, F.; Camp, N.V.; Dollé, F.; Kuhnast, B.; Hinnen, F.; Damont, A.; Boutin, H.; James, M.; Kassiou, M.; Tavitian, B. Comparative evaluation of the translocator protein radioligands 11C-DPA-713, 18F-DPA-714, and 11C-PK11195 in a rat model of acute neuroinflammation. J. Nucl. Med. 2009, 50, 468–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martín, A.; Boisgard, R.; Kassiou, M.; Dollé, F.; Tavitian, B. Reduced PBR/TSPO expression after minocycline treatment in a rat model of focal cerebral ischemia: A PET study using [18F]DPA-714. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2011, 13, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doorduin, J.; Klein, H.C.; Dierckx, R.A.; James, M.; Kassiou, M.; de Vries, E.F.J. [11C]-DPA-713 and [18F]-DPA-714 as new PET tracers for TSPO: A comparison with [11C]-(R)-PK11195 in a rat model of herpes encephalitis. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2009, 11, 386–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sarda-Mantel, L.; Alsac, J.M.; Boisgard, R.; Hervatin, F.; Montravers, F.; Tavitian, B.; Michel, J.B.; Le Guludec, D. Comparison of 18F-fluoro-deoxy-glucose, 18F-fluoro-methyl-choline, and 18F-DPA714 for positron-emission tomography imaging of leukocyte accumulation in the aortic wall of experimental abdominal aneurysms. J. Vasc. Surg. 2012, 56, 765–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pottier, G.; Bernards, N.; Dollé, F.; Boisgard, R. [18F]DPA-714 as a biomarker for positron emission tomography imaging of rheumatoid arthritis in an animal model. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2014, 16, R69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gent, Y.Y.J.; Weijers, K.; Molthoff, C.F.M.; Windhorst, A.D.; Huisman, M.C.; Kassiou, M.; Jansen, G.; Lammertsma, A.A.; van der Laken, C.J. Promising potential of new generation translocator protein tracers providing enhanced contrast of arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2014, 16, R70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuszpit, K.; Hollidge, B.S.; Zeng, X.; Stafford, R.G.; Daye, S.; Zhang, X.; Basuli, F.; Golden, J.W.; Swenson, R.E.; Smith, D.R.; et al. [18F]DPA-714 PET imaging reveals global neuroinflammation in Zika Virus-infected mice. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2018, 20, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keller, T.; Krzyczmonik, A.; Forsback, S.; Picón, F.R.L.; Kirjavainen, A.K.; Takkinen, J.; Rajander, J.; Cacheux, F.; Damont, A.; Dollé, F.; et al. Radiosynthesis and preclinical evaluation of [18F]F-DPA, a novel pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine acetamide TSPO radioligand, in healthy Sprague Dawley rats. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2017, 19, 736–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tang, D.; Hight, M.R.; McKinley, E.T.; Fu, A.; Buck, J.R.; Smith, R.A.; Tantawy, M.N.; Peterson, T.E.; Colvin, D.C.; Ansari, M.S.; et al. Quantitative preclinical imaging of TSPO expression in glioma using N,N-diethyl-2-(2-(4-(2-18F-fluoroethoxy)phenyl)-5,7-dimethylpyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-3-yl)acetamide. J. Nucl. Med. 2012, 53, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Médran-Navarrete, V.; Bernards, N.; Kuhnast, B.; Damont, A.; Pottier, G.; Peyronneau, M.A.; Kassiou, M.; Marguet, F.; Puech, F.; Boisgard, R.; et al. [18F]DPA-C5yne, a novel fluorine-18-labelled analogue of DPA-714: Radiosynthesis and preliminary evaluation as a radiotracer for imaging neuroinflammation with PET. J. Label Compd. Radiopharm. 2014, 57, 410–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, D.; Fujinaga, M.; Hatori, A.; Zhang, Y.; Yamasaki, T.; Xie, L.; Mori, W.; Kumata, K.; Liu, J.; Manning, H.C.; et al. Evaluation of the novel TSPO radiotracer 2-(7-butyl-2-(4-(2-([18F]fluoroethoxy)phenyl)-5-methylpyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-3-yl)-N,N-diethylacetamide in a preclinical model of neuroinflammation. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 150, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, D.; Li, J.; Nickels, M.L.; Huang, G.; Cohen, A.S.; Manning, H.C. Preclinical evaluation of a novel TSPO PET ligand 2-(7-butyl-2-(4-(2-[18F]fluoroethoxy)phenyl)-5-methylpyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-3-yl)-N,N-diethylacetamide (18F-VUIIS1018A) to image glioma. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2019, 21, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, Y.D.; Kang, S.; Park, H.; Cheong, I.K.; Chang, K.A.; Lee, S.Y.; Jung, J.H.; Lee, B.C.; Lim, S.T.; Kim, H.K. Novel potential pyrazolopyrimidine based translocator protein ligands for the evaluation of neuroinflammation with PET. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 159, 292–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verweij, S.L.; Stiekema, L.C.A.; Delewi, R.; Zheng, K.H.; Moens, S.J.B.; Kroon, J.; Stroes, C.I.; Versloot, M.; Piek, J.J.; Verberne, H.J.; et al. Prolonged hematopoietic and myeloid cellular response in patients after an acute coronary syndrome measured with 18F-DPA-714 PET/CT. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2018, 45, 1956–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]












© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gomes, P.M.O.; Silva, A.M.S.; Silva, V.L.M. Pyrazoles as Key Scaffolds for the Development of Fluorine-18-Labeled Radiotracers for Positron Emission Tomography (PET). Molecules 2020, 25, 1722. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25071722
Gomes PMO, Silva AMS, Silva VLM. Pyrazoles as Key Scaffolds for the Development of Fluorine-18-Labeled Radiotracers for Positron Emission Tomography (PET). Molecules. 2020; 25(7):1722. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25071722
Chicago/Turabian StyleGomes, Pedro M. O., Artur M. S. Silva, and Vera L. M. Silva. 2020. "Pyrazoles as Key Scaffolds for the Development of Fluorine-18-Labeled Radiotracers for Positron Emission Tomography (PET)" Molecules 25, no. 7: 1722. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25071722
APA StyleGomes, P. M. O., Silva, A. M. S., & Silva, V. L. M. (2020). Pyrazoles as Key Scaffolds for the Development of Fluorine-18-Labeled Radiotracers for Positron Emission Tomography (PET). Molecules, 25(7), 1722. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25071722