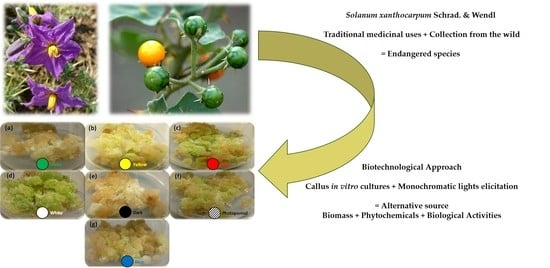
Interactive Effects of Wide-Spectrum Monochromatic Lights on Phytochemical Production, Antioxidant and Biological Activities of Solanum xanthocarpum Callus Cultures
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Effects of Lights on Biomass Accumulation in S. xanthocarpum
2.2. Total Phenolic and Flavonoid Contents in S. xanthocarpum
2.3. HPLC Analysis of Phytochemicals
2.4. In Vitro Antioxidant Activities
2.5. In Vitro Cell Free Anti-Diabetic Potential
2.6. In Vitro Cell Free Anti-Aging Assays
2.7. In Vitro Cell Free Anti-Inflammatory Potential of S. xanthocarpum Callus Extracts
2.8. Correlations Analysis
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Reagents
3.2. Seed Collection and Germination
3.3. Callus Culture Establishment
3.4. Lights Exposure Conditions
3.5. Extracts Preparation
3.6. Total Phenolic and Total Flavonoid Contents
3.7. HPLC Analysis
3.8. In vitro Cell-Free Antioxidant Assays
3.8.1. DPPH Free Radical Scavenging Assay
3.8.2. FRAP Assay (Ferric Reducing Antioxidant Power)
3.8.3. ABTS Assay
3.9. In Vitro Cell Free Anti-Diabetic Assays
3.9.1. α-Amylase Inhibition Assay
3.9.2. α-Glucosidase Inhibition Assay
3.10. In vitro Cell Free Anti-Aging Assays
3.10.1. Inhibition of AGEs Formation
3.10.2. Elastase Inhibition Assay
3.10.3. Tyrosinase Inhibition Assay
3.10.4. Collagenase Inhibition Assay
3.10.5. Hyaluronidase Assay
3.11. Anti-Inflammatory Activities
3.11.1. COX-1 and COX-2 Inhibition Assay
3.11.2. 15-LOX Inhibition Assay
3.11.3. sPLA2 Inhibition Assay
3.12. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NAA | Naphthalene acetic acid |
| BAP | 6-Benzyl adenine |
| DPPH | 2,2-Diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl |
| HPLC | High-performance liquid chromatography |
| MS | Murashige and Skoog |
| TPC | Total phenolic content |
| TFC | Total flavonoid content |
| DW | Dry weight |
| FW | Fresh weight |
| PGRs | Plant growth regulators |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| PAL | Phenylalanine ammonia-lyase |
| FRAP | Ferric reducing antioxidant power |
| ABTS | 2,2-Azinobis (3-ethylbenzthiazoline-6-sulphonic acid) |
| AGE | Advanced glycation end products |
| COX-1 | cyclooxygenase-1 |
| COX-2 | cyclooxygenase-2 |
| sPLA2 | phospholipase A2 |
| 15-LOX | lipoxygenase |
References
- World Health Organization. WHO Traditional Medicine Strategy: 2014–2023; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013; ISBN 9241506091. [Google Scholar]
- Sultana, S.; Asif, H.M.; Akhtar, N.; Ahmad, K. Medicinal plants with potential antipyretic activity: A review. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Dis. 2015, 5, S202–S208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrovska, B.B. Historical review of medicinal plants′ usage. Pharmacogn. Rev. 2012, 6, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, F.-S.; Weng, J.-K. Demystifying traditional herbal medicine with modern approach. Nat. Plants 2017, 3, 17109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pardhi, P.; Jain, A.P.; Ganeshpurkar, A.; Rai, G. Anti-microbial, Anti-oxidant and Anthelmintic Activity of Crude Extract of Solanum xanthocarpum. Pharmacogn. J. 2010, 2, 400–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, T.; Gupta, R.K.; Sweety, K.; Eswaran, B.; Vijayakumar, M.; Rao, C.V. Nephroprotective activity of Solanum xanthocarpum fruit extract against gentamicin–induced nephrotoxicity and renal dysfunction in experimental rodents. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2012, 5, 686–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, S.; Sharma, U.K.; Sharma, A.K.; Pandey, A.K. Protective efficacy of Solanum xanthocarpum root extracts against free radical damage: phytochemical analysis and antioxidant effect. Cell. Mol. Boil. 2012, 58, 171–178. [Google Scholar]
- Poongothai, K.; Ponmurugan, P.; Ahmed, K.S.Z.; Kumar, B.S.; Sheriff, S. Antihyperglycemic and antioxidant effects of Solanum xanthocarpum leaves (field grown & in vitro raised) extracts on alloxan induced diabetic rats. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2011, 4, 778–785. [Google Scholar]
- Kar, D.; Maharana, L.; Pattnaik, S.; Dash, G.K. Studies on hypoglycaemic activity of Solanum xanthocarpum Schrad. & Wendl. fruit extract in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2006, 108, 251–256. [Google Scholar]
- Anwikar, S.; Bhitre, M. Study of the synergistic anti-inflammatory activity of Solanum xanthocarpum Schrad and Wendl and Cassia fistula Linn. Int. J. Ayurveda Res. 2010, 1, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ambavade, S.D.; More, S.K.; Lande, A.A.; Jagdale, P.G.; Adkar, P. Evaluation of anti-inflammatory activity of Solanum xanthocarpum Schrad and Wendl (Kaṇṭakāri) extract in laboratory animals. Anc. Sci. Life 2013, 32, 222–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sinha, S.C. Medicinal Plants of Manipur; Mass & Sinha: Imphal, India, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Emmanuel, S.; Ignacimuthu, S.; Perumalsamy, R.; Amalraj, T. Antiinflammatory activity of Solanum trilobatum. Fitoterapia 2006, 77, 611–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saiyed, I.Z.; Kanga, D.D. Chemical examination of the fruits of Solanum xanthocarpum. Proc. Proc. Math. Sci. 1936, 4, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heble, M.R.; Narayanaswami, S.; Chadha, M.S. Diosgenin and beta-Sitosterol: Isolation from Solanum Xanthocarpum Tissue Cultures. Science 1968, 161, 1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kusano, G.; Beisler, J.; Sato, Y. Steroidal constituents of Solanum xanthocarpum. Phytochemistry 1973, 12, 397–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heble, M.; Narayanaswami, S.; Chadha, M. Hormonal control of steroid synthesis in Solanum xanthocarpum tissue cultures. Phytochemistry 1971, 10, 2393–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourgaud, F.; Hehn, A.; Larbat, R.; Doerper, S.; Gontier, E.; Kellner, S.; Matern, U. Biosynthesis of coumarins in plants: A major pathway still to be unravelled for cytochrome P450 enzymes. Phytochem. Rev. 2006, 5, 293–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamat, F.; Olry, A.; Doerper, S.; Vialart, G.; Ullmann, P.; Werck-Reichhart, D.; Bourgaud, F.; Hehn, A. CYP98A22, a phenolic ester 3’-hydroxylase specialized in the synthesis of chlorogenic acid, as a new tool for enhancing the furanocoumarin concentration in Ruta graveolens. BMC Plant. Boil. 2012, 12, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gandhi, G.R.; Ignacimuthu, S.; Paulraj, M.G.; Sasikumar, P. Antihyperglycemic activity and antidiabetic effect of methyl caffeate isolated from Solanum torvum Swartz. fruit in streptozotocin induced diabetic rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 670, 623–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, T.I.; Frost, S. Floral biodiversity: A question of survival in the Indian Thar Desert. Environmentalist 2001, 21, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundar, A.N.; Jawahar, M. In vitro plant regeneration from leaf and stem explants of Solanum xanthocarpum Schard & Wendl.—An important medicinal herb. J. Agric. Technol. 2011, 7, 301–306. [Google Scholar]
- Verpoorte, R.; Contin, A.; Memelink, J. Biotechnology for the production of plant secondary metabolites. Phytochem. Rev. 2002, 1, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman; Amin, M.; Islam; Sultana, R. Mass propagation of Solanum surattense Bum. using direct adventitious shoot organogenesis from internode. Acta Agric. Slov. 2011, 97, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Zubaida, Y.; Khan, M.A.; Shinwari, Z.K. A new variety of Solanum surattense Burm. from Pakistan. Pakistan. J. Bot. 2009, 41, 2097–2103. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, S.D.; Jatothu, B. Fundamentals and applications of light-emitting diodes (LEDs) in in vitro plant growth and morphogenesis. Plant. Biotechnol. Rep. 2013, 7, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jao, R.-C.; Fang, W. Effects of Frequency and Duty Ratio on the Growth of Potato Plantlets In Vitro Using Light-emitting Diodes. HortScience 2004, 39, 375–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jao, R.-C.; Lai, C.-C.; Fang, W.; Chang, S.-F. Effects of Red light on the Growth of Zantedeschia Plantlets in vitro and Tuber Formation Using Light-emitting Diodes. HortScience 2005, 40, 436–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nhut, D.; Hong, L.; Watanabe, H.; Goi, M.; Tanaka, M. Growth of Banana Plantlets Cultured In Vitro under Red and Blue Light-Emitting Diode (LED) Irradiation Source. Acta Hortic. 2002, 575, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, K.; Yanagi, T.; Takita, S.; Tanaka, M.; Higuchi, T.; Ushida, Y.; Watanabe, H. Development of Plant Growth Apparatus Using Blue And Red Led as Artificial Light Source. Acta Hortic. 1996, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheeba, E.; Palanivel, S. Callus Induction and Antifungal Studies on Solanum surattense Burm. F. Mid. East. J. Sci. Res. 2013, 16, 122–126. [Google Scholar]
- Siegień, I.; Adamczuk, A.; Wróblewska, K. Light affects in vitro organogenesis of Linum usitatissimum L. and its cyanogenic potential. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2012, 35, 781–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peng, S.; Krieg, D.R.; Girma, F.S. Leaf photosynthetic rate is correlated with biomass and grain production in grain sorghum lines. Photosynth. Res. 1991, 28, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tariq, U.; Ali, Y.; Abbasi, B.H. Morphogenic and biochemical variations under different spectral lights in callus cultures of Artemisia absinthium L. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Boil. 2014, 130, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullah, M.A.A.; Tungmunnithum, D.; Garros, L.; Drouet, S.; Hano, C.; Abbasi, B.H. Effect of Ultraviolet-C Radiation and Melatonin Stress on Biosynthesis of Antioxidant and Antidiabetic Metabolites Produced in In Vitro Callus Cultures of Lepidium sativum L. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ali, M.; Abbasi, B.H. Light-induced fluctuations in biomass accumulation, secondary metabolites production and antioxidant activity in cell suspension cultures of Artemisia absinthium L. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Boil. 2014, 140, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadeem, M.; Ahmed, W.; Zahir, A.; Hano, C.; Hano, C. Salicylic acid-enhanced biosynthesis of pharmacologically important lignans and neo lignans in cell suspension culture of Linum ussitatsimum L. Eng. Life Sci. 2018, 19, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shah, M.; Ullah, M.A.A.; Drouet, S.; Younas, M.; Tungmunnithum, D.; Giglioli-Guivarc’H, N.; Hano, C.; Abbasi, B.H. Interactive Effects of Light and Melatonin on Biosynthesis of Silymarin and Anti-Inflammatory Potential in Callus Cultures of Silybum marianum (L.) Gaertn. Molecules 2019, 24, 1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khan, T.; Ullah, M.A.; Garros, L.; Hano, C.; Abbasi, B.H. Synergistic effects of melatonin and distinct spectral lights for enhanced production of anti-cancerous compounds in callus cultures of Fagonia indica. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Boil. 2019, 190, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adil, M.; Abbasi, B.H.; Khan, T. Interactive effects of melatonin and light on growth parameters and biochemical markers in adventitious roots of Withania somnifera L. Plant. Cell Tissue Organ. Cult. (PCTOC) 2015, 123, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, N.; Rab, A.; Ahmad, N. Light-induced biochemical variations in secondary metabolite production and antioxidant activity in callus cultures of Stevia rebaudiana (Bert). J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Boil. 2016, 154, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, E.; Ouzounis, T.; Giday, H.; Schipper, R.; Heuvelink, E.; Marcelis, L. Adding Blue to Red Supplemental Light Increases Biomass and Yield of Greenhouse-Grown Tomatoes, but Only to an Optimum. Front. Plant. Sci. 2019, 9, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tan, J.; Bednarek, P.; Liu, J.; Schneider, B.; Svatoš, A.; Hahlbrock, K. Universally occurring phenylpropanoid and species-specific indolic metabolites in infected and uninfected Arabidopsis thaliana roots and leaves. Phytochemistry 2004, 65, 691–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ali, M.B.; Khatun, S.; Hahn, E.-J.; Paek, K.Y. Enhancement of phenylpropanoid enzymes and lignin in Phalaenopsis orchid and their influence on plant acclimatisation at different levels of photosynthetic photon flux. Plant. Growth Regul. 2006, 49, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csepregi, K.; Hideg, E. Phenolic Compound Diversity Explored in the Context of Photo-Oxidative Stress Protection. Phytochem. Anal. 2017, 29, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hohtola, A.; Jaakola, L. Activation of flavonoid biosynthesis by solar radiation in bilberry (Vaccinium myrtillus L.) leaves. Planta 2004, 218, 721–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rukh, G.; Ahmad, N.; Rab, A.; Ahmad, N.; Fazal, H.; Akbar, F.; Ullah, I.; Mukhtar, S.; Samad, N. Photo-dependent somatic embryogenesis from non-embryogenic calli and its polyphenolics content in high-valued medicinal plant of Ajuga bracteosa. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Boil. 2019, 190, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idrees, M.; Sania, B.; Hafsa, B.; Kumari, S.; Khan, H.; Fazal, H.; Ahmad, I.; Akbar, F.; Ahmad, N.; Ali, S.; et al. Spectral lights trigger biomass accumulation and production of antioxidant secondary metabolites in adventitious root cultures of Stevia rebaudiana (Bert.). Comptes Rendus Boil. 2018, 341, 334–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.-Y.; Park, S.-A.; Park, B.-J.; Lee, Y.; Oh, M.-M. Growth and antioxidant phenolic compounds in cherry tomato seedlings grown under monochromatic light-emitting diodes. Hortic. Environ. Biotechnol. 2014, 55, 506–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, S.; Raghuvanshi, R.; Bhardwaj, P.; Sood, H.; Saxena, S.; Chaurasia, O.P. Influence of light quality on growth, secondary metabolites production and antioxidant activity in callus culture of Rhodiola imbricata Edgew. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Boil. 2018, 183, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazal, H.; Abbasi, B.H.; Ahmad, N.; Ali, S.S.; Akbar, F.; Kanwal, F. Correlation of different spectral lights with biomass accumulation and production of antioxidant secondary metabolites in callus cultures of medicinally important Prunella vulgaris L. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Boil. 2016, 159, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shohael, A.; Ali, M.; Yu, K.; Hahn, E.; Islam, R.; Paek, K.Y. Effect of light on oxidative stress, secondary metabolites and induction of antioxidant enzymes in Eleutherococcus senticosus somatic embryos in bioreactor. Process. Biochem. 2006, 41, 1179–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, M.-L.; Murthy, H.; Paek, K.Y. Effects of light emitting diodes (LEDs) on the in vitro induction and growth of bulblets of Lilium oriental hybrid ‘Pesaro’. Sci. Hortic. 2002, 94, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, M.A.; Tungmunnithum, D.; Garros, L.; Hano, C.; Abbasi, B.H. Monochromatic lights-induced trends in antioxidant and antidiabetic polyphenol accumulation in in vitro callus cultures of Lepidium sativum L. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Boil. 2019, 196, 111505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitazaki, K.; Fukushima, A.; Nakabayashi, R.; Okazaki, Y.; Kobayashi, M.; Mori, T.; Nishizawa, T.; Reyes-Chin-Wo, S.; Michelmore, R.W.; Saito, K.; et al. Metabolic Reprogramming in Leaf Lettuce Grown Under Different Light Quality and Intensity Conditions Using Narrow-Band LEDs. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyes, L.F.; Cisneros-Zevallos, L. Wounding Stress Increases the Phenolic Content and Antioxidant Capacity of Purple-Flesh Potatoes (Solanum tuberosumL.). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 5296–5300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbasi, B.H.; Tian, C.-L.; Murch, S.J.; Saxena, P.K.; Liu, C.-Z. Light-enhanced caffeic acid derivatives biosynthesis in hairy root cultures of Echinacea purpurea. Plant. Cell Rep. 2007, 26, 1367–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwai, M.; Ohta, M.; Tsuchiya, H.; Suzuki, T. Enhanced accumulation of caffeic acid, rosmarinic acid and luteolin-glucoside in red perilla cultivated under red diode laser and blue LED illumination followed by UV-A irradiation. J. Funct. Foods 2010, 2, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, T.; Kobayashi, E.; Nakamura, Y.; Kobayashi, H. Polyphenol biofortification of tea leaves by exposure to light-emitting diode (LED). In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on O-CHA (Tea) Culture and Science [Online], Shizuoka Convention & Arts Center “GRANSHIP”, Shizuoka, Japan, 26–28 October 2010; ogawa1/1–ogawa1/4. Available online: http://sfns.u-shizuoka-ken.ac.jp/pctech/ICOS10-pr-p-31.pdf (accessed on 28 January 2020).
- Younas, M.; Drouet, S.; Nadeem, M.; Giglioli-Guivarc’H, N.; Hano, C.; Abbasi, B.H. Differential accumulation of silymarin induced by exposure of Silybum marianum L. callus cultures to several spectres of monochromatic lights. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Boil. 2018, 184, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, K.; Roychoudhury, A. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) and response of antioxidants as ROS-scavengers during environmental stress in plants. Front. Environ. Sci. 2014, 2, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alexieva, V.; Sergiev, I.; Karanov, E.; Mapelli, S. The effect of drought and ultraviolet radiation on growth and stress markers in pea and wheat. Plant. Cell Environ. 2001, 24, 1337–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.-W.; Anderson, D. Reactive oxygen species-induced DNA damage and its modification: A chemical investigation. Mutat. Res. Mol. Mech. Mutagen. 1997, 379, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittler, R. Oxidative stress, antioxidants and stress tolerance. Trends Plant. Sci. 2002, 7, 405–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuolienė, G.; Brazaitytė, A.; Urbonavičiūtė, A.; Šabajevienė, G.; Duchovskis, P. The effect of red and blue light component on the growth and development of frigo strawberries. Žemdirbystė (Agriculture) 2010, 2, 99–104. [Google Scholar]
- Schlesier, K.; Harwat, M.; Böhm, V.; Bitsch, R. Assessment of antioxidant activity by using different in vitro methods. Free. Radic. Res. 2002, 36, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashry, N.A. Impact of secondary metabolites and related enzymes in flax resistance and/or susceptibility to powdery mildew. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2012, 11, 78–85. [Google Scholar]
- Engelsma, G. The Influence of Light of Different Spectral Regions on the Synthesis of Phenolic Compounds In Gherkin Seedings, In Relation to Photomorphogenesis: VI. Phenol Synthesis and PHOTOPERIODISM. Acta Bot. Neerl. 1969, 18, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelsma, G. A Comparative Investigation of the Control of Phenylalanine Ammonia-Lyase Activity in Gherkin and Red Cabbage Hypocotyls. Acta Bot. Neerl. 1970, 19, 403–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- I Aruoma, O. Methodological considerations for characterizing potential antioxidant actions of bioactive components in plant foods. Mutat. Res. Mol. Mech. Mutagen. 2003, 523, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, S.; Leong, L.; Williamkoh, J. Antioxidant activities of aqueous extracts of selected plants. Food Chem. 2006, 99, 775–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kedare, S.B.; Singh, R.P. Genesis and development of DPPH method of antioxidant assay. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 48, 412–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mishra, A.; Kumar, S.; Bhargava, A.; Sharma, B.; Pandey, A.K. Studies on in vitro antioxidant and antistaphylococcal activities of some important medicinal plants. Cell. Mol. Boil. 2011, 57, 16–25. [Google Scholar]
- Hano, C.; Corbin, C.; Drouet, S.; Quéro, A.; Rombaut, N.; Savoire, R.; Molinié, R.; Thomasset, B.; Mesnard, F.; Lainé, E. The lignan (+)-secoisolariciresinol extracted from flax hulls is an effective protectant of linseed oil and its emulsion against oxidative damage. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2017, 119, 1600219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manivannan, A.; Soundararajan, P.; Halimah, N.; Ko, C.H.; Jeong, B.R. Blue LED light enhances growth, phytochemical contents, and antioxidant enzyme activities of Rehmannia glutinosa cultured in vitro. Hortic. Environ. Biotechnol. 2015, 56, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olokoba, A.B.; Obateru, O.A.; Olokoba, L.B. Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Review of Current Trends. Oman Med. J. 2012, 27, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hano, C.; Renouard, S.; Molinié, R.; Corbin, C.; Barakzoy, E.; Doussot, J.; Lamblin, F.; Lainé, E. Flaxseed (Linum usitatissimum L.) extract as well as (+)-secoisolariciresinol diglucoside and its mammalian derivatives are potent inhibitors of α-amylase activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 3007–3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adisakwattana, S.; Chantarasinlapin, P.; Thammarat, H.; Yibchok-Anun, S. A series of cinnamic acid derivatives and their inhibitory activity on intestinal?-glucosidase. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2009, 24, 1194–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oboh, G.; Agunloye, O.; Adefegha, A.; Akinyemi, A.; Ademiluyi, A.O. Caffeic and chlorogenic acids inhibit key enzymes linked to type 2 diabetes (in vitro): A comparative study. J. Basic Clin. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2015, 26, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabakaran, D.; AshokKumar, N. Antihyperglycemic effect of esculetin modulated carbohydrate metabolic enzymes activities in streptozotocin induced diabetic rats. J. Funct. Foods 2012, 4, 776–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.H.; Park, J.E.; Han, J.S. Scopoletin inhibits α-glucosidase in vitro and alleviates postprandial hyperglycemia in mice with diabetes. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 834, 152–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.H.; Park, J.E.; Han, J.S. Scopoletin increases glucose uptake through activation of PI3K and AMPK signaling pathway and improves insulin sensitivity in 3T3-L1 cells. Nutr. Res. 2020, 74, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkel, T.; Holbrook, N.J. Oxidants, oxidative stress and the biology of ageing. Nature 2000, 408, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkogkolou, P.; Böhm, M. Advanced glycation end products: Key players in skin aging? Derm. Endocrinol. 2012, 4, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fraser, D.; Hansen, K. Making sense of advanced glycation end products and their relevance to diabetic complications. Inter. Diabetes Monit. 2005, 17, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Abbasi, B.H.; Siddiquah, A.; Tungmunnithum, D.; Bose, S.; Younas, M.; Garros, L.; Drouet, S.; Giglioli-Guivarc’H, N.; Hano, C. Isodon rugosus (Wall. ex Benth.) Codd In Vitro Cultures: Establishment, Phytochemical Characterization and In Vitro Antioxidant and Anti-Aging Activities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Garcia-Jimenez, A.; Garcia-Molina, F.; Puche, J.A.A.T.P.; Saura-Sanmartin, A.; Garcia-Ruiz, P.A.; Ortiz-Lopez, A.; Rodríguez-López, J.N.; Garcia-Canovas, F.; Muñoz-Muñoz, J.L. Catalysis and inhibition of tyrosinase in the presence of cinnamic acid and some of its derivatives. Int. J. Boil. Macromol. 2018, 119, 548–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishizawa, S.; Yamaoka, H.; Matsui, M.; Hirabayashi, S.; Hoshi, K.; Koshima, I.; Yamaoka, K. Selection and Effect of Ointment Bases for Preparing Collagenase Inhibitor Ointment Using High-Performance Liquid Chromatography and Franzcell Apparatus. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2009, 62, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshima, N.; Narukawa, Y.; Takeda, T.; Kiuchi, F. Collagenase inhibitors from Viola yedoensis. J. Nat. Med. 2012, 67, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rathee, P.; Chaudhary, H.; Rathee, S.; Rathee, D.; Kumar, V.; Kohli, K. Mechanism of action of flavonoids as anti-inflammatory agents: A review. Inflamm. Allergy Drug Targets 2009, 8, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, A.; Ligresti, A.; Longo, R.; Russo, A.; Borrelli, F.; Sautebin, L. The inhibitory effect of propolis and caffeic acid phenethyl ester on cyclooxygenase activity in J774 macrophages. Phytomedicine 2002, 9, 530–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.; Cho, S.K.; Jeong, K.-J.; Park, J.-W.; Park, W.-J. Caffeic acid, morin hydrate and quercetin partially attenuate sulfur mustard-induced cell death by inhibiting the lipoxygenase pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 14, 4454–4460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moon, P.-D.; Lee, B.-H.; Jeong, H.-J.; An, H.-J.; Park, S.-J.; Kim, H.-R.; Ko, S.-G.; Um, J.-Y.; Hong, S.-H.; Kim, H.-M. Use of scopoletin to inhibit the production of inflammatory cytokines through inhibition of the IκB/NF-κB signal cascade in the human mast cell line HMC-1. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2007, 555, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Dai, Y.; Hao, H.; Pan, R.; Yao, X.; Wang, Z. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Scopoletin and Underlying Mechanisms. Pharm. Boil. 2008, 46, 854–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keizo, S.; Hiromichi, O.; Shigeru, A. Selective inhibition of platelet lipoxygenase by esculetin. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Lipids Lipid Metab. 1982, 713, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazir, M.; Tungmunnithum, D.; Bose, S.; Drouet, S.; Garros, L.; Giglioli-Guivarc’H, N.; Abbasi, B.H.; Hano, C. Differential Production of Phenylpropanoid Metabolites in Callus Cultures ofOcimum basilicumL. with Distinct In VitroAntioxidant Activities and In VivoProtective Effects against UV stress. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 1847–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadeghian, H.; Jabbari, A. 15-Lipoxygenase inhibitors: A patent review. Expert Opin. Ther. Patents 2015, 26, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kammoun, M.; Miladi, S.; Ben Ali, Y.; Damak, M.; Gargouri, Y.; Sofiane, B. In vitro study of the PLA2 inhibition and antioxidant activities of Aloe vera leaf skin extracts. Lipids Heal. Dis. 2011, 10, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Murashige, T.; Skoog, F. A Revised Medium for Rapid Growth and Bio Assays with Tobacco Tissue Cultures. Physiol. Plant. 1962, 15, 473–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, N.; Fazal, H.; Abbasi, B.H.; Rashid, M.; Mahmood, T.; Fatima, N. Efficient regeneration and antioxidant potential in regenerated tissues of Piper nigrum L. Plant. Cell Tissue Organ. Cult. (PCTOC) 2010, 102, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahir, A.; Abbasi, B.H.; Adil, M.; Anjum, S.; Zia, M.; Haq, I.U. Synergistic Effects of Drought Stress and Photoperiods on Phenology and Secondary Metabolism of Silybum marianum. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2014, 174, 693–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singleton, V.L.; Rossi, J.A. Colorimetry of totalphenolics with phospho-molybdic-phosphotungstic acid reagents. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 1965, 16, 144–158. [Google Scholar]
- Mozetič, B.; Trebše, P.; Hribar, J. Determination and Quantitation of Anthocyanins and Hydroxycinnamic Acids in Different Cultivars of Sweet Cherries (Prunus avium L.) from Nova Gorica Region (Slovenia). Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2002, 40. [Google Scholar]
- Benzie, I.; Strain, J. The Ferric Reducing Ability of Plasma (FRAP) as a Measure of “Antioxidant Power”: The FRAP Assay. Anal. Biochem. 1996, 239, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tagliazucchi, D.; Verzelloni, E.; Bertolini, D.; Conte, A. In vitro bio-accessibility and antioxidant activity of grape polyphenols. Food Chem. 2010, 120, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Ramsay, A.; Paetz, C.; Tatsis, E.; Renouard, S.; Hano, C.; Grand, E.; Fliniaux, O.; Roscher, A.; Mesnard, F.; et al. Concentration Kinetics of Secoisolariciresinol Diglucoside and its Biosynthetic Precursor Coniferin in Developing Flaxseed. Phytochem. Anal. 2012, 24, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaewseejan, N.; Siriamornpun, S. Bioactive components and properties of ethanolic extract and its fractions from Gynura procumbens leaves. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2015, 74, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittenauer, J.; Mäckle, S.; Sußmann, D.; Schweiggert-Weisz, U.; Carle, R. Inhibitory effects of polyphenols from grape pomace extract on collagenase and elastase activity. Fitoterapia 2015, 101, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, W.-M.; Huang, Q.; Lin, M.-Z.; Ou-Yang, C.; Huang, W.-Y.; Wang, Y.-X.; Xu, K.-L.; Feng, H.-L. Condensed Tannins from Longan Bark as Inhibitor of Tyrosinase: Structure, Activity, and Mechanism. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 908–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolakul, P.; Sripanidkulchai, B. Phytochemicals and anti-aging potentials of the extracts from Lagerstroemia speciosa and Lagerstroemia floribunda. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2017, 109, 707–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of Solanum xanthocarpum extracts are available from the authors. |











| Light Treatment | Phytochemicals (mg/g DW) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Caffeic Acid | Methyl-Caffeate | Scopoletin | Esculetin | |
| Photoperiod | 0.32 ± 0.03 d | 6.64 ± 0.85 d | 2.07 ± 0.08 a,b | 0.62 ± 0.06 a,b |
| Yellow | 0.44 ± 0.01 c | 9.69 ± 1.33 c | 1.66 ± 0.06 c | 0.52 ± 0.05 b |
| Red | 0.40 ± 0.04 c,d | 9.73 ± 1.85 b,c,d | 2.08 ± 0.09 a,b | 0.56 ± 0.06 a,b |
| Blue | 0.57 ± 0.06 a | 17.19 ± 1.79 a | 2.28 ± 0.13 a | 0.68 ± 0.07 a |
| White light | 0.48 ± 0.01 b | 12.75 ± 1.41 b,c | 1.68 ± 0.07 c | 0.53 ± 0.04 b |
| Dark | 0.45 ± 0.04 b,c | 13.44 ± 1.75 a,b | 1.70 ± 0.11 c | 0.54 ± 0.05 b |
| Green | 0.43 ± 0.03 b,c | 9.33 ± 1.34 c | 1.88 ± 0.12 b,c | 0.56 ± 0.02 b |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Usman, H.; Ullah, M.A.; Jan, H.; Siddiquah, A.; Drouet, S.; Anjum, S.; Giglioli-Guviarc’h, N.; Hano, C.; Abbasi, B.H. Interactive Effects of Wide-Spectrum Monochromatic Lights on Phytochemical Production, Antioxidant and Biological Activities of Solanum xanthocarpum Callus Cultures. Molecules 2020, 25, 2201. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25092201
Usman H, Ullah MA, Jan H, Siddiquah A, Drouet S, Anjum S, Giglioli-Guviarc’h N, Hano C, Abbasi BH. Interactive Effects of Wide-Spectrum Monochromatic Lights on Phytochemical Production, Antioxidant and Biological Activities of Solanum xanthocarpum Callus Cultures. Molecules. 2020; 25(9):2201. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25092201
Chicago/Turabian StyleUsman, Hazrat, Muhammad Asad Ullah, Hasnain Jan, Aisha Siddiquah, Samantha Drouet, Sumaira Anjum, Nathalie Giglioli-Guviarc’h, Christophe Hano, and Bilal Haider Abbasi. 2020. "Interactive Effects of Wide-Spectrum Monochromatic Lights on Phytochemical Production, Antioxidant and Biological Activities of Solanum xanthocarpum Callus Cultures" Molecules 25, no. 9: 2201. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25092201
APA StyleUsman, H., Ullah, M. A., Jan, H., Siddiquah, A., Drouet, S., Anjum, S., Giglioli-Guviarc’h, N., Hano, C., & Abbasi, B. H. (2020). Interactive Effects of Wide-Spectrum Monochromatic Lights on Phytochemical Production, Antioxidant and Biological Activities of Solanum xanthocarpum Callus Cultures. Molecules, 25(9), 2201. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25092201