High Surface Area Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles with Tunable Size in the Sub-Micrometer Regime: Insights on the Size and Porosity Control Mechanisms
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
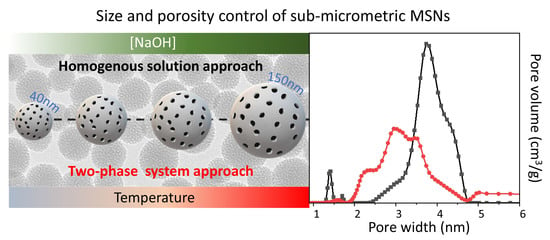
2.1. Synthesis of MSNs: Homogenous Solution Approach
2.2. Synthesis of MSNs: A Two-Phase System Approach
2.3. MSNs Textural Properties
2.4. Assessment of MSNs Toxicity on Cell Viability of Endothelial Cell Line
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Synthesis of MSNs: Homogenous Solution
3.3. Synthesis of MSNs: Two-Phase Approach
3.4. Characterization Techniques
3.5. MSN Cell Viability Test
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Jarmolińska, S.; Feliczak-Guzik, A.; Nowak, I. Synthesis, Characterization and Use of Mesoporous Silicas of the Following Types SBA-1, SBA-2, HMM-1 and HMM-2. Materials 2020, 13, 4385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivieri, F.; Castaldo, R.; Cocca, M.; Gentile, G.; Lavorgna, M. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles as carriers of active agents for smart anticorrosive organic coatings: A critical review. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 9091–9111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, N.; Lee, J.-H.; Cho, E.-B. Recent Trends in Morphology-Controlled Synthesis and Application of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Baeckmann, C.; Guillet-Nicolas, R.; Renfer, D.; Kählig, H.; Kleitz, F. A Toolbox for the Synthesis of Multifunctionalized Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 17496–17510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, S.; Derakhshankhah, H.; Alaei, L.; Fattahi, A.; Varnamkhasti, B.S.; Saboury, A.A. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles for therapeutic/diagnostic applications. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 109, 1100–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niculescu, V.-C. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Bio-Applications. Front. Mater. 2020, 7, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Da’na, E. Adsorption of heavy metals on functionalized-mesoporous silica: A review. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2017, 247, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Na, J.; Konarova, M.; Wakihara, T.; Yamauchi, Y.; Salomon, C.; Gawande, M.B. Functional Mesoporous Silica Nanomaterials for Catalysis and Environmental Applications. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2020, 93, 1459–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, W.; Wei, W.; Li, J.; Qi, X.; Zuo, G.; Chen, Q.; Pan, X.; Dong, W. Amine-functionalized magnetic mesoporous silica nanoparticles for DNA separation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 387, 1116–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motahar, S.; Nikkam, N.; Alemrajabi, A.A.; Khodabandeh, R.; Toprak, M.S.; Muhammed, M. A novel phase change material containing mesoporous silica nanoparticles for thermal storage: A study on thermal conductivity and viscosity. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2014, 56, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castaldo, R.; de Luna, M.S.; Siviello, C.; Gentile, G.; Lavorgna, M.; Amendola, E.; Cocca, M. On the acid-responsive release of benzotriazole from engineered mesoporous silica nanoparticles for corrosion protection of metal surfaces. J. Cult. Herit. 2020, 44, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florek, J.; Caillard, R.; Kleitz, F. Evaluation of mesoporous silica nanoparticles for oral drug delivery—Current status and perspective of MSNs drug carriers. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 15252–15277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stöber, W.; Fink, A.; Bohn, E. Controlled growth of monodisperse silica spheres in the micron size range. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1968, 26, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.-H.; Vivero-Escoto, J.L.; Slowing, I.I.; Fang, I.J.; Trewyn, B.G.; Lin, V.S.Y. Surfactant-assisted controlled release of hydrophobic drugs using anionic surfactant templated mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 6234–6244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Xu, L.-L.; Jiang, J.-G.; Calin, N.; Lam, K.-F.; Zhang, S.-J.; Wu, H.-H.; Wu, G.-D.; Albela, B.; Bonneviot, L.; et al. Facile Large-Scale Synthesis of Monodisperse Mesoporous Silica Nanospheres with Tunable Pore Structure. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 2427–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, L.; Gao, C.; Wu, X.; Chen, Q.; Shu, P.; Ding, Z.; Che, S. Anionic surfactants templating route for synthesizing silica hollow spheres with different shell porosity. Solid State Sci. 2011, 13, 721–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruk, M. Access to Ultralarge-Pore Ordered Mesoporous Materials through Selection of Surfactant/Swelling-Agent Micellar Templates. Acc. Chem. Res. 2012, 45, 1678–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Hartono, S.B.; Jin, Y.G.; Li, Z.; Lu, G.Q.; Qiao, S.Z. A facile vesicle template route to multi-shelled mesoporous silica hollow nanospheres. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 4595–4601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Niu, D.; Jiang, Y.; Xu, C.; Pan, S.; He, J.; Chen, J.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y. Morphology Evolution and Spatially Selective Functionalization of Hierarchically Porous Silica Nanospheres for Improved Multidrug Delivery. Chem. Mater. 2017, 29, 10377–10385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eltohamy, M.; Shin, U.S.; Kim, H.-W. Silica nanoparticles with enlarged nanopore size for the loading and release of biological proteins. Mater. Lett. 2011, 65, 3570–3573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Kruk, M. Versatile Surfactant/Swelling-Agent Template for Synthesis of Large-Pore Ordered Mesoporous Silicas and Related Hollow Nanoparticles. Chem. Mater. 2015, 27, 679–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, D.; Liu, Z.; Li, Y.; Luo, X.; Zhang, J.; Gong, J.; Shi, J. Monodispersed and Ordered Large-Pore Mesoporous Silica Nanospheres with Tunable Pore Structure for Magnetic Functionalization and Gene Delivery. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 4947–4953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.; Sun, Z.; Luo, W.; Li, Y.; Elzatahry, A.A.; Al-Enizi, A.M.; Deng, Y.; Zhao, D. New Insight into the Synthesis of Large-Pore Ordered Mesoporous Materials. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 1706–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Huang, H.; Dong, Y.; Sui, X.; Jian, B.; Zhu, W. A Comparative Study of the Use of Mesoporous Carbon and Mesoporous Silica as Drug Carriers for Oral Delivery of the Water-Insoluble Drug Carvedilol. Molecules 2019, 24, 1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moodley, T.; Singh, M. Sterically Stabilised Polymeric Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Improve Doxorubicin Efficiency: Tailored Cancer Therapy. Molecules 2020, 25, 742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Slowing, I.I.; Wu, C.-W.; Vivero-Escoto, J.L.; Lin, V.S.-Y. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Reducing Hemolytic Activity Towards Mammalian Red Blood Cells. Small 2009, 5, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozafarinia, M.; Karimi, S.; Farrokhnia, M.; Esfandiari, J. In vitro breast cancer targeting using Trastuzumab-conjugated mesoporous silica nanoparticles: Towards the new strategy for decreasing size and high drug loading capacity for drug delivery purposes in MSN synthesis. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2021, 316, 110950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Hu, J.; Wang, F.; Liu, H. Preparation and drug release application of pH and light dual-stimuli- responsive nanocarrier based on mesoporous silica nanoparticles. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2019, 40, 1725–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadhav, S.A.; Miletto, I.; Brunella, V.; Berlier, G.; Scalarone, D. Controlled post-synthesis grafting of thermoresponsive poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) on mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2015, 26, 1070–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferris, D.P.; Lu, J.; Gothard, C.; Yanes, R.; Thomas, C.R.; Olsen, J.-C.; Stoddart, J.F.; Tamanoi, F.; Zink, J.I. Synthesis of Biomolecule-Modified Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Targeted Hydrophobic Drug Delivery to Cancer Cells. Small 2011, 7, 1816–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Wang, Y.; Peng, B. Chitosan-Capped Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as pH-Responsive Nanocarriers for Controlled Drug Release. Chem. An. Asian J. 2014, 9, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mondragón, L.; Mas, N.; Ferragud, V.; de la Torre, C.; Agostini, A.; Martínez-Máñez, R.; Sancenón, F.; Amorós, P.; Pérez-Payá, E.; Orzáez, M. Enzyme-responsive intracellular-controlled release using silica mesoporous nanoparticles capped with ε-poly-L-lysine. Chemistry 2014, 20, 5271–5281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, P.; Guo, S.; Yu, H.; Li, X. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles (MSNs) for Detoxification of Hazardous Organophorous Chemicals. Small 2014, 10, 2404–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Hu, Y.; Xin, R.; Zhang, B.; Li, J.; Ding, X.; Hou, Y.; Yang, L.; Cai, K. Surface functionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticles with natural proteins for reduced immunotoxicity. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2014, 102, 3781–3794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribes, À.; Aznar, E.; Bernardos, A.; Marcos, M.D.; Amorós, P.; Martínez-Máñez, R.; Sancenón, F. Fluorogenic Sensing of Carcinogenic Bisphenol A using Aptamer-Capped Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles. Chemistry 2017, 23, 8581–8584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palanikumar, L.; Choi, E.S.; Cheon, J.Y.; Joo, S.H.; Ryu, J.-H. Noncovalent Polymer-Gatekeeper in Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as a Targeted Drug Delivery Platform. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 957–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Zhang, H.; Cao, C.; Zhang, J.; Li, F.; Huang, Q. Quaternized Chitosan-Capped Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as Nanocarriers for Controlled Pesticide Release. Nanomaterials 2016, 6, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, T.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, H. Phospholipid-Coated Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Acting as Lubricating Drug Nanocarriers. Polymers 2018, 10, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Melendez-Rodriguez, B.; Figueroa-Lopez, K.J.; Bernardos, A.; Martínez-Máñez, R.; Cabedo, L.; Torres-Giner, S.; Lagaron, J.M. Electrospun Antimicrobial Films of Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) Containing Eugenol Essential Oil Encapsulated in Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meka, A.K.; Jenkins, L.J.; Dàvalos-Salas, M.; Pujara, N.; Wong, K.Y.; Kumeria, T.; Mariadason, J.M.; Popat, A. Enhanced Solubility, Permeability and Anticancer Activity of Vorinostat Using Tailored Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shan, Y.; Cao, L.; Xu, C.; Zhao, P.; Cao, C.; Li, F.; Xu, B.; Huang, Q. Sulfonate-Functionalized Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as Carriers for Controlled Herbicide Diquat Dibromide Release through Electrostatic Interaction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, M.-K.; Ki, D.-H.; Na, Y.-G.; Lee, H.-S.; Baek, J.-S.; Lee, J.-Y.; Lee, H.-K.; Cho, C.-W. Optimization of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles through Statistical Design of Experiment and the Application for the Anticancer Drug. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, S.; Sahare, P.D. Photoluminescence studies of stilbene laser dye incorporated mesoporous silica nanoparticle (MSN) with sulphur dioxide. J. Porous Mater. 2014, 21, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, C.; Zhou, J.; Du, S.; Peng, S. Autophagy upregulation promotes macrophages to escape mesoporous silica nanoparticle (MSN)-induced NF-κB-dependent inflammation. Inflamm. Res. 2016, 65, 325–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrido-Cano, I.; Candela-Noguera, V.; Herrera, G.; Cejalvo, J.M.; Lluch, A.; Marcos, M.D.; Sancenon, F.; Eroles, P.; Martínez-Máñez, R. Biocompatibility and internalization assessment of bare and functionalised mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2021, 310, 110593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-García, D.; Sommerova, L.; Martisova, A.; Skoupilova, H.; Prashar, S.; Vaculovic, T.; Kanicky, V.; del Hierro, I.; Hrstka, R.; Gómez-Ruiz, S. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles functionalized with a dialkoxide diorganotin(IV) compound: In search of more selective systems against cancer cells. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2020, 300, 110154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katagiri, K.; Yamazaki, S.-I.; Inumaru, K.; Koumoto, K. Anti-reflective coatings prepared via layer-by-layer assembly of mesoporous silica nanoparticles and polyelectrolytes. Polym. J. 2015, 47, 190–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, G.-F.; Chen, W.-H.; Liu, Y.; Lei, Q.; Zhuo, R.-X.; Zhang, X.-Z. Multifunctional Enveloped Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Subcellular Co-delivery of Drug and Therapeutic Peptide. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zeng, D.; Zhang, H.; Wang, B.; Sang, K.; Yang, J. Effect of Ammonia Concentration on Silica Spheres Morphology and Solution Hydroxyl Concentration in Stober Process. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2015, 15, 7407–7411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, H.; Guo, L.; He, Q.; Chen, F.; Zhou, J.; Feng, J.; Shi, J. Hollow/Rattle-Type Mesoporous Nanostructures by a Structural Difference-Based Selective Etching Strategy. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 529–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Wu, W.B.; Mak, C.L.; Wong, K.H. Growth of highly oriented of Pb(Zrx, Ti1−x)O3 film on porous silicon. Thin Solid Film. 2001, 397, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warring, S.L.; Beattie, D.A.; McQuillan, A.J. Surficial Siloxane-to-Silanol Interconversion during Room-Temperature Hydration/Dehydration of Amorphous Silica Films Observed by ATR-IR and TIR-Raman Spectroscopy. Langmuir 2016, 32, 1568–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaya, H.; Ngo, D.; Gin, S.; Kim, S.H. Spectral changes in Si–O–Si stretching band of porous glass network upon ingress of water. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2020, 527, 119722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, R.M.; Marques, A.C. Characterization of Sol–Gel Materials by Infrared Spectroscopy. In Handbook of Sol-Gel Science and Technology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Capeletti, L.B.; Zimnoch, J.H. Fourier Transform Infrared and Raman Characterization of Silica-Based Materials. In Applications of Molecular Spectroscopy to Current Research in the Chemical and Biological Sciences; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.-H.; Mou, C.-Y.; Lin, H.-P. Synthesis of mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 3862–3875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghimire, P.P.; Jaroniec, M. Renaissance of Stöber method for synthesis of colloidal particles: New developments and opportunities. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 584, 838–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thommes, M.; Kaneko, K.; Neimark, A.V.; Olivier, J.P.; Rodriguez-Reinoso, F.; Rouquerol, J.; Sing, K.S.W. Physisorption of gases, with special reference to the evaluation of surface area and pore size distribution (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2015, 87, 1051–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grun, M.; Matsumoto, K.K.U.A.; Tsutsumi, K. Novel Pathways for the Preparation of Mesoporous Mcm-41 Materials—Control of Porosity and Morphology. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 1999, 27, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norouzi, M.; Yathindranath, V.; Thliveris, J.A.; Kopec, B.M.; Siahaan, T.J.; Miller, D.W. Doxorubicin-loaded iron oxide nanoparticles for glioblastoma therapy: A combinational approach for enhanced delivery of nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 11292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Bari, G.; Gentile, E.; Latronico, T.; Corriero, G.; Fasano, A.; Nonnis Marzano, C.; Liuzzi, G.M. Inhibitory Effect of Aqueous Extracts from Marine Sponges on the Activity and Expression of Gelatinases A (MMP-2) and B (MMP-9) in Rat Astrocyte Cultures. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0129322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]







| Tinjection °C | treaction h | tageing h | [NaOH] mM | H2O/EtOH Volume Ratio | Average Size nm | Size Distribution σ% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MSN_H1 | 50 | 3 | 24 | 5 | 150:2 | * | --- |
| MSN_H2 | 50 | 3 | 24 | 5 | 50:2 | ** | --- |
| MSN_H3 | 50 | 1 | 24 | 8 | 50:2 | 35 | 11 |
| MSN_H4 | 50 | 3 | 24 | 8 | 50:2 | 47 | 13 |
| MSN_H5 | 50 | 3 | 24 | 10 | 50:2 | 64 | 15 |
| MSN_H6 | 50 | 3 | 24 | 13 | 50:2 | 135 | 17 |
| MSN_H7 | 50 | 3 | 4 | 13 | 50:2 | 54 | 11 |
| MSN_H8 | 30 | 3 | 24 | 13 | 50:2 | 73 | 16 |
| MSN_H9 | 50 | 3 | 24 | 13 | 30:2 | 102 | 16 |
| Tinjection °C | treaction Hours | tageing Hours | [NaOH] mM | H2O/Ethyl Acetate Volume Ratio | Average Size nm | Size Distribution σ% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MSN_Het1 | 50 | 3 | 24 | 2 | 50:2 | * | --- |
| MSN_Het2 | 50 | 3 | 24 | 5 | 50:2 | 70 | 13 |
| MSN_Het3 | 50 | 3 | 24 | 13 | 50:2 | 73 | 19 |
| MSN_Het4 | 30 | 3 | 24 | 13 | 50:2 | 55 | 16 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rizzi, F.; Castaldo, R.; Latronico, T.; Lasala, P.; Gentile, G.; Lavorgna, M.; Striccoli, M.; Agostiano, A.; Comparelli, R.; Depalo, N.; et al. High Surface Area Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles with Tunable Size in the Sub-Micrometer Regime: Insights on the Size and Porosity Control Mechanisms. Molecules 2021, 26, 4247. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26144247
Rizzi F, Castaldo R, Latronico T, Lasala P, Gentile G, Lavorgna M, Striccoli M, Agostiano A, Comparelli R, Depalo N, et al. High Surface Area Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles with Tunable Size in the Sub-Micrometer Regime: Insights on the Size and Porosity Control Mechanisms. Molecules. 2021; 26(14):4247. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26144247
Chicago/Turabian StyleRizzi, Federica, Rachele Castaldo, Tiziana Latronico, Pierluigi Lasala, Gennaro Gentile, Marino Lavorgna, Marinella Striccoli, Angela Agostiano, Roberto Comparelli, Nicoletta Depalo, and et al. 2021. "High Surface Area Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles with Tunable Size in the Sub-Micrometer Regime: Insights on the Size and Porosity Control Mechanisms" Molecules 26, no. 14: 4247. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26144247
APA StyleRizzi, F., Castaldo, R., Latronico, T., Lasala, P., Gentile, G., Lavorgna, M., Striccoli, M., Agostiano, A., Comparelli, R., Depalo, N., Curri, M. L., & Fanizza, E. (2021). High Surface Area Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles with Tunable Size in the Sub-Micrometer Regime: Insights on the Size and Porosity Control Mechanisms. Molecules, 26(14), 4247. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26144247