Biodiversity of Secondary Metabolites Compounds Isolated from Phylum Actinobacteria and Its Therapeutic Applications
Abstract
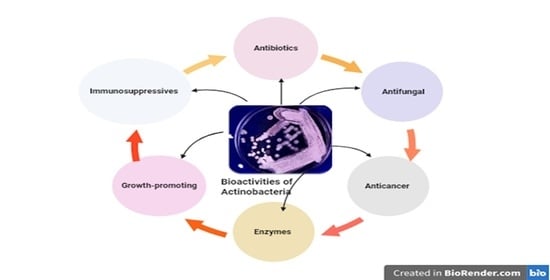
:1. Introduction
2. Methods and Protocol
2.1. Study Design and Search Strategy
2.2. Data Analysis
3. Primary and Secondary Metabolites Natural Products
4. History of Isolation of Secondary Metabolites from Actinobacteria
5. Microbial Ecology of Actinobacteria
5.1. Actinobacteria in Terrestrial Environments
5.2. Actinobacteria in Aquatic and Marine Environments
5.3. Thermophilic Actinobacteria
5.4. Alkaliphilic and Haloalkaliphilic Actinobacteria
6. The Important Antibiotics Isolated from Actinobacteria against Drug-Resistant Pathogens
| Antibiotic | Producer | Chemical Class | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cephamycin C | Nocardia lactamdurans | B- Lactam | [61] |
| Chlortetracycline | S. aureofaciens | Tetracycline | [62] |
| Clavulanic acid | S. clavuligerus | B- Lactam | [63] |
| Cycloserine | S. orchidaceus | Peptide | [64] |
| Daptomycin | S. rodeosporus | Lipopeptide | [65] |
| Daunorubicin | S. Peucetius | Peptide | [66] |
| FK506 | S.tubercidicus | Macrolide | [67] |
| Fortimicin | Micromonospora olivasterospora | Aminoglycoside | [68] |
| Fosfomycin | S. fradiae | Phosphoric acid | [69] |
| Fumaramidmycin | S. kurssanovii | Alkaloids | [70] |
| Gentamycin | Micromonospora spp | Aminoglycoside | [71] |
| Kanamycin | S. kanamyceticus | Aminoglycoside | [72] |
| Lincomycinn | S. lincolnensis | Sugar—amide | [73] |
| Neomycin | S. fradiae | Aminoglycoside | [74] |
| Nikkomycin | S. tendae | Nucleoside | [75] |
| Nocardicin | Nocardia uniformis | B- Lactam | [76] |
| Novobiocin | S. neveus | Aminocoumarin | [77] |
| Oleandomycin | S. antibioticus | Macrolide | [78] |
| Oxytetracycline | S. rimosus | Tetracycline | [79] |
| Paromomycin | S.rimosus forma | Aminoglycoside | [80] |
| Rifamycin | Amycolatopsis Ansamycin | RNA polymerase (PK) | [81] |
| Spiramycin | S. ambofaciens | Macrolide (PK) | [82] |
| Streptomycin | S. griseus | Aminoglycoside | [83] |
| Tetracycline | S. aureofaciens | Tetracycline (PK) | [84] |
| Thienamycin | S. cattleya | β-Lactam Peptidoglycan | [85] |
| Tobramycin | S. tenebrarius | Aminoglycoside | [86] |
| Vancomycin | S.orientalis | Peptidoglycan | [87] |
7. Production of Enzymes from Actinobacteria
8. Mechanism of Bioactive Compounds from Actinobacteria against Drug-Resistant Pathogens
9. Conclusions and Future Prospects
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carvalho, I.T.; Santos, L. Antibiotics in the aquatic environments: A review of the European scenario. Environ. Int. 2016, 94, 736–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, I.; Girão, M.; Alexandrino, D.; Ribeiro, T.; Santos, C.; Pereira, F.; Mucha, A.; Urbatzka, R.; Leão, P.; Carvalho, M. Diversity and Bioactive Potential of Actinobacteria Isolated from a Coastal Marine Sediment in Northern Portugal. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, D.; Zou, L.; Zhou, D.; Chen, Y.; Gao, Z.; Feng, R.; Zhang, M.; Li, K.; Xie, J.; Wang, W. Taxonomy and Broad-Spectrum Antifungal Activity of Streptomyces sp. SCA3-4 Isolated From Rhizosphere Soil of Opuntia stricta. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girão, M.; Ribeiro, I.; Ribeiro, T.; Azevedo, I.C.; Pereira, F.; Urbatzka, R.; Leão, P.; Carvalho, M.F. Actinobacteria Isolated From Laminaria ochroleuca: A Source of New Bioactive Compounds. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kandel, S.L.; Joubert, P.M.; Doty, S.L. Bacterial Endophyte Colonization and Distribution within Plants. Microorganisms 2017, 5, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frank, A.C.; Guzmán, J.P.S.; Shay, J.E. Transmission of Bacterial Endophytes. Microorganisms 2017, 5, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salam, N.; Jiao, J.-Y.; Zhang, X.-T.; Li, W.-J. Update on the classification of higher ranks in the phylum Actinobacteria. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 1331–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passari, A.K.; Chandra, P.; Leo, V.V.; Mishra, V.K.; Kumar, B.; Singh, B.P. Production of potent antimicrobial compounds from Streptomyces cyaneofuscatus associated with fresh water sediment. Front Microbiol. 2017, 8, 68. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.-Y.; Yang, Z.-W.; Asem, M.D.; Fang, B.-Z.; Salam, N.; Alkhalifah, D.H.M.; Hozzein, W.N.; Nie, G.-X.; Li, W.-J. Streptomyces desertarenae sp. nov., a novel actinobacterium isolated from a desert sample. Antonie Leeuwenhoek 2019, 112, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bérdy, J. Bioactive Microbial Metabolites. J. Antibiot. 2005, 58, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shivlata, L.; Satyanarayana, T. Thermophilic and alkaliphilic Actinobacteria: Biology and potential applications. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, T.; Su, C.; Lin, Y.; Wang, S.; Xu, Z.; Song, J. Precise species detection of traditional Chinese patent medicine by shotgun metagenomic sequencing. Phytomedicine 2018, 47, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.F.; Li, X.J.; Zhang, H.Y. Natural products and drug discovery. EMBO Rep. 2009, 10, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chaudhary, A.K.; Dhakal, D.; Sohng, J.K. An insight into the “-omics” based engineering of Streptomycetes for second-ary metabolite overproduction. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 968518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Demain, A.L.; Fang, A. The natural functions of secondary metabolites. In History of Modern Biotechnology I; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2000; pp. 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waksman, S.A.; Woodruff, H.B. The Soil as a Source of Microorganisms Antagonistic to Disease-Producing Bacteria. J. Bacteriol. 1940, 40, 581–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schatz, A.; Bugle, E.; Waksman, S.A. Streptomycin, a Substance Exhibiting Antibiotic Activity Against Gram-Positive and Gram-Negative Bacteria. Exp. Biol. Med. 1944, 55, 66–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodruff, H.B.; Selman, A. Waksman, Winner of the 1952 Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicine. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meklat, A.; Bouras, N.; Mokrane, S.; Zitouni, A.; Djemouai, N.; Klenk, H.-P.; Sabaou, N.; Mathieu, F. Isolation, Classifica-tion and Antagonistic Properties of Alkalitolerant Actinobacteria from Algerian Saharan Soils. Geomicrobiol. J. 2020, 37, 826–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoskisson, P.; Fernández-Martínez, L.T. Regulation of specialised metabolites in Actinobacteria—Expanding the paradigms. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2018, 10, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silva, L.J.; Crevelin, E.J.; Souza, D.T.; Júnior, G.L.; De Oliveira, V.M.; Ruiz, A.L.T.G.; Rosa, L.H.; Moraes, L.A.B.; Melo, I.S. Actinobacteria from Antarctica as a source for anticancer discovery. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibb, M.J. Regulation of secondary metabolism in streptomycetes. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2005, 8, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busi, S.; Pattnaik, S.S. Current status and applications of Actinobacteria in the production of anticancerous compounds. In New and Future Developments in Microbial Biotechnology and Bioengineering; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 137–153. [Google Scholar]
- Zin, N.M.; Remali, J.; Nasrom, M.N.; Ishak, S.A.; Baba, M.S.; Jalil, J. Bioactive compounds fractionated from endophyte Streptomyces SUK 08 with promising ex-vivo antimalarial activity. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2017, 7, 1062–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshaibani, M.; Jalil, J.; Sidik, N.; Edrada-Ebel, R.; Zin, N.M. Isolation and characterization of cyclo-(tryptophanyl-prolyl) and chloramphenicol from Streptomyces sp. SUK 25 with antimethicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus activity. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2016, 10, 1817–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ozakin, S.; Davis, R.W.; Umile, T.P.; Pirinccioglu, N.; Kizil, M.; Celik, G.; Sen, A.; Minbiole, K.P.C.; Ince, E. The isolation of tetrangomycin from terrestrial Streptomyces sp. CAH29: Evaluation of antioxidant, anticancer, and anti-MRSA activity. Med. Chem. Res. 2016, 25, 2872–2881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, R.; El-Gendy, A.; Ahmed, R.R.; Hassan, H.; El-Kabbany, H.M.; Merdash, A.G. Exploring the Antimicrobial and Antitumor Potentials of Streptomyces sp. AGM12-1 Isolated from Egyptian Soil. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dimri, A.G.; Chauhan, A.; Aggarwal, M. In vitro antibacterial characterization of Streptosporangium sp. (AI-21) a new soil isolate against food borne bacteria. Sci. Arch. 2020, 1, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheema, M.T.; Fatima, A.; Sajid, I. Molecular Identification, Bioactivity Screening and Metabolic Fingerprinting of the Actinomycetes of Chenab River Sediments. Br. Microbiol. Res. J. 2016, 17, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Shin, D.; Kim, S.-H.; Park, W.; Shin, Y.; Kim, W.K.; Lee, S.K.; Oh, K.-B.; Shin, J.; Oh, D.-C. Borrelidins C–E: New Antibacterial Macrolides from a Saltern-Derived Halophilic Nocardiopsis sp. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Krishnamoorthy, M.; Dharmaraj, D.; Rajendran, K.; Karuppiah, K.; Balasubramanian, M.; Ethiraj, K. Pharmacological activities of coral reef associated actinomycetes, Saccharopolyspora sp. IMA1. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2020, 28, 101748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulus, C.Y.; Rebets, B.; Tokovenko, S.; Nadmid, L.P.; Terekhova, M.; Myronovskyi, S.B.; Zotchev, C.; Rückert, S.B.; Zahler, S. New natural products identified by combined genomics-metabolomics profiling of marine Streptomyces sp. MP131-18. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.-M.; Liu, B.-L.; Zheng, X.-H.; Huang, X.-J.; Li, H.-Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, T.-T.; Sun, D.-Y.; Lin, B.-R.; Zhou, G.-X. Anandins A and B, two rare steroidal alkaloids from a marine Streptomyces anandii H41-59. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sarmiento-Vizcaíno, A.; Braña, A.F.; Pérez-Victoria, I.; Martín, J.; De Pedro, N.; De la Cruz, M.; Díaz, C.; Vicente, F.; Acuña, J.L.; Reyes, F.; et al. A new natural product with cytotoxic activity against tumor cell lines produced by deep-sea sediment derived Micromonospora matsumotoense M-412 from the Avilés Canyon in the Cantabrian Sea. Mar. Drugs. 2017, 15, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, N.; Song, F. Bioprospecting of novel and bioactive compounds from marine actinomycetes isolated from South China Sea sediments. Curr. Microbiol. 2018, 75, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waters, A.L.; Peraud, O.; Kasanah, N.; Sims, J.W.; Kothalawala, N.; Anderson, M.A.; Abbas, S.H.; Rao, K.V.; Jupally, V.R.; Kelly, M. An analysis of the sponge Acanthostrongylophora igens’ microbiome yields an Actinomycete that produces the natural product manzamine A. Front. Mar. Sci. 2014, 1, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mahapatra, G.P.; Raman, S.; Nayak, S.; Gouda, S.; Das, G.; Patra, J.K. Metagenomics approaches in discovery and development of new bioactive compounds from marine actinomycetes. Curr. Microbiol. 2020, 77, 645–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandimath, A.P.; Karad, D.D.; Gupta, S.G.; Kharat, A.S. Consortium inoculum of five thermo-tolerant phosphate solubilising Actinomycetes for multipurpose biofertiliser preparation. Iran J. Microbiol. 2017, 9, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mohammadipanah, F.; Wink, J. Actinobacteria from Arid and Desert Habitats: Diversity and Biological Activity. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 6, 1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Verma, E.; Chakraborty, S.; Tiwari, B.; Mishra, A.K. Antimicrobial Compounds from Actinobacteria: Synthetic Pathways and Applications. In New and Future Developments in Microbial Biotechnology and Bioengineering; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Dhabi, N.A.; Esmail, G.A.; Duraipandiyan, V.; Arasu, M.V. Chemical profiling of Streptomyces sp. Al-Dhabi-2 recovered from an extreme environment in Saudi Arabia as a novel drug source for medical and industrial applications. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2019, 26, 758–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halket, G.; Herron, P.; Munro, C. Isolation of thermophilic Actinobacteria from compost and identification of bioactive compounds with antimicrobial properties. Access Microbiol. 2020, 2, 954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borsodi, A.K.; Szili-Kovács, T.; Schumann, P.; Spröer, C.; Márialigeti, K.; Tóth, E. Nesterenkonia pannonica sp. nov., a novel alkaliphilic and moderately halophilic actinobacterium. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 4116–4120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arayes, M.A.; Mabrouk, M.E.M.; Sabry, S.A.; Abdella, B. Diversity and characterization of culturable haloalkaliphilic bacteria from two distinct hypersaline lakes in northern Egypt. Biologia 2021, 76, 751–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thumar, J.T.; Singh, S.P. Repression of alkaline protease in salt-tolerant alkaliphilic Streptomyces clavuligerus strain Mit-1 under the influence of amino acids in minimal medium. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 2011, 16, 1180–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakrar, F.; Kikani, B.; Sharma, A.; Singh, S. Stability of Alkaline Proteases from Haloalkaliphilic Actinobacteria Probed by Circular Dichroism Spectroscopy. Appl. Biochem. Micro. 2018, 54, 591–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gohel, S.D.; Singh, S.P. Molecular Phylogeny and Diversity of the Salt-Tolerant Alkaliphilic Actinobacteria Inhabiting Coastal Gujarat, India. Geomicrobiol. J. 2018, 35, 775–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nithya, K.; Muthukumar, C.; Biswas, B.; Alharbi, N.S.; Kadaikunnan, S.; Khaled, J.M.; Dhanasekaran, D. Desert Actinobacteria as a source of bioactive compounds production with a special emphases on Pyridine-2,5-diacetamide a new pyridine alkaloid produced by Streptomyces sp. DA3-7. Microbiol. Res. 2018, 207, 116–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Liu, Y.; Sheng, Y.; Xiang, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Cizdziel, J.V. Effect of prothioconazole on the degradation of microplastics derived from mulching plastic film: Apparent change and interaction with heavy metals in soil. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 260, 113988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yücel, S.; Yamaç, M. Selection of Streptomyces isolates from Turkish karstic caves against antibiotic resistant microorganisms. Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 23, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Goodfellow, M.; Fiedler, H.-P. A guide to successful bioprospecting: Informed by Actinobacterial systematics. Antonie Leeuwenhoek 2010, 98, 119–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajid, I.; Shaaban, K.A.; Hasnain, S. Identification, isolation and optimization of antifungal metabolites from the Streptomyces Malachitofuscus ctf9. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2011, 42, 592–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Inahashi, Y.; Matsumoto, A.; Omura, S.; Takahashi, Y. Streptosporangium oxazolinicum sp. nov., a novel endophytic actinomycete producing new antitrypanosomal antibiotics, spoxazomicins. J. Antibiot. 2011, 64, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, M.; Wei, W.; Ge, M.; Chen, D.; Sheng, X. A new antibacterial lipopeptide found by UPLC-MS from an actinomycetes Streptomycessp. HCCB10043. Nat. Prod. Res. 2013, 27, 2190–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishimoto, S.; Nishimura, S.; Hattori, A.; Tsujimoto, M.; Hatano, M.; Igarashi, M.; Kakeya, H. Chlorocatechelins A and B fromStreptomycessp.: New Siderophores Containing Chlorinated Catecholate Groups and an Acylguanidine Structure. Org. Lett. 2014, 16, 6108–6111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khieu, T.-N.; Liu, M.-J.; Nimaichand, S.; Quach, N.-T.; Chu-Ky, S.; Phi, Q.-T.; Vu, T.-T.; Nguyen, T.-D.; Xiong, Z.; Prabhu, D.M.; et al. Characterization and evaluation of antimicrobial and cytotoxic effects of Streptomyces sp. HUST012 isolated from medicinal plant Dracaena cochinchinensis Lour. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Castillo, U.; Harper, J.K.; Strobel, G.A.; Sears, J.; Alesi, K.; Ford, E.; Lin, J.; Hunter, M.; Maranta, M.; Ge, H.; et al. Kakadumycins, novel antibiotics fromStreptomycessp. NRRL 30566, an endophyte ofGrevillea pteridifolia. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2003, 224, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sujatha, P.; Raju, K.B.; Ramana, T. Studies on a new marine streptomycete BT-408 producing polyketide antibiotic SBR-22 effective against methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Microbiol. Res. 2005, 160, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.-C.; Kim, J.-H.; Ha, J.-W.; Park, N.-S.; Sohng, J.-K.; Lee, J.-W.; Park, S.-C.; Kim, M.-S.; Seong, C.-N. Production and bi-ological activity of laidlomycin, anti-MRSA/VRE antibiotic from Streptomyces sp. CS684. J. Microbiol. 2007, 45, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Laidi, R.F.; Sifour, M.; Sakr, M.; Hacène, H. A new actinomycete strain SK4-6 producing secondary metabolite effective against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2008, 24, 2235–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacovelli, R.; Zwahlen, R.D.; Bovenberg, R.A.; Driessen, A.J. Biochemical characterization of the Nocardia lactamdurans ACV synthetase. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0231290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, R.R.; Iniyan, A.M.; Prakash, V.S.G. Isolation of a small molecule with anti–MRSA activity from a mangrove symbiont Streptomyces sp. PVRK–1 and its biomedical studies in Zebrafish embryos. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2011, 1, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ser, H.-L.; Law, J.W.-F.; Chaiyakunapruk, N.; Jacob, S.A.; Palanisamy, U.D.; Chan, K.-G.; Goh, B.-H.; Lee, L.-H. Fermentation conditions that affect clavulanic acid production in Streptomyces clavuligerus: A systematic review. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schade, S.; Paulus, W. D-cycloserine in neuropsychiatric diseases: A systematic review. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2016, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamaguchi, M.; Goto, K.; Hirose, Y.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Sumitomo, T.; Nakata, M.; Nakano, K.; Kawabata, S. Identification of evolutionarily conserved virulence factor by selective pressure analysis of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Commun. Biol. 2019, 2, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, W.; Do, T.; Zhang, G.; Kahne, D.; Meredith, T.C.; Walker, S. Antibiotic Combinations That Enable One-Step, Targeted Mutagenesis of Chromosomal Genes. ACS Infect. Dis. 2018, 4, 1007–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, S.; Loeffler, A.; Kadlec, K. Bacterial resistance to antimicrobial agents and its impact on veterinary and human medicine. Adv. Vet. Dermatol. 2017, 8, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Touchon, M.; Sousa, J.A.M.D.; Rocha, E.P. Embracing the enemy: The diversification of microbial gene repertoires by phage-mediated horizontal gene transfer. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2017, 38, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, G.; Saigal, S.; Elongavan, A. Action and resistance mechanisms of antibiotics: A guide for clinicians. J. Anaesthesiol. Clin. Pharmacol. 2017, 33, 300–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bello, I.A.; Ndukwe, G.I.; Amupitan, J.O.; Ayo, R.G.; Shode, F.O. Syntheses and biological activity of some derivatives of C-9154 antibiotic. Int. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 2012, 148235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boumehira, A.; El Enshasy, H.A.; Hacene, H.; Elsayed, E.A.; Aziz, R.; Park, E.Y. Recent Progress on the Development of Antibiotics from the Genus Micromonospora. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 2016, 21, 199–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nelson, R.A.; Pope, J.A., Jr.; Luedemann, G.M.; McDaniel, L.E.; Schaffner, C.P. Crisamicin A, a new antibiotic from Micromonospora. I. Taxonomy of the producing strain, fermentation, isolation, physico-chemical characterization and antimicrobial properties. J. Antibiot. 1986, 39, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Soliveri, J.; Laborda, F. PA-5 and PA-7, pentaene and heptaene macrolide antibiotics produced by a new isolate of Streptoverticillium from Spanish soil. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1987, 25, 366–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozasa, T.; Suzuki, K.; Sasamata, M.; Tanaka, K.; Kobori, M.; Kadota, S.; Nagai, K.; Saito, T.; Watanabe, S.; Iwanami, M. Novel antitumor antibiotic phospholine. 1. Production, isolation and characterization. J. Antibiot. 1989, 42, 1331–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schimana, J.; Fiedler, H.-P.; Groth, I.; Submuth, R.; Beil, W.; Walker, M.; Zeeck, A. Simocyclinones, Novel Cytostatic Angucyclinone Antibiotics Produced by Streptomyces antibioticus Tue 6040. I. Taxonomy, Fermentation, Isolation and Biological Activities. J. Antibiot. 2000, 53, 779–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Igarashi, Y.; Ogawa, M.; Sato, Y.; Saito, N.; Yoshida, R.; Kunoh, H.; Onaka, H.; Furumai, T. Fistupyrone, a novel inhibitor of the infection of Chinese cabbage by Alternaria brassicicola, from Streptomyces sp. TP-A0569. J. Antibiot. 2000, 53, 1117–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Flinspach, K.; Rückert, C.; Kalinowski, J.; Heide, L.; Apel, A.K. Draft genome sequence of Streptomyces niveus NCIMB 11891, producer of the aminocoumarin antibiotic novobiocin. Genome Announc. 2014, 2, e011461-3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, S.H.; Ryu, M.; Yoon, Y.J.; Kim, D.-M.; Lee, E.Y. Glycosylation of various flavonoids by recombinant oleandomycin glycosyltransferase from Streptomyces antibioticus in batch and repeated batch modes. Biotechnol. Lett. 2012, 34, 499–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.; Wang, W.; Wang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Jia, X.; Li, S.; Yuan, F.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, K. Identification of a cluster-situated activator of oxytetracycline biosynthesis and manipulation of its expression for improved oxytetracycline production in Streptomyces rimosus. Microb. Cell Fact. 2015, 14, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ogawara, H. Comparison of antibiotic resistance mechanisms in antibiotic-producing and pathogenic bacteria. Molecules 2019, 24, 3430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ye, F.; Shi, Y.; Zhao, S.; Li, Z.; Wang, H.; Lu, C.; Shen, Y. 8-Deoxy-Rifamycin Derivatives from Amycolatopsis mediterranei S699 ΔrifT Strain. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thibessard, A.; Haas, D.; Gerbaud, C.; Aigle, B.; Lautru, S.; Pernodet, J.-L.; Leblond, P. Complete genome sequence of Streptomyces ambofaciens ATCC 23877, the spiramycin producer. J. Biotechnol. 2015, 214, 117–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishigaki, Y.; Akanuma, G.; Yoshida, M.; Horinouchi, S.; Kosono, S.; Ohnishi, Y. Protein acetylation involved in streptomycin biosynthesis in Streptomyces griseus. J. Proteom. 2017, 155, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vastrad, B.M.; Neelagund, S.E. Optimizing the medium conditions for production of tetracycline by solid state fermentation of Streptomyces aureofaciens NCIM 2417 using statistical experimental methods. J. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 1, 29–44. [Google Scholar]
- Braña, A.F.; Rodríguez, M.; Pahari, P.; Rohr, J.; García, L.A.; Blanco, G. Activation and silencing of secondary metabolites in Streptomyces albus and Streptomyces lividans after transformation with cosmids containing the thienamycin gene cluster from Streptomyces cattleya. Arch. Microbiol. 2014, 196, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hong, W.; Yan, S. Engineering Streptomyces tenebrarius to synthesize single component of carbamoyl tobramycin. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2012, 55, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, K.G.; Chen, H.I.; Lucas, T.H. Safety of topical vancomycin powder in neurosurgery. Surg. Neurol. Int. 2016, 7, S919–S926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Choi, H.J.; Kim, D.W.; Choi, Y.W.; Lee, Y.G.; Lee, Y.-I.; Jeong, Y.K.; Joo, W.H. Broad-spectrum In vitro antimicrobial activities of Streptomyces sp. strain BCNU 1001. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 2012, 17, 576–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajan, B.M.; Kannabiran, K. Extraction and identification of anti-bacterial secondary metabolites from marine Streptomyces sp. VITBRK2. Int. J. Mol. Cell Med. 2014, 3, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kannan, R.R.; Iniyan, A.M.; Vincent, S.G.P. Production of a compound against methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) from Streptomyces rubrolavendulae ICN3 & its evaluation in zebrafish embryos. Indian J. Med. Res. 2014, 139, 913–920. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ser, H.-L.; Ab Mutalib, N.-S.; Yin, W.-F.; Chan, K.-G.; Goh, B.H.; Lee, L.-H. Evaluation of Antioxidative and Cytotoxic Activities of Streptomyces pluripotens MUSC 137 Isolated from Mangrove Soil in Malaysia. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chawawisit, K.; Bhoopong, P.; Phupong, W.; Lertcanawanichakul, M. 2, 4-Di-tert-butylphenol, the bioactive compound produced by Streptomyces sp. KB1. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 5, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhakyashree, K.; Kannabiran, K. Actinomycetes mediated targeting of drug resistant MRSA pathogens. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2020, 32, 260–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemung, H.M.; Tan, L.T.-H.; Khan, T.M.; Chan, K.-G.; Pusparajah, P.; Goh, B.-H.; Lee, L.-H. Streptomyces as a prominent resource of future anti-MRSA drugs. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djinni, I.; Defant, A.; Kecha, M.; Mancini, I. Metabolite profile of marine--derived endophytic Streptomyces sundarbansensis WR 1 L 1 S 8 by liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry and evaluation of culture conditions on antibacterial activity and mycelial growth. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 116, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, G.; Lin, H.; Wang, C.; Hong, K.; Liu, Y.; Li, J. 1H and 13C assignments of two new macrocyclic lactones isolated from Streptomyces sp. 211726 and revised assignments of azalomycins F3a, F4a and F5a. Magn. Reason. Chem. 2011, 49, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rho, J.-R.; Subramaniam, G.; Choi, H.; Kim, E.-H.; Ng, S.P.; Yoganathan, K.; Ng, S.; Buss, A.D.; Butler, M.S.; Gerwick, W.H. Gargantulide A, a complex 52-membered macrolactone showing antibacterial activity from Streptomyces sp. Org. Lett. 2015, 17, 1377–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lacret, R.; Oves-Costales, D.; Gómez, C.; Díaz, C.; De la Cruz, M.; Pérez-Victoria, I.; Vicente, F.; Genilloud, O.; Reyes, F. New ikarugamycin derivatives with antifungal and antibacterial properties from Streptomyces zhaozhouensis. Mar. Drugs. 2015, 13, 128–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Norouzi, H.; Khorasgani, M.R.; Danesh, A. Anti-MRSA activity of a bioactive compound produced by a marine Streptomyces and its optimization using statistical experimental design. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2019, 22, 1073–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, M.; Manhas, R.K. Purification and characterization of actinomycins from Streptomyces strain M7 active against methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus and vancomycin resistant Enterococcus. BMC Microbiol. 2019, 19, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haste, N.M.; Thienphrapa, W.; Tran, D.N.; Loesgen, S.; Sun, P.; Nam, S.-J.; Jensen, P.; Fenical, W.; Sakoulas, G.; Nizet, V.; et al. Activity of the thiopeptide antibiotic nosiheptide against contemporary strains of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J. Antibiot. 2012, 65, 593–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lewin, G.R.; Carlos, C.; Chevrette, M.G.; Horn, H.A.; McDonald, B.R.; Stankey, R.J.; Fox, B.G.; Currie, C.R. Evolution and ecology of Actinobacteria and their bioenergy applications. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 70, 235–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaur, T.; Rani, R.; Manhas, R.K. Biocontrol and plant growth promoting potential of phylogenetically new Streptomyces sp. MR14 of rhizospheric origin. AMB Express 2019, 9, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Verma, A.; Singh, H.; Anwar, S.; Chattopadhyay, A.; Tiwari, K.K.; Kaur, S.; Dhilon, G.S. Microbial keratinases: Industrial enzymes with waste management potential. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2017, 37, 476–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, S.; Soofiani, N.M.; Lundh, T.; Mahboubi, A.; Kiessling, A.; Taherzadeh, M.J. Evaluation of Filamentous Fungal Biomass Cultivated on Vinasse as an Alternative Nutrient Source of Fish Feed: Protein, Lipid, and Mineral Composition. Fermentation 2019, 5, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, Y.; Yang, Y.; Ren, Y.; Xia, J.; Liu, F.; Li, Y.; Tang, X.-F.; Tang, B. Extracellular production, characterization, and engineering of a polyextremotolerant subtilisin-like protease from feather-degrading Thermoactinomyces vulgaris strain CDF. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 605771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gadde, U.D.; Oh, S.; Lillehoj, H.S.; Lillehoj, E.P. Retracted Article: Antibiotic growth promoters virginiamycin and bacitracin methylene disalicylate alter the chicken intestinal metabolome. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jiang, C.; Wang, H.; Kang, Q.; Liu, J.; Bai, L. Cloning and Characterization of the Polyether Salinomycin Biosynthesis Gene Cluster of Streptomyces albus XM211. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 994–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vishnupriya, B.; Sundaramoorthi, C.; Kalaivani, M.; Selvam, K. Production of lipase from Streptomyces griseus and evaluation of Bioparameters. Int. J. Chem. Tech. Res. 2010, 2, 1380–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taibi, Z.; Saoudi, B.; Boudelaa, M.; Trigui, H.; Belghith, H.; Gargouri, A.; Ladjama, A. Purification and biochemical characterization of a highly thermostable xylanase from Actinomadura sp. strain Cpt20 isolated from poultry compost. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2012, 166, 663–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prakash, D.; Nawani, N.; Prakash, M.; Bodas, M.; Mandal, A.; Khetmalas, M.; Kapadnis, B. Actinomycetes: A repertory of green catalysts with a potential revenue resource. Biomed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 264020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, N.; Poorna, C.A.; Prema, P. Purification and partial characterization of polygalacturonase from Streptomyces lydicus. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 6697–6701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Govindaraji, P.K.; Vuppu, S. Characterisation of pectin and optimization of pectinase enzyme from novel Streptomyces fumigatiscleroticus VIT-SP4 for drug delivery and concrete crack-healing applications: An eco-friendly approach. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 27, 3529–3540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nithya, K.; Muthukumar, C.; Kadaikunnan, S.; Alharbi, N.S.; Khaled, J.M.; Dhanasekaran, D. Purification, characterization, and statistical optimization of a thermostable α-amylase from desert actinobacterium Streptomyces fragilis DA7-7. 3 Biotech 2017, 7, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uma Maheswari, R. Phenotypic and Genotypic Characterisation of Vancomycin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus among MRSA Isolates in a Tertiary Care Hospital. Master’s Thesis, Tirunelveli Medical College, Tirunelvel, India, 2019. Available online: http://repository-tnmgrmu.ac.in/id/eprint/11129 (accessed on 23 August 2019).







| Bioactive Compound | Producer | Chemical Group | Bioactivity | Source of Isolation | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unknown | M72, M1, M71, W38, W108 and M93 | N/A | Anti-bacterial | Chenab River Sediments | [29] |
| Lynamicins, spiroindimicins | Streptomyces sp. | Bisindole pyrrole | Anti-bacterial | Deep sea marine sediment | [32] |
| Anandins | Streptomyces anandii | Steroidal Alkaloids | Cytotoxic | Marine sediments from mangrove zone | [33] |
| Paulomycin G | Micromonospora matsumotoense | Paulomycin derivatives | Anti-tumor properties | Deep sea marine sediment | [34] |
| Rifamycin B | Salinispora sp. | Polyketides | Anti-bacterial | Sediment | [35] |
| Manzamine A | Micromonospora sp. | Alkaloid | Antimalarial | Symbiont to sponge Acanthostrongylophora | [36] |
| Violapyrone B | Streptomyces somaliensis | α-pyrone | Anti-bacterial | Deep sea marine sediment | [37] |
| Bioactive Compound | Producer | Chemical Class | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thermomycin | Streptomycesthermophilus | Polyketide Antibiotic | [40] |
| Anthramycin | Streptomycesrefuineus | Benzodiazepine Alkaloid | [40] |
| Pyridine-2,5-diacetamide | Streptomyces sp. DA3-7 | Antimicrobial | [48] |
| 1, 4-butanediol, adipic acid, & terephthalic acid | Thermomonospora fusca | aliphatic-aromatic copolyesters | [49] |
| Antibiotic | Producer | Chemical Class | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Angumicynones A (1); Angumicynones B (2); Angucyclinones analogues compounds 3–8 | Streptomyces sp. MC004 | Angucyclic quinones | [94] |
| Watasemycin A (3) | Thiazostatins | ||
| Pulicatin G (4) and aerugine (5) | Benzyl thiazole and thiazoline | ||
| Polyketide [2-hydroxy-5-((6-hydroxy-4-oxo-4H-pyran-2-yl) methyl)-2-propylchroman-4-one] | Streptomyces sundarbansensis WR1L1S8 | N/A | [95] |
| Azalomycin F5a (1) and its four derivative compounds: | Streptomyces hygroscopicus var. azalomyceticus | Polyhydroxy macrolide | [96] |
| Gargantulide A | Streptomyces sp. A42983 | Macrolactone | [97] |
| New Ikarugamycins: Compound 1: Isoikarugamycin; Compound 2: 28-N-methylikarugamycin; Compound 3: 30-oxo-28-N-methyl-ikarugamycin; Compound 4: Ikarugamycin; Compound 5: MKN-003B; Compound 6: 1 H-indole-3-carboxaldehyde; Compound 7: Phenylethanoic acid | Streptomyces zhaozhouensis CA-185989 | Compounds 1- 4: Pentacyclic tetramic acid macrolactams; Compound 5: Butenolide; Compound 6: Indole; Compound 7: Acetic acid | [98] |
| Pyrrole-Like Structure | Streptomyces sp. MN41 | pyrrole | [99] |
| actinomycins V, X2 and D. | Streptomyces antibioticus NBRC 12838T | Actinomycins | [100] |
| Abyssomicin C | Actinobacteria | polyketide | [93] |
| laidlomycin | Streptomyces sp. CS684 | affecting the metabolism | [89] |
| Neocitreamicins I and II | Nocardia | [93] | |
| Etamycin | Actinomycetes strains CNS-575 | cyclic peptide | [101] |
| Dichloromethane | Actinobacteria (I-400A, B1-T61, M10-77) | N/A | [93] |
| 2, 4-dichloro-5-sulfamoyl benzoic acid (DSBA) | Streptomyces sp. VITBRK2 | N/A | [93] |
| Enzyme | Producer | Use | Application in Industry | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Protease | Thermoactinomyces sp., | Detergents | Detergent | [106] |
| Nocardiopsissp.,S | Cheese making | Food | [106] | |
| Pactum, Streptomyces | Clarification—low-calorie beer | Brewing | [107] | |
| Hermoviolaceus, SSp. | Dehairing | Leather | [107] | |
| Cellulase | S. Thermobifida | Removal of stains | Detergent | [108] |
| Halotolerans, S. Sp., Ruber | Denim finishing, softening of cotton | Textile | [106] | |
| Deinking, modification of fibres | Paper and pulp | [108] | ||
| Lipase | S. griseus | Removal of stains | Detergent | [109] |
| Stability of dough and conditioning | Baking | [109] | ||
| Cheese flavouring | Dairy | [110] | ||
| Xylanase | Actinomadura Sp. | Conditioning of dough | Baking | [110] |
| Digestibility | Animal feed | [111] | ||
| Bleach boosting | Paper and pulp | [111] | ||
| Pectinase | S. lydicus | Clarification, mashing | Beverage | [112] |
| Scouring | Textile | [113] | ||
| Amylase | S. erumpens | Deinking, drainage | Paper and pulp | [114] |
| Removal of stains | Detergent | [114] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al-shaibani, M.M.; Radin Mohamed, R.M.S.; Sidik, N.M.; Enshasy, H.A.E.; Al-Gheethi, A.; Noman, E.; Al-Mekhlafi, N.A.; Zin, N.M. Biodiversity of Secondary Metabolites Compounds Isolated from Phylum Actinobacteria and Its Therapeutic Applications. Molecules 2021, 26, 4504. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26154504
Al-shaibani MM, Radin Mohamed RMS, Sidik NM, Enshasy HAE, Al-Gheethi A, Noman E, Al-Mekhlafi NA, Zin NM. Biodiversity of Secondary Metabolites Compounds Isolated from Phylum Actinobacteria and Its Therapeutic Applications. Molecules. 2021; 26(15):4504. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26154504
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-shaibani, Muhanna Mohammed, Radin Maya Saphira Radin Mohamed, Nik Marzuki Sidik, Hesham Ali El Enshasy, Adel Al-Gheethi, Efaq Noman, Nabil Ali Al-Mekhlafi, and Noraziah Mohamad Zin. 2021. "Biodiversity of Secondary Metabolites Compounds Isolated from Phylum Actinobacteria and Its Therapeutic Applications" Molecules 26, no. 15: 4504. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26154504
APA StyleAl-shaibani, M. M., Radin Mohamed, R. M. S., Sidik, N. M., Enshasy, H. A. E., Al-Gheethi, A., Noman, E., Al-Mekhlafi, N. A., & Zin, N. M. (2021). Biodiversity of Secondary Metabolites Compounds Isolated from Phylum Actinobacteria and Its Therapeutic Applications. Molecules, 26(15), 4504. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26154504