Lipemia in the Plasma Sample Affects Fentanyl Measurements by Means of HPLC-MS2 after Liquid-Liquid Extraction
Abstract
:1. Introduction
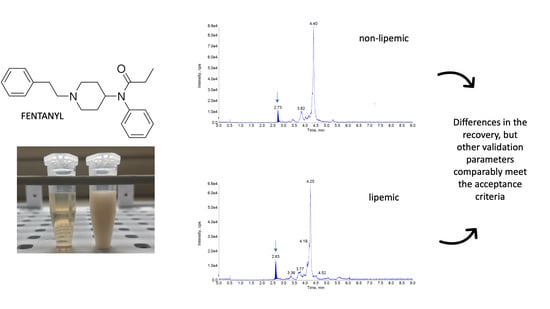
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Reagents
4.2. Standard Solutions
4.3. High Performance Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry
4.4. Validation Procedure
4.5. Matrix Collection and Preparation
4.6. Sample Extraction Procedure
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Nikolac, N. Lipemia: Causes, Interference Mechanisms, Detection and Management. Biochem. Med. 2014, 24, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Parks, E.J. Recent Findings in the Study of Postprandial Lipemia. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2001, 3, 462–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastromas, S.; Terzi, A.-B.; Tousoulis, D.; Koulouris, S. Postprandial Lipemia: An under-Recognized Atherogenic Factor in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus. Int. J. Cardiol. 2008, 126, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kroll, M.H. Evaluating Interference Caused by Lipemia. Clin. Chem. 2004, 50, 1968–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farmer, R.G.; Winkelman, E.I.; Brown, H.B.; Lewis, L.A. Hyperlipoproteinemia and Pancreatitis. Am. J. Med. 1973, 54, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saland, J.M.; Satlin, L.M.; Zalsos-Johnson, J.; Cremers, S.; Ginsberg, H.N. Impaired Postprandial Lipemic Response in Chronic Kidney Disease. Kidney Int. 2016, 90, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goulet, O.J.; Cai, W.; Seo, J.-M. Lipid Emulsion Use in Pediatric Patients Requiring Long-Term Parenteral Nutrition. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2020, 44, S55–S67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothschild, L.; Bern, S.; Oswald, S.; Weinberg, G. Intravenous Lipid Emulsion in Clinical Toxicology. Scand. J. Trauma Resusc. Emerg. Med. 2010, 18, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krenzer, J.; Nelson, A.; Robakowski, T.; Grant, K.; Galior, K.; Hackenmueller, S.A. Lipemic Interference in Basic Metabolic Panels: Increasing the Lipemia Index Threshold in Order to Decrease the Frequency of Ultracentrifugation. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2020, 154 (Suppl. 1), S15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- French, D.; Smollin, C.; Ruan, W.; Wong, A.; Drasner, K.; Wu, A.H.B. Partition Constant and Volume of Distribution as Predictors of Clinical Efficacy of Lipid Rescue for Toxicological Emergencies. Clin. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 801–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, R.P.; Gasparetto, J.C.; de Oliveira Vilhena, R.; de Francisco, T.M.G.; Martins, C.A.F.; Cardoso, M.A.; Pontarolo, R.; de Carvalho, K. Simultaneous Determination of Levodopa, Carbidopa, Entacapone, Tolcapone, 3-O-Methyldopa and Dopamine in Human Plasma by an HPLC–MS/MS Method. Bioanalysis 2015, 7, 207–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derogis, P.B.M.; Sanches, L.R.; De Aranda, V.F.; Colombini, M.P.; Mangueira, C.L.P.; Katz, M.; Faulhaber, A.C.L.; Mendes, C.E.A.; Ferreira, C.E.D.S.; França, C.N.; et al. Determination of Rivaroxaban in Patient’s Plasma Samples by Anti-Xa Chromogenic Test Associated to High Performance Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry (HPLC-MS/MS). PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0171272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, G.A.S.; Boing, A.C. Hospitalizations and Deaths from Drug Poisoning and Adverse Reactions in Brazil: An Analysis from 2000 to 2014. Cad. Saude Publica 2018, 34, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiao, Y.; Li, X.; Fu, X. A Rapid and Simple LC–MS/MS Method for Personalized Busulfan Dosing in Pediatric Patients Undergoing Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation (HSCT). Clin. Chim. Acta 2018, 479, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalakam, S.P.; Tambe, V.S.; Deodhar, M.N.; Prakya, V.; Waghmode, J.; Pawar, P. Direct Chiral HPLC-MS/MS Method for Determination of R-Lacosamide in Human Plasma. Pharm. Chem. J. 2020, 54, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, C.; Zhang, Z.P.; Karnes, H.T. A Study of Matrix Effects on an LC/MS/MS Assay for Olanzapine and Desmethyl Olanzapine. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2004, 35, 1149–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonel, A.; Yetisgin, A. False Negative D Vitamin Measurement in LC-MS/MS Method Due to Hyperlipidemia: Case Report. Comb. Chem. High Throughput Screen. 2019, 22, 428–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanley, T.H. The Fentanyl Story. J. Pain 2014, 15, 1215–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armenian, P.; Vo, K.T.; Barr-Walker, J.; Lynch, K.L. Fentanyl, Fentanyl Analogs and Novel Synthetic Opioids: A Comprehensive Review. Neuropharmacology 2018, 134, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Day, J.; Slawson, M.; Lugo, R.A.; Wilkins, D. Analysis of Fentanyl and Norfentanyl in Human Plasma by Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry Using Electrospray Ionization. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2003, 27, 513–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cooreman, S.; Deprez, C.; Martens, F.; Van Bocxlaer, J.; Croes, K. A Comprehensive LC-MS-Based Quantitative Analysis of Fentanyl-like Drugs in Plasma and Urine. J. Sep. Sci. 2010, 33, 2654–2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almousa, A.A.; Ikeda, R.; Wada, M.; Kuroda, N.; Hanajiri, R.-K.; Nakashima, K. HPLC-UV Method Development for Fentanyl Determination in Rat Plasma and Its Application to Elucidate Pharmacokinetic Behavior after i.p. Administration to Rats. J. Chromatogr. B 2011, 879, 2941–2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bista, S.R.; Lobb, M.; Haywood, A.; Hardy, J.; Tapuni, A.; Norris, R. Development, Validation and Application of an HPLC–MS/MS Method for the Determination of Fentanyl and nor-Fentanyl in Human Plasma and Saliva. J. Chromatogr. B 2014, 960, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blanco, M.E.; Encinas, E.; González, O.; Rico, E.; Vozmediano, V.; Suárez, E.; Alonso, R.M. Quantitative Determination of Fentanyl in Newborn Pig Plasma and Cerebrospinal Fluid Samples by HPLC-MS/MS. Drug Test. Anal. 2015, 7, 804–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bista, S.R.; Haywood, A.; Norris, R.; Good, P.; Tapuni, A.; Lobb, M.; Hardy, J. Saliva versus Plasma for Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Studies of Fentanyl in Patients with Cancer. Clin. Ther. 2015, 37, 2468–2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleba, J.; Kim, J. Determination of Morphine, Fentanyl and Their Metabolites in Small Sample Volumes Using Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2020, 44, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solassol, I.; Bressolle, F.; Caumette, L.; Garcia, F.; Poujol, S.; Culine, S.; Pinguet, F. Inter- and Intraindividual Variabilities in Pharmacokinetics of Fentanyl After Repeated 72-Hour Transdermal Applications in Cancer Pain Patients. Ther. Drug Monit. 2005, 27, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coopman, V.; Cordonnier, J.; Pien, K.; Van Varenbergh, D. LC–MS/MS Analysis of Fentanyl and Norfentanyl in a Fatality Due to Application of Multiple Durogesic® Transdermal Therapeutic Systems. Forensic Sci. Int. 2007, 169, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pichini, S.; Solimini, R.; Berretta, P.; Pacifici, R.; Busardò, F.P. Acute Intoxications and Fatalities From Illicit Fentanyl and Analogues: An Update. Ther. Drug Monit. 2018, 40, 38–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, M.; Carter, S.; Bennett, P. LC-MS Bioanalysis of Drugs in Hemolyzed and Lipemic Samples. In Handbook of LC-MS Bioanalysis; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 16 September 2013; pp. 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimzadeh, H.; Yamini, Y.; Gholizade, A.; Sedighi, A.; Kasraee, S. Determination of Fentanyl in Biological and Water Samples Using Single-Drop Liquid–Liquid–Liquid Microextraction Coupled with High-Performance Liquid Chromatography. Anal. Chim. Acta 2008, 626, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swaminathan, S.K.; Fisher, J.; Kandimalla, K.K. Sensitive Determination of Fentanyl in Low-Volume Serum Samples by LC-MS/MS. AAPS PharmSciTech 2018, 19, 2812–2817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambropoulos, J.; Spanos, G.A.; Lazaridis, N.V. Development and Validation of an HPLC Assay for Fentanyl, Alfentanil, and Sufentanil in Swab Samples. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2000, 23, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portier, E.J.G.; De Blok, K.; Butter, J.J.; Van Boxtel, C.J. Simultaneous Determination of Fentanyl and Midazolam Using High-Performance Liquid Chromatography with Ultraviolet Detection. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Sci. Appl. 1999, 723, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malkawi, A.H.; Al-Ghananeem, A.M.; Crooks, P.A. Development of a GC-MS Assay for the Determination of Fentanyl Pharmacokinetics in Rabbit Plasma after Sublingual Spray Delivery. AAPS J. 2008, 10, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fryirsa, B.; Woodhouse, A.; Huang, J.L.; Dawson, M.; Mather, L.E. Determination of Subnanogram Concentrations of Fentanyl in Plasma by Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry: Comparison with Standard Radioimmunoassay. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Appl. 1997, 688, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, T.; Jørgenrud, B.; Strand, D.H. Determination of Buprenorphine, Fentanyl and LSD in Whole Blood by UPLC–MS-MS. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2013, 37, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Busardò, F.P.; Carlier, J.; Giorgetti, R.; Tagliabracci, A.; Pacifici, R.; Gottardi, M.; Pichini, S. Ultra-High-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry Assay for Quantifying Fentanyl and 22 Analogs and Metabolites in Whole Blood, Urine, and Hair. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seymour, C.; Shaner, R.L.; Feyereisen, M.C.; Wharton, R.E.; Kaplan, P.; Hamelin, E.I.; Johnson, R.C. Determination of Fentanyl Analog Exposure Using Dried Blood Spots with LC-MS-MS. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2019, 43, 266–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rab, E.; Flanagan, R.J.; Hudson, S. Detection of Fentanyl and Fentanyl Analogues in Biological Samples Using Liquid Chromatography–High Resolution Mass Spectrometry. Forensic Sci. Int. 2019, 300, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huynh, N.H.; Tyrefors, N.; Ekman, L.; Johansson, M. Determination of Fentanyl in Human Plasma and Fentanyl and Norfentanyl in Human Urine Using LC-MS/MS. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2005, 37, 1095–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hisada, T.; Katoh, M.; Hitoshi, K.; Kondo, Y.; Fujioka, M.; Toyama, Y.; Ieda, H.; Gocho, S.; Nadai, M. A Simple Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry Method for Determination of Plasma Fentanyl Concentration in Rats and Patients with Cancer Pain. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2013, 36, 412–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Strayer, K.E.; Antonides, H.M.; Juhascik, M.P.; Daniulaityte, R.; Sizemore, I.E. LC-MS/MS-Based Method for the Multiplex Detection of 24 Fentanyl Analogues and Metabolites in Whole Blood at Sub Ng ML−1 Concentrations. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 514–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Matuszewski, B.K.; Constanzer, M.L.; Chavez-Eng, C.M. Strategies for the Assessment of Matrix Effect in Quantitative Bioanalytical Methods Based on HPLC-MS/MS. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 3019–3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tikhomirov, M.; Poźniak, B.; Śniegocki, T. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry for Buprenorphine Evaluation in Plasma—Application to Pharmacokinetic Studies in Rabbits. Molecules 2021, 26, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flieger, J.; Święch-Zubilewicz, A.; Śniegocki, T.; Dolar-Szczasny, J.; Pizoń, M. Determination of Tryptophan and Its Major Metabolites in Fluid from the Anterior Chamber of the Eye in Diabetic Patients with Cataract by Liquid Chromotography Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS/MS). Molecules 2018, 23, 3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Śniegocki, T.; Sell, B.; Giergiel, M.; Posyniak, A. QuEChERS and HPLC-MS/MS Combination for the Determination of Chloramphenicol in Twenty Two Different Matrices. Molecules 2019, 24, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, S.-N.; Wang, T.F.; Caprioli, R.M.; Mo, B.P.N. Determination of Plasma Fentanyl by Gc-mass Spectrometry and Pharmacokinetic Analysis. J. Pharm. Sci. 1981, 70, 1276–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.; Ballantyne, J.A.; Baker, A.B. A Sensitive Assay for the Simultaneous Measurement of Alfentanil and Fentanyl in Plasma. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 1996, 14, 667–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cases, E.; Cayot, P. Effect of Apolar Phase Dielectric Constant on Interfacial Properties of β-Lactoglobulin (Dielectric Constant and Interfacial Properties of β-Lactoglobulin). Food Hydrocoll. 2005, 19, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landolf, K.M.; Rivosecchi, R.M.; Goméz, H.; Sciortino, C.M.; Murray, H.N.; Padmanabhan, R.R.; Sanchez, P.G.; Harano, T.; Sappington, P.L. Comparison of Hydromorphone versus Fentanyl-Based Sedation in Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation: A Propensity-Matched Analysis. Pharmacother. J. Hum. Pharmacol. Drug Ther. 2020, 40, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepnowski, P.; Synak, E.; Szafranek, B.; Kaczyński, Z. Techniki Separacyjne; Wydaw. Uniw. Gdańskiego: Gdańsk, Poland, 2010; pp. 206–221. [Google Scholar]
- ICH, I. Q2 (R1): Validation of Analytical Procedures: Text and Methodology. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/scientific-guideline/ich-q-2-r1-validation-analytical-procedures-text-methodology-step-5_en.pdf (accessed on 1 June 2021).
- Williams, A. EURACHEM/CITAC Workshop on Recent Developments in Measurement Uncertainty. Accredit. Qual. Assur. 2012, 17, 111–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- González, O.; Blanco, M.E.; Iriarte, G.; Bartolomé, L.; Maguregui, M.I.; Alonso, R.M. Bioanalytical Chromatographic Method Validation According to Current Regulations, with a Special Focus on the Non-Well Defined Parameters Limit of Quantification, Robustness and Matrix Effect. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1353, 10–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Férézou, J.; Gulik, A.; Domingo, N.; Milliat, F.; Dedieu, J.C.; Dunel-Erb, S.; Chevalier, C.; Bach, A.C. Intralipid 10%: Physicochemical Characterization. Nutrition 2001, 17, 930–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Matrix | LOD [µg/L] | LOQ [µg/L] | Matrix Effect (%) | Concentration Range (µg/L) | Determination Coefficient | Calibration Curve |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| normal plasma | 0.005 | 0.015 | 4.0 ± 2.6% | 0.02–80 | 0.980 | y = 0.065x + 0.03 |
| lipemic plasma | 0.008 | 0.02 | 6.1 ± 3.6% | 0.02–80 | 0.980 | y = 0.0485x + 0.03 |
| Level | Repeatability (RSDr,%) (n = 6) | Within-Lab Reproducibility (RSDwR,%) (n = 18) | Expanded Uncertainty (µg/L) | Recovery [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.02 µg/L | 5.9 ± 6.1 | 6.7 ± 4.8 | 0.02 ± 0.006 | - |
| 0.1 µg/L | 4.8 ± 4.6 | 5.6 ± 4.4 | 0.1 ± 0.03 | - |
| 0.5 µg/L | 4.6 ± 3.0 | 4.8 ± 4.1 | 0.5 ± 0.12 | 107.7 ± 1.4 |
| 2.5 µg/L | 4.4 ± 3.1 | 4.2 ± 4.6 | 2.5 ± 0.60 | - |
| 10 µg/L | 2.8 ± 2.6 | 3.4 ± 3.2 | 10 ± 2.10 | 111.1 ± 2.5 |
| 40 µg/L | 4.2 ± 3.4 | 4.7 ± 3.6 | 40 ± 12.8 | - |
| 80 µg/L | 3.7 ± 2.9 | 4.9 ± 3.1 | 80 ± 18.3 | 103.6 ± 9.5 |
| Level | Repeatability (RSDr,%) (n = 6) | Within-Lab Reproducibility (RSDwR,%) (n = 18) | Expanded Uncertainty (µg/L) | Recovery [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.02 µg/L | 7.9 ± 5.1 | 8.7 ± 4.8 | 0.02 ± 0.008 | - |
| 0.1 µg/L | 5.8 ± 4.3 | 6.6 ± 4.2 | 0.1 ± 0.03 | - |
| 0.5 µg/L | 4.4 ± 3.6 | 4.4 ± 4.3 | 0.5 ± 0.14 | 46.4 ± 5.0 |
| 2.5 µg/L | 4.1 ± 3.0 | 4.2 ± 4.1 | 2.5 ± 0.50 | - |
| 10 µg/L | 3.4 ± 2.6 | 3.9 ± 3.8 | 10 ± 2.20 | 32.0 ± 4.8 |
| 40 µg/L | 3.2 ± 4.6 | 5.3 ± 3.3 | 40 ± 13.4 | - |
| 80 µg/L | 3.5 ± 23.9 | 4.3 ± 3.5 | 80 ± 20.7 | 73.5 ± 7.7 |
| Analyte | Precursor Ion (m/z) | Ion Transition (m/z) | Declustering Potential (eV) | Entrance Potential (eV) | Colision Energy (eV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fentanyl | 337.0 | 188.0 105.0 | 101 101 | 10 10 | 29 43 |
| Fentanyl-D5 | 342.0 | 188.0 | 101 | 10 | 29 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tikhomirov, M.; Śniegocki, T.; Poźniak, B. Lipemia in the Plasma Sample Affects Fentanyl Measurements by Means of HPLC-MS2 after Liquid-Liquid Extraction. Molecules 2021, 26, 4514. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26154514
Tikhomirov M, Śniegocki T, Poźniak B. Lipemia in the Plasma Sample Affects Fentanyl Measurements by Means of HPLC-MS2 after Liquid-Liquid Extraction. Molecules. 2021; 26(15):4514. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26154514
Chicago/Turabian StyleTikhomirov, Marta, Tomasz Śniegocki, and Błażej Poźniak. 2021. "Lipemia in the Plasma Sample Affects Fentanyl Measurements by Means of HPLC-MS2 after Liquid-Liquid Extraction" Molecules 26, no. 15: 4514. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26154514
APA StyleTikhomirov, M., Śniegocki, T., & Poźniak, B. (2021). Lipemia in the Plasma Sample Affects Fentanyl Measurements by Means of HPLC-MS2 after Liquid-Liquid Extraction. Molecules, 26(15), 4514. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26154514