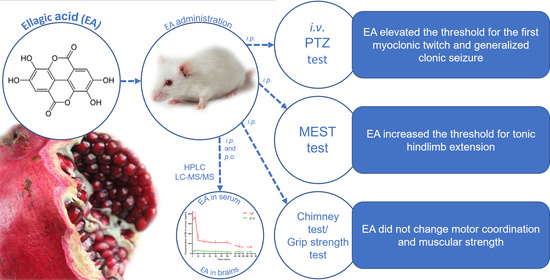
Effect of Ellagic Acid on Seizure Threshold in Two Acute Seizure Tests in Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Brain and Serum Concentrations of EA in Mice
2.2. Effect of EA in the PTZ-Induced Seizure Threshold Test
2.3. Effect of EA in the MEST Test
2.4. Effects of EA on Motor Coordination and Muscular Strength in Mice
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Drugs
4.3. Pharmacokinetic Study of EA
4.4. Intravenous PTZ Seizure Threshold Test
4.5. Maximal Electroshock Seizure Test
4.6. Grip-Strength Test
4.7. Chimney Test
4.8. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Moshe, S.L.; Perucca, E.; Ryvlin, P.; Tomson, T. Epilepsy: New advances. Lancet 2015, 385, 884–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billakota, S.; Devinsky, O.; Kim, K.W. Why we urgently need improved epilepsy therapies for adult patients. Neuropharmacology 2020, 170, 107855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perucca, P.; Gilliam, F.G. Adverse effects of antiepileptic drugs. Lancet Neurol. 2012, 11, 792–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, E.M.; Krupnick, A.S.; Heur, Y.-H.; Blinzler, J.A.; Nims, R.W.; Stoner, G.D. Extraction, stability, and quantitation of ellagic acid in various fruits and nuts. J. Food Compos. Anal. 1989, 2, 338–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raudone, L.; Bobinaite, R.; Janulis, V.; Viskelis, P.; Trumbeckaite, S. Effects of raspberry fruit extracts and ellagic acid on respiratory burst in murine macrophages. Food Funct. 2014, 5, 1167–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeb, A. Ellagic acid in suppressing in vivo and in vitro oxidative stresses. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2018, 448, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyadarsini, K.I.; Khopde, S.M.; Kumar, S.S.; Mohan, H. Free radical studies of ellagic acid, a natural phenolic antioxidant. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 2200–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.M.; Cho, J.S.; Kim, T.H.; Lee, Y.I. Ellagic acid protects hepatocytes from damage by inhibiting mitochondrial production of reactive oxygen species. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2010, 64, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Garhy, A.M.; Abd El-Raouf, O.M.; El-Sayeh, B.M.; Fawzy, H.M.; Abdallah, D.M. Ellagic acid antiinflammatory and antiapoptotic potential mediate renoprotection in cisplatin nephrotoxic rats. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2014, 28, 472–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanduja, K.L.; Avti, P.K.; Kumar, S.; Mittal, N.; Sohi, K.K.; Pathak, C.M. Anti-apoptotic activity of caffeic acid, ellagic acid and ferulic acid in normal human peripheral blood mononuclear cells: A Bcl-2 independent mechanism. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2006, 1760, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saba; Khan, S.; Parvez, S.; Chaudhari, B.; Ahmad, F.; Anjum, S.; Raisuddin, S. Ellagic acid attenuates bleomycin and cyclophosphamide-induced pulmonary toxicity in Wistar rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 58, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, O.; Escargueil-Blanc, I.; Meilhac, O.; Basile, J.P.; Laranjinha, J.; Almeida, L.; Salvayre, R.; Negre-Salvayre, A. Effect of dietary phenolic compounds on apoptosis of human cultured endothelial cells induced by oxidized LDL. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1998, 123, 565–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goodwin, E.C.; Atwood, W.J.; DiMaio, D. High-Throughput Cell-Based Screen for Chemicals That Inhibit Infection by Simian Virus 40 and Human Polyomaviruses. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 5630–5639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nohynek, L.J.; Alakomi, H.L.; Kahkonen, M.P.; Heinonen, M.; Helander, I.M.; Oksman-Caldentey, K.M.; Puupponen-Pimia, R.H. Berry phenolics: Antimicrobial properties and mechanisms of action against severe human pathogens. Nutr. Cancer 2006, 54, 18–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Vinayak, M. Ellagic acid induces novel and atypical PKC isoforms and promotes caspase-3 dependent apoptosis by blocking energy metabolism. Nutr. Cancer 2014, 66, 675–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossi, M.R.; Berni, A.; Pepe, G.; Filippi, S.; Meschini, R.; Papeschi, C.; Natarajan, A.T.; Palitti, F. Evaluation of the effects of ellagic acid (EA) on 7,12-dimethylbenz(α) anthracene (DMBA) induced micronuclei in mammalian cells in vitro and in vivo. Toxicol. Lett. 2014, 224, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahin, M.; Ahmad, I.; Gupta, R.C.; Aqil, F. Punicalagin and ellagic acid demonstrate antimutagenic activity and inhibition of benzo[a]pyrene induced DNA adducts. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 467465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanduja, K.L.; Gandhi, R.K.; Pathania, V.; Syal, N. Prevention of N-nitrosodiethylamine-induced lung tumorigenesis by ellagic acid and quercetin in mice. Food Chem. Toxicol. 1999, 37, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, T.; Setzer, W.N.; Nabavi, S.F.; Orhan, I.E.; Braidy, N.; Sobarzo-Sanchez, E.; Nabavi, S.M. Insights Into Effects of Ellagic Acid on the Nervous System: A Mini Review. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2016, 22, 1350–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfei, S.; Turrini, F.; Catena, S.; Zunin, P.; Grilli, M.; Pittaluga, A.M.; Boggia, R. Ellagic acid a multi-target bioactive compound for drug discovery in CNS? A narrative review. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 183, 111724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.; Singh, A.K.; Kumar, R.; Jamieson, S.; Pandey, A.K.; Bishayee, A. Neuroprotective Potential of Ellagic Acid: A Critical Review. Adv. Nutr. 2021, 12, 1211–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkaki, A.; Farbood, Y.; Dolatshahi, M.; Mansouri, S.M.; Khodadadi, A. Neuroprotective Effects of Ellagic Acid in a Rat Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Acta Med. Iran. 2016, 54, 494–502. [Google Scholar]
- Busto, R.; Serna, J.; Perianes-Cachero, A.; Quintana-Portillo, R.; Garcia-Seisdedos, D.; Canfran-Duque, A.; Paino, C.L.; Lerma, M.; Casado, M.E.; Martin-Hidalgo, A.; et al. Ellagic acid protects from myelin-associated sphingolipid loss in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2018, 1863, 958–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojanathammanee, L.; Puig, K.L.; Combs, C.K. Pomegranate polyphenols and extract inhibit nuclear factor of activated T-cell activity and microglial activation in vitro and in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer disease. J. Nutr. 2013, 143, 597–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hartman, R.E.; Shah, A.; Fagan, A.M.; Schwetye, K.E.; Parsadanian, M.; Schulman, R.N.; Finn, M.B.; Holtzman, D.M. Pomegranate juice decreases amyloid load and improves behavior in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 2006, 24, 506–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, A.B.; Panchal, S.S.; Shah, A. Ellagic acid: Insights into its neuroprotective and cognitive enhancement effects in sporadic Alzheimer’s disease. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2018, 175, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farbood, Y.; Sarkaki, A.; Dianat, M.; Khodadadi, A.; Haddad, M.K.; Mashhadizadeh, S. Ellagic acid prevents cognitive and hippocampal long-term potentiation deficits and brain inflammation in rat with traumatic brain injury. Life Sci. 2015, 124, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girish, C.; Raj, V.; Arya, J.; Balakrishnan, S. Evidence for the involvement of the monoaminergic system, but not the opioid system in the antidepressant-like activity of ellagic acid in mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 682, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreres, F.; Grosso, C.; Gil-Izquierdo, A.; Valentao, P.; Andrade, P.B. Ellagic acid and derivatives from Cochlospermum angolensis Welw. Extracts: HPLC-DAD-ESI/MSn profiling, quantification and in vitro anti-depressant, anti-cholinesterase and anti-oxidant activities. Phytochem. Anal. 2013, 24, 534–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bedel, H.A.; Kencebay Manas, C.; Ozbey, G.; Usta, C. The antidepressant-like activity of ellagic acid and its effect on hippocampal brain derived neurotrophic factor levels in mouse depression models. Nat. Prod. Res. 2018, 32, 2932–2935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhingra, D.; Chhillar, R. Antidepressant-like activity of ellagic acid in unstressed and acute immobilization-induced stressed mice. Pharmacol. Rep. 2012, 64, 796–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhingra, D.; Jangra, A. Antiepileptic activity of ellagic acid, a naturally occurring polyphenolic compound, in mice. J. Funct. Foods 2014, 10, 364–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Barrio, R.; Truchado, P.; Ito, H.; Espin, J.C.; Tomas-Barberan, F.A. UV and MS identification of Urolithins and Nasutins, the bioavailable metabolites of ellagitannins and ellagic acid in different mammals. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 1152–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeram, N.P.; Lee, R.; Heber, D. Bioavailability of ellagic acid in human plasma after consumption of ellagitannins from pomegranate (Punica granatum L.) juice. Clin. Chim. Acta 2004, 348, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tomas-Barberan, F.A.; Gonzalez-Sarrias, A.; Garcia-Villalba, R.; Nunez-Sanchez, M.A.; Selma, M.V.; Garcia-Conesa, M.T.; Espin, J.C. Urolithins, the rescue of “old” metabolites to understand a “new” concept: Metabotypes as a nexus among phenolic metabolism, microbiota dysbiosis, and host health status. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2017, 61, 1500901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espin, J.C.; Gonzalez-Barrio, R.; Cerda, B.; Lopez-Bote, C.; Rey, A.I.; Tomas-Barberan, F.A. Iberian pig as a model to clarify obscure points in the bioavailability and metabolism of ellagitannins in humans. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 10476–10485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bala, I.; Bhardwaj, V.; Hariharan, S.; Kharade, S.V.; Roy, N.; Ravi Kumar, M.N. Sustained release nanoparticulate formulation containing antioxidant-ellagic acid as potential prophylaxis system for oral administration. J. Drug Target. 2006, 14, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Missiry, M.A.; Othman, A.I.; Amer, M.A.; Sedki, M.; Ali, S.M.; El-Sherbiny, I.M. Nanoformulated ellagic acid ameliorates pentylenetetrazol-induced experimental epileptic seizures by modulating oxidative stress, inflammatory cytokines and apoptosis in the brains of male mice. Metab. Brain Dis. 2020, 35, 385–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, T.; Ma, H.; Liu, W.; Niesen, D.B.; Shah, N.; Crews, R.; Rose, K.N.; Vattem, D.A.; Seeram, N.P. Pomegranate’s Neuroprotective Effects against Alzheimer’s Disease Are Mediated by Urolithins, Its Ellagitannin-Gut Microbial Derived Metabolites. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2016, 7, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasperotti, M.; Passamonti, S.; Tramer, F.; Masuero, D.; Guella, G.; Mattivi, F.; Vrhovsek, U. Fate of microbial metabolites of dietary polyphenols in rats: Is the brain their target destination? ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2015, 6, 1341–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, L.; Yin, P.; Ma, C.; Liu, Y. Method development and validation for pharmacokinetic and tissue distributions of ellagic acid using ultrahigh performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS/MS). Molecules 2014, 19, 18923–18935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Espin, J.C.; Larrosa, M.; Garcia-Conesa, M.T.; Tomas-Barberan, F. Biological significance of urolithins, the gut microbial ellagic Acid-derived metabolites: The evidence so far. Evid Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2013, 2013, 270418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lei, F.; Xing, D.M.; Xiang, L.; Zhao, Y.N.; Wang, W.; Zhang, L.J.; Du, L.J. Pharmacokinetic study of ellagic acid in rat after oral administration of pomegranate leaf extract. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2003, 796, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smart, R.C.; Huang, M.T.; Chang, R.L.; Sayer, J.M.; Jerina, D.M.; Conney, A.H. Disposition of the naturally occurring antimutagenic plant phenol, ellagic acid, and its synthetic derivatives, 3-O-decylellagic acid and 3,3’-di-O-methylellagic acid in mice. Carcinogenesis 1986, 7, 1663–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teel, R.W.; Martin, R.M. Disposition of the plant phenol ellagic acid in the mouse following oral administration by gavage. Xenobiotica 1988, 18, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Press, R.E.; Hardcastle, D. Some physico-chemical properties of ellagic acid. J. Appl. Chem. 1969, 19, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teel, R.W. Distribution and metabolism of ellagic acid in the mouse following intraperitoneal administration. Cancer Lett. 1987, 34, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, H.S. Chemoconvulsants. In Neuropharmacology Methods in Epilepsy Research; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1998; pp. 27–40. [Google Scholar]
- Löscher, W. Preclinical assessment of proconvulsant drug activity and its relevance for predicting adverse events in humans. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 610, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castel-Branco, M.M.; Alves, G.L.; Figueiredo, I.V.; Falcao, A.C.; Caramona, M.M. The maximal electroshock seizure (MES) model in the preclinical assessment of potential new antiepileptic drugs. Methods Find. Exp. Clin. Pharmacol. 2009, 31, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, G.; Bauer, S.; Nowak, M.; Norwood, B.; Tackenberg, B.; Rosenow, F.; Knake, S.; Oertel, W.H.; Hamer, H.M. Cytokines and epilepsy. Seizure 2011, 20, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sudha, K.; Rao, A.V.; Rao, A. Oxidative stress and antioxidants in epilepsy. Clin. Chim. Acta 2001, 303, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.; Guan, Q.W.; Chen, F.H.; Xia, Q.X.; Yin, X.X.; Zhou, H.H.; Mao, X.Y. Antioxidants Targeting Mitochondrial Oxidative Stress: Promising Neuroprotectants for Epilepsy. Oxid Med. Cell Longev. 2020, 2020, 6687185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishnoi, S.; Raisuddin, S.; Parvez, S. Glutamate Excitotoxicity and Oxidative Stress in Epilepsy: Modulatory Role of Melatonin. J. Environ. Pathol. Toxicol. Oncol. 2016, 35, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukhopadhyay, B.; Gavel, R.; Gongopadhyay, A.N.; Vashistha, P.; Rani, A.; Mishra, S.P. Correlation of Oxidative Damage with Pro-Inflammatory Markers (IL-6, TNF-α) in Meningocele. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2016, 10, BC08–BC10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pauletti, A.; Terrone, G.; Shekh-Ahmad, T.; Salamone, A.; Ravizza, T.; Rizzi, M.; Pastore, A.; Pascente, R.; Liang, L.P.; Villa, B.R.; et al. Targeting oxidative stress improves disease outcomes in a rat model of acquired epilepsy. Brain 2017, 140, 1885–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patsoukis, N.; Zervoudakis, G.; Panagopoulos, N.T.; Georgiou, C.D.; Angelatou, F.; Matsokis, N.A. Thiol redox state (TRS) and oxidative stress in the mouse hippocampus after pentylenetetrazol-induced epileptic seizure. Neurosci. Lett. 2004, 357, 83–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, D.H.; Lee, M.J.; Kim, J.H. Antioxidant and apoptosis-inducing activities of ellagic acid. Anticancer Res. 2006, 26, 3601–3606. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kiasalari, Z.; Heydarifard, R.; Khalili, M.; Afshin-Majd, S.; Baluchnejadmojarad, T.; Zahedi, E.; Sanaierad, A.; Roghani, M. Ellagic acid ameliorates learning and memory deficits in a rat model of Alzheimer’s disease: An exploration of underlying mechanisms. Psychopharmacology 2017, 234, 1841–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farbood, Y.; Sarkaki, A.; Dolatshahi, M.; Taqhi Mansouri, S.M.; Khodadadi, A. Ellagic Acid Protects the Brain Against 6-Hydroxydopamine Induced Neuroinflammation in a Rat Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Basic Clin. Neurosci. 2015, 6, 83–89. [Google Scholar]
- Taghi Mansouri, M.; Naghizadeh, B.; Ghorbanzadeh, B.; Farbood, Y. Central and peripheral antinociceptive effects of ellagic acid in different animal models of pain. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 707, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbanzadeh, B.; Mansouri, M.T.; Hemmati, A.A.; Naghizadeh, B.; Mard, S.A.; Rezaie, A. Involvement of l-arginine/NO/cGMP/K(ATP) channel pathway in the peripheral antinociceptive actions of ellagic acid in the rat formalin test. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2014, 126, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansouri, M.T.; Naghizadeh, B.; Ghorbanzadeh, B. Involvement of opioid receptors in the systemic and peripheral antinociceptive actions of ellagic acid in the rat formalin test. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2014, 120, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olgar, Y.; Ozturk, N.; Usta, C.; Puddu, P.E.; Ozdemir, S. Ellagic acid reduces L-type Ca2+ current and contractility through modulation of NO-GC-cGMP pathways in rat ventricular myocytes. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2014, 64, 567–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rundfeldt, C.; Koch, R.; Richter, A.; Mevissen, M.; Gerecke, U.; Löscher, W. Dose-dependent anticonvulsant and proconvulsant effects of nitric oxide synthase inhibitors on seizure threshold in a cortical stimulation model in rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1995, 274, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedele, E.; Raiteri, M. In vivo studies of the cerebral glutamate receptor/NO/cGMP pathway. Prog. Neurobiol. 1999, 58, 89–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banach, M.; Piskorska, B.; Czuczwar, S.J.; Borowicz, K.K. Nitric oxide, epileptic seizures, and action of antiepileptic drugs. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2011, 10, 808–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prast, H.; Philippu, A. Nitric oxide as modulator of neuronal function. Prog. Neurobiol. 2001, 64, 51–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, N.; Khan, I.; Khan, H.; Ayub, B.; Abdel-Halim, H.; Gavande, N. Anxiolytic Potential of Natural Flavonoids. SM J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 4, 1018s. [Google Scholar]
- Svob Strac, D.; Pivac, N.; Smolders, I.J.; Fogel, W.A.; De Deurwaerdere, P.; Di Giovanni, G. Monoaminergic Mechanisms in Epilepsy May Offer Innovative Therapeutic Opportunity for Monoaminergic Multi-Target Drugs. Front. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binder, D.K. The role of BDNF in epilepsy and other diseases of the mature nervous system. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2004, 548, 34–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandary, B.S.K.; Sharmila, K.P.; Kumari, N.S.; Bhat, S.V. Acute and subacute toxicity study of the ethanol extracts of Punica granatum (linn). Whole fruit and seeds and synthetic ellagic acid in swiss albino mice. Asian J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 2013, 6, 192–198. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, C.; Dadhaniya, P.; Hingorani, L.; Soni, M.G. Safety assessment of pomegranate fruit extract: Acute and subchronic toxicity studies. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2008, 46, 2728–2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Socała, K.; Wlaź, P. Acute Seizure Tests Used in Epilepsy Research: Step-by-Step Protocol of the Maximal Electroshock Seizure (MES) Test, the Maximal Electroshock Seizure Threshold (MEST) Test, and the Pentylenetetrazole (PTZ)-Induced Seizure Test in Rodents. In Experimental and Translational Methods to Screen Drugs Effective Against Seizures and Epilepsy; Vohora, D., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 79–102. [Google Scholar]
- Kimball, A.W.; Burnett, W.T., Jr.; Doherty, D.G. Chemical protection against ionizing radiation. I. Sampling methods for screening compounds in radiation protection studies with mice. Radiat. Res. 1957, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boissier, J.R.; Tardy, J.; Diverres, J.C. Une nouvelle methode simple pour explorer l’action ‘tranquilistante’: Le test de la cheminee. Med. Exp. 1960, 3, 81–84. [Google Scholar]



| Treatment (mg/kg) | Impairment of Motor Performance (%) | Neuromuscular Strength (mN/g) |
|---|---|---|
| Control | 0 | 32.4 ± 1.2 |
| VPA (150) | 0 | 32.2 ± 0.8 |
| EA (100) | 0 | 32.3 ± 1.3 |
| EA (200) | 0 | 30.1 ± 0.9 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pieróg, M.; Socała, K.; Wyska, E.; Poleszak, E.; Wlaź, P. Effect of Ellagic Acid on Seizure Threshold in Two Acute Seizure Tests in Mice. Molecules 2021, 26, 4841. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26164841
Pieróg M, Socała K, Wyska E, Poleszak E, Wlaź P. Effect of Ellagic Acid on Seizure Threshold in Two Acute Seizure Tests in Mice. Molecules. 2021; 26(16):4841. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26164841
Chicago/Turabian StylePieróg, Mateusz, Katarzyna Socała, Elżbieta Wyska, Ewa Poleszak, and Piotr Wlaź. 2021. "Effect of Ellagic Acid on Seizure Threshold in Two Acute Seizure Tests in Mice" Molecules 26, no. 16: 4841. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26164841
APA StylePieróg, M., Socała, K., Wyska, E., Poleszak, E., & Wlaź, P. (2021). Effect of Ellagic Acid on Seizure Threshold in Two Acute Seizure Tests in Mice. Molecules, 26(16), 4841. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26164841