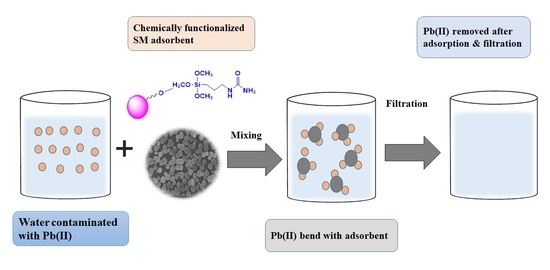
Efficient Removal of Pb(II) from Aqueous Medium Using Chemically Modified Silica Monolith
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Apparatus
2.2. Preparation of Silica Monolith Particles
2.3. Chemical Modification of Silica Monolith Particles
2.4. Characterization of Adsorbent
2.5. Adsorption of Pb(II) on Chemically Modified Silica Monolith
2.6. Adsorption Isotherm Study
2.7. Kinetic Study
2.8. Batch to Batch Reproducibility
2.9. Experimental Quality Evaluation
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Morphology of the Adsorbent
3.2. Particle Size and Pore Size Distribution of the Adsorbent
3.3. The Effect of Concentration, Adsorbent Dose, Contact Time and pH on Pb(II) Removal
3.3.1. The Effect of Concentration
3.3.2. The Effect of Adsorbent Dose
3.3.3. The Effect of Contact Time
3.3.4. The Effect of pH
3.4. Adsorption Isotherm Study
3.4.1. Freundlich Adsorption Isotherm
3.4.2. Langmuir Adsorption Isotherm
3.4.3. Temkin Adsorption Isotherm
3.5. Adsorption Kinetics
3.5.1. Pseudo First-Order Kinetic Model
3.5.2. Pseudo Second-Order Model
3.5.3. Intra-Particles Diffusion Model
3.6. Desorption, Regeneration and Reuse of the Adsorbent
3.7. Comparison of Chemically Modified SM for Pb(II) Removal with Other Adsorbents
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Boskabady, M.; Marefati, N.; Farkhondeh, T.; Shakeri, F.; Farshbaf, A.; Boskabady, M.H. The effect of environmental lead exposure on human health and the contribution of inflammatory mechanisms, a review. Environ. Int. 2018, 120, 404–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, F.; Yin, G.; Gao, Y.; Liu, D.; Xie, J.; Ouyang, L.; Fan, Y.; Yu, H.; Zha, Z.; Wang, K. Toxicity assessment due to prenatal and lactational exposure to lead, cadmium and mercury mixtures. Environ. Int. 2019, 133, 105192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, M.; Khalili, N.; Razi, S.; Keshavarz-Fathi, M.; Khalili, N.; Rezaei, N. Effects of lead and cadmium on the immune system and cancer progression. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2020, 18, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, R.M.; Laxen, D. Lead pollution. In Causes and Control; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Verma, R.; Dwivedi, P. Heavy metal water pollution-A case study. Recent Res. Sci. Technol. 2013, 5, 98–99. [Google Scholar]
- Fabini, D. Quantifying the Potential for Lead Pollution from Halide Perovskite Photovoltaics. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2015, 6, 3546–3548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Renberg, I.; Brännvall, M.-L.; Bindler, R.; Emteryd, O. Atmospheric lead pollution history during four millennia (2000 BC to 2000 AD) in Sweden. AMBIO J. Hum. Environ. 2000, 29, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarma, P.; Kumar, R.; Pakshirajan, K. Batch and Continuous Removal of Copper and Lead from Aqueous Solution using Cheaply Available Agricultural Waste Materials. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2015, 9, 635–648. [Google Scholar]
- Soetaredjo, F.E.; Kurniawan, A.; Ki, O.L.; Ismadji, S. Incorporation of selectivity factor in modeling binary component adsorption isotherms for heavy metals-biomass system. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 219, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Won, S.W.; Kotte, P.; Wei, W.; Lim, A.; Yun, Y.-S. Biosorbents for recovery of precious metals. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 160, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, I.; Gupta, V.K.; Khan, T.A.; Asim, M. Removal of arsenate from aqueous solution by electro-coagulation method using Al-Fe electrodes. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2012, 7, 1898–1907. [Google Scholar]
- Sellaoui, L.; Soetaredjo, F.E.; Ismadji, S.; Bonilla-Petriciolet, A.; Belver, C.; Bedia, J.; Lamine, A.B.; Erto, A. Insights on the statistical physics modeling of the adsorption of Cd2+ and Pb2+ ions on bentonite-chitosan composite in single and binary systems. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 354, 569–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, D.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, S.; Shi, W.; Zhang, Z.; Lei, Z.; Yang, Y. Adsorption of cesium from aqueous solution using agricultural residue–walnut shell: Equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic modeling studies. Water Res. 2013, 47, 2563–2571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hemavathy, R.; Saravanan, A.; Kumar, P.S.; Vo, D.-V.N.; Karishma, S.; Jeevanantham, S. Adsorptive removal of Pb (II) ions onto surface modified adsorbents derived from Cassia fistula seeds: Optimization and modelling study. Chemosphere 2021, 283, 131276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azmi, S.N.H.; Al-Balushi, M.; Al-Siyabi, F.; Al-Hinai, N.; Khurshid, S. Adsorptive removal of Pb (II) ions from groundwater samples in Oman using carbonized Phoenix dactylifera seed (Date stone). J. King Saud Univ.-Sci. 2020, 32, 2931–2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singha, B.; Das, S.K. Removal of Pb (II) ions from aqueous solution and industrial effluent using natural biosorbents. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2012, 19, 2212–2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, M.; Guha, A.K.; Ray, L. Adsorption of lead on cucumber peel. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 151, 603–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özer, A. Removal of Pb (II) ions from aqueous solutions by sulphuric acid-treated wheat bran. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 141, 753–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuithitikul, K.; Phromrak, R.; Saengngoen, W. Utilization of chemically treated cashew-nut shell as potential adsorbent for removal of Pb (II) ions from aqueous solution. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghasemi, M.; Naushad, M.; Ghasemi, N.; Khosravi-Fard, Y. A novel agricultural waste based adsorbent for the removal of Pb (II) from aqueous solution: Kinetics, equilibrium and thermodynamic studies. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2014, 20, 454–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saka, C.; Şahin, Ö.; Küçük, M.M. Applications on agricultural and forest waste adsorbents for the removal of lead (II) from contaminated waters. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 9, 379–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, K.; Zhu, H. Removal of Pb2+ from aqueous solution by adsorption on chemically modified muskmelon peel. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 4424–4434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahriyari Far, H.; Hasanzadeh, M.; Najafi, M.; Masale Nezhad, T.R.; Rabbani, M. Efficient Removal of Pb (II) and Co (II) Ions from Aqueous Solution with a Chromium-Based Metal–Organic Framework/Activated Carbon Composites. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2021, 60, 4332–4341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.A.; Kamala-Kannan, S.; Lee, K.-J.; Park, Y.-J.; Shea, P.J.; Lee, W.-H.; Kim, H.-M.; Oh, B.-T. Removal of Pb (II) from aqueous solution by a zeolite–nanoscale zero-valent iron composite. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 217, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, J.; Niu, Y.; Ren, B.; Chen, H.; Zhang, S.; Jin, J.; Zhang, Y. Synthesis of Schiff base functionalized superparamagnetic Fe3O4 composites for effective removal of Pb (II) and Cd (II) from aqueous solution. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 347, 574–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Zhao, D.; Wang, X. Removal of Pb (II) and Cu (II) from aqueous solution using multiwalled carbon nanotubes/iron oxide magnetic composites. Water Sci. Technol. 2011, 63, 917–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheshmani, S.; Nematzadeh, M.A.; Shokrollahzadeh, S.; Ashori, A. Preparation of graphene oxide/chitosan/FeOOH nanocomposite for the removal of Pb (II) from aqueous solution. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 80, 475–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, D.; Chen, C.; Wang, X. Application of polyaniline and multiwalled carbon nanotube magnetic composites for removal of Pb (II). Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 185, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raji, F.; Saraeian, A.; Pakizeh, M.; Attarzadeh, F. Removal of Pb (ii) from aqueous solution by mesoporous silica MCM-41 modified by ZnCl2: Kinetics, thermodynamics, and isotherms. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 37066–37077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, C.; Jiang, W.; Liang, J.; Sun, X.; Guan, Y. Removal of Pb (II) from aqueous solutions by adsorption on magnetic bentonite. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 1315–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mondal, M.K. Removal of Pb (II) from aqueous solution by adsorption using activated tea waste. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2010, 27, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthik, R.; Meenakshi, S. Removal of Pb (II) and Cd (II) ions from aqueous solution using polyaniline grafted chitosan. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 263, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva Alves, D.C.; Healy, B.; Pinto, L.A.; Cadaval, T.R.; Breslin, C.B. Recent developments in chitosan-based adsorbents for the removal of pollutants from aqueous environments. Molecules 2021, 26, 594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Ma, X.; Cai, H.; Ma, Z.; Liang, H. Study on the Adsorption of CuFe2O4-Loaded Corncob Biochar for Pb(II). Molecules 2020, 25, 3456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordin, N.A.; Abdul Rahman, N.; Abdullah, A.H. Effective Removal of Pb(II) Ions by Electrospun PAN/Sago Lignin-Based Activated Carbon Nanofibers. Molecules 2020, 25, 3081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, P.; Zhang, P.; Li, K.; Kumari, B.; Li, D.; Mei, X. Silver Nanoclusters Encapsulated into Metal–Organic Frameworks for Rapid Removal of Heavy Metal Ions from Water. Molecules 2019, 24, 2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liang, X.-X.; Wang, N.; Qu, Y.-L.; Yang, L.-Y.; Wang, Y.-G.; Ouyang, X.-K. Facile Preparation of Metal-Organic Framework (MIL-125)/Chitosan Beads for Adsorption of Pb(II) from Aqueous Solutions. Molecules 2018, 23, 1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pang, J.-H.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Yang, X.-J. Solvothermal synthesis of nano-CeO2 aggregates and its application as a high-efficient arsenic adsorbent. Rare Met. 2019, 38, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.-C.; Lei, Y.; Jiao, W.; Liu, Y.-F.; Mu, C.-H.; Jian, X. A review of helical carbon materials structure, synthesis and applications. Rare Met. 2021, 40, 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.; Zhang, X.; Guo, Y.; Mu, C.; Zhou, P.; Yin, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.; Lu, H.; Jian, X. Hybrid silica-carbon bilayers anchoring on FeSiAl surface with bifunctions of enhanced anti-corrosion and microwave absorption. Carbon 2021, 173, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Saeed, K.; Mabood, F. Removal of chromium (VI) from aqueous medium using chemically modified banana peels as efficient low-cost adsorbent. Alex. Eng. J. 2016, 55, 2933–2942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ali, A. Removal of Mn (II) from water using chemically modified banana peels as efficient adsorbent. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2017, 7, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Saeed, K. Decontamination of Cr (VI) and Mn (II) from aqueous media by untreated and chemically treated banana peel: A comparative study. Desalination Water Treat. 2015, 53, 3586–3591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Saeed, K. Phenol removal from aqueous medium using chemically modified banana peels as low-cost adsorbent. Desalination Water Treat. 2016, 57, 11242–11254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Ali, F.; Cheong, W.J. Sedimentation assisted preparation of ground particles of silica monolith and their C18 modification resulting in a chromatographic phase of improved separation efficiency. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1525, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freundlich, H. Over the adsorption in solution. J. Phys. Chem. 1906, 57, 1100–1107. [Google Scholar]
- Manyangadze, M.; Chikuruwo, N.M.; Narsaiah, T.B.; Chakra, C.S.; Charis, G.; Danha, G.; Mamvura, T.A. Adsorption of lead ions from wastewater using nano silica spheres synthesized on calcium carbonate templates. Heliyon 2020, 6, e05309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmuir, I. The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1918, 40, 1361–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tempkin, M.; Pyzhev, V. Kinetics of ammonia synthesis on promoted iron catalyst. Acta Phys. Chim. USSR 1940, 12, 327–356. [Google Scholar]
- Trewyn, B.G.; Slowing, I.I.; Giri, S.; Chen, H.-T.; Lin, V.S.-Y. Synthesis and functionalization of a mesoporous silica nanoparticle based on the sol–gel process and applications in controlled release. Acc. Chem. Res. 2007, 40, 846–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tran, C.V.; Quang, D.V.; Nguyen Thi, H.P.; Truong, T.N.; La, D.D. Effective Removal of Pb (II) from Aqueous Media by a New Design of Cu–Mg Binary Ferrite. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 7298–7306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.; McKay, G. A comparison of chemisorption kinetic models applied to pollutant removal on various sorbents. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 1998, 76, 332–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weber, W.J., Jr.; Morris, J.C. Kinetics of adsorption on carbon from solution. J. Sanit. Eng. Div. 1963, 89, 31–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saber-Samandari, S.; Saber-Samandari, S.; Nezafati, N.; Yahya, K. Efficient removal of lead (II) ions and methylene blue from aqueous solution using chitosan/Fe-hydroxyapatite nanocomposite beads. J. Environ. Manag. 2014, 146, 481–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Xie, F.; Chen, S.; Fu, B. The removal of Pb (II) and Cd (II) with hydrous manganese dioxide: Mechanism on zeta potential and adsorption behavior. Environ. Technol. 2019, 41, 3219–3232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidari, A.; Younesi, H.; Mehraban, Z. Removal of Ni (II), Cd (II), and Pb (II) from a ternary aqueous solution by amino functionalized mesoporous and nano mesoporous silica. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 153, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alijani, H.; Beyki, M.H.; Shariatinia, Z.; Bayat, M.; Shemirani, F. A new approach for one step synthesis of magnetic carbon nanotubes/diatomite earth composite by chemical vapor deposition method: Application for removal of lead ions. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 253, 456–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.V.; Dai Tran, L.; Nguyen, T.N. Preparation of chitosan/magnetite composite beads and their application for removal of Pb (II) and Ni (II) from aqueous solution. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2010, 30, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltani, R.D.C.; Khorramabadi, G.S.; Khataee, A.; Jorfi, S. Silica nanopowders/alginate composite for adsorption of lead (II) ions in aqueous solutions. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2014, 45, 973–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Shi, L.; Gao, L.; Wei, Q.; Cui, L.; Hu, L.; Yan, L.; Du, B. The removal of lead ions from aqueous solution by using magnetic hydroxypropyl chitosan/oxidized multiwalled carbon nanotubes composites. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 451, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayalakshmi, K.; Devi, B.M.; Latha, S.; Gomathi, T.; Sudha, P.; Venkatesan, J.; Anil, S. Batch adsorption and desorption studies on the removal of lead (II) from aqueous solution using nanochitosan/sodium alginate/microcrystalline cellulose beads. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 104, 1483–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Zheng, Z.; Li, Y. Characterization and lead adsorption properties of activated carbons prepared from cotton stalk by one-step H3PO4 activation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 181, 440–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Gao, Y.; Li, Y. Preparation and chelation adsorption property of composite chelating material poly (amidoxime)/SiO2 towards heavy metal ions. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 158, 542–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellaoui, L.; Soetaredjo, F.E.; Ismadji, S.; Benguerba, Y.; Dotto, G.L.; Bonilla-Petriciolet, A.; Rodrigues, A.E.; Lamine, A.B.; Erto, A. Equilibrium study of single and binary adsorption of lead and mercury on bentonite-alginate composite: Experiments and application of two theoretical approaches. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 253, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thirumavalavan, M.; Wang, Y.-T.; Lin, L.-C.; Lee, J.-F. Monitoring of the structure of mesoporous silica materials tailored using different organic templates and their effect on the adsorption of heavy metal ions. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 8165–8174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, A.; Bhushan, B.; Gupta, V.; Sharma, P. Chemically activated carbon from lignocellulosic wastes for heavy metal wastewater remediation: Effect of activation conditions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 493, 228–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Googerdchian, F.; Moheb, A.; Emadi, R.; Asgari, M. Optimization of Pb (II) ions adsorption on nanohydroxyapatite adsorbents by applying Taguchi method. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 349, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moattari, R.M.; Rahimi, S.; Rajabi, L.; Derakhshan, A.A.; Keyhani, M. Statistical investigation of lead removal with various functionalized carboxylate ferroxane nanoparticles. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 283, 276–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.-H.; Omer, A.M.; Ouyang, X.k.; Yu, D. Fabrication of carboxylated cellulose nanocrystal/sodium alginate hydrogel beads for adsorption of Pb (II) from aqueous solution. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 108, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Huang, Y.; Wang, M.; Wu, G.; Geng, T.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, A. Macroporous calcium alginate aerogel as sorbent for Pb2+ removal from water media. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 3185–3192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aden, M.; Husson, J.; Monney, S.; Franchi, M.; Knorr, M.; Euvrard, M. Biosorption of Pb (II) ions from aqueous solution using alginates extracted from Djiboutian seaweeds and deposited on silica particles. Pure Appl. Chem. 2019, 91, 459–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zong, L.; Wang, A. A nanoporous hydrogel based on vinyl-functionalized alginate for efficient absorption and removal of Pb2+ ions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 62, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Average Particle Size (µm) | Pore Size (Å) | Pore Volume (cm3/g) | Surface Area (m2/g) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bare SM | 2.4 | 342 | 1.87 | 124 |
| Chemically modified SM | 2.8 | 310 | 1.74 | 113 |
| Isotherm | Adsorption Isotherm Parameters | |
|---|---|---|
| Freundlich | 1/n | 0.334 |
| KF (mg/g) | 7.431 | |
| R2 | 0.997 | |
| Langmuir | qmax (mg/g) | 574.71 |
| K (L/mg) | 0.0603 | |
| R2 | 0.999 | |
| Temkin | BT (KJmol−1) | 48.533 |
| KT (Lmg−1) | 0.5541 | |
| R2 | 0.999 | |
| C0 (mg/L) | Pseudo First Order Experimental | Pseudo First Order Calculated | Pseudo Second Order Calculated | Intra-Particle Diffusion Values Calculated | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qe (mg/g) | K1 | qe | R2 | qe (mg/g) | K2 | R2 | R2 | Ki (mgg−1min−1) | |
| 100 | 235.30 | 0.0483 | 173.67 | 0.9993 | 165.34 | 0.0543 | 0.998 | 0.9943 | 3.35 |
| 300 | 340.62 | 0.0417 | 296.56 | 0.9926 | 322.12 | 0.0456 | 0.997 | 0.9978 | 2.34 |
| 600 | 412.80 | 0.0627 | 337.34 | 0.9978 | 387.30 | 0.0367 | 0.999 | 0.9945 | 4.56 |
| 900 | 441.31 | 0.0538 | 345.21 | 0.9998 | 392.71 | 0.0334 | 0.995 | 0.9825 | 4.56 |
| Adsorbent | qmax (mg/g) | Ref |
|---|---|---|
| Cu–Mg Binary Ferrite | 57.7 | [54] |
| Hydrous manganese dioxide | 140.3 | [55] |
| Amino-grafted mesoporous silica (NH2-MCM-41) | 54 | [56] |
| Magnetic carbon nanotubes/diatomite | 60 | [57] |
| Chitosan/magnetite composite beads | 63 | [58] |
| Silica nano-powders/alginate | 83 | [59] |
| Magnetic hydroxypropyl CS/multiwalled carbon nanotubes | 101 | [60] |
| Nano-CS/sodium alginate/microcrystalline cellulose beads | 114 | [61] |
| Cotton stalk activated carbon | 119 | [62] |
| Poly(amidoxime)/SiO2 | 120 | [63] |
| Bentonite-alginate composite | 162 | [64] |
| Mesoporous silica materials (MCM-48) | 169 | [65] |
| 4-(chloro-2-mercaptophenyl) carbamodithioate (ACMPC) doped with mesoporous silica | 188 | [66] |
| Nanohydroxyapatite–alginate | 236 | [67] |
| Fumarate ferroxane | 243 | [68] |
| Cellulose nanocrystal/sodium alginate | 338 | [69] |
| Macroporous calcium alginate aerogel | 390 | [70] |
| Alg·S + SiO2 | 439 | [71] |
| Alg·S + SiO2NH2 | 585 | [71] |
| Hydrogel based on vinyl-functionalized alginate | 784 | [72] |
| CS/Fe-hydroxyapatite composite bead | 1385 | [51] |
| Chemically modified SM | 792 | This study |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ali, A.; Alharthi, S.; Ahmad, B.; Naz, A.; Khan, I.; Mabood, F. Efficient Removal of Pb(II) from Aqueous Medium Using Chemically Modified Silica Monolith. Molecules 2021, 26, 6885. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26226885
Ali A, Alharthi S, Ahmad B, Naz A, Khan I, Mabood F. Efficient Removal of Pb(II) from Aqueous Medium Using Chemically Modified Silica Monolith. Molecules. 2021; 26(22):6885. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26226885
Chicago/Turabian StyleAli, Ashraf, Sarah Alharthi, Bashir Ahmad, Alia Naz, Idrees Khan, and Fazal Mabood. 2021. "Efficient Removal of Pb(II) from Aqueous Medium Using Chemically Modified Silica Monolith" Molecules 26, no. 22: 6885. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26226885
APA StyleAli, A., Alharthi, S., Ahmad, B., Naz, A., Khan, I., & Mabood, F. (2021). Efficient Removal of Pb(II) from Aqueous Medium Using Chemically Modified Silica Monolith. Molecules, 26(22), 6885. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26226885