Total Synthesis of Decahydroquinoline Poison Frog Alkaloids ent-cis-195A and cis-211A
Abstract
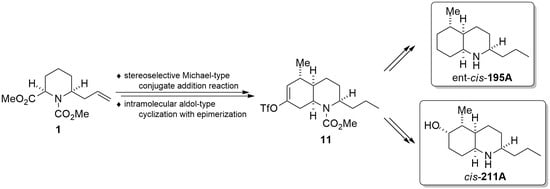
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemistry
3.1.1. General Information
3.1.2. Synthesis of (6R)-2-Phenylsulfanyl-6-propyl-piperidine-1,2-dicarboxylic Acid Dimethyl Ester (3)
3.1.3. Synthesis of (6R)-6-Propyl-5,6-dihydro-4H-pyridine-1,2-dicarboxylic Acid Dimethyl Ester (4)
3.1.4. Synthesis of (2R, 3S, 6R)-6-Propyl-3-vinyl-piperidine-1,2-dicarboxylic Acid Dimethyl ester (5)
3.1.5. Synthesis of (2S, 3S, 6R)-2-Methoxycarbonylmethyl-6-propyl-3-vinyl-piperidine-1-carboxylic Acid Methyl Ester (6)
3.1.6. Synthesis of (2S, 3S, 6R)-2-[(Methoxy-methyl-carbamoyl)-methyl]-6-propyl-3-vinyl-piperidine-1-carboxylic Acid Methyl Ester (7)
3.1.7. Synthesis of (2S, 3S, 6R)-2-(2-Oxo-propyl)-6-propyl-3-vinyl-piperidine-1-carboxylic Acid Methyl Ester (8)
3.1.8. Synthesis of (2S, 3S, 6R)-3-Formyl-2-(2-oxo-propyl)-6-propyl-piperidine-1-carboxylic Acid Methyl Ester (9)
3.1.9. Synthesis of (2R, 4aR, 8aS)-7-Oxo-2-propyl-3,4,4a,7,8,8a-hexahydro-2H-quinoline-1-carboxylic Acid Methyl Ester (10c)
3.1.10. Synthesis of (2R, 4aR, 5R, 8aR)-5-Methyl-2-propyl-7-trifluoromethane-sulfonyloxy-3,4,4a,5,8,8a-hexahydro-2H-quinoline-1-carboxylic Acid Methyl Ester (11)
3.1.11. Synthesis of (2R, 4aR, 5R, 8aR)-5-Methyl-2-propyl-octahydro-quinoline-1-carboxylic Acid Methyl Ester (12)
3.1.12. Synthesis of (2R, 4aR, 5R, 8aR)-5-Methyl-2-propyldecahydroquinoline (ent-cis-195A)
3.1.13. Synthesis of (2R, 4aR, 5R, 8aR)-5-Methyl-2-propyl-3,4,4a,5,8,8a-hexahydro-2H-quinoline-1-carboxylic Acid Methyl Ester (13)
3.1.14. Synthesis of (2R, 4aR, 5R, 6R, 8aR)-6-Hydroxy-5-methyl-2-propyl-octahydro-quinoline-1-carboxylic Acid Methyl Ester (15)
3.1.15. Synthesis of (2R, 4aR, 5R, 8aR)-5-Methyl-6-oxo-2-propyl-octahydro-quinoline-1-carboxylic Acid Methyl Ester (19)
3.1.16. Synthesis of (2R, 4aR, 5R, 6S, 8aR)-6-Hydroxy-5-methyl-2-propyl-octahydro-quinoline-1-carboxylic Acid Methyl Ester (16)
3.1.17. Synthesis of (2R, 4aR, 5R, 6S, 8aR)-5-Methyl-2-propyldecahydroquinoline-6-ol (cis-211A)
3.1.18. Synthesis of (2R, 4aR, 5R, 6R, 8aR)-5-Methyl-2-propyldecahydroquinoline-6-ol (6-epi-211A)
3.2. Electrophysiological Recording of Nicotinic ACh Receptor-Mediated Current in Xenopus Oocytes
3.3. Ligand-Binding Assays
3.4. In Vitro Effect of the Compound on the Transport of Cationic Compounds at the BBB and Inner BRB
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Daly, J.W.; Spande, T.F.; Garraffo, H.M. Alkaloids from Amphibian Skin: A Tabulation of Over Eight-Hundred Compounds. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 1556–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badio, B.; Daly, J.W. Epibatidine, a potent analgetic and nicotinic agonist. Mol. Pharmacol. 1994, 45, 563–569. [Google Scholar]
- Daly, J.W.; Nishizawa, Y.; Padgett, W.L.; Tokuyama, T.; McCloskey, P.J.; Waykole, L.; Schultz, A.G.; Aronstam, R.S. Decahydroquinoline alkaloids: Noncompetitive blockers for nicotinic acetylcholine receptor-channels in pheochromocytoma cells and Torpedo electroplax. Neurochem. Res. 1991, 16, 1207–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, J.W.; Tokuyama, T.; Habermehl, G.; Karle, I.L.; Witkop, B. Frog venoms. Isolation and structure of pumiliotoxin C. Lieb. Ann. Chem. 1969, 729, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibuka, T.; Inubushi, Y.; Saji, I.; Tanaka, K.; Masaki, N. Total synthesis of dl-pumiliotoxin c hydrochloride and its crystal structure. Tetrahedron Lett. 1975, 16, 323–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oppolzer, W.; Fröstl, W. The total synthesis of (+/-)-pumiliotoxin-C. Helv. Chim. Acta 1975, 58, 593–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habermehl, G.; Andres, H.; Miyahara, K.; Witkop, B.; Daly, J.W. Synthese von Pumiliotoxin C. Lieb. Ann. Chem. 1976, 1577–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overman, L.E.; Jessup, P.J. Synthetic applications of N-acylamino-1,3-dienes. An efficient stereospecific total synthesis of dl-pumiliotoxin C, and a general entry to cis-decahydroquinoline alkaloids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1978, 100, 5179–5185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattori, K.; Matsumura, Y.; Miyazaki, T.; Maruoka, K.; Yamamoto, H. Successive Beckmann rearrangement-alkylation sequence by organoaluminum reagents. Simple route to dl-pumiliotoxin C. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1981, 103, 7368–7370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeBel, N.A.; Balasubramanian, N. Stereospecific synthesis of 2,3,6-trisubstituted piperidines: An efficient total synthesis of (±)-pumiliotoxin C. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1989, 111, 3363–3368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comins, D.L.; Dehghani, A. N-acyldihydropyridones as synthetic intermediates. A short synthesis of (±)-pumiliotoxin C. Tetrahedron Lett. 1991, 32, 5697–5700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandi, A.; Cordero, F.M.; Goti, A.; Guarna, A. The isoxazoline-5-spirocyclopropane route to (±)-Pumiliotoxin C. Tetrahedron Lett. 1992, 33, 6697–6700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polniaszek, R.P.; Dillard, L.D. Stereospecific total syntheses of decahydroquinoline alkaloids (±)-195A and (±)-2-epi-195A. J. Org. Chem. 1992, 57, 4103–4110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulvannan, K.; Stille, J.R. Decahydroquinoline construction through aza-annulation: A stereoselective synthesis of (±)-5-epipumiliotoxin C. Tetrahedron Lett. 1993, 34, 6673–6676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyers, A.I.; Milot, G. α-Alkylation and stereochemistry of cis- and trans-decahydroquinolines mediated by the formamidine and Boc activating groups. Synthesis of pumiliotoxin C. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1993, 115, 6652–6660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, G.; Praveen, M. Regioselective Haller-Bauer Cleavage in Tricyclo-[5.2.1.02,6]dec-8-ene-3,10-dione. A Total Synthesis of (±)-Pumiliotoxin C. J. Org. Chem. 1995, 60, 279–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Back, T.G.; Nakajima, K. Use of an acetylenic sulfone as an alkene dipole equivalent in the synthesis of (±)-pumiliotoxin C. Tetrahedron Lett. 1997, 38, 989–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuethe, J.T.; Padwa, A. The tandem Pummerer-isomünchnone route to (±)-pumiliotoxin C. Tetrahedron Lett. 1997, 38, 1505–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padwa, A.; Heidelbaugh, T.M.; Kuethe, J.T. Using the Pummerer cyclization-deprotonation-cycloaddition cascade of imidosulfoxides for alkaloid synthesis. J. Org. Chem. 2000, 65, 2368–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akashi, M.; Sato, Y.; Mori, M. Synthesis of pumiliotoxine C from molecular nitrogen as a nitrogen Source. J. Org. Chem. 2001, 66, 7873–7874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijk, E.W.; Panella, L.; Pinho, P.; Naasz, R.; Meetsma, A.; Minnaard, A.J.; Feringa, B.L. The asymmetric synthesis of (-)-pumiliotoxin C using tandem catalysis. Tetrahedron 2004, 60, 9687–9693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gärtner, M.; Qu, J.; Helmchen, G. Enantioselective Syntheses of the Alkaloids cis-195A (Pumiliotoxin C) and trans-195A Based on Multiple Applications of Asymmetric Catalysis. J. Org. Chem. 2012, 77, 1186–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokuyama, T.; Nishimori, N.; Shimada, S.; Edwards, M.W.; Daly, J.W. New classes of amidine, indolizidine and quinolizidine alkaloids from a poison-frog, Dendrobates pumilio (Dendrobatidae). Tetrahedron 1987, 43, 643–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyooka, N.; Tanaka, K.; Momose, T.; Daly, J.W.; Garraffo, H.M. Highly stereoselective construction of trans(2,3)-cis(2,6)-trisubstituted piperidines: An application to the chiral synthesis of Dendrobates alkaloids. Tetrahedron 1997, 53, 9553–9574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyooka, N.; Okumura, M.; Nemoto, H. Stereodivergent Process for the Synthesis of the Decahydroquinoline Type of Dendrobatid Alkaloids. J. Org. Chem. 2002, 67, 6078–6081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyooka, N.; Fukutome, A.; Nemoto, H.; Daly, J.W.; Spande, T.F.; Garraffo, H.M.; Kaneko, T. Synthesis of alkaloid 223A and a structural revision. Org. Lett. 2002, 4, 1715–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyooka, N.; Nemoto, H. First enantioselective synthesis of (+)-quinolizidine 207I: Determination of the absolute stereochemistry. Tetrahedron Lett. 2003, 44, 569–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyooka, N.; Fukutome, A.; Shinoda, H.; Nemoto, H. Total synthesis of the antipode of alkaloid 205B. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2003, 42, 3808–3810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuneki, H.; You, Y.; Toyooka, N.; Kagawa, S.; Kobayashi, S.; Sasaoka, T.; Nemoto, H.; Kimura, I.; Dani, J.A. Alkaloids indolizidine 235B′, quinolizidine 1-epi-207I, and the tricyclic 205B are potent and selective noncompetitive inhibitors of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Mol. Pharmacol. 2004, 66, 1061–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Toyooka, N.; Nemoto, H.; Kawasaki, M.; Martin Garraffo, H.; Spande, T.F.; Daly, J.W. Enantioselective syntheses of two 5, 9E diastereomers of 223V, an alkaloid from the poison frog Dendrobates pumilio. Tetrahedron 2005, 61, 1187–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyooka, N.; Dejun, Z.; Nemoto, H.; Garraffo, H.M.; Spande, T.F.; Daly, J.W. The enantioselective synthesis of poison-frog alkaloids (-)-203A, (-)-209B, (-)-231C, (-)-233D, and (-)-235B″. Tetrahedron Lett. 2006, 47, 577–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyooka, N.; Dejun, Z.; Nemoto, H.; Garraffo, H.M.; Spande, T.F.; Daly, J.W. Enantioselective syntheses of poison-frog alkaloids: 219F and 221I and an epimer of 193E. Tetrahedron Lett. 2006, 47, 581–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyooka, N.; Kobayashi, S.; Zhou, D.; Tsuneki, H.; Wada, T.; Sakai, H.; Nemoto, H.; Sasaoka, T.; Garraffo, H.M.; Spande, T.F.; et al. Synthesis of poison-frog alkaloids 233A, 235U, and 251AA and their inhibitory effects on neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2007, 17, 5872–5875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toyooka, N.; Zhou, D.; Nemoto, H.; Tezuka, Y.; Kadota, S.; Andriamaharavo, N.R.; Garraffo, H.M.; Spande, T.F.; Daly, J.W. Efficient enantio- and diastereodivergent synthesis of poison-frog alkaloids 251O and trans-223B. J. Org. Chem. 2009, 74, 6784–6791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Tsuneki, H.; Urata, N.; Tezuka, Y.; Wada, T.; Sasaoka, T.; Sakai, H.; Saporito, R.A.; Toyooka, N. Synthesis and biological activities of the 3,5-disubstituted indolizidine poison frog alkaloid 239Q and its congeners. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2012, 7082–7092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, J.; Saporito, R.A.; Toyooka, N. Enantiodivergent synthesis of the quinolizidine poison frog alkaloid 195C. Tetrahedron 2013, 69, 10311–10315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, T.; Yamamoto, T.; Kato, D.; Kawasaki, M.; Saporito, R.A.; Toyooka, N. Synthesis of 8-deoxypumiliotoxin 193H and 9-deoxyhomopumiliotoxin 207O. Tetrahedron Lett. 2018, 59, 3797–3800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Okada, T.; Ozaki, T.; Yamamoto, T.; Kasahara, H.; Kawasaki, M.; Toyooka, N. Divergent Syntheses of Pumiliotoxin-Type Poison-Frog Alkaloids. ChemistrySelect 2021, 6, 1939–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demizu, Y.; Shiigi, H.; Mori, H.; Matsumoto, K.; Onomura, O. Convenient synthesis of an enantiomerically pure bicyclic prolineand its N-oxyl derivatives. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 2008, 19, 2659–2665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Comins, D.L.; Dehghani, A. Pyridine-derived triflating reagents: An improved preparation of vinyl triflates from metallo enolates. Tetrahedron Lett. 1992, 42, 6299–6302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwabuchi, Y. Discovery and Exploitation of AZADO: The Highly Active Catalyst for Alcohol Oxidation. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2013, 61, 1197–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Changeux, J.P. Golden anniversary of the nicotinic receptor. Neuron 2020, 107, 14–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corradi, J.; Bouzat, C. Understanding the bases of function and modulation of α7 nicotinic receptors: Implications for drug discovery. Mol. Pharmacol. 2016, 90, 288–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dineley, K.T.; Pandya, A.A.; Yakel, J.L. Nicotinic ACh receptors as therapeutic targets in CNS disorders. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2015, 36, 96–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Warnick, J.E.; Jessup, P.J.; Overman, L.E.; Eldefrawi, M.E.; Nimit, Y.; Daly, J.W.; Albuquerque, E.X. Pumiliotoxin-C and synthetic analogues. A new class of nicotinic antagonists. Mol. Pharmacol. 1982, 22, 565–573. [Google Scholar]
- Tega, Y.; Akanuma, S.; Kubo, Y.; Terasaki, T.; Hosoya, K. Blood-to-brain influx transport of nicotine at the rat blood–brain barrier: Involvement of a pyrilamine-sensitive organic cation transport process. Neurochem. Int. 2013, 62, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubo, Y.; Kusagawa, Y.; Tachikawa, M.; Akanuma, S.; Hosoya, K. Involvement of a Novel Organic Cation Transporter in Verapamil Transport Across the Inner Blood-Retinal Barrier. Pharm. Res. 2013, 30, 847–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosoya, K.; Takashima, T.; Tetsuka, K.; Nagura, T.; Ohtsuki, S.; Takanaga, H.; Ueda, M.; Yanai, N.; Obinata, M.; Terasaki, T. mRNA Expression and Transport Characterization of Conditionally Immortalized Rat Brain Capillary Endothelial Cell Lines; a New in vitro BBB Model for Drug Targeting. J. Drug Target. 2000, 8, 357–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosoya, K.; Tomi, M.; Ohtsuki, S.; Takanaga, H.; Ueda, M.; Yanai, N.; Obinata, M.; Terasaki, T. Conditionally Immortalized Retinal Capillary Endothelial Cell Lines (TR-iBRB) Expressing Differentiated Endothelial Cell Functions Derived from a Transgenic Rat. Exp. Eye Res. 2001, 72, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dwoskin, L.P.; Wooters, T.E.; Sumithran, S.P.; Siripurapu, K.B.; Joyce, B.M.; Lockman, P.R.; Manda, V.K.; Ayers, J.T.; Zhang, Z.; Deaciuc, A.G.; et al. N,N’-Alkane-diyl-bis-3-picoliniums as nicotinic receptor antagonists: Inhibition of nicotine-evoked dopamine release and hyperactivity. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2008, 326, 563–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tachikawa, M.; Okamoto, M.; Hirose, S.; Yoneyama, D.; Akanuma, S.; Terasaki, T.; Hosoya, K. Inner Blood-Retinal Barrier Mediates L-Isomer-Predominant Transport of Serine. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 100, 3892–3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Conditions | Percentage of Control | |
|---|---|---|
| [3H]Nicotine Uptake | [3H]Verapamil Uptake | |
| Control | 100 ± 5 | 100 ± 4 |
| ent-cis-195A | 31.6 ± 1.7 * | 66.9 ± 2.5 * |
| cis-211A | 60.0 ± 3.5 * | 70.6 ± 4.1 * |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Okada, T.; Wu, N.; Takashima, K.; Ishimura, J.; Morita, H.; Ito, T.; Kodama, T.; Yamasaki, Y.; Akanuma, S.-i.; Kubo, Y.; et al. Total Synthesis of Decahydroquinoline Poison Frog Alkaloids ent-cis-195A and cis-211A. Molecules 2021, 26, 7529. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26247529
Okada T, Wu N, Takashima K, Ishimura J, Morita H, Ito T, Kodama T, Yamasaki Y, Akanuma S-i, Kubo Y, et al. Total Synthesis of Decahydroquinoline Poison Frog Alkaloids ent-cis-195A and cis-211A. Molecules. 2021; 26(24):7529. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26247529
Chicago/Turabian StyleOkada, Takuya, Naizhen Wu, Katsuki Takashima, Jungoh Ishimura, Hiroyuki Morita, Takuya Ito, Takeshi Kodama, Yuhei Yamasaki, Shin-ichi Akanuma, Yoshiyuki Kubo, and et al. 2021. "Total Synthesis of Decahydroquinoline Poison Frog Alkaloids ent-cis-195A and cis-211A" Molecules 26, no. 24: 7529. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26247529
APA StyleOkada, T., Wu, N., Takashima, K., Ishimura, J., Morita, H., Ito, T., Kodama, T., Yamasaki, Y., Akanuma, S. -i., Kubo, Y., Hosoya, K. -i., Tsuneki, H., Wada, T., Sasaoka, T., Shimizu, T., Sakai, H., Dwoskin, L. P., Hussaini, S. R., Saporito, R. A., & Toyooka, N. (2021). Total Synthesis of Decahydroquinoline Poison Frog Alkaloids ent-cis-195A and cis-211A. Molecules, 26(24), 7529. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26247529