Cu-Doped ZnO Nanoparticles for Non-Enzymatic Glucose Sensing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Structural and Morphological Characterization and Chemical Studies of CuxZn1−xO NPs
2.2. Electrochemical Characterization of the CuxZn1−xO/ITO Modified Electrodes
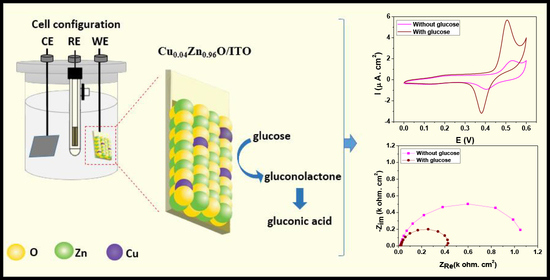
2.3. Electrochemical Study of Glucose Sensing at the Cu0.04Zn0.96O/ITO Electrode
2.3.1. Cyclic Voltammetry (CV)
2.3.2. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy
2.3.3. Differential Pulse Voltammetry (DPV) Detection of Glucose
2.4. Interferences and Practical Application of Cu0.04Zn0.96O/ITO Electrodes
2.5. Practical Applications
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Reagents
3.2. Synthesis of CuxZn1−xO NPs
3.3. Electrode Preparation
3.4. Characterization of the CuxZn1−xO NPs
3.5. Electrochemical Characterizations
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Chavali, M.S.; Nikolova, M.P. Metal oxide nanoparticles and their applications in nanotechnology. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmad, R.; Tripathy, N.; Ahn, M.-S.; Bhat, K.S.; Mahmoudi, T.; Wang, Y.; Yoon-Bong, H.; Kwon, D.-W.; Yang, H.-Y.; Hahn, Y.-B. Highly Efficient Non-Enzymatic Glucose Sensor Based on CuO Modified Vertically-Grown ZnO Nanorods on Electrode. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Phuruangrat, A.; Siri, S.; Wadbua, P.; Thongtem, S.; Thongtem, T. Microwave-assisted synthesis, photocatalysis and antibacterial activity of Ag nanoparticles supported on ZnO flowers. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2019, 126, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saboor, A.; Shah, S.M.; Hussain, H. Band gap tuning and applications of ZnO nanorods in hybrid solar cell: Ag-doped verses Nd-doped ZnO nanorods. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2019, 93, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, M.; Ju, D.; Xu, H.; Cao, B. High-performance gas sensor based on ZnO nanowires functionalized by Au nanoparticles. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 199, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitta, S.B.; Murahari, P.; Nandanapalli, K.R.; Mudusu, D.; Karuppannan, R.; Whang, D. Si/ZnO heterostructures for efficient diode and water-splitting applications. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2018, 43, 16015–16023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beitollahi, H.; Tajik, S.; Nejad, F.G.; Safaei, M. Recent advances in ZnO nanostructure-based electrochemical sensors and biosensors. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 5826–5844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.; Braydich-Stolle, L.K.; Schrand, A.M.; Murdock, R.C.; Yu, K.O.; Mattie, D.M.; Schlager, J.J.; Terrones, H. Toxicity Evaluation for Safe Use of Nanomaterials: Recent Achievements and Technical Challenges. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 1549–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aini, B.N.; Siddiquee, S.; Ampon, K.; Rodrigues, K.F.; Suryani, S. Development of glucose biosensor based on ZnO nanoparticles film and glucose oxidase-immobilized eggshell membrane. Sens. Bio-Sensing Res. 2015, 4, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Corso, C.D.; Dickherber, A.; Hunt, W.D. An investigation of antibody immobilization methods employing organosilanes on planar ZnO surfaces for biosensor applications. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2008, 24, 805–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.-L.; Lin, J.-H.; Hsu, D.-X.; Wang, S.-H.; Lin, S.-Y.; Hsueh, T.-J. Enhanced non-enzymatic glucose biosensor of ZnO nanowires via decorated Pt nanoparticles and illuminated with UV/green light emitting diodes. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 238, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, C.-H.; Zhang, R.-J.; Chen, X.; Zheng, Y.-X.; Wang, S.-Y.; Liu, J.; Dai, N.; Chen, L.-Y. Effects of Al Doping on the Properties of ZnO Thin Films Deposited by Atomic Layer Deposition. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shatnawi, M.; Alsmadi, A.; Bsoul, I.; Salameh, B.; Mathai, M.; Alnawashi, G.; Alzoubi, G.M.; Al-Dweri, F.; Bawa’Aneh, M. Influence of Mn doping on the magnetic and optical properties of ZnO nanocrystalline particles. Results Phys. 2016, 6, 1064–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kati, N. Investigation of Optical and Morphological Properties of Co Doped ZnO Nanomaterials. Turk. J. Sci. Technol. 2019, 14, 41–48. [Google Scholar]
- Pascariu, P.; Tudose, I.V.; Suchea, M.; Koudoumas, E.; Fifere, N.; Airinei, A. Preparation and characterization of Ni, Co doped ZnO nanoparticles for photocatalytic applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 448, 481–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meshki, M.; Behpour, M.; Masoum, S. Application of Fe doped ZnO nanorods-based modified sensor for determination of sulfamethoxazole and sulfamethizole using chemometric methods in voltammetric studies. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2015, 740, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.-B.; Ameen, S.; Akhtar, M.S.; Shin, H. Iron-nickel co-doped ZnO nanoparticles as scaffold for field effect transistor sensor: Application in electrochemical detection of hexahydropyridine chemical. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 275, 422–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Hou, P.; Petropoulos, E.; Feng, Y.; Yu, Y.; Xue, L.; Yang, L. High Efficient Visible-Light Photocatalytic Performance of Cu/ZnO/rGO Nanocomposite for Decomposing of Aqueous Ammonia and Treatment of Domestic Wastewater. Front. Chem. 2018, 6, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muthukumaran, S.; Gopalakrishnan, R. Structural, FTIR and photoluminescence studies of Cu doped ZnO nanopowders by co-precipitation method. Opt. Mater. 2012, 34, 1946–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, M.; Ghosh, A.; Thangavel, R. Experimental and theoretical investigations of structural and optical properties of copper doped ZnO nanorods. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2015, 74, 756–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, A.; Ali, M.A.; Ibrahim, E.; Osman, M. Influence of Cu doping on structural, morphological, photoluminescence, and electrical properties of ZnO nanostructures synthesized by ice-bath assisted sonochemical method. J. Alloy. Compd. 2016, 683, 399–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-J.; Kim, B.-S.; Cho, C.R.; Jeong, S.-Y. A study of magnetic and optical properties of Cu-doped ZnO. Phys. Status Solidi (b) 2004, 241, 1533–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandekar, K.V.; Shkir, M.; Al-Shehri, B.M.; Al Faifyb, S.; Halor, R.G.; Khane, A.; Al-Namshah, K.S.; Hamdy, M.S. Visible light sensitive Cu doped ZnO: Facile synthesis, characterization and high photocatalytic response. Mater. Charact. 2020, 165, 110387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammara, S.; Shamaila, S.; Zafar, N.; Bokhari, A.; Sabah, A.; Shabbir, S.A. Nonenzymatic glucose sensor with high performance electrodeposited nickel/copper/carbon nanotubes nanocomposite electrode. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2018, 120, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivasankar, K.; Rani, K.K.; Wang, S.-F.; Devasenathipathy, R.; Lin, C.-H. Copper Nanoparticle and Nitrogen Doped Graphite Oxide Based Biosensor for the Sensitive Determination of Glucose. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jeong, H.; Nguyen, D.M.; Lee, M.S.; Kim, H.G.; Ko, S.C.; Kwac, L.K. N-doped graphene-carbon nanotube hybrid networks attaching with gold nanoparticles for glucose non-enzymatic sensor. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 90, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, D.-W.; Lee, S.; Seo, M.; Chung, T.D. Recent advances in electrochemical non-enzymatic glucose sensors—A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1033, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Wang, F.; Chen, Z.; Qiu, Y.; Zhai, T.; Hu, M.; Zhang, C.; Huang, K. Flower-like MoS 2 decorated with Cu 2 O nanoparticles for non-enzymatic amperometric sensing of glucose. Talanta 2017, 167, 593–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teymourian, H.; Barfidokht, A.; Wang, J. Electrochemical glucose sensors in diabetes management: An updated review (2010–2020). Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 7671–7709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juska, V.B.; Pemble, M.E. A Critical Review of Electrochemical Glucose Sensing: Evolution of Biosensor Platforms Based on Advanced Nanosystems. Sensors 2020, 20, 6013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Li, L.; Zhou, W.; Shao, Z.; Chen, X. Advances in non-enzymatic glucose sensors based on metal oxides. J. Mater. Chem. B 2016, 4, 7333–7349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Numan, A.; Shahid, M.M.; Omar, F.S.; Ramesh, K.; Ramesh, S. Facile fabrication of cobalt oxide nanograin-decorated reduced graphene oxide composite as ultrasensitive platform for dopamine detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 238, 1043–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, S. Nanoparticles-assembled NiO nanosheets templated by graphene oxide film for highly sensitive non-enzymatic glucose sensing. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 238, 788–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Boo, H.; Chung, T.D. Electrochemical non-enzymatic glucose sensors. Anal. Chim. Acta 2006, 556, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmoud, A.; Echabaane, M.; Omri, K.; El Mir, L.; Ben Chaabane, R. Development of an impedimetric non enzymatic sensor based on ZnO and Cu doped ZnO nanoparticles for the detection of glucose. J. Alloy. Compd. 2019, 786, 960–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Kaushal, A.; Bdikin, I.; Saravanan, K.V.; Ferreira, J.M. Effect of Ni doping on structural and optical properties of Zn 1−x Ni x O nanopowder synthesized via low cost sono-chemical method. Mater. Res. Bull. 2015, 70, 430–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iribarren, A.; Hernández-Rodríguez, E.; Maqueira, L. Structural, chemical and optical evaluation of Cu-doped ZnO nanoparticles synthesized by an aqueous solution method. Mater. Res. Bull. 2014, 60, 376–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allred, A. Electronegativity values from thermochemical data. J. Inorg. Nucl. Chem. 1961, 17, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhal, S.; Kaur, J.; Namgyal, T.; Sharma, R. Cu-doped ZnO nanoparticles: Synthesis, structural and electrical properties. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2012, 407, 1223–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanh, N.T.; Tri, N.L.M.; Van Thuan, D.; Tung, M.H.T.; Pham, T.-D.; Minh, T.D.; Trang, H.T.; Binh, M.T.; Nguyen, M.V. Monocrotophos pesticide effectively removed by novel visible light driven Cu doped ZnO photocatalyst. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2019, 382, 111923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slimi, O.; Djouadi, D.; Hammiche, L.; Chelouche, A.; Touam, T. Structural and optical properties of Cu doped ZnO aerogels synthesized in supercritical ethanol. J. Porous Mater. 2017, 25, 595–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousseau, G.; Fattahi, M.; Grambow, B.; Desgranges, L.; Boucher, F.; Ouvrard, G.; Millot, N.; Niepce, J. Synthesis and characterization of nanometric powders of UO2+x, (Th,U)O2+x and (La,U)O2+x. J. Solid State Chem. 2009, 182, 2591–2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallika, A.; Ramachandrareddy, A.; SowriBabu, K.; Reddy, K.V. Synthesis and optical characterization of aluminum doped ZnO nanoparticles. Ceram. Int. 2014, 40, 12171–12177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suwanboon, S.; Amornpitoksuk, P.; Sukolrat, A.; Muensit, N. Optical and photocatalytic properties of La-doped ZnO nanoparticles prepared via precipitation and mechanical milling method. Ceram. Int. 2013, 39, 2811–2819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmugam, V.; Jeyaperumal, K.S. Investigations of visible light driven Sn and Cu doped ZnO hybrid nanoparticles for photocatalytic performance and antibacterial activity. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 449, 617–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, N.; Kumar, S.; Ghosh, A.K.; Chatterjee, S.; Jha, S.N.; Bhattacharyya, D. Structural investigations of (Mn, Dy) co-doped ZnO nanocrystals using X-ray absorption studies. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 56662–56675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yogamalar, N.R.; Bose, A.C. Absorption–emission study of hydrothermally grown Al:ZnO nanostructures. J. Alloy. Compd. 2011, 509, 8493–8500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, D.B.; Netting, C.H.; Saviot, L.; Pighini, C.; Millot, N.; Aymes, D.; Liu, H.-L. Far-Infrared Absorption by Acoustic Phonons in Titanium Dioxide Nanopowders. J. Nanoelectron. Optoelectron. 2006, 1, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arguello, C.A.; Rousseau, D.L.; Porto, S.P.S. First-Order Raman Effect in Wurtzite-Type Crystals. Phys. Rev. 1969, 181, 1351–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesh, R.S.; Navaneethan, M.; Mani, G.K.; Ponnusamy, S.; Tsuchiya, K.; Muthamizhchelvan, C.; Kawasaki, S.; Hayakawa, Y. Influence of Al doping on the structural, morphological, optical, and gas sensing properties of ZnO nanorods. J. Alloy. Compd. 2017, 698, 555–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, J.; Ghosh, R.; Giri, P.K. Tuning the visible photoluminescence in Al doped ZnO thin film and its application in label-free glucose detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 254, 681–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, L.; Lupan, O.; Chai, G.; Khallaf, H.; Ono, L.; Cuenya, B.R.; Tiginyanu, I.; Ursaki, V.; Sontea, V.; Schulte, A. Synthesis and characterization of Cu-doped ZnO one-dimensional structures for miniaturized sensor applications with faster response. Sensors Actuators A Phys. 2013, 189, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuriakose, S.; Satpati, B.; Mohapatra, S. Highly efficient photocatalytic degradation of organic dyes by Cu doped ZnO nanostructures. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 25172–25181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.K.; Dutta, R.K.; Pandey, A.C. Doping dependent room-temperature ferromagnetism and structural properties of dilute magnetic semiconductor ZnO:Cu2+ nanorods. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2009, 321, 4001–4005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chartier, A.; D’Arco, P.; Dovesi, R.; Saunders, V.R. Ab initio Hartree-Fock investigation of the structural, electronic, and magnetic properties of Mn3O4. Phys. Rev. B 1999, 60, 14042–14048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antony, A.; Poornesh, P.; Kityk, I.V.; Ozga, K.; Jedryka, J.; Rakus, P.; Wojciehcowski, A. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, Raman and photoluminescence studies on formation of defects in Cu:ZnO thin films and its role in nonlinear optical features. Laser Phys. 2018, 28, 095405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zeferino, R.S.; Flores, M.B.; Pal, U.R. Photoluminescence and Raman Scattering in Ag-doped ZnO Nanoparticles. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 109, 014308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Liu, X.-C.; Zhou, R.-W.; Chen, H.-M.; Zhuo, S.-Y.; Shi, E.-W. Strong correlation between oxygen vacancy and ferromagnetism in Yb-doped ZnO thin films. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 116, 243910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Yang, W.; Song, T.; Li, C.; Zhang, L.; Wang, H.; Chai, L. Cu doped Fe3O4 magnetic adsorbent for arsenic: Synthesis, property, and sorption application. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 50011–50018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, M.; Mahapatra, P.; Thangavel, R. Structural, optical and electrochemical properties of Al and Cu co-doped ZnO nanorods synthesized by a hydrothermal method. Thin Solid Films 2016, 612, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavanya, N.; Fazio, E.; Neri, F.; Bonavita, A.; Leonardi, S.G.; Neri, G.; Sekar, C. Electrochemical sensor for simultaneous determination of ascorbic acid, uric acid and folic acid based on Mn-SnO2 nanoparticles modified glassy carbon electrode. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2016, 770, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavanya, N.; Sekar, C.; Ficarra, S.; Tellone, E.; Bonavita, A.; Leonardi, S.G.; Neri, G. A novel disposable electrochemical sensor for determination of carbamazepine based on Fe doped SnO2 nanoparticles modified screen-printed carbon electrode. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 62, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terbouche, A.; Lameche, S.; Ait-Ramdane-Terbouche, C.; Guerniche, D.; Lerari, D.; Bachari, K.; Hauchard, D. A new electrochemical sensor based on carbon paste electrode/Ru(III) complex for determination of nitrite: Electrochemical impedance and cyclic voltammetry measurements. Meas. J. Int. Meas. Confed. IMEKO 2016, 92, 524–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Faria, R.A.D.; Iden, H.; Heneine, L.G.D.; Matencio, T.; Messaddeq, Y. Non-Enzymatic Impedimetric Sensor Based on 3-Aminophenylboronic Acid Functionalized Screen-Printed Carbon Electrode for Highly Sensitive Glucose Detection. Sensors 2019, 19, 1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shrivastava, A.; Gupta, V.B. Methods for the determination of limit of detection and limit of quantitation of the analytical methods. Chron. Young Sci. 2011, 2, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahhoseini, L.; Mohammadi, R.; Ghanbari, B.; Shahrokhian, S. Ni(II) 1D-coordination polymer/C60-modified glassy carbon electrode as a highly sensitive non-enzymatic glucose electrochemical sensor. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 478, 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalifa, Z.; Zahran, M.; Zahran, M.A.-H.; Azzem, M.A. Mucilage-capped silver nanoparticles for glucose electrochemical sensing and fuel cell applications. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 37675–37682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Chen, Q.; Jia, L.; Zhao, Q.; Jiang, J. Networked cobaltous phosphate decorated with nitrogen-doped reduced graphene oxide for non-enzymatic glucose sensing. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 283, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J.; Wang, Y.; Pan, J.; Chen, Z.; Wang, C.; Chen, J.; Wu, Z.; Yangyue. Non-enzymatic glucose sensor based on ZnO–CeO2 whiskers. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 239, 122051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Guo, H.; Wang, Z.; Long, Y.; Li, W.; Tu, Y. Au@Cu2O core-shell structure for high sensitive non-enzymatic glucose sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 255, 2510–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekaran, N.I.; Manickam, M. A sensitive and selective non-enzymatic glucose sensor with hollow Ni-Al-Mn layered triple hydroxide nanocomposites modified Ni foam. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 288, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grochowska, K.; Ryl, J.; Karczewski, J.; Śliwiński, G.; Cenian, A.; Siuzdak, K. Non-enzymatic flexible glucose sensing platform based on nanostructured TiO2—Au composite. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2019, 837, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagadeesan, M.; Movlaee, K.; Krishnakumar, T.; Leonardi, S.; Neri, G. One-step microwave-assisted synthesis and characterization of novel CuO nanodisks for non-enzymatic glucose sensing. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2019, 835, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Xia, C.; Wang, S.; Han, F.; Akbari, M.K.; Hai, Z.; Zhuiykov, S. Electrochemical non-enzymatic glucose sensor based on hierarchical 3D Co3O4/Ni heterostructure electrode for pushing sensitivity boundary to a new limit. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 267, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omri, K.; Bettaibi, A.; Khirouni, K.; El Mir, L. The optoelectronic properties and role of Cu concentration on the structural and electrical properties of Cu doped ZnO nanoparticles. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2018, 537, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, D.; Singh, F.; Das, R. X-ray diffraction analysis by Williamson-Hall, Halder-Wagner and size-strain plot methods of CdSe nanoparticles- a comparative study. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 239, 122021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halder, N.C.; Wagner, C.N.J. Separation of particle size and lattice strain in integral breadth measurements. Acta Crystallogr. 1966, 20, 312–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millot, N.; Begin-Colin, S.; Perriat, P.; Le Caër, G. Structure, Cation Distribution, and Properties of Nanocrystalline Titanomagnetites Obtained by Mechanosynthesis: Comparison with Soft Chemistry. J. Solid State Chem. 1998, 139, 66–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millot, N.; Aymes, D.; Bernard, F.; Niepce, J.C.; Traverse, A.; Bouree, F.; Cheng, B.L.; Perriat, P. Particle Size Dependency of Ternary Diagrams at the Nanometer Scale: Evidence of TiO2 Clusters in Fe-Based Spinels. J. Phys. Chem. B 2003, 107, 5740–5750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getie, S.; Belay, A.; Chandra Reddy, A.R.; Belay, Z. Synthesis and Characterizations of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles for Antibacterial Applications. J. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. 2017, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velumani, S.; Narayandass, S.K.; Mangalaraj, D. Structural characterization of hot wall deposited cadmium selenide thin films. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 1998, 13, 1016–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Chai, G.; Zhao, X.; Dai, Y.; Qi, Y. Effect of different copper sources on the morphology of cuprous oxide and its application as a non-enzymatic glucose sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 321, 128485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]















| NPs | Lattice Constants (nm) | Strain | δ (10−4) (nm−2) | Particle Size (nm) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | c | ||||
| ZnO | 0.2862 | 0.4957 | 0.1 | 3.95 | 50.3 |
| Cu0.01Zn0.99O | 0.2861 | 0.4956 | 0.09 | 3.92 | 50.5 |
| Cu0.02Zn0.98O | 0.2860 | 0.4955 | 0.08 | 3.84 | 51 |
| Cu0.03Zn0.97O | 0.2859 | 0.4953 | 0.08 | 3.81 | 51.2 |
| Cu0.04Zn0.96O | 0.2856 | 0.4947 | 0.08 | 3.11 | 56.7 |
| Electrodes | Rs (10−3) (kΩ·cm2) | CPE1 (µF) | n1 | Rct (10−3) (kΩ·cm2) | CPE2 (µF) | n2 | Rad (10−3) (kΩ·cm2) | χ2 (10−4) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZnO | 66.4 | 7.2 ± 0.1 | 0.98 | 706.9 ± 0.2 | 2.6 ± 0.1 | 0.98 | 2520.3 ± 0.2 | 5.56 |
| Cu0.01Zn0.99O | 64.8 | 8.6 ± 0.2 | 0.99 | 636.2 ± 0.2 | 6.4 ± 0.1 | 0.99 | 2028.6 ± 0.1 | 7.26 |
| Cu0.02Zn0.98O | 47.9 | 19.1 ± 0.1 | 0.98 | 569.3 ± 0.1 | 9.9 ± 0.1 | 0.97 | 1327.8 ± 0.1 | 5.12 |
| Cu0.03Zn0.97O | 25.2 | 34.5 ± 0.1 | 0.97 | 542.6 ± 0.1 | 13.9 ± 0.1 | 0.97 | 990.3 ± 0.2 | 2.89 |
| Cu0.04Zn0.96O | 17.5 | 35.6 ± 0.2 | 0.99 | 302.9 ± 0.1 | 15.7 ± 0.2 | 0.99 | 810.5 ± 0.1 | 3.74 |
| Glucose Concentration (M) | Rs (10−3) (kΩ·cm2) | CPE1 (µF) | n1 | Rct (10−3) (kΩ·cm2) | CPE2 (µF) | n2 | Rad (10−3) (kΩ·cm2) | χ2 (10−4) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 17.5 | 35.6 ± 0.2 | 0.99 | 302.9 ± 0.1 | 15.7 ± 0.2 | 0.99 | 810.5 ± 0.1 | 3.74 |
| 10−9 | 17.4 | 36.6 ± 0.5 | 0.98 | 243.2 ± 0.1 | 16.1 ± 0.2 | 0.99 | 607.2 ± 0.1 | 5.62 |
| 10−8 | 17.2 | 36.4 ± 0.6 | 0.99 | 192.2 ± 0.1 | 15.8 ± 0.1 | 0.99 | 508.4 ± 0.2 | 2.35 |
| 10−7 | 17.5 | 36.2 ± 0.2 | 0.97 | 151.2 ± 0.2 | 15.6 ± 0.3 | 0.98 | 450.7 ± 0.2 | 6.24 |
| 10−6 | 17.0 | 36.1 ± 0.1 | 0.98 | 131.8 ± 0.1 | 15.2 ± 0.1 | 0.99 | 390.3 ± 0.1 | 6.45 |
| 10−5 | 16.8 | 35.9 ± 0.3 | 0.97 | 102.1 ± 0.2 | 16.2 ± 0.2 | 0.98 | 342.5 ± 0.1 | 3.59 |
| 10−4 | 16.7 | 36.3 ± 0.5 | 0.98 | 94.2 ± 0.2 | 16.2 ± 0.1 | 0.99 | 326.6 ± 0.1 | 6.12 |
| Electrode Material | Linear Range (μM) | Detection Limit (μM) | Analytical Technique | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ni(II)-CP/C60 | 10 to 3 × 103 | 4.3 | Amp | [66] |
| Mucilage-AgNPs/GC | 10 to 2.2 × 103 | 10 | SWV | [67] |
| Net-Co3(PO4)2/NG | 0.05 to 2 × 103 | 1 | Amp | [68] |
| ZnO/CeO2 whisker | 0.5 to 300 | 0.22 | DPV | [69] |
| Au@Cu2O | 50 to 2 × 103 | 18 | CV | [70] |
| HLTH/NF | 15 to 8 × 103 | 1.49 | Amp | [71] |
| Au-TiO2 NTs | 50 to 3 × 103 | 50 | CV | [72] |
| CuO nanodisks | 2 to 2.5 × 103 | 0.2 | Amp | [73] |
| Cu0.04Zn0.96O | 10−3 to 100 | 7 × 10−4 | DPV | This work |
| Sample | Added Concentration (μM) | Found (μM) | Recoveries (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Human serum | 0.05 | 0.04 | 80.0 |
| 5 | 4.98 | 99.6 | |
| 500 | 497 | 99.4 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mahmoud, A.; Echabaane, M.; Omri, K.; Boudon, J.; Saviot, L.; Millot, N.; Chaabane, R.B. Cu-Doped ZnO Nanoparticles for Non-Enzymatic Glucose Sensing. Molecules 2021, 26, 929. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26040929
Mahmoud A, Echabaane M, Omri K, Boudon J, Saviot L, Millot N, Chaabane RB. Cu-Doped ZnO Nanoparticles for Non-Enzymatic Glucose Sensing. Molecules. 2021; 26(4):929. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26040929
Chicago/Turabian StyleMahmoud, Amira, Mosaab Echabaane, Karim Omri, Julien Boudon, Lucien Saviot, Nadine Millot, and Rafik Ben Chaabane. 2021. "Cu-Doped ZnO Nanoparticles for Non-Enzymatic Glucose Sensing" Molecules 26, no. 4: 929. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26040929
APA StyleMahmoud, A., Echabaane, M., Omri, K., Boudon, J., Saviot, L., Millot, N., & Chaabane, R. B. (2021). Cu-Doped ZnO Nanoparticles for Non-Enzymatic Glucose Sensing. Molecules, 26(4), 929. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26040929