Sweet-Tasting Ionic Conjugates of Local Anesthetics and Vasoconstrictors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
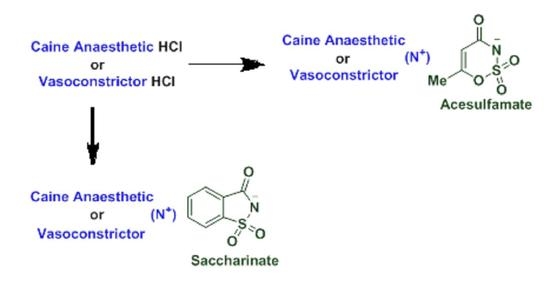
2.1. Synthesis of Novel Acesulfame and Saccharin Salts of Local Anesthetics
2.2. pH Study of the Aqueous Solutions of Novel Salts
2.3. Thermal Pain Testing
2.4. Statistical Analyses
2.5. Palatability Assessment
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Animal Studies
3.2. Synthesis of Acesulfamates and Saccharinates for the Caines 3a–d, and 4a–d
3.3. Synthesis of Oxybuprocaine Acesulfame 3e and Saccharinate 4e
3.4. Synthesis of Epinephrine Acesulfamate 6a and Epinephrine Saccharinate 6b
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Kjaergaard, M.; Moiniche, S.; Olsen, K. Wound infiltration with local anesthetics for post-operative pain relief in lumbar spine surgery: A systematic review. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 2012, 56, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.K.; Sharon, V.R. A review of local anesthetics: Minimizing risk and side effects in cutaneous surgery. Derm. Surg. 2016, 43, 173–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoni-Rugiu, P.; Sykes, P.J. A History of Plastic Surgery; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 157–166. [Google Scholar]
- Stoelting, R.K.; Miller, R.D. Basics of Anesthesia; Churchill Livingstone: London, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Goudra, B.; Arora, S. Out of Operating Room Anesthesia; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Peden, C.J.; Cook, S.C. Sedation for dental and other procedures. Anaesth. Intens. Care 2014, 15, 362–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strazar, A.R.; Leynes, P.G.; Lalonde, D.H. Minimizing the pain of local anesthesia injection. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2013, 132, 675–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roderick, F.A. Anesthesia for the cosmetic patient: An American perspective. In International Textbook of Aesthetic Surgery; Scudeli, N., Toth, B.A., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 75–82. [Google Scholar]
- Burkle, C.; Pasternak, J.; Armstrong, M.; Keegan, M. Patient perspectives on informed consent for anaesthesia and surgery: American attitudes. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 2013, 57, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Appukuttan, D.; Subramanian, S.; Tadepalli, A.; Damodaran, L.K. Dental anxiety among adults: An epidemiological study in South India. N. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2015, 7, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ando, T.; Shimoo, Y.; Nakasato, M.; Yoshida, H. Development and clinical evaluation of new topical anesthetic formulations for dental care. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2016, 39, 423–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wei, Y.; Nedley, M.P.; Bhaduri, S.B.; Bredzinski, X.; Boddu, S.S. Masking the bitter taste of injectable lidocaine HCl formulation for dental procedures. Aaps Pharmscitech. 2015, 16, 455–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hotta, M.; Endo, S.; Tomita, H. Taste disturbance in two patients after dental anesthesia by inferior alveolar nerve block. Acta Otolaryngol. 2002, 546, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, S.C.; Lalonde, D.H. How acidic is the lidocaine we are injecting, and how much bicarbonate should we add? Can. J. Plast. Surg. 2012, 20, 71–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Breu, A.; Rosenmeier, K.; Kujat, R.; Angele, P.; Zink, W. The cytotoxicity of bupivacaine, ropivacaine, and mepivacaine on human chondrocytes and cartilage. Anesth Analg. 2013, 117, 514–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyttä, J.; Heinonen, E.; Rosenberg, P.; Wahlström, T.; Gripenberg, J.; Huopaniemi, T. Effects of repeated bupivacaine administration on sciatic nerve and surrounding muscle tissue in rats. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 1986, 30, 625–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romañuk, C.; Linck, Y.G.; Chattah, A.; Monti, G.; Cuffini, S.; Garland, M.; Baggio, R.; Manzo, R.; Olivera, M. Crystallographic, thermal and spectroscopic characterization of a ciprofloxacin saccharinate polymorph. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 391, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartholomaus, J.; Kugelmann, H.; Ziegler, I. Sustained-Release form of Administration Containing Tramadol Saccharinate; Patent and Trademark Office: Alexandria, VA, USA, 2001.
- Nockemann, P.; Thijs, B.; Driesen, K.; Janssen, C.R.; Van Hecke, K.; Van Meervelt, L.; Kossmann, S.; Kirchner, B.; Binnemans, K. Choline saccharinate and choline acesulfamate: Ionic liquids with low toxicities. J. Phys. Chem. B. 2007, 111, 5254–5263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rogers, R.; Daly, D.T.; Swatloski, R.P.; Hough, W.L.; Davis, J.H.; Smiglak, M.; Pernak, J.; Spear, S.K. Multi-Functional Ionic Liquid Compositions for Overcoming Polymorphism and Imparting Improved Properties for Active Pharmaceutical, Biological, Nutritional, and Energetic Ingredients; Patent and Trademark Office: Alexandria, VA, USA, 2012.
- Lebedyeva, I.O.; Oliferenko, A.A.; Oliferenko, P.V.; Hromas, R.A.; Neubert, J.K.; Caudle, R.M.; Wickersham, J.; Castleman, W.L.; Altschuler, G.I.; Ostrov, D.A.; et al. Ionic conjugates of lidocaine and sweeteners as better tasting local anesthetics for dentistry. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 8492–8498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulsen, S.; Koch, G.; Espelid, I.; Haubek, D. Pediatric Dentistry: A Clinical Approach, 3th ed.; Haukali, G., Lundeberg, S., Ostergaard, B.H., Haubek, D., Eds.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2016; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Tengler, M.; McMahen, R. Compositions and Methods of Making Rapidly Dissolving Ionically Masked Formulations; Patent and Trademark Office: Alexandria, VA, USA, 2014.
- Keles, S.; Kocaturk, O. The Effect of Oral Dexmedetomidine premedication on preoperative cooperation and emergence delirium in children undergoing dental procedures. Biomed. Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 6742183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, D.N.; Fresno, N.; Pérez-Fernández, R.; Frizzo, C.P.; Goya, P.; Marco, C.; Martins, M.A.P.; Elguero, J. Brønsted acid–base pairs of drugs as dual ionic liquids: NMR ionicity studies. Tetrahedron 2015, 71, 676–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuivalainen, A.M.; Ebeling, F.; Rosenberg, P. Warmed and buffered lidocaine for pain relief during bone marrow aspiration and biopsy: A randomized and controlled trial. Scand. J. Pain 2014, 5, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hargreaves, K.; Dubner, R.; Brown, F.; Flores, C.; Joris, J. A new and sensitive method for measuring thermal nociception in cutaneous hyperalgesia. Pain 1988, 32, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, E.M.; Mills, R.; Nolan, T.A.; Jenkins, A.C.; Mustafa, G.; Lloyd, C.; Caudle, R.M.; Neubert, J.K. Use of the operant orofacial pain assessment device (OPAD) to measure changes in nociceptive behavior. J. Vis. Exp. 2013, 10, e50336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, L.J.; Shih, A.; Miletic, G.; Miletic, V. Continual systemic infusion of lidocaine provides analgesia in an animal model of neuropathic pain. Pain 2002, 97, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Compound Name and Structure | Compound Name and Structure |
|---|---|
 Mepivacaine acesulfamate 3a |  Mepivacaine saccharinate 4a |
 Bupivacaine acesulfamate 3b |  Bupivacaine saccharinate 4b |
 Prilocaine acesulfamate 3c |  Prilocaine saccharinate 4c |
 Articaine acesulfamate 3d |  Articaine saccharinate 4d |
 Oxybuprocaine acesulfamate 3e |  Oxybuprocaine saccharinate 4e |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Neubert, J.K.; Oliferenko, A.A.; Oliferenko, P.V.; Emets, S.V.; Ostrov, D.A.; Altschuler, G.I.; Calkins, J.; Wickersham, J.; Hromas, R.; Lebedyeva, I.O. Sweet-Tasting Ionic Conjugates of Local Anesthetics and Vasoconstrictors. Molecules 2021, 26, 983. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26040983
Neubert JK, Oliferenko AA, Oliferenko PV, Emets SV, Ostrov DA, Altschuler GI, Calkins J, Wickersham J, Hromas R, Lebedyeva IO. Sweet-Tasting Ionic Conjugates of Local Anesthetics and Vasoconstrictors. Molecules. 2021; 26(4):983. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26040983
Chicago/Turabian StyleNeubert, John K., Alexander A. Oliferenko, Polina V. Oliferenko, Sergey V. Emets, David A. Ostrov, Gary I. Altschuler, Joe Calkins, Jay Wickersham, Robert Hromas, and Iryna O. Lebedyeva. 2021. "Sweet-Tasting Ionic Conjugates of Local Anesthetics and Vasoconstrictors" Molecules 26, no. 4: 983. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26040983
APA StyleNeubert, J. K., Oliferenko, A. A., Oliferenko, P. V., Emets, S. V., Ostrov, D. A., Altschuler, G. I., Calkins, J., Wickersham, J., Hromas, R., & Lebedyeva, I. O. (2021). Sweet-Tasting Ionic Conjugates of Local Anesthetics and Vasoconstrictors. Molecules, 26(4), 983. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26040983