Rosmanol and Carnosol Synergistically Alleviate Rheumatoid Arthritis through Inhibiting TLR4/NF-κB/MAPK Pathway
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials
2.2. Preparation of Rosmanol and Carnosol
2.3. Chemicals and Antibodies
2.4. Animals
2.5. Establishment of CIA DBA/1 Mouse Model
2.6. Evaluation of Arthritis Severity
2.7. Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) Staining
2.8. ELISA
2.9. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
2.10. Western Blot
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
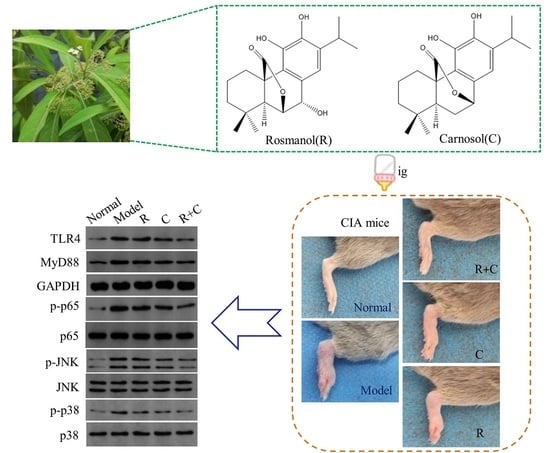
3.1. Rosmanol and Carnosol Synergistically Alleviated RA Pathologies in CIA Mice
3.2. Rosmanol and Carnosol Synergistically Alleviated Synovitis in CIA Mice
3.3. Rosmanol and Carnosol Synergistically Decreased Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines in Serum
3.4. Rosmanol and Carnosol Synergistically Inhibited the TLR4/NF-κB Pathway
3.5. Rosmanol and Carnosol Synergistically Inhibited MAPK Activation
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
Abbreviations
| BIIC | bovine type II collagen |
| CIA | collagen-induced arthritis |
| H&E | hematoxylin and eosin |
| IL-6 | interleukin 6 |
| JNK | c-Jun N-terminal kinase |
| MAPK | mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| MCP-1 | monocyte chemotactic protein 1 |
| MyD88 | myeloid differentiation factor 88 |
| NF-κB | nuclear factor κB |
| RA | rheumatoid arthritis |
| TLR4 | Toll-like receptor 4 |
| TNF-α | tumor necrosis factor α |
References
- Scott, D.L.; Wolfe, F.; Huizing, T.W. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 2010, 376, 1094–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kour, G.; Haq, S.A.; Bajaj, B.K.; Gupta, P.N.; Ahmed, Z. Phytochemical add-on therapy to DMARDs therapy in rheumatoid arthritis: In vitro and in vivo bases, clinical evidence and future trends. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 169, 105618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Lyu, J.T.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, X.M.; Jiang, H.; Lin, Z.J. Comparative efficacy, safety and cost of oral Chinese patent medicines for rheumatoid arthritis: A Bayesian network meta-analysis. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2020, 20, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Li, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, S.; Nie, X.; Chen, Y.; Fu, Q.; Jiang, M.; Fu, C.; He, Y. Total glucosides of paeony: A review of its phytochemistry, role in autoimmune diseases, and mechanisms of action. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 258, 112913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, W.; Ma, C.; Ruan, J.; Long, H.; Wang, Y. Sinomenine inhibits the progression of rheumatoid arthritis by regulating the secretion of inflammatory cytokines and monocyte/macrophage subsets. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, J.Q.; Qiu, L.; Zou, L.H.; Wei, Q.; Miao, J.H.; Yao, X.S. Two new phenylethanoid glycosides from Callicarpa longissima. Helv. Chim. Acta 2015, 98, 482–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.W.; Cheng, Y.B.; Liaw, C.C.; Chen, C.H.; Guh, J.H.; Hwang, T.L.; Tsai, J.S.; Wang, W.B.; Shen, Y.C. Bioactive diterpenes from Callicarpa longissima. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 689–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamahara, M.; Sugimura, K.; Kumagai, A.; Fuchino, H.; Kuroi, A.; Kagawa, M.; Itoh, Y.; Kawahara, H.; Nagaoka, Y.; Iida, O.; et al. Callicarpa longissima extract, carnosol-rich, potently inhibits melanogenesis in B16F10 melanoma cells. J. Nat. Med. 2016, 70, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, J.Q. Studies on the Constituents of Callicarpa longissima. Ph.D. Thesis, Jinan University, Guangzhou, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kawamura, T.; Momozane, T.; Sanosaka, M.; Sugimura, K.; Iida, O.; Fuchino, H.; Funaki, S.; Shintani, Y.; Inoue, M.; Minami, M.; et al. Carnosol is a potent lung protective agent: Experimental study on mice. Transplant. Proc. 2015, 47, 1657–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haraguchi, H.; Saito, T.; Okamura, N.; Yagi, A. Inhibition of lipid peroxidation and superoxide generation by diterpenoids from Rosmarinus officinalis. Planta Med. 1995, 61, 333–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrade, J.M.; Faustino, C.; Garcia, C.; Ladeiras, D.; Reis, C.P.; Rijo, P. Rosmarinus officinalis L.: An update review of its phytochemistry and biological activity. Future Sci. OA 2018, 4, FSO283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abdelhalim, A.; Karim, N.; Chebib, M.; Aburjai, T.; Khan, I.; Johnston, G.A.; Hanrahan, J. Antidepressant, anxiolytic and antinociceptive activities of constituents from Rosmarinus Officinalis. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 18, 448–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khan, I.; Karim, N.; Ahmad, W.; Abdelhalim, A.; Chebib, M. GABA-A receptor modulation and anticonvulsant, anxiolytic, and antidepressant activities of constituents from Artemisia indica Linn. Evid.-Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2016, 2016, 1215393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lai, C.S.; Lee, J.H.; Ho, C.T.; Liu, C.B.; Wang, J.M.; Wang, Y.J.; Pan, M.H. Rosmanol potently inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced iNOS and COX-2 expression through downregulating MAPK, NF-kappaB, STAT3 and C/EBP signaling pathways. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 10990–10998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.H.; Huang, H.S.; Wu, P.T.; Jou, I.M.; Pan, M.H.; Chang, W.C.; Wang, D.D.; Wang, J.M. Role of macrophage CCAAT/enhancer binding protein delta in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis in collagen-induced arthritic mice. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e45378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwager, J.; Richard, N.; Fowler, A.; Seifert, N.; Raederstorff, D. Carnosol and related substances modulate chemokine and cytokine production in macrophages and chondrocytes. Molecules 2016, 21, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.Q.; Szodoray, P.; Zeher, M. Toll-like receptor pathways in autoimmune diseases. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2016, 50, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tak, P.P.; Firestein, G.S. NF-kappaB: A key role in inflammatory diseases. J. Clin. Investig. 2001, 107, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thalhamer, T.; McGrath, M.A.; Harnett, M.M. MAPKs and their relevance to arthritis and inflammation. Rheumatology 2008, 47, 409–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, Z.; Boyle, D.L.; Chang, L.; Bennett, B.; Karin, M.; Yang, L.; Manning, A.M.; Firestein, G.S. C-Jun N-terminal kinase is required for metalloproteinase expression and joint destruction in inflammatory arthritis. J. Clin. Investig. 2001, 108, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Ye, Y.; Shi, Y.; Dang, J.; Feng, X.; Chen, Y.; Liu, F.; Olsen, N.; Huang, J.; Zheng, S.G. Sonic hedgehog regulates proliferation, migration and invasion of synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis via JNK signaling. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuenda, A.; Rousseau, S. P38 MAP-kinases pathway regulation, function and role in human diseases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2007, 1773, 1358–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schett, G.; Zwerina, J.; Firestein, G. The p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2008, 67, 909–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.; Du, J.; Ou, Y.; Xu, H.; Chen, X.; Zhou, A.; He, L.; Cao, Y. Degradation pathway of carnosic acid in methanol solution through isolation and structural identification of its degradation products. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2013, 237, 617–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyoshi, M.; Liu, S. Collagen-induced arthritis models. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1868, 3–7. [Google Scholar]
- Yeremenko, N.; Härle, P.; Cantaert, T.; van Tok, M.; van Duivenvoorde, L.M.; Bosserhoff, A.; Baeten, D. The cartilage protein melanoma inhibitory activity contributes to inflammatory arthritis. Rheumatology 2014, 53, 438–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cardiff, R.D.; Miller, C.H.; Munn, R.J. Manual hematoxylin and eosin staining of mouse tissue sections. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2014, 2014, 655–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arjumand, S.; Shahzad, M.; Shabbir, A.; Yousaf, M.Z. Thymoquinone attenuates rheumatoid arthritis by downregulating TLR2, TLR4, TNF-α, IL-1, and NFκB expression levels. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 111, 958–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, A.L.; Payandeh, Z.; Mohammadkhani, N.; Mubarak, S.M.H.; Zakeri, A.; Alagheband Bahrami, A.; Brockmueller, A.; Shakibaei, M. Recent advances in understanding the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis: New treatment strategies. Cells 2021, 10, 3017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buhrmann, C.; Brockmueller, A.; Mueller, A.L.; Shayan, P.; Shakibaei, M. Curcumin attenuates environment-derived osteoarthritis by Sox9/NF-kB signaling axis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shakibaei, M.; Csaki, C.; Nebrich, S.; Mobasheri, A. Resveratrol suppresses interleukin-1beta-induced inflammatory signaling and apoptosis in human articular chondrocytes: Potential for use as a novel nutraceutical for the treatment of osteoarthritis. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2008, 76, 1426–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akone, S.H.; Ntie-Kang, F.; Stuhldreier, F.; Ewonkem, M.B.; Noah, A.M.; Mouelle, S.E.M.; Müller, R. Natural products impacting DNA methyltransferases and histone deacetylases. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Xie, L. TranSynergy: Mechanism-driven interpretable deep neural network for the synergistic prediction and pathway deconvolution of drug combinations. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2021, 17, e1008653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, G.; Wang, X.; Sun, H.; Qin, Y.; Fu, M. Carnosic acid (CA) attenuates collagen-induced arthritis in db/db mice via inflammation suppression by regulating ROS-dependent p38 pathway. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2017, 108, 418–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youn, J.; Lee, K.H.; Won, J.; Huh, S.J.; Yun, H.S.; Cho, W.G.; Paik, D.J. Beneficial effects of rosmarinic acid on suppression of collagen induced arthritis. J. Rheumatol. 2003, 30, 1203–1207. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zheng, F.; Gao, G.; Yan, S.; Zhang, L.; Wang, L.; Cai, X.; Wang, X.; Xu, D.; Wang, J. MiR-548a-3p regulates inflammatory response via TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway in rheumatoid arthritis. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 1133–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, L.; Pan, Z.; Ning, D.; Fu, Y. Rosmanol and Carnosol Synergistically Alleviate Rheumatoid Arthritis through Inhibiting TLR4/NF-κB/MAPK Pathway. Molecules 2022, 27, 78. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27010078
Li L, Pan Z, Ning D, Fu Y. Rosmanol and Carnosol Synergistically Alleviate Rheumatoid Arthritis through Inhibiting TLR4/NF-κB/MAPK Pathway. Molecules. 2022; 27(1):78. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27010078
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Lianchun, Zhenghong Pan, Desheng Ning, and Yuxia Fu. 2022. "Rosmanol and Carnosol Synergistically Alleviate Rheumatoid Arthritis through Inhibiting TLR4/NF-κB/MAPK Pathway" Molecules 27, no. 1: 78. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27010078
APA StyleLi, L., Pan, Z., Ning, D., & Fu, Y. (2022). Rosmanol and Carnosol Synergistically Alleviate Rheumatoid Arthritis through Inhibiting TLR4/NF-κB/MAPK Pathway. Molecules, 27(1), 78. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27010078