Enhanced Photodynamic Efficacy Using 1,8-Naphthalimides: Potential Application in Antibacterial Photodynamic Therapy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Synthesis of 1,8-Naphthalimide Derivatives
2.2. Photophysical Characteristics
2.3. Molecular Logic Behavior of Probes NI1 and NI2 by H+ and HO− as Inputs
2.4. Dyeing of Modified Cotton Fabric with NI1 and NI2
2.5. Colorimetric Characteristics of Cotton Fabrics Treated with Dendrimers P1 and P2
2.6. Photo-Oxidation Studies of NI1 and NI2 and on Dyed Cotton Fabric
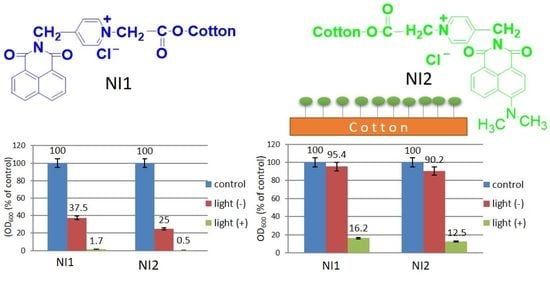
2.7. Effect of Light Irradiation on Bacterial Growth
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Synthesis of 2-(Pyridin-4-ylmethyl)-1H-benzo[de]isoquinoline-1,3(2H)-dione (NI1)
3.2. Synthesis of 6-Nitro-2-(pyridin-4-ylmethyl)-1H-benzo[de]isoquinoline-1,3(2H)-dione (NI0)
3.3. Synthesis of 6-(Dimethylamino)-2-(pyridin-4-ylmethyl)-1H-benzo[de]isoquinoline-1,3(2H)-dione (NI2)
3.4. Dyeing the Cotton Fabric with NI1 and NI2
3.5. Materials and Methods
3.6. In Vitro Antimicrobial Assay
3.7. Iodometric Absorption Measurements
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Carl, N.; Otto, C. Antibiotic resistance-problems, progress, and prospects. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 1761–1763. [Google Scholar]
- Yagui, M. Antimicrobial resistance: A new approach and opportunity. Rev. Peru Med. Exp. Salud Publica 2018, 35, 7–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Liu, C.; Su, M.; Rong, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, K.; Li, X.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, X.; et al. Recent advances in 4-hydroxy-1,8-naphthalimide-based small-molecule fluorescent probes. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2021, 448, 214153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, H.H.; Addla, D.; Lv, J.S.; Zhou, C.H. Heterocyclic naphthalimides as new skeleton structure of compounds with increasingly expanding relational medicinal applications. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2016, 16, 3303–3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carretero, G.P.B.; Saraiva, G.K.V.; Rodrigues, M.A.; Kiyota, S.; Bemquerer, M.P.; Chaimovich, H.; Cuccovia, I.M. Naphthalimide-Containing BP100 Leads to Higher Model Membranes Interactions and Antimicrobial Activity. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Xu, Y.; Qian, X. Naphthalimides and analogues as antitumor agents: A review on molecular design, bioactivity and mechanism of action. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2018, 29, 1741–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panchenko, P.A.; Fedorova, O.A.; Fedorov, Y.V. Fluorescent and colorimetric chemosensors for cations based on 1,8-naphthalimide derivatives: Design principles and optical signalling mechanisms. Russ. Chem. Rev. 2014, 83, 155–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabchev, I.; Staneva, D.; Betcheva, R. Fluorescent dendrimers as sensors for biologically important metal cation. Curr. Med. Chem. 2012, 29, 4976–4983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geraghty, G.; Wynne, V.; Elmes, R.B.P. 1,8-Naphthalimide based fluorescent sensors for enzymes. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2021, 437, 213713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodangeh, M.; Grabchev, I.; Staneva, D.; Gharanjig, K. 1,8-Naphthalimide Derivatives as Dyes for Textile and Polymeric Materials: A Review. Fibers Polym. 2021, 22, 2368–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudeika, D. A review of investigation on 4-substituted 1,8-naphthalimide derivatives. Synth. Met. 2020, 262, 116328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesquita, M.Q.; Dias, C.J.; Neves, M.G.P.M.S.; Almeida, A.; Faustino, M.A.F. Revisiting Current Photoactive Materials for Antimicrobial Photodynamic Therapy. Molecules 2018, 23, 2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warrier, A.; Mazumder, N.; Prabhu, S.; Satyamoorthy, K.; Sreepathy, K.; Murali, T.S. Photodynamic therapy to control microbial biofilms. Photodiagn. Photodyn. Ther. 2021, 33, 102090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Qin, R.; Zaat, S.A.J.; Breukink, E.; Heger, M. Antibacterial photodynamic therapy: Overview of a promising approach to fight antibiotic-resistant bacterial infections. J. Clin. Transl. Res. 2015, 1, 140–167. [Google Scholar]
- Ghorbani, J.; Rahban, D.; Aghamiri, S.; Teymouri, A.; Bahador, A. Photosensitizers in antibacterial photodynamic therapy: An overview. Laser Ther. 2018, 27, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staneva, D.; Vasileva-Tonkova, E.; Grozdanov, P.; Vilhelmova-Ilieva, N.; Nikolova, I.; Grabchev, I. Synthesis and photophysical characterisation of 3-bromo-4-dimethylamino-1,8-naphthalimides and their evaluation as agents for antibacterial photodynamic therapy. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2020, 401, 112730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staneva, D.; Atanasova, D.; Nenova, A.; Vasileva-Tonkova, E.; Grabchev, I. Cotton fabric modified with a PAMAM dendrimer with encapsulated copper nanoparticles: Antimicrobial activity. Materials 2021, 14, 7832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manov, H.; Staneva, D.; Vasileva-Tonkova, E.; Grozdanov, P.; Nikolova, I.; Stoyanov, S.; Grabchev, I. Photosensitive dendrimers as a good alternative to antimicrobial photodynamic therapy of Gram-negative bacteria. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2021, 419, 113480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manov, H.; Staneva, D.; Vasileva-Tonkova, E.; Alexandrova, R.; Stoyanova, R.; Kukeva, R.; Stoyanov, S.; Grabchev, I. A new Cu(II) complex of modified PAMAM dendrimer with 1,8-naphthalimide. Antibacterial and anticancer activity investigations. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2022, 12, 5534–5547. [Google Scholar]
- Barooah, N.; Tamuly, C.; Baruah, J.B. Synthesis, characterisation of few N-substituted 1,8-naphthalimide derivatives and their copper(II) complexes. J. Chem. Sci. 2005, 117, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacGregor, K.A.; McCluskey, A. Ionic liquids accelerate access to N-substituted-1,8-naphthalimides. Tetrahedron Lett. 2011, 52, 767–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duke, R.M.; Veale, E.B.; Pfeffer, F.M.; Kruger, P.E.; Gunnlaugsson, T. Colorimetric and fluorescent anion sensors: An overview of recent developments in the use of 1,8-naphthalimide-based chemosensors. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 3936–3953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexiou, M.S.; Tychopoulous, V.; Chorbanian, S.; Tyman, J.H.P.; Brown, R.G.; Brittain, P.I. The UV-visible absorption and fluorescence of some substituted 1,8-naphthalimides and naphthalic anhydrides. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1990, 2, 837–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabchev, I.; Mokreva, P.; Gancheva, V.; Terlemezyan, L. Synthesis and structural dependence of the functional properties of new green fluorescent poly(propyleneamine) dendrimers. J. Mol. Struct. 2013, 1038, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabchev, I. Photophysical Charactheristics of Polymerizable 1,8-Naphthalimide Dyes and their Copolymers with Styrene or Methylmethacrylate. Dyes Pigments 1998, 38, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, A.; Georgiev, N.; Bojinov, V. Low Molecular Weight Probe for Selective Sensing of PH and Cu2+ Working as Three INHIBIT Based Digital Comparator. J. Fluoresc. 2022, 32, 405–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, A.; Georgiev, N.; Bojinov, V. A fluorescent bichromophoric “off-on-off” pH probe as a molecular logic device (half-subtractor and digital comparator) operating by controlled PET and ICT processes. Dyes Pigments 2019, 162, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adlhart, C.; Verran, J.; Azevedo, N.F.; Olmez, H.; Keinänen-Toivola, M.M.; Gouveia, I.; Melo, L.F.; Crijns, F. Surface modifications for antimicrobial effects in the healthcare setting: A critical overview. J. Hosp. Infect. 2018, 99, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staneva, D.; Vasileva-Tonkova, E.; Grabchev, I. Chemical modification of cotton fabric with 1,8-naphthalimide for use as heterogeneous sensor and antibacterial textile. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2019, 382, 111924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosinger, J.; Mosinger, B. Photodynamic sensitizers assay: Rapid and sensitive iodometric measurement. Experientia 1995, 51, 106–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, L.; Yiming, X. Iodine-sensitized oxidation of ferrous ions under UV and visible light: The influencing factors and reaction mechanism. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2013, 12, 2084–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Chen, W.; Dong, T.; Lv, Z.; Zheng, S.; Cao, X.; Wei, Q.; Ghiladi, R.A.; Wang, Q. Color-Variable Photodynamic Antimicrobial Wool/Acrylic Blended Fabrics. Materials 2020, 13, 4141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sperandio, F.F.; Huang, Y.-Y.; Hamblin, M.R. Antimicrobial photodynamic therapy to kill Gram-negative bacteria. Recent Pat. Antiinfect. Drug Discov. 2013, 8, 108–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Almeida, A.; Faustino, M.A.F.; Tomé, J.P.C. Photodynamic inactivation of bacteria: Finding the effective targets. Future Med. Chem. 2015, 7, 1221–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| λA nm | logε | λF * nm | υA − υF cm−1 | ΦF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acetonitrile | 343 | 3.94 | 380 | 2838 | 0.030 |
| N,N-dimethylformamide | 350 | 3.88 | 385 | 2594 | 0.004 |
| Ethanol | 334 | 3.87 | 385 | 3960 | 0.060 |
| Dioxane | 332 | 3.88 | 379 | 3735 | 0.020 |
| Water | 345 | 3.95 | 398 | 3860 | 0.070 |
| Dichloromethane | 334 | 3.85 | 381 | 3693 | 0.050 |
| Tetrahydrofuran | 333 | 3.71 | 378 | 3572 | 0.020 |
| λA nm | logε | λF * nm | υA − υF cm−1 | ΦF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acetonitrile | 422 | 3.68 | 524 | 4612 | 0.011 |
| N,N-dimethylformamide | 425 | 3.64 | 530 | 4661 | 0.090 |
| Dimethyl sulfoxide | 435 | 3.62 | 540 | 4470 | 0.153 |
| Ethanol | 425 | 3.67 | 535 | 4838 | 0.030 |
| Dioxane | 412 | 3.63 | 509 | 4625 | 0.325 |
| Water | 450 | 3.62 | 545 | 3874 | 0.022 |
| Dichloromethane | 420 | 3.65 | 500 | 3810 | 0.170 |
| Tetrahydrofuran | 418 | 3.68 | 512 | 4392 | 0.191 |
| Inputs | Outputs | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Input 1 | Input 2 | Output 1 | Output 2 |
| H+ | HO− | F 535 nm (NI2) | F 390 nm (probe NI1) |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Logic gate | INHIBIT | XNOR | |
| L* | a* | b* | X | Y | Z | x | y | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cotton | 92.97 | −0.09 | 2.11 | 78.55 | 82.90 | 86.01 | 0.3174 | 0.3350 |
| Cotton—NI1 | 92.57 | −0.39 | 4.15 | 77.55 | 82.00 | 82.27 | 0.3207 | 0.3391 |
| Cotton—NI2 | 84.30 | 1.28 | 31.58 | 61.84 | 64.65 | 37.89 | 0.3762 | 0.3933 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Staneva, D.; Said, A.I.; Vasileva-Tonkova, E.; Grabchev, I. Enhanced Photodynamic Efficacy Using 1,8-Naphthalimides: Potential Application in Antibacterial Photodynamic Therapy. Molecules 2022, 27, 5743. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27185743
Staneva D, Said AI, Vasileva-Tonkova E, Grabchev I. Enhanced Photodynamic Efficacy Using 1,8-Naphthalimides: Potential Application in Antibacterial Photodynamic Therapy. Molecules. 2022; 27(18):5743. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27185743
Chicago/Turabian StyleStaneva, Desislava, Awad I. Said, Evgenia Vasileva-Tonkova, and Ivo Grabchev. 2022. "Enhanced Photodynamic Efficacy Using 1,8-Naphthalimides: Potential Application in Antibacterial Photodynamic Therapy" Molecules 27, no. 18: 5743. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27185743
APA StyleStaneva, D., Said, A. I., Vasileva-Tonkova, E., & Grabchev, I. (2022). Enhanced Photodynamic Efficacy Using 1,8-Naphthalimides: Potential Application in Antibacterial Photodynamic Therapy. Molecules, 27(18), 5743. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27185743