Thermoresponsive Dual-Structured Gel Emulsions Stabilized by Glycyrrhizic Acid Nanofibrils in Combination with Monoglyceride Crystals
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
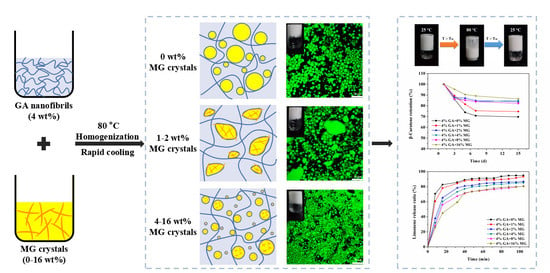
2.1. Formation of GA−MG Dual-Structured Gel Emulsions
2.2. Microstructure of GA−MG Dual-Structured Gel Emulsions
2.3. Mechanical Properties of GA−MG Dual-Structured Gel Emulsions
2.4. Thermoresponsive GA−MG Dual-Structured Gel Emulsions
2.5. Cargo Encapsulation and Stability in Dual-Structured Gel Emulsions
2.6. Controlled Limonene Release in Dual-Structured Gel Emulsions
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Preparation of Monoglyceride (MG) Oleogels
3.3. Preparation of GA−MG Dual-Structured Gel Emulsions
3.4. Droplet Size Measurements
3.5. Polarized Light Microscopy (PLM)
3.6. Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy (CLSM)
3.7. Rheological Measurements
3.8. Large Deformation Mechanical Properties
3.9. XRD Analysis
3.10. Cargo Stability of GA−MG Dual-Structured Gel Emulsions
3.11. Limonene Release of GA−MG Dual-Structured Gel Emulsions
3.12. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Torres, O.; Murray, B.; Sarkar, A. Emulsion microgel particles: Novel encapsulation strategy for lipophilic molecules. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 55, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, E. Emulsion gels: The structuring of soft solids with protein-stabilized oil droplets. Food Hydrocoll. 2012, 28, 224–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.R.; Dewettinck, K. Edible oil structuring: An overview and recent updates. Food Funct. 2016, 7, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Patel, A.R.; Rajarethinem, P.S.; Cludts, N.; Lewille, B.; De Vos, W.H.; Lesaffer, A.; Dewettinck, K. Biopolymer-based structuring of liquid oil into soft solids and oleogels using water-continuous emulsions as templates. Langmuir 2015, 31, 2065–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Calligaris, S.; Mirolo, G.; Da Pieve, S.; Arrighetti, G.; Nicoli, M.C. Effect of oil type on formation, structure and thermal properties of γ-oryzanol and β-sitosterol-based organogels. Food Biophys. 2014, 9, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bollom, M.A.; Clark, S.; Acevedo, N.C. Development and characterization of a novel soy lecithin-stearic acid and whey protein concentrate bigel system for potential edible applications. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 101, 105570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, A.J.; Silva, P.; Maciel, F.; Pastrana, L.M.; Cunha, R.L.; Cerqueira, M.A.; Vicente, A.A. Hybrid gels: Influence of oleogel/hydrogel ratio on rheological and textural properties. Food Res. Int. 2019, 116, 1298–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shakeel, A.; Farooq, U.; Gabriele, D.; Marangoni, A.G.; Lupi, F.R. Bigels and multi-component organogels: An overview from rheological perspective. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 111, 106190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Mao, L.; Hou, Z.; Miao, S.; Gao, Y. Development of emulsion gels for the delivery of functional food ingredients: From structure to functionality. Food Eng. Rev. 2019, 11, 245–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagiri, S.S.; Singh, V.K.; Kulanthaivel, S.; Banerjee, I.; Basak, P.; Battachrya, M.; Pal, K. Stearate organogel–gelatin hydrogel based bigels: Physicochemical, thermal, mechanical characterizations and in vitro drug delivery applications. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2015, 43, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakeel, A.; Lupi, F.R.; Gabriele, D.; Baldino, N.; De Cindio, B. Bigels: A unique class of materials for drug delivery applications. Soft Matter 2018, 16, 77–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.K.; Banerjee, I.; Agarwal, T.; Pramanik, K.; Bhattacharya, M.K.; Pal, K. Guar gum and sesame oil based novel bigels for controlled drug delivery. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2014, 123, 582–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, H.; Mao, L.; Cui, M.; Liu, J.; Gao, Y. Development of food-grade bigels based on κ-carrageenan hydrogel and monoglyceride oleogels as carriers for β-carotene: Roles of oleogel fraction. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 105, 105855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, K.; Zulfakar, M.H. Novel fish oil-based bigel system for controlled drug delivery and its influence on immunomodulatory activity of imiquimod against skin cancer. Pharm. Res. 2017, 34, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Z.; Sun, Y.; Ma, L.; Guo, J.; Wang, J.; Yin, S.; Yang, X. Thermoresponsive structured emulsions based on the fibrillar self-assembly of natural saponin glycyrrhizic acid. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Z.; Sun, Y.; Ma, L.; Yang, X.; Guo, J.; Yin, S. Responsive emulsion gels with tunable properties formed by self-assembled nanofibrils of natural saponin glycyrrhizic acid for oil structuring. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 2394–2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Xu, M.; Xie, J.; Su, E.; Wan, Z.; Sagis, L.M.; Yang, X. Large amplitude oscillatory shear (LAOS) for nonlinear rheological behavior of heterogeneous emulsion gels made from natural supramolecular gelators. Food Res. Int. 2021, 140, 110076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asl, M.N.; Hosseinzadeh, H. Review of pharmacological effects of Glycyrrhiza sp. and its bioactive compounds. Phytother. Res. 2008, 22, 709–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, A.; Adamcik, J.; Bolisetty, S.; Handschin, S.; Mezzenga, R. Fibrillar networks of glycyrrhizic acid for hybrid nanomaterials with catalytic features. Angew. Chem. 2015, 127, 5498–5502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Li, Q.; Du, Z.; Su, E.; Liu, X.; Wan, Z.; Yang, X. A natural supramolecular saponin hydrogelator for creation of ultrastable and thermostimulable food-grade foams. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 6, 1900417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Wan, Z.; Yang, X. Multiple water-in-oil-in-water emulsion gels based on self-assembled saponin fibrillar network for photosensitive cargo protection. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 9735–9743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Ma, L.; Li, Q.; Wu, J.; Wan, Z.; Ngai, T.; Yang, X. Robust and highly adaptable high internal phase gel emulsions stabilized solely by a natural saponin hydrogelator glycyrrhizic acid. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 280–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valoppi, F.; Calligaris, S.; Barba, L.; Šegatin, N.; Poklar Ulrih, N.; Nicoli, M.C. Influence of oil type on formation, structure, thermal, and physical properties of monoglyceride-based organogel. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2017, 119, 1500549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacomozzi, A.; Palla, C.; Carrín, M.E.; Martini, S. Tailoring physical properties of monoglycerides oleogels using high-intensity ultrasound. Food Res. Int. 2020, 134, 109231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, L.; Calligaris, S.; Barba, L.; Miao, S. Monoglyceride self-assembled structure in O/W emulsion: Formation, characterization and its effect on emulsion properties. Food Res. Int. 2014, 58, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Pieve, S.; Calligaris, S.; Co, E.; Nicoli, M.C.; Marangoni, A.G. Shear nanostructuring of monoglyceride organogels. Food Biophys. 2010, 5, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, N.E.; Marangoni, A.G.; Wright, A.J.; Rogers, M.A.; Rush, J.W. Potential food applications of edible oil organogels. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2009, 20, 470–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wan, Z.; Yang, X. Glycyrrhizic acid: Self-assembly and applications in multiphase food systems. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2022, 43, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khurana, R.; Coleman, C.; Ionescu-Zanetti, C.; Carter, S.A.; Krishna, V.; Grover, R.K.; Roy, R.; Singh, S. Mechanism of thioflavin T binding to amyloid fibrils. J. Struct. Biol. 2005, 151, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thivilliers, F.; Laurichesse, E.; Saadaoui, H.; Leal-Calderon, F.; Schmitt, V. Thermally induced gelling of oil-in-water emulsions comprising partially crystallized droplets: The impact of interfacial crystals. Langmuir 2008, 24, 13364–13375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal-Calderon, F.; Thivilliers, F.; Schmitt, V. Structured emulsions. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 12, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, E.; Chen, J. Heat-set whey protein emulsion gels: Role of active and inactive filler particles. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 1999, 20, 197–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Xu, M.; Yang, Y.; Guo, J.; Wan, Z.; Yang, X. Tailoring structure and properties of long-lived emulsion foams stabilized by a natural saponin glycyrrhizic acid: Role of oil phase. Food Res. Int. 2021, 150, 110733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behera, B.; Sagiri, S.S.; Singh, V.K.; Pal, K.; Anis, A. Mechanical properties and delivery of drug/probiotics from starch and non-starch based novel bigels: A comparative study. Starch-Stärke 2014, 66, 865–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Li, S.; Jiang, Q.; Tan, Y.; Liu, Y.; Meng, Z. Interfacial interaction of small molecular emulsifiers tea saponin and monoglyceride: Relationship to the formation and stabilization of emulsion gels. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 117, 106737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredrick, E.; Walstra, P.; Dewettinck, K. Factors governing partial coalescence in oil-in-water emulsions. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 153, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaiskou, S.; Blekas, G.; Paraskevopoulou, A. Aroma release from gum arabic or egg yolk/xanthan-stabilized oil-in-water emulsions. Food Res. Int. 2008, 41, 637–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Zhao, L.; Tian, S.; Wen, H.; Gou, X.; Ngai, T. Gelatin particle-stabilized high-internal phase emulsions for use in oral delivery systems: Protection effect and in vitro digestion study. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 900–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; He, M.; Yang, H.; Wang, N.; Kong, Y.; Li, Y.; Teng, F. Effect of soybean lipophilic protein–methyl cellulose complex on the stability and digestive properties of water–in–oil–in–water emulsion containing vitamin B12. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 629, 127364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.-W.; Guo, J.; Wang, J.-M.; Yin, S.-W.; Yang, X.-Q. Controlled volatile release of structured emulsions based on phytosterols crystallization. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 56, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, D.; Appelqvist, I.; Piyasiri, U.; Delahunty, C. In vitro measurement of volatile release in model lipid emulsions using proton transfer reaction mass spectrometry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 2264–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.J.; Guo, J.; Wang, J.M.; Yang, X.Q. Effect of interfacial composition and crumbliness on aroma release in soy protein/sugar beet pectin mixed emulsion gels. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2016, 96, 4449–4456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, J.; Li, Q.; Du, R.; Yu, X.; Wan, Z.; Yang, X. Thermoresponsive Dual-Structured Gel Emulsions Stabilized by Glycyrrhizic Acid Nanofibrils in Combination with Monoglyceride Crystals. Molecules 2022, 27, 6542. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27196542
Chen J, Li Q, Du R, Yu X, Wan Z, Yang X. Thermoresponsive Dual-Structured Gel Emulsions Stabilized by Glycyrrhizic Acid Nanofibrils in Combination with Monoglyceride Crystals. Molecules. 2022; 27(19):6542. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27196542
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Jialing, Qing Li, Ruijie Du, Xinke Yu, Zhili Wan, and Xiaoquan Yang. 2022. "Thermoresponsive Dual-Structured Gel Emulsions Stabilized by Glycyrrhizic Acid Nanofibrils in Combination with Monoglyceride Crystals" Molecules 27, no. 19: 6542. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27196542
APA StyleChen, J., Li, Q., Du, R., Yu, X., Wan, Z., & Yang, X. (2022). Thermoresponsive Dual-Structured Gel Emulsions Stabilized by Glycyrrhizic Acid Nanofibrils in Combination with Monoglyceride Crystals. Molecules, 27(19), 6542. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27196542