Fast Assembly of Metal Organic Framework UiO-66 in Acid-Base Tunable Deep Eutectic Solvent for the Acetalization of Benzaldehyde and Methanol
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Synthesis, Characterization, and Calculation of DESs
2.3. Acetalization Experiments
3. Results and Discussion
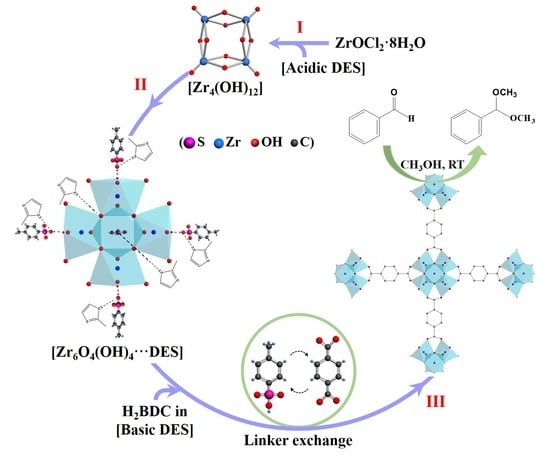
3.1. Fast Assembly of UiO-66
3.2. Characterization of UiO-66
3.3. Formation Process of UiO-66
3.4. Benzaldehyde Acetalization with Methanol
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
Abbreviations
| DES | deep eutectic solvent |
| MOF | metal–organic framework |
| UiO-66 | Zr6O4(OH)4(BDC)6 |
| IL | ionic liquid |
| HB | hydrogen bond |
| HBD | hydrogen bond donor |
| HBA | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| DMF | N,N-dimethylformamide |
| MIm | 2-methyl imidazole |
| PTSA | p-toluenesulfonic acid |
| H2BDC | terephthalic acid |
| BTC | 1,3,5-benzenetricarboxylate |
| XRD | X-ray diffraction |
References
- Rowsell, J.L.C.; Yaghi, O.M. Strategies for hydrogen storage in metal–organic frameworks. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 4670–4679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Xie, L.; Wang, X.; Liu, X.; Li, J.; Li, J. Applications of metal–organic frameworks for green energy and environment: New advances in adsorptive gas separation, storage and removal. Green Energy Environ. 2018, 3, 191–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Rodríguez, G.; Taima-Mancera, I.; Lago, A.B.; Ayala, J.H.; Pasán, J.; Pino, V. Mixed functionalization of organic ligands in UiO-66: A tool to design metal-organic frameworks for tailored microextraction. Molecules 2019, 24, 3656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Horcajada, P.; Chalati, T.; Serre, C.; Gillet, B.; Sebrie, C.; Baati, T.; Eubank, J.F.; Heurtaux, D.; Clayette, P.; Kreuz, C.; et al. Porous metal–organic-framework nanoscale carriers as a potential platform for drug delivery and imaging. Nat. Mater. 2010, 9, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, J.; Kuo, C.-H.; Chou, L.-Y.; Liu, D.-Y.; Weerapana, E.; Tsung, C.-K. Optimized metal-organic-framework nanospheres for drug delivery: Evaluation of small-molecule encapsulation. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 2812–2819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Chen, Z.; Huang, C.; Gao, L.; Dong, T.; Hu, J. Hollow CdS nanotubes with ZIF-8 as co-catalyst for enhanced photocatalytic activity. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 606, 1882–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahabi, A.H.; Norouzi, F.; Sheibani, E.; Rahimi-Nasrabadi, M. Functionalized Zr-UiO-67 metal-organic frameworks: Structural landscape and application. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2021, 445, 214050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, L.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, H.-L.; Xu, Q. Metal–organic frameworks as platforms for catalytic applications. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1703663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.-M.; He, C.-T.; Liu, Y.; Liao, P.-Q.; Zhou, D.-D.; Zhang, J.-P.; Chen, X.-M. A metal–organic framework with a pore size/shape suitable for strong binding and close packing of methane. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 4674–4678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.-S.; Lu, Y.; Chen, K.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, P.; Sun, W.-Y. Metal–organic frameworks with catalytic centers: From synthesis to catalytic application. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2019, 378, 262–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Feng, L.; Wang, K.C.; Pang, J.; Bosch, M.; Lollar, C.; Sun, Y.; Qin, J.; Yang, X.; Zhang, P.; et al. Stable metal–organic frameworks: Design, synthesis, and applications. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1704303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liang, Z.; Qu, C.; Xia, D.; Zou, R.; Xu, Q. Atomically dispersed metal sites in MOF-based materials for electrocatalytic and photocatalytic energy conversion. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 9604–9633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taima-Mancera, I.; González-Rodríguez, G.; Pasán, J.; Ayala, J.H.; Ruiz-Pérez, C.; Afonso, A.M.; Lago, A.B.; Pino, V. Influence of ligand functionalization of UiO-66-based metal-organic frameworks when used as sorbents in dispersive solid-phase analytical microextraction for different aqueous organic pollutants. Molecules 2018, 23, 2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Q.; Yuan, W.; Liang, J.; Li, J. Synthesis and hydrogen storage studies of metal−organic framework UiO-66. Int. J. Hydrogen. Energ. 2013, 38, 13104–13109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-G.; Cheng, Q.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, X.-Z. Controlled nucleation and controlled growth for size predicable synthesis of nanoscale metal-organic frameworks (MOFs): A general and scalable approach. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 7836–7840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decker, G.E.; Stillman, Z.; Attia, L.; Fromen, C.A.; Bloch, E.D. Controlling size, defectiveness, and fluorescence in nanoparticle UiO-66 through water and ligand modulation. Chem. Mater. 2019, 31, 4831–4839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeStefano, M.R.; Islamoglu, T.; Garibay, S.J.; Hupp, J.T. Room-temperature synthesis of UiO-66 and thermal modulation of densities of defect sites. Chem. Mater. 2017, 29, 1357–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Gao, W.; Zhang, L.; Liu, W.; Lu, J.; Wanga, Z.; Denga, Y.-J. Microwave-assisted synthesis of UIO-66 and its adsorption performance towards dyes. Cryst. Eng. Comm. 2014, 16, 7037–7042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.-H.; Lo, W.-S.; Kuo, Y.-W.; Chen, W.-J.; Lin, C.-H.; Shieh, F.-K. Green and rapid synthesis of zirconium metal–organic frameworks via mechanochemistry: UiO-66 analog nanocrystals obtained in one hundred seconds. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 5818–5821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, N.; Lin, X.; Li, M.; Li, L.; Ye, C.; Chen, J.; Qiu, T. Ionic liquid@ amphiphilic silica nanoparticles: Novel catalysts for converting waste cooking oil to biodiesel. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 18054–18061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Wu, T.; Han, B. Preparation of catalytic materials using ionic liquids as the media and functional components. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 6810–6827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Zhou, T.; Chen, L.; Ye, Y.; Qi, Z.; Freund, H.; Sundmacher, K. Selective oxidation of cyclohexanol to cyclohexanone in the ionic liquid1-octyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 9354–9356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhu, Q.; Wang, Z.; Chen, L.; Cheng, H.; Qi, Z. Ionic-liquid-controlled two-dimensional monolayer Bi2MoO6 and its adsorption of azo molecules. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2018, 1, 5083–5091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petkovic, M.; Seddon, K.R.; Rebelo, L.P.N.; Pereira, C.S. Ionic liquids: A pathway to environmental acceptability. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 1383–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, L.; Zhang, J.; Li, J.; Han, B.; Xue, Z.; Yang, G. Surfactant-directed assembly of mesoporous metal–organic framework nanoplates in ionic liquids. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 8688–8690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, J.; Peng, L.; Kang, X.; Han, B.; Wu, T.; Sang, X.; Ma, X. Gas promotes the crystallization of nano-sized metal–organic frameworks in ionic liquid. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 11445–11448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, X.; Zhang, J.; Xiang, J.; Cui, J.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, J.; Wu, Z.; Li, Z.; Mo, G.; Xu, Y.; et al. Ionic liquid accelerates the crystallization of Zr-based metal–organic frameworks. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qin, L.; Li, J.; Cheng, H.; Chen, L.; Qi, Z.; Yuan, W. Association extraction for vitamin E recovery from deodorizer distillate by in situ formation of deep eutectic solvent. AIChE J. 2017, 63, 2212–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Xiong, Y.; Qin, H.; Qi, Z. Advances of ionic liquids and deep eutectic solvents in green processes of biomass-derived 5-hydroxymethylfurfural. ChemSusChem 2022, 15, e202102635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Hu, X.; Wang, J.; Cheng, H.; Chen, L.; Qi, Z. Overview of acidic deep eutectic solvents on synthesis, properties and applications. Green Energy Environ. 2020, 5, 8–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Qi, Z. Application of deep eutectic solvents for hard-to-separate liquid systems. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 274, 119027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagle, D.V.; Zhao, H.; Baker, G.A. Deep eutectic solvents: Sustainable media for nanoscale and functional materials. Acc. Chem. Res. 2014, 47, 2299–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, T.; Cheng, H.; Richards, R.; Qi, Z. A microwave assisted ionic liquid route to prepare bivalent Mn5O8 nanoplates for 5-hydroxymethylfurfural oxidation. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 17902–17914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Lou, F.; Cheng, H.; Qi, Z. Uniform heterostructured MnOx/MnCO3/Fe2O3 nanocomposites assembled in an ionic liquid for highly selective oxidation of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural. New J. Chem. 2021, 45, 12050–12063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Chen, L.; Fang, Y.; Wang, A.; Chen, C.; Yan, Z. Facile synthesis of zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 (ZIF-8) by forming imidazole-based deep eutectic solvent. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 2018, 268, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Song, Z.; Zeng, Q.; Cheng, H.; Chen, L.; Qi, Z. Bifunctional imidazole-PTSA deep eutectic solvent for synthesizing long-chain ester IBIBE in reactive extraction. AIChE J. 2019, 65, 675–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Zhou, Y.; Zeng, Q.; Cheng, H.; Chen, L.; Zhang, B.; Qi, Z. Efficient Knoevenagel condensation catalyzed by imidazole-based halogen-free deep eutectic solvent at room temperature. Green Energy Environ. 2020, 5, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavka, J.H.; Jakobsen, S.; Olsbye, U.; Guillou, N.; Lamberti, C.; Bordiga, S.; Lillerud, K.P. A new zirconium inorganic building brick forming metal organic frameworks with exceptional stability. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 13850–13851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shearer, G.C.; Chavan, S.; Ethiraj, J.; Vitillo, J.G.; Svelle, S.; Olsbye, U.; Lamberti, C.; Bordiga, S.; Lillerud, K.P. Tuned to perfection: Ironing out the defects in metal–organic framework UiO-66. Chem. Mater. 2014, 26, 4068–4071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zhang, T.; Chen, L.; Cheng, H.; Qi, Z. Self-developed fabrication of manganese oxides microtubes with efficient catalytic performance for the selective oxidation of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 13122–13132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaate, A.; Roy, P.; Godt, A.; Lippke, J.; Waltz, F.; Wiebcke, M.; Behrens, P. Modulated synthesis of Zr-based metal-organic frameworks: From nano to single crystals. Chem. Eur. J. 2011, 17, 6643–6651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taddei, M.; Dümbgen, K.C.; Bokhoven, J.A.; Ranocchiari, M. Aging of the reaction mixture as a tool to modulate the crystallite size of UiO-66 into the low nanometer range. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 6411–6414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, L.; Li, X.; Hurlock, M.J.; Tu, X.; Zhang, Q. Hierarchically porous UiO-66: Facile synthesis, characterization and application. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 11817–11820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Chen, L.; Qi, Z. One-pot synthesis of gold nanoparticles embedded in silica for cyclohexane oxidation. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2013, 3, 1123–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Li, W.; Tang, B. Facile synthesis of amorphous UiO-66 (Zr-MOF) for supercapacitor application. J. Alloy. Compd. 2018, 733, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwalla, H.; Jana, K.; Maity, A.; Kesharwani, M.K.; Ganguly, B.; Das, A. Hydrogen bonding interaction between active methylene hydrogen atoms and an anion as a binding motif for anion recognition: Experimental studies and theoretical rationalization. J. Phys. Chem. A. 2014, 118, 2656–2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, L.; Yang, W.; Chen, L.; Cheng, H.; Qi, Z. Fabrication of spinel CoMn2O4 hollow spheres for highly selective aerobic oxidation of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural to 2,5-diformylfuran. Catal. Today 2020, 347, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Witkamp, G.-J.; Verpoorte, R.; Choi, Y.H. Tailoring properties of natural deep eutectic solvents with water to facilitate their applications. Food. Chem. 2015, 187, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chwaleba, D.; Ilczyszyn, M.M.; Ilczyszyn, M.; Ciunik, Z. Glycine–methanesulfonic acid (1:1) and glycine–p-toluenesulfonic acid (1:1) crystals: Comparison of structures, hydrogen bonds, and vibrations. J. Mol. Struct. 2007, 831, 119–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Mo, F.; Cheng, H.; Qi, Z. Brønsted acidic deep eutectic solvent based on imidazole and p-toluenesulfonic acid intensified Prins condensation of styrene with formaldehyde. Chem. Lett. 2021, 50, 1194–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Ka, D.; Jung, H.; Cho, K.; Jin, Y.; Kim, M. UiO-66-NH2 and zeolite-templated carbon composites for the degradation and adsorption of nerve agents. Molecules 2021, 26, 3837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karagiaridi, O.; Bury, W.; Mondloch, J.E.; Hupp, J.T.; Farha, O.K. Solvent-assisted linker exchange: An alternative to the de novo synthesis of unattainable metal-organic frameworks. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 4530–4540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arrozi, U.S.F.; Wijaya, H.W.; Patah, A.; Permana, Y. Efficient acetalization of benzaldehydes using UiO-66 and UiO-67: Substrates accessibility or Lewis acidity of zirconium. Appl. Catal. A-Gen. 2015, 506, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caratelli, C.; Hajek, J.; Cirujano, F.G.; Waroquier, M.; Xamena, F.X.L.; Speybroeck, V.V. Nature of active sites on UiO-66 and beneficial influence of water in the catalysis of Fischer esterification. J. Catal. 2017, 352, 401–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vermoortele, F.; Bueken, B.; Bars, G.L.; Voorde, B.V.; Vandichel, M.; Houthoofd, K.; Vimont, A.; Daturi, M.; Waroquier, M.; Speybroeck, V.V.; et al. Synthesis modulation as a tool to increase the catalytic activity of metal–organic frameworks: The unique case of UiO-66(Zr). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 11465–11468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhakshinamoorthy, A.; Alvaro, M.; Garciaa, H. Metal organic frameworks as solid acid catalysts for acetalization of aldehydes with methanol. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2010, 352, 3022–3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbst, A.; Khutia, A.; Janiak, C. Brønsted instead of lewis acidity in functionalized mil-101cr mofs for efficient heterogeneous (nano-MOF) catalysis in the condensation reaction of aldehydes with alcohols. Inorg. Chem. 2014, 53, 7319–7333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entry | Catalysts | Time (h) | Conversion (%) | Reference |
| 1 | none | 1 | 2 | This work |
| 2 | UiO-66-DES | 1 | 94 | This work |
| 3 | UiO-66-DMF | 1 | 93 | This work |
| 4 | UiO-66 | 1 | 91 | [52] |
| 5 | ZrOCl2 b | 1 | 29 | This work |
| 6 | ZrCl4 | 1 | 55 | [53] |
| 7 | ZnCl2 | 1; 24 | 40; 39 | [53] |
| 8 | H2BDC | 1 | 13 | This work |
| 9 | Al2(BDC)3 | 24 | 66 | [56] |
| 10 | Cr(BDC) | 1.5 | 73 | [57] |
| 11 | Cu3(BTC)2 | 2; 24 | 63; 88 | [56] |
| 12 | Fe(BTC) | 2; 24 | 49; 71 | [56] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, L.; Ye, X.; Zhang, T.; Qin, H.; Cheng, H.; Qi, Z. Fast Assembly of Metal Organic Framework UiO-66 in Acid-Base Tunable Deep Eutectic Solvent for the Acetalization of Benzaldehyde and Methanol. Molecules 2022, 27, 7246. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27217246
Chen L, Ye X, Zhang T, Qin H, Cheng H, Qi Z. Fast Assembly of Metal Organic Framework UiO-66 in Acid-Base Tunable Deep Eutectic Solvent for the Acetalization of Benzaldehyde and Methanol. Molecules. 2022; 27(21):7246. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27217246
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Lifang, Xiangzhu Ye, Ting Zhang, Hao Qin, Hongye Cheng, and Zhiwen Qi. 2022. "Fast Assembly of Metal Organic Framework UiO-66 in Acid-Base Tunable Deep Eutectic Solvent for the Acetalization of Benzaldehyde and Methanol" Molecules 27, no. 21: 7246. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27217246
APA StyleChen, L., Ye, X., Zhang, T., Qin, H., Cheng, H., & Qi, Z. (2022). Fast Assembly of Metal Organic Framework UiO-66 in Acid-Base Tunable Deep Eutectic Solvent for the Acetalization of Benzaldehyde and Methanol. Molecules, 27(21), 7246. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27217246