Molecularly Imprinted Methyl-Modified Hollow TiO2 Microspheres
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
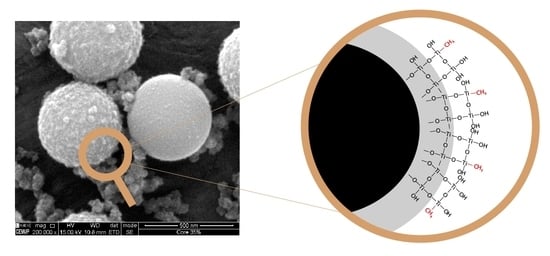
2.1. Morphological and Compositional Properties of the Microspheres
2.2. Textural Properties of the Microspheres
2.3. Sorptive Features of Microspheres
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials and Reagents
3.2. Methods
3.2.1. Synthesis of Methyl-Modified Hollow TiO2 Microspheres
3.2.2. Characterization of the Composites and Batch Sorption Studies: Isotherms and Respective Data Treatment
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dash, S.; Mishra, S.; Patel, S.; Mishra, B.K. Organically modified silica: Synthesis and applications due to its surface interaction with organic molecules. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 140, 77–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owens, G.J.; Singh, R.K.; Foroutan, F.; Alqaysi, M.; Han, C.M.; Mahapatra, C.; Kim, H.W.; Knowles, J.C. Sol-gel based materials for biomedical applications. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2016, 77, 1–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, B.; Meng, F.; Khan, M.W.; Qin, R.; Liu, X. Synthesis of hollow TiO2@g-C3N4/Co3O4 core-shell microspheres for effective photooxidation degradation of tetracycline and MO. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 13133–13143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porcu, S.; Castellino, M.; Roppolo, I.; Carbonaro, C.M.; Palmas, S.; Mais, L.; Casula, M.F.; Neretina, S.; Hughes, R.A.; Secci, F.; et al. Highly efficient visible light phenyl modified carbon nitride/TiO2 photocatalyst for environmental applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 531, 147394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Meng, F.; Khan, M.W.; Qin, R.; Liu, X. Facile synthesis of AgNPs modified TiO2@g-C3N4 heterojunction composites with enhanced photocatalytic activity under simulated sunlight. Mater. Res. Bull. 2020, 121, 110641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porcu, S.; Secci, F.; Ricci, P.C. Advances in Hybrid Composites for Photocatalytic Applications: A Review. Molecules 2022, 27, 6828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubert, U. Chemical modification of titanium alkoxides for sol-gel processing. J. Mater. Chem. 2005, 15, 3701–3715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gbureck, U.; Probst, J.; Thull, R. Polymerization behaviour of organically modified titanium alkoxides in solution. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2003, 27, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethi, K.; Roy, I. Organically modified titania nanoparticles for sustained drug release applications. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 456, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunitake, T.; Lee, S.W. Molecular imprinting in ultrathin titania gel films via surface sol-gel process. Anal. Chim. Acta 2004, 504, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-García, M.E.; Laíño, R.B. Molecular imprinting in sol-gel materials: Recent developments and applications. Microchim. Acta 2005, 149, 19–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanah, A.N.; Safitri, N.; Zulfa, A.; Neli, N.; Rahayu, D. Factors affecting preparation of molecularly imprinted polymer and methods on finding template-monomer interaction as the key of selective properties of the materials. Molecules 2021, 26, 5612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markowitz, M.A.; Kust, P.R.; Klaehn, J.; Deng, G.; Gaber, B.P. Surface-imprinted silica particles: The effects of added organosilanes on catalytic activity. Anal. Chim. Acta 2001, 435, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susanti, I.; Mutakin, M.; Hasanah, A.N. Factors affecting the analytical performance of molecularly imprinted mesoporous silica. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2022, 33, 469–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markowitz, M.A.; Deng, G.; Gaber, B.P. Effects of added organosilanes on the formation and adsorption properties of silicates surface-imprinted with an organophosphonate. Langmuir 2000, 16, 6148–6155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markowitz, M.A.; Deng, G.; Burleigh, M.C.; Wong, E.M.; Gaber, B.P. Influence of quaternary amine organosilane structure on the formation and adsorption properties of surface-imprinted silicates. Langmuir 2001, 17, 7085–7092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güney, S.; Cebeci, F. Selective electrochemical sensor for theophylline based on an electrode modified with imprinted sol-gel film immobilized on carbon nanoparticle layer. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 208, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Luo, Y.; He, M.; Huo, P.; Chen, T.; Shi, W.; Yan, Y.; Pan, J.; Ma, Z.; Yang, S. Preparation and performance of a novel magnetic conductive imprinted photocatalyst for selective photodegradation of antibiotic solution. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 18373–18382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Huo, P.; Luo, Y.; Liu, X.; Wu, D.; Gao, X.; Li, C.; Yan, Y. Performance of molecularly imprinted photocatalysts based on fly-ash cenospheres for selective photodegradation of single and ternary antibiotics solution. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2013, 378, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, V.R.A.; Azenha, M.A.; Pereira, C.M.; Silva, A.F. Preparation of molecularly imprinted hollow TiO2 microspheres for selective photocatalysis. Chem. Eng. J. Adv. 2021, 5, 100071–100083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, V.R.A.; Azenha, M. Crystallization of Hollow TiO2 into Anatase at Mild Conditions, for Improved Surface Recognition in Selective Photocatalysis. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2022, 648, 118912–118925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.C.; Sung, M.J.; Cha, J.K. Evaluation of titanium alkoxides and aryloxides in the Kulinkovich cyclopropanation of carboxylic esters. Tetrahedron Lett. 2001, 42, 2059–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winsel, H.; Gazizova, V.; Kulinkovich, O.; Pavlov, V.; De Meijere, A. Facile preparation of (phosphorylalkyl)-functionalized cyclopropanols and cyclopropylamines. Synlett 1999, 1999–2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiedemann, S.; Marek, I.; De Meijere, A. Functionalized aminocyclopropanes from functionalized organozinc compounds and N,N-dialkylcarboxamides. Synlett 2002, 879–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voigt, T.; Winsel, H.; de Meijere, A. Easy Access to (n + 3)-Dimethylamino-1-ethenylbicyclo[n.1.0]alkanes and their Facile Conversion to Ring-annelated Cyclopentadienes. Synlett 2002, 2002, 1362–1364. [Google Scholar]
- De Meijere, A.; Chaplinski, V.; Winsel, H.; Kordes, M.; Stecker, B.; Gazizova, V.; Savchenko, A.I.; Boese, R.; Schill, F. Cyclopropylamines from N,N-dialkylcarboxamides and grignard reagents in the presence of titanium tetraisopropoxide or methyltitanium triisopropoxide. Chem.—Eur. J. 2010, 16, 13862–13875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, M.S.M.; Plantier-Royon, R.; Szymoniak, J.; Bertus, P.; Behr, J.B. Synthesis of a 5-spirocyclopropyl deoxyrhamnojirimycin as a constrained naringinase inhibitor. Synthesis (Stuttgart) 2007, 3589–3594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, W.H.; Tokunaga, N.; Hayashi, T. Palladium- or nickel-catalyzed cross-coupling of organotitanium reagents with aryl triflates and halides. Synlett 2002, 871–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Zhang, S.; Wang, L.; Liu, R.; Zeng, Y.; Xia, X.; Liu, Y.; Luo, S. Facile synthesis of bird’s nest-like TiO2 microstructure with exposed (001) facets for photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 391, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, V.R.A.; Azenha, M.A.; Mêna, M.T.; Moura, C.; Pereira, C.M.; Pérez-Martín, R.I.; Vázquez, J.A.; Silva, A.F. Cationic imprinting of Pb(II) within composite networks based on bovine or fish chondroitin sulfate. J. Mol. Recognit. 2018, 31, e2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferreira, V.R.A.; Azenha, M.A.; Pereira, C.M.; Silva, A.F. Cation-bioimprinted mesoporous polysaccharide/sol–gel composites prepared in media containing choline chloride-based deep eutectic solvents. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2020, 137, 19–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhogal, S.; Kaur, K.; Malik, A.K.; Sonne, C.; Lee, S.S.; Kim, K.H. Core-shell structured molecularly imprinted materials for sensing applications. TrAC—Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 133, 116043–116055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titirici, M.M.; Sellergren, B. Peptide recognition via hierarchical imprinting. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2004, 378, 1913–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarpelli, F.; Mastropietro, T.F.; Poerio, T.; Godbert, N. Mesoporous TiO2 Thin Films: State of the Art. In Titanium Dioxide—Material of a Sustainable Environment, 2nd ed; Yang, D., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK; Volume 2, pp. 11236–11266. [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kadhirvel, P.; Azenha, M.; Shinde, S.; Schillinger, E.; Gomes, P.; Sellergren, B.; Silva, A.F. Imidazolium-based functional monomers for the imprinting of the anti-inflammatory drug naproxen: Comparison of acrylic and sol-gel approaches. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1314, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gesztelyi, R.; Zsuga, J.; Kemeny-Beke, A.; Varga, B.; Juhasz, B.; Tosaki, A. The Hill equation and the origin of quantitative pharmacology. Arch. Hist. Exact Sci. 2012, 66, 427–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battista, E.; Scognamiglio, P.L.; di Luise, N.; Raucci, U.; Donati, G.; Rega, N.; Netti, P.A.; Causa, F. Turn-on fluorescence detection of protein by molecularly imprinted hydrogels based on supramolecular assembly of peptide multi-functional blocks. J. Mater. Chem. B 2018, 6, 1207–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El-Sharif, H.F.; Hawkins, D.M.; Stevenson, D.; Reddy, S.M. Determination of protein binding affinities within hydrogel-based molecularly imprinted polymers (HydroMIPs). Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 15483–15489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wulff, G. Molecular Imprinting in Cross-Linked Materials with the Aid of Molecular Templates—A Way towards Artificial Antibodies. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1995, 34, 1812–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svenson, J.; Karlsson, J.G.; Nicholls, I.A. 1H Nuclear magnetic resonance study of the molecular imprinting of (-)-nicotine: Template self-association, a molecular basis for cooperative ligand binding. J. Chromatogr. A 2004, 1024, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Methyl-Modified TiO2 Microspheres | Nitrogen Adsorption Technique | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| * Surface Area/Thickness (m2/g/nm) | ** Average Pore Size (nm) | ** Pore Volume/Thickness (103.cm3/g/nm) | |
| Methyl-C-MIM | 1.73 | 4.6 | 2.0 |
| Methyl-C-NIM | 1.27 | 4.8 | 1.3 |
| Methyl-H-MIM | 1.25 | 3.8 | 3.9 |
| Methyl-H-NIM | 0.47 | 3.2 | 1.9 |
| Methyl-C-HCl-MIM | 1.55 | 3.8 | 2.2 |
| Methyl-C-HCl-NIM | 1.04 | 4.2 | 0.9 |
| Methyl-H-HCl-MIM | 0.85 | 4.3 | 2.7 |
| Methyl-H-HCl-NIM | 0.37 | 4.8 | 1.8 |
| Methyl-C-HCl-MIM-250 | 1.51 | 4.0 | 1.0 |
| Methyl-C-HCl-NIM-250 | 0.91 | 3.3 | 1.4 |
| Methyl-H-HCl-MIM-250 | 0.31 | 2< | 1.4 |
| Methyl-H-HCl-NIM-250 | 0.14 | 3.8 | 0.4 |
| Methyl-C-HCl-MIM-200 | 1.73 | 3.7 | 2.2 |
| Methyl-C-HCl-NIM-200 | 0.95 | 3.6 | 1.7 |
| Methyl-H-HCl-MIM-200 | 0.37 | 2< | 2.0 |
| Methyl-H-HCl-NIM-200 | 0.18 | 4.2 | 0.7 |
| Methyl-C-HCl-MIM-150 | 1.75 | 3.8 | 2.5 |
| Methyl-C-HCl-NIM-150 | 1.01 | 3.4 | 1.2 |
| Methyl-H-HCl-MIM-150 | 0.44 | 2< | 3.0 |
| Methyl-H-HCl-NIM-150 | 0.21 | 4.2 | 1.1 |
| Methyl-Modified TiO2 Microspheres | Model | Isotherm Parameters a | IF (qmax) | α (qmax) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kb | qmax (mg/g) | ||||||
| Bil | Pro | Bil | Pro | ||||
| Methyl-H-NIM-HCl | L-F | 0.52 ± 0.03 | 0.55 ± 0.02 | 32 ± 2 | 39 ± 1 | 1.5 | 0.8 |
| Methyl-H-MIM-HCl | H | 11.30 ± 4.21 | 9.61 ± 5.32 | 49 ± 3 | 43 ± 5 | 1.1 | |
| Methyl-C-NIM-HCl | L-F | 0.32 ± 0.03 | 0.33 ± 0.08 | 31 ± 2 | 46 ± 7 | 1.4 | 0.7 |
| Methyl-C-MIM-HCl | H | 9.61 ± 5.32 | 5.93 ± 2.31 | 43 ± 5 | 43 ± 5 | 1 | |
| Methyl-H-NIM-HCl-250 | L-F | 0.29 ± 0.03 | 0.33 ± 0.12 | 26 ± 3 | 15 ± 1 | 1.2 | 1.7 |
| Methyl-H-MIM-HCl-250 | H | 13.23 ± 4.31 | 7.82 ± 2.53 | 30 ± 3 | 16 ± 2 | 1.9 | |
| Methyl-C-NIM-HCl-250 | L-F | 0.73 ± 0.03 | 0.43 ± 0.08 | 28 ± 1 | 25 ± 1 | 1.0 | 1.1 |
| Methyl-C-MIM-HCl-250 | H | 2.11 ± 0.83 | 1.14 ± 0.75 | 28 ± 2 | 27 ± 3 | 1.0 | |
| Methyl-H-NIM-HCl-200 | L-F | 0.66 ± 0.03 | 0.40 ± 0.02 | 22 ± 2 | 14 ± 1 | 1.0 | 1.6 |
| Methyl-H-MIM-HCl-200 | H | 2.53 ± 1.72 | 1.52 ± 0.64 | 23 ± 2 | 13 ± 1 | 1.8 | |
| Methyl-C-NIM-HCl-200 | L-F | 0.26 ± 0.02 | 0.60 ± 0.03 | 18 ± 1 | 21 ± 1 | 1.2 | 0.8 |
| Methyl-C-MIM-HCl-200 | H | 1.91 ± 1.24 | 1.81 ± 1.25 | 22 ± 2 | 22 ± 2 | 1.0 | |
| Methyl-H-NIM-HCl-150 | L-F | 0.29 ± 0.03 | 0.36 ± 0.02 | 25 ± 3 | 16 ± 1 | 1.2 | 1.6 |
| Methyl-H-MIM-HCl-150 | H | 5.92 ± 1.94 | 4.08 ± 2.22 | 30 ± 3 | 18 ± 2 | 1.7 | |
| Methyl-C-NIM-HCl-150 | L-F | 0.30 ± 0.06 | 0.22 ±0.02 | 21 ± 3 | 31 ± 1 | 1.1 | 0.7 |
| Methyl-C-MIM-HCl-150 | H | 8.71 ± 2.82 | 6.10± 4.23 | 23 ± 2 | 39 ± 3 | 0.6 | |
| Methyl-H-NIM | L-F | 0.40 ± 0.03 | 0.26 ± 0.03 | 32 ± 1 | 46 ± 4 | 1.8 | 0.7 |
| Methyl-H-MIM | H | 10.44 ± 3.22 | 9.51± 2.82 | 58 ± 4 | 52 ± 5 | 1.1 | |
| Methyl-C-NIM | L-F | 0.38 ±0.02 | 0.13 ±0.04 | 37 ± 2 | 50 ± 9 | 1.4 | 0.7 |
| Methyl-C-MIM | H | 20.53 ± 5.43 | 10.51± 1.94 | 53 ± 5 | 44 ± 3 | 1.2 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ferreira, V.R.A.; Azenha, M.A.; Pereira, C.M.; Silva, A.F. Molecularly Imprinted Methyl-Modified Hollow TiO2 Microspheres. Molecules 2022, 27, 8510. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27238510
Ferreira VRA, Azenha MA, Pereira CM, Silva AF. Molecularly Imprinted Methyl-Modified Hollow TiO2 Microspheres. Molecules. 2022; 27(23):8510. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27238510
Chicago/Turabian StyleFerreira, Vanessa R. A., Manuel A. Azenha, Carlos M. Pereira, and António F. Silva. 2022. "Molecularly Imprinted Methyl-Modified Hollow TiO2 Microspheres" Molecules 27, no. 23: 8510. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27238510
APA StyleFerreira, V. R. A., Azenha, M. A., Pereira, C. M., & Silva, A. F. (2022). Molecularly Imprinted Methyl-Modified Hollow TiO2 Microspheres. Molecules, 27(23), 8510. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27238510