A Review of Microalgae- and Cyanobacteria-Based Biodegradation of Organic Pollutants
Abstract
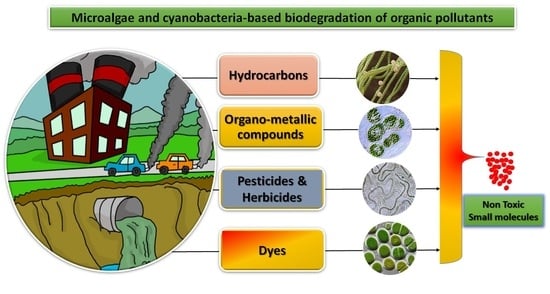
:1. Introduction
2. Organic Pollutants
2.1. Organic Hydrocarbons
2.2. Organic Dyes
2.3. Organometallic Compounds
2.4. Pesticides and Herbicides
3. Algae as an Organic Biodegradation
3.1. Bioremediation of Organic Pollutants by Microalgae
3.1.1. Dyes
3.1.2. Organic Hydrocarbon
3.1.3. Phenolic Compounds
3.1.4. Pesticides and Herbicides
3.2. Bioremediation of Organic Pollutants by Cyanobacteria
3.2.1. Dyes
3.2.2. Organic Hydrocarbon
3.2.3. Phenolic Compounds
3.2.4. Pesticides and Herbicides
4. Advantages of Phycoremediation Treatment
5. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, J. Environmental Problems of Human Settlements and Countermeasures Based on Ecological Engineering. In Study of Ecological Engineering of Human Settlements; Springer Nature: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. Health Risks of Persistent Organic Pollutants from Long-Range Transboundary Air Pollution; WHO Regional Office for Europe: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2003; Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/107471 (accessed on 20 December 2021).
- Martinez-Jeronimo, F.; Cruz-Cisneros, J.L.; Garcia-Hernandez, L. A comparison of the response of Simocephalus mixtus (Cladocera) and Daphnia magna to contaminated freshwater sediments. Ecotoxicol Environ. Saf. 2008, 71, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amores-Sanchez, I.; Terrón-Orellana, M.d.C.; González-Becerra, A.E.; de Villegas, T.G.-D. Potential of microalgae and cyanobacteria in bioremediation of distillery wastewaters. ICIDCA Sobre Los Deriv. Caña Azúcar 2015, 49, 58–70. [Google Scholar]
- El-Sheekh, M.; El-Dalatony, M.; Thakur, N.; Zheng, Y.; Salama, E.-S. Role of microalgae and cyanobacteria in wastewater treatment: Genetic engineering and omics approaches. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potter, W.J. Cultivation Theory and Research—A Conceptual Critique. Hum. Commun. Res. 1993, 19, 564–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.H.A.; Ayaz, M.; Arshad, M.; Yousaf, S.; Khan, M.A.; Anees, M.; Sultan, A.; Nawaz, I.; Iqbal, M. Biogeochemical Cycle, Occurrence and Biological Treatments of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs). Iran. J. Sci. Technol. A 2018, 43, 1393–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wild, S.R.; Berrow, M.L.; Jones, K.C. The Persistence of Polynuclear Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) in Sewage Sludge Amended Agricultural Soils. Environ. Pollut. 1991, 72, 141–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perelo, L.W. Review: In situ and bioremediation of organic pollutants in aquatic sediments. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 177, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jennifer, E.A.; Abou-Elwafa, A.M.; Stuart, H. Pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) in the freshwater aquatic environment. Emerg. Contam. 2017, 3, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Sun, Y.; Rathour, R.; Pandey, A.; Thakur, I.S.; Tsang, D.C.W. Algae as potential feedstock for the production of biofuels and value-added products: Opportunities and challenges. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 716, 137116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Kumar, S.; Kumar, S. Biodegradation kinetics of phenol and catechol using Pseudomonas putida MTCC 1194. Biochem. Eng. J. 2005, 22, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.Z.; An, H. UV/TiO2 photocatalytic oxidation of commercial dyes in aqueous solutions. Chemosphere 1995, 31, 4157–4170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sheekh, M.M.; Abou El-Souod, G. Biodegradation of basic fuchsin and methyl red by the blue green algae Hydrocoleum oligotrichum and Oscillatoria limnetica. Environ. Eng. Manag. J. 2016, 15, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksu, Z. Application of biosorption for the removal of organic pollutants: A review. Process. Biochem 2005, 40, 997–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Iyengar, L.; Pandey, A. Bacterial Decolorization and Degradation of Azo Dyes. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2007, 59, 73–84. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, H.; Muhammed, S.K. Biosorption of crystal violet from water on leaf biomass of Calotropis procera. J. Environ. Technol. 2008, 3, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andleeb, S.; Atiq, N.; Parmar, A.; Robson, G.D.; Ahmed, S. An HPLC method development for the assessment of degradation products of anthraquinone dye. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 176, 597–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- House, J.E.; House, K.A. Chapter 22—Organometallic Compounds. In Descriptive Inorganic Chemistry, 3rd ed.; House, J.E., House, K.A., Eds.; Academic Press: Boston, MA, USA, 2016; pp. 371–393. [Google Scholar]
- Egorova, K.S.; Ananikov, V.P. Toxicity of Metal Compounds: Knowledge and Myths. Organometallics 2017, 36, 4071–4090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoch, M. Organotin compounds in the environment—An Overviw. Appl. Geochmistry 2001, 16, 719–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okoro, H.K.; Fatoki, O.S.; Adekola, F.A.; Ximba, B.J.; Snyman, R.G. Organotin Compounds. In Encyclopedia of Toxicology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014; pp. 720–725. [Google Scholar]
- Aydinalp, C.; Porca, M.M. The effects of pesticides in water resources. J. Cent. Eur. Agric. 2004, 5, 5–12. [Google Scholar]
- Mastovska, K.; Wylie, P.L. Evaluation of a new column backflushing set-up in the gas chromatographic-tandem mass spectrometric analysis of pesticide residues in dietary supplements. J. Chromatogr A 2012, 1265, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indrajit, S.; Samir, V. Analysis of Pesticide Residues in Drinking Water as Per Bureau of Indian Standards Using The Agilent 7000 gc/ms/ms with Pesticides Analyzer; Agilent Technologies: Santa Clara, CA, USA, 2016; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Mondal, M.; Halder, G.; Oinam, G.; Indrama, T.; Tiwari, O.N. Bioremediation of Organic and Inorganic Pollutants Using Microalgae. In New and Future Developments in Microbial Biotechnology and Bioengineering; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 223–235. [Google Scholar]
- Fomina, M.; Gadd, G.M. Biosorption: Current perspectives on concept, definition and application. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 160, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, B.; Sellamuthu, B.; Ouarda, Y.; Drogui, P.; Tyagi, R.D.; Buelna, G. Review on fate and mechanism of removal of pharmaceutical pollutants from wastewater using biological approach. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 224, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Derco, J.; Vrana, B. Introductory Chapter: Biosorption. In Biosorption; Derco, J., Vrana, B., Eds.; Intech Open: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Razak, S.B.A.; Sharip, Z. The potential of phycoremediation in controlling eutrophication in tropical lake and reservoir: A review. Desalination Water Treat. 2020, 180, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corpuz, M.V.A.; Borea, L.; Senatore, V.; Castrogiovanni, F.; Buonerba, A.; Oliva, G.; Ballesteros, F., Jr.; Zarra, T.; Belgiorno, V.; Choo, K.H.; et al. Wastewater treatment and fouling control in an electro algae-activated sludge membrane bioreactor. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 786, 147475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, G.; Shanmugam, S.; Sivaramakrishnan, R.; Kumar, D.; Mathimani, T.; Brindhadevi, K.; Pugazhendhi, A.; Rajendran, K. Mechanism and challenges behind algae as a wastewater treatment choice for bioenergy production and beyond. Fuel 2021, 285, 119093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emparan, Q.; Harun, R.; Danquah, M.K. Role of Phycoremediation for Nutrient Removal from Wastewaters: A Review. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2019, 17, 889–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, E.M.; Sureshkumar, S.; Sankar, T.V.; Divya, K.R. Phycoremediation in aquaculture; a win-win paradigm. Environ. Technol. Rev. 2020, 9, 67–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sheekh, M.; Bedaiwy, M.; Osman, M.; Ismail, M. Mixotrophic and heterotrophic growth of some microalgae using extract of fungal-treated wheat bran. Int. J. Recycl. Org. Waste Agric. 2012, 1, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pathak, J.; Rajneesh; Maurya, P.K.; Singh, S.P.; Häder, D.-P.; Sinha, R.P. Cyanobacterial Farming for Environment Friendly Sustainable Agriculture Practices: Innovations and Perspectives. Front. Environ. Sci. 2018, 6, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurens, L.M.L.; Chen-Glasser, M.; McMillan, J.D. A perspective on renewable bioenergy from photosynthetic algae as feedstock for biofuels and bioproducts. Algal Res. 2017, 24, 261–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chekroun, K.B.; Sánchez, E.; Baghour, M. The role of algae in bioremediation of organic pollutants. Int. Res. J. Public Environ. Health 2014, 1, 19–32. [Google Scholar]
- Gonçalves, A.L. The Use of Microalgae and Cyanobacteria in the Improvement of Agricultural Practices: A Review on Their Biofertilising, Biostimulating and Biopesticide Roles. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, M.M.; Ismail, G.A.; El-Sheekh, M.M. Potential assessment of some micro- and macroalgal species for bioethanol and biodiesel production. Energy Sources Part. A 2020, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, C.M. Algae and Water Pollution: The Identification, Significance, and Control of Algae in Water Supplies and in Polluted Water; Castle House Publications: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, Z.I.; Ahmad, K.; Siddique, S.; Ahmad, T.; Bashir, H.; Munir, M.; Mahpara, S.; Malik, I.S.; Wajid, K.; Ugulu, I.; et al. A study on the transfer of chromium from meadows to grazing livestock: An assessment of health risk. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2020, 27, 26694–26701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitt, D.; Müller, A.; Csögör, Z.; Frimmel, F.H.; Posten, C. The adsorption kinetics of metal ions onto different microalgae and siliceous earth. Water Res. 2001, 35, 779–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mona, S.; Kaushik, A.; Kaushik, C.P. Biosorption of reactive dye by waste biomass of Nostoc linckia. Ecol. Eng. 2011, 37, 1589–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Dong, D.; Zhang, L.; Song, Z.; Hua, X.; Guo, Z. Response of Freshwater Biofilms to Antibiotic Florfenicol and Ofloxacin Stress: Role of Extracellular Polymeric Substances. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pflugmacher, S.; Sandermann, J.H. Cytochrome P450 monooxygenases for fatty acids and xenobiotics in marine macroalgae. Plant Physiol. 1998, 117, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiong, J.Q.; Kurade, M.B.; Jeon, B.H. Can Microalgae Remove Pharmaceutical Contaminants from Water? Trends Biotechnol. 2018, 36, 30–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, B.; Schlosser, D. First laccase in green algae: Purification and characterization of an extracellular phenol oxidase from Tetracystis aeria. Planta 2014, 240, 1225–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Kang, S.; Xiong, R.; Chen, M. Environment-Friendly Removal Methods for Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals. Sustainability 2020, 12, 7615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilal, M.; Rasheed, T.; Sosa-Hernandez, J.E.; Raza, A.; Nabeel, F.; Iqbal, H.M.N. Biosorption: An Interplay between Marine Algae and Potentially Toxic Elements—A Review. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baghour, M. Algal Degradation of Organic Pollutants. In Handbook of Ecomaterials; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 565–586. [Google Scholar]
- Gera, G.; Yewalkar, S.; Nene, S. Chapter 18: Remediation of Domestic and Industrial Effl uents Using Algae. In Algal Biorefinery: An Integrated Approach; Das, D., Ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Brar, A.; Kumar, M.; Vivekanand, V.; Pareek, N. Photoautotrophic microorganisms and bioremediation of industrial effluents: Current status and future prospects. 3 Biotech 2017, 7, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Potin, O.; Rafin, C.; Veignie, E. Bioremediation of an aged polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs)-contaminated soil by filamentous fungi isolated from the soil. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2004, 54, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martha Radmann, E.; Etiele, G.D.M.; Cibele, F.D.O.; Kellen, Z.; Jorge, A.V.C. Microalgae cultivation for biosurfactant production. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2015, 9, 2283–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rahman, K.S.M.; Banat, I.M.; Thahira, J.; Thayumanavan, T.; Lakshmanaperumalsamy, P. Bioremediation of gasoline contaminated soil by a bacterial consortium amended with poultry litter, coir pith and rhamnolipid biosurfactant. Bioresour. Technol. 2002, 81, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stance, K.; Swackham, D.L. Factors affecting phytoplankton species-specific differences in accumulation of 40 polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs). Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1994, 13, 1849–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escapa, C.; Coimbra, R.; Nuevo, C.; Vega, S.; Paniagua, S.; García, A.; Calvo, L.; Otero, M. Valorization of Microalgae Biomass by Its Use for the Removal of Paracetamol from Contaminated Water. Water 2017, 9, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Correa-Reyes, G.; Viana, M.T.; Marquez-Rocha, F.J.; Licea, A.F.; Ponce, E.; Vazquez-Duhalt, R. Nonylphenol algal bioaccumulation and its effect through the trophic chain. Chemosphere 2007, 68, 662–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakurai, T.; Aoki, M.; Ju, X.; Ueda, T.; Nakamura, Y.; Fujiwara, S.; Umemura, T.; Tsuzuki, M.; Minoda, A. Profiling of lipid and glycogen accumulations under different growth conditions in the sulfothermophilic red alga Galdieria sulphuraria. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 200, 861–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Subashchandrabose, S.R.; Logeshwaran, P.; Venkateswarlu, K.; Naidu, R.; Megharaj, M. Pyrene degradation by Chlorella sp. MM3 in liquid medium and soil slurry: Possible role of dihydrolipoamide acetyltransferase in pyrene biodegradation. Algal Res. 2017, 23, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sheekh, M.M.; Abomohra, A.; Eladel, H.; Battah, M.; Mohammed, S. Screening of different species of Scenedesmus isolated from Egyptian freshwater habitats for biodiesel production. Renew. Energy 2018, 129, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldaby, E.S.E.; Mawad, A.M.M. Pyrene biodegradation capability of two different microalgal strains. Global Nest J. 2018, 3, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishchi, T.; Sibi, G. Azo Dye Degradation by Chlorella vulgaris: Optimization and Kinetics. Int. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 14, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, H.H. Algal decolorization and degradation of monoazo and diazo dyes. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2008, 11, 1310–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- El-Sheekh, M.M.; Gharieb, M.M.; Abou-El-Souod, G.W. Biodegradation of dyes by some green algae and cyanobacteria. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2009, 63, 699–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verasoundarapandian, G.; Lim, Z.S.; Radziff, S.B.M.; Taufik, S.H.; Puasa, N.A.; Shaharuddin, N.A.; Merican, F.; Wong, C.-Y.; Lalung, J.; Ahmad, S.A. Remediation of Pesticides by Microalgae as Feasible Approach in Agriculture: Bibliometric Strategies. Agronomy 2022, 12, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, G.; Pollio, A.; Previtera, L.; Stanzione, M.; Temussi, F. Removal of low molecular weight phenols from olive oil mill wastewater using microalgae. Biotechnol. Lett. 2003, 25, 1657–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynn, S.G.; Price, D.J.; Birge, W.J.; Kilham, S.S. Effect of nutrient availability on the uptake of PCB congener 2,2′,6,6′-tetrachlorobiphenyl by a diatom (Stephanodiscus minutulus) and transfer to a zooplankton (Daphnia pulicaria). Aquat. Toxicol. 2007, 83, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sheekh, M.M.; Abou-El-Souod, G.; El Asrag, H. Biodegradation of some dyes by the green Alga Chlorella vulgaris and the Cyanobacterium Aphanocapsa elachista. Egypt J. Bot. 2018, 58, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, J.; Alvarez, P.; Arbib, Z.; Garrido, C.; Barragan, J.; Perales, J.A. Effect of nitrogen and phosphorus concentration on their removal kinetic in treated urban wastewater by Chlorella vulgaris. Int. J. Phytoremediat. 2011, 13, 884–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, S.L.; Chu, W.L.; Phang, S.M. Use of Chlorella vulgaris for bioremediation of textile wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 7314–7322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jinqi, L.; Houtian, L. Degradation of azo dyes by algae. Environ. Pollut. 1992, 75, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ergene, A.; Ada, K.; Tan, S.; Katırcıoğlu, H. Removal of Remazol Brilliant Blue R dye from aqueous solutions by adsorption onto immobilized Scenedesmus quadricauda: Equilibrium and kinetic modeling studies. Desalination 2009, 249, 1308–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sheekh, M.; Bedaiwy, M.; Osman, M.; Ismail, M. Influence of Molasses on Growth, Biochemical Composition and Ethanol Production of the Green Algae Chlorella vulgaris and Scenedesmus obliquus. J. Agric. Eng. Biotechnol. 2014, 2, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olguín, E.J.; Sánchez-Galván, G. Heavy metal removal in phytofiltration and phycoremediation: The need to differentiate between bioadsorption and bioaccumulation. N. Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulbry, W.; Kondrad, S.; Pizarro, C.; Kebede-Westhead, E. Treatment of dairy manure effluent using freshwater algae: Algal productivity and recovery of manure nutrients using pilot-scale algal turf scrubbers. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 8137–8142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radziff, S.B.M.; Ahmad, S.A.; Shaharuddin, N.A.; Merican, F.; Kok, Y.Y.; Zulkharnain, A.; Gomez-Fuentes, C.; Wong, C.Y. Potential Application of Algae in Biodegradation of Phenol: A Review and Bibliometric Study. Plants 2021, 10, 2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Olsen, S.I. A critical review of biochemical conversion, sustainability and life cycle assessment of algal biofuels. Appl. Energy 2011, 88, 3548–3555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco, M.M.; Hoeltz, M.; Moraes, M.S.; Schneider, R.C. Microalgae: Cultivation techniques and wastewater phycoremediation. J. Environ. Sci Health A Tox. Hazard. Subst. Environ. Eng. 2015, 50, 585–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.W.; Yuan, D.X.; Lin, Q.M.; Yang, T.L. Accumulation and biodegradation of phenanthrene and fluoranthene by the algae enriched from a mangrove aquatic ecosystem. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2008, 56, 1400–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Sheekh, M.M.; Hamouda, R.A. Biodegradation of crude oil by some cyanobacteria under heterotrophic conditions. Desalin. Water Treat. 2013, 52, 1448–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Lai, X.; Chen, B.; Lin, L.; Fang, L.; Tam, N.F.; Luan, T. Chlorophyll catalyse the photo-transformation of carcinogenic benzo[a]pyrene in water. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Cai, F.; Luan, T.; Lin, L.; Chen, B. Pyrene metabolites by bacterium enhancing cell division of green alga Selenastrum capricornutum. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 689, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takáčová, A.; Smolinská, M.; Ryba, J.; Mackuľak, T.; Jokrllová, J.; Hronec, P.; Čík, G. Biodegradation of Benzo[a]Pyrene through the use of algae. Open Chem. 2014, 12, 1133–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.B.; Shaikh, S.; Jain, K.R.; Desai, C.; Madamwar, D. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons: Sources, Toxicity, and Remediation Approaches. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 562813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGenity, T.J.; Folwell, B.D.; McKew, B.A.; Sanni, G.O. Marine crude-oil biodegradation: A central role for interspecies interactions. Aquat. Biosyst. 2012, 8, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghasemi, Y.; Rasoul-Amini, S.; Fotooh-Abadi, E. The Biotransformation, Biodegradation, and Bioremediation of Organic Compounds by Microalgae. J. Phycol. 2011, 47, 969–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sheekh, M.M.; Hamouda, R.A.; Nizam, A.A. Biodegradation of crude oil by Scenedesmus obliquus and Chlorella vulgaris growing under heterotrophic conditions. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2013, 82, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, J.D.; Colwell, R.R.; Petrakis, L. Degradation of Petroleum by an Alga, Prototheca zopfii. Appl. Microbiol. 1975, 3, 79–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, B.; Schlosser, D.; Reisser, W. First description of a laccase-like enzyme in soil algae. Arch. Microbiol. 2010, 192, 759–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Zuhair, S.; Nabil, M.; Abdi, Y.; Al Sayyed, M.; Taher, H. High Concentration Phenol Removal Using Freshwater Microalgae. Int. J. Biotechnol. Wellness Ind. 2016, 5, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gattullo, C.E.; Bahrs, H.; Steinberg, C.E.; Loffredo, E. Removal of bisphenol A by the freshwater green alga Monoraphidium braunii and the role of natural organic matter. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 416, 501–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klekner, V.; Kosaric, N. Degradation of phenols by algae. Environ. Technol. 1992, 13, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semple, K.T.; Cain, R.B.; Schmidt, S. Biodegradation of aromatic compounds by microalgae. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1999, 170, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Liu, Y.X. Dimethyl phthalate biodegradation by Dunaliella tertiolecta. J. Environ. Sci. 1998, 10, 296–301. [Google Scholar]
- Avila, R.; Peris, A.; Eljarrat, E.; Vicent, T.; Blanquez, P. Biodegradation of hydrophobic pesticides by microalgae: Transformation products and impact on algae biochemical methane potential. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 754, 142114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Xiao, H.; He, N.; Sun, D.; Duan, S. Biosorption and Biodegradation of the Environmental Hormone Nonylphenol by Four Marine Microalgae. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutherland, D.L.; Ralph, P.J. Microalgal bioremediation of emerging contaminants—Opportunities and challenges. Water Res. 2019, 164, 114921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roesle, P.; Stempfle, F.; Hess, S.K.; Zimmerer, J.; Río Bártulos, C.; Lepetit, B.; Eckert, A.; Kroth, P.G.; Mecking, S. Synthetic Polyester from Algae Oil. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 6800–6804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kauss, P.; Hutchinson, T.C.; Soto, C.; Hellebust, J.; Griffiths, M. The Toxicity of Crude Oil and its Components to Freshwater Algae. Int. Oil Spill Conf. Proc. 1973, 1973, 703–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madadi, R.; Pourbabaee, A.A.; Tabatabaei, M.; Zahed, M.A.; Naghavi, M.R. Treatment of petrochemical wastewater by the green algae Chlorella vulgaris. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2016, 10, 555–560. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Z.P.; Luo, K.; Zhang, S.; Zheng, Q.; Yang, H. Bioaccumulation and catabolism of prometryne in green algae. Chemosphere 2012, 87, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurade, M.B.; Kim, J.R.; Govindwar, S.P.; Jeon, B.-H. Insights into microalgae mediated biodegradation of diazinon by Chlorella vulgaris: Microalgal tolerance to xenobiotic pollutants and metabolism. Algal Res. 2016, 20, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethunathan, N.; Megharaj, M.; Chen, Z.L.; Williams, B.D.; Lewis, G.; Naidu, R. Algal Degradation of a Known Endocrine Disrupting Insecticide, α-Endosulfan, and Its Metabolite, Endosulfan Sulfate, in Liquid Medium and Soil. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 3030–3035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Megharaj, M.; Madhavi, D.R.; Sreenivasulu, C.; Umamaheswari, A.; Venkateswarlu, K. Biodegradation of Methyl Parathion by Soil Isolates of Microalgae and Cyanobacteria Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1994, 53, 292–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schocken, M.J.; Mao, J.; Schabacker, D.J. Microbial Transformations of the Fungicide Cyprodinil (CGA-219417). J. Agric. Food Chem. 1997, 45, 3647–3651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Qiu, C.B.; Zhou, Y.; Jin, Z.P.; Yang, H. Bioaccumulation and degradation of pesticide fluroxypyr are associated with toxic tolerance in green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Ecotoxicology 2011, 20, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Barreiro, O.; Rioboo, C.; Herrero, C.; Cid, A. Removal of triazine herbicides from freshwater systems using photosynthetic microorganisms. Environ. Pollut. 2006, 144, 266–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Subashchandrabose, S.R.; Ramakrishnan, B.; Megharaj, M.; Venkateswarlu, K.; Naidu, R. Mixotrophic cyanobacteria and microalgae as distinctive biological agents for organic pollutant degradation. Environ. Int. 2013, 51, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thies, F.; Backhaus, T.; Bossmann, B.; Grimme, L.H. Xenobiotic Biotransformation in Unicellular Green Algae (Involvement of Cytochrome P450 in the Activation and Selectivity of the Pyridazinone Pro-Herbicide Metflurazon). Plant Physiol. 1996, 112, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Subramanian, M.; Shanks, J.V. Role of Plants in the Transformation of Explosives. In Phytoremediation: Transformation and Control of Contaminants; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003; pp. 387–408. [Google Scholar]
- Basak, B.; Bhunia, B.; Dey, A. Studies on the potential use of sugarcane bagasse as carrier matrix for immobilization of Candida tropicalis PHB5 for phenol biodegradation. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2014, 93, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sheekh, M.M.; Metwally, M.A.; Allam, N.; Hemdan, H.E. Simulation Treatment of Industrial Wastewater Using Microbiological Cell Immobilization Technique. Iran. J. Sci Technol. A 2020, 44, 595–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, T.G.; Jin, J.; Chan, S.M.N.; Wong, Y.S.; Tam, N.F.Y. Biosorption and biodegradation of tributyltin (TBT) by alginate immobilized Chlorella vulgaris beads in several treatment cycles. Process. Biochem. 2006, 41, 1560–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Huang, G.; Yaoting, Y.U. Immobilization of microalgae for biosorption and degradation of butyltin chlorides. Art. Cells Blood Subs. Immob. Biotech. 1998, 26, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutherland, D.L.; Howard-Williams, C.; Turnbull, M.H.; Broady, P.A.; Craggs, R.J. Enhancing microalgal photosynthesis and productivity in wastewater treatment high rate algal ponds for biofuel production. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 184, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, S.-H.; Chen, Y.-D.; Qu, W.-Y.; Liu, F.-Y.; Wang, Y. Algal culture and biofuel production using wastewater. In Biofuels from Algae; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 167–198. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Ogden, K. Recycled wastewater from anaerobic digestion of lipid extracted algae as a source of nutrients. Fuel 2017, 210, 705–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz, R.; Guieysse, B.; Mattiasson, B. Phenanthrene biodegradation by an algal-bacterial consortium in two-phase partitioning bioreactors. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2003, 61, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, S.A.; Raposo, M.F.; Castro, P.M.; Morais, R.M. Biodegradation of p-chlorophenol by a microalgae consortium. Water Res. 2004, 38, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Ghosh, A.K.; Pal, P. Synergy of biofuel production with waste remediation along with value-added co-products recovery through microalgae cultivation: A review of membrane-integrated green approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 698, 134169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opeolu, B.O.; Bamgbose, O.; Arowolo, T.A.; Adetunji, M.T. Utilization of biomaterials as adsorbents for heavy metals removal from aqueous matrices. Sci. Res. Essays 2010, 5, 1780–1787. [Google Scholar]
- EL-Naggar, A.H.; EL-Sheekh, M.M. Abolishing cadmium toxicity in Chlorella vulgaris by ascorbic acid, calcium, glucose and reduced glutathione. Environ. Pollut. 1998, 101, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.K.; Choudhary, K.K.; Kumar, M.; Negi, A.; Rai, H. Bioremediation and cyanobacteria: An overview. Bionano Front. 2012, 9, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shashirekha, S.; Uma, L.; Subramanian, G. Phenol degradation by the marine cyanobacterium Phormidium valderianum BDU 30501. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1997, 19, 130–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parikh, A.; Madamwar, D. Textile dye decolorization using cyanobacteria. Biotechnol. Lett. 2005, 27, 323–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayazıt, G.; Tastan, B.E.; Gül, Ü.D. Biosorption, Isotherm and Kinetic Properties of Common Textile Dye by Phormidium animale. Glob. NEST J. 2019, 22, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirooka, T.; Akiyama, Y.; Tsuji, N.; Nakamura, T.; Nagase, H.; Hirata, K.; Miyamoto, K. Removal of hazardous phenols by microalgae under photoautotrophic conditions. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2003, 95, 200–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, V.; Joseph, A. Microalgae in Petrochemical Effluent: Growth and Biosorption of Total Dissolved Solids. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2001, 66, 522–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsdotter, K. Wastewater treatment with microalgae—A literature review. Vatten 2006, 62, 31–38. [Google Scholar]
- Vijayalakshmi, K.; Latha, S.; Rose, M.; Sudha, P. Industrial Applications of Alginate. In Industrial Applications of Marine Biopolymers; CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; pp. 545–575. [Google Scholar]
- Adam, S.; Kumar, P.S.; Santhanam, P.S.; Kumar, S.D.; Prabhavathi, P. Bioremediation of Tannery Wastewater Using Immobilized Marine Microalga Tetraselmis sp.: Experimental Studies and Pseudo-Second Order Kinetics. J. Mar. Biol. Oceanogr. 2015, 4, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emparan, Q.; Harun, R.; Sing Jye, Y. Efficiency of pollutants removal in treated palm oil mill effluent (TPOME) using different concentrations of sodium alginate-immobilized Nannochloropsis sp. cells. Int. J. Phytoremediat. 2021, 23, 454–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, C.; Naseera, K.; Ram, A.; Meena, R.M.; Ramaiah, N. Bioremediation of tannery wastewater by a salt-tolerant strain of Chlorella vulgaris. J. Appl. Phycol. 2017, 29, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellamatrice, P.M.; Silva-Stenico, M.E.; Moraes, L.A.; Fiore, M.F.; Monteiro, R.T. Degradation of textile dyes by cyanobacteria. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2017, 48, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Babu, B.; Wu, J.-T. Biodegradation of Phthalate Esters by Cyanobacteria. J. Phycol 2010, 46, 1106–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abed Raeid, M.M. Interaction between cyanobacteria and aerobic heterotrophic bacteria in the degradation of hydrocarbons. Int. Biodeter. Biodegr. 2010, 64, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, I.I.B. Biodegradability of Hydrocarbons by Cyanobacteria. J. Phycol. 2010, 46, 818–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagasathya, A.; Thajuddin, N. Decolourization of Paper Mill Effluent Using Hypersaline Cyanobacterium. Res. J. Environ. Sci. 2008, 2, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghukumar, C.; Vipparty, V.; David, J.J.; Chandramohan, D. Degradation of crude oil by marine cyanobacteria. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2001, 57, 433–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaillan, F.; Gugger, M.; Saliot, A.; Coute, A.; Oudot, J. Role of cyanobacteria in the biodegradation of crude oil by a tropical cyanobacterial mat. Chemosphere 2006, 62, 1574–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safonova, E.; Kvitko, K.V.; Iankevitch, M.I.; Surgko, L.F.; Afti, I.A.; Reisser, W. Biotreatment of Industrial Wastewater by Selected Algal-Bacterial Consortia. Eng. Life Sci. 2004, 4, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sabagh, M.R.; Abd Eldaim, M.A.; Mahboub, D.H.; Abdel-Daim, M. Effects of Spirulina Platensis Algae on Growth Performance, Antioxidative Status and Blood Metabolites in Fattening Lambs. J. Agric. Sci. 2014, 6, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cohen, Y. Bioremediation of oil by marine microbial mats. Int. Microbiol. 2002, 5, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sen, S.; Karn, S.K. Cyanobacteria: The Eco-friendly Tool for the Treatment of Industrial Wastewater. In Environmental Contaminants: Ecological Implications and Management; Bharagava, R.N., Ed.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- El-Sheekh, M.M.; Ghareib, M.M.; Abou El-Souod, G.W. Biodegradation of Phenolic and Polycyclic Aromatic Compounds by Some Algae and Cyanobacteria. J. Bioremediat. Biodegrad. 2012, 3, 1000133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, B.E. Degradation of phenolic compounds by fresh-water algae. Plant Sci. Lett. 1977, 8, 213–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caceres, T.P.; Megharaj, M.; Naidu, R. Biodegradation of the pesticide fenamiphos by ten different species of green algae and cyanobacteria. Curr. Microbiol. 2008, 57, 643–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, G.; Sekar, S.; Sampoornam, S. Biodegradation and utilization of organophosphorus pesticides by cyanobacteria. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 1994, 33, 129–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunakumara, K.K.I.U.; Walpola, B.C.; Yoon, M.H. Metabolism and degradation of glyphosate in aquatic cyanobacteria: A review. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2013, 7, 4084–4090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuritz, T.; Wolk, C.P. Use of Filamentous Cyanobacteria for Biodegradation of Organic Pollutants. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1995, 61, 234–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fumin, M.; James, P.E.; Gary, S.S. Chapter 21. Genetically Engineered Microorganisms and Bioremediation; Wiley: Knoxville, TN, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Madanat, O.; AlSalka, Y.; Ramadan, W.; Bahnemann, D.W. TiO2 Photocatalysis for the Transformation of Aromatic Water Pollutants into Fuels. Catalysts 2021, 11, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crini, G.; Lichtfouse, E. Advantages and disadvantages of techniques used for wastewater treatment. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2018, 17, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stott, R. Fate and Behaviour of Parasites in Wastewater Treatment Systems. In Handbook of Water and Wastewater Microbiology; Academic Press: London, UK, 2003; pp. 491–521. [Google Scholar]
- Li, A.; Kosonen, R.; Hagström, K. Industrial Ventilation Design Method; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 19–37. [Google Scholar]
- Karthik, V.; Saravanan, K.; Bharathi, P.; Dharanya, V.; Meiaraj, C. An overview of treatments for the removal of textile dyes. J. Chem. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 7, 301–307. [Google Scholar]
- Pacheco, D.; Rocha, A.C.; Pereira, L.; Verdelhos, T. Microalgae Water Bioremediation: Trends and Hot Topics. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walter, U.; Beyer, M.; Klein, J.; Rehm, H.J. Degradation of pyrene by Rhodococcus sp. UW1. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1991, 34, 671–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usha, M.S.; Sanjay, M.K.; Gaddad, S.M.; Shivannavar, C.T. Degradation Of H-Acid By Free And Immobilized Cells Of Alcaligenes Latus. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2010, 41, 931–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kneifel, H.; Elmendorff, K.; Hegewald, E.; Soeder, C.J. Biotransformation of 1-naphthalenesulfonic acid by the green alga Scenedesmus obliquus. Arch. Microbiol. 1997, 167, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnoor, J.L.; Licht, L.A.; McCutcheon, S.C.; Wolfe, N.L.; Carreira, L.H. Phytoremediation of organic and nutrient contaminants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1995, 29, 318A–323A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmood, Q.; Mirza, N.; Shaheen, S. Phytoremediation Using Algae and Macrophytes. In Phytoremediation: Management of Environmental Contaminants; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 265–289. [Google Scholar]




| Pollutants | Algae Species | Organic Pollutants | Degradation Rate % | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dyes | Chlorella spp. | Pyrene | 78.71 | [63] |
| Chlorella vulgaris | Azo dye | ≥90 | [64] | |
| Sc. Bijugatus | Tartrazine | 57 | [65] | |
| Volvox aureus | Basic cationic (10 ppm) | 82 | [66] | |
| Hydrocarbon | Chlorella spp. | Pyrene | 78.71 | [63] |
| Sc. Obliquus-bacterial consortium | Oil wastes | 84.2 | [67] | |
| Phenols | Ankistrodesmus braunii and Sc. Quadricauda | phenols | 70 | [68] |
| Pesticides | Nannochloris oculata | Lindane (0.1 mg/L) | 73 | [68] |
| Chlamydomonas reinhardtii | Isoproturon (50 µg/L) | 15.1 | [69] |
| Pollutants | Algae Species | Organic Pollutants | Degradation Rate % | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dyes | Nostoc linckia HA 46 | Toxic reactive red 198 dye | 94 | [44] |
| N. muscorum | Tartrazine | 70 | [65] | |
| Nostoc linckia | Azo dye | 81.97 | [66] | |
| Oscillatoria rubescens | Basic Fuchsin (5 ppm) | 94 | [66] | |
| Phormidium ceylanicum | Acid Red 97 | 89 | [127] | |
| Ph. animale | Remazol Black B (RBB) | 99.66 | [128] | |
| Chroococcus minutus | Amido Black 10B (100 mg L−1) | 55 | [127] | |
| Gloeocapsa pleurocapsoides | FF Sky Blue (100 mg L−1) | 90 | [127] | |
| Hydrocarbon | Prototheca zopfii | Saturated aliphatic hydrocarbons | 49 ±11 | [90] |
| Prototheca zopfii | Aromatic compounds | 26.5 ± 14.5 | [90] | |
| Oscillatoria sp. | Pyrene | 95 | [63] | |
| Phenol | Anabeana variabilis | O-nitrophenol (ONP) | 100 | [129] |
| Pesticides & herbicides | Oscillatoria quadripunctulata | Biocides | 40 | [130] |
| Disadvantages | Advantages | Process |
|---|---|---|
| Phycoremediation |
|
|
| Fungi and bacteria |
|
|
| Activated sludge |
|
|
| Chemical precipitation |
|
|
| UV/H2O2 |
|
|
| Electrochemical oxidation |
|
|
| Ozonation |
|
|
| TiO2 |
|
|
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Touliabah, H.E.-S.; El-Sheekh, M.M.; Ismail, M.M.; El-Kassas, H. A Review of Microalgae- and Cyanobacteria-Based Biodegradation of Organic Pollutants. Molecules 2022, 27, 1141. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27031141
Touliabah HE-S, El-Sheekh MM, Ismail MM, El-Kassas H. A Review of Microalgae- and Cyanobacteria-Based Biodegradation of Organic Pollutants. Molecules. 2022; 27(3):1141. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27031141
Chicago/Turabian StyleTouliabah, Hussein El-Sayed, Mostafa M. El-Sheekh, Mona M. Ismail, and Hala El-Kassas. 2022. "A Review of Microalgae- and Cyanobacteria-Based Biodegradation of Organic Pollutants" Molecules 27, no. 3: 1141. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27031141
APA StyleTouliabah, H. E. -S., El-Sheekh, M. M., Ismail, M. M., & El-Kassas, H. (2022). A Review of Microalgae- and Cyanobacteria-Based Biodegradation of Organic Pollutants. Molecules, 27(3), 1141. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27031141