Obtaining Aromatic Extracts from Portuguese Thymus mastichina L. by Hydrodistillation and Supercritical Fluid Extraction with CO2 as Potential Flavouring Additives for Food Applications
Abstract
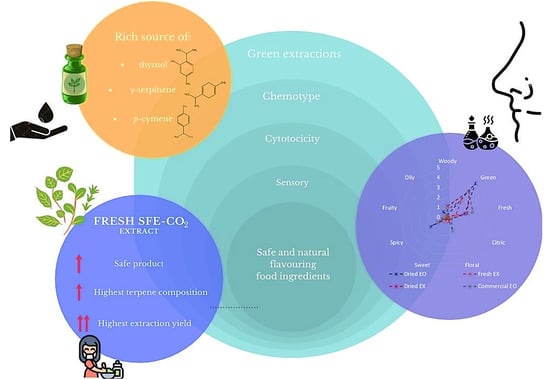
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Plant Material
2.3. Essential Oil and Hydrolate Isolation
2.4. SFE-CO2 T. mastichina L. Extraction
2.5. Volatile Composition Determined by GC-MS Assay
2.6. Odour Perception and Description of T. mastichina L. Volatile Compounds
2.6.1. Odour Detection Threshold (ODT)
2.6.2. Quantitative Descriptive Analysis (QDA)
2.7. Cytotoxicity Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Extraction Yields of T. mastichina L. Product
3.2. Chemical Composition of T. mastichina L. Product
3.3. Cytotoxicity Assay of T. mastichina L. Products
3.4. Sensory Odour Evaluation of T. mastichina L. Products
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nabavi, S.M.; Marchese, A.; Izadi, M.; Curti, V.; Daglia, M.; Nabavi, S.F. Plants belonging to the genus Thymus as antibacterial agents: From farm to pharmacy. Food Chem. 2015, 173, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghimi, R.; Ghaderi, L.; Rafati, H.; Aliahmadi, A.; McClements, D.J. Superior antibacterial activity of nanoemulsion of Thymus daenensis essential oil against E. coli. Food Chem. 2016, 194, 410–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tohidi, B.; Rahimmalek, M.; Trindade, H. Review on essential oil, extracts composition, molecular and phytochemical properties of Thymus species in Iran. Ind. Crops Prod. 2019, 134, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emami, Z.E.; Siadat, S.A.; Bakhshandeh, A.; Pirbalouti, A.G.; Hashemi, M.; Maggi, F.; Morshedloo, R.M. Application of combined fertilizers improves biomass, essential oil yield, aroma profile, and antioxidant properties of Thymus daenensis Celak. Ind. Crops Prod. 2018, 121, 434–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornari, T.; Vicente, G.; Vázquez, E.; García-Risco, M.R.; Reglero, G. Isolation of essential oil from different plants and herbs by supercritical fluid extraction. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1250, 34–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mancini, E.; Senatore, F.; Del Monte, D.; De Martino, L.; Grulova, D.; Scognamiglio, M.; Snoussi, M.; De Feo, V. Studies on chemical composition, antimicrobial and antioxidant activities of five Thymus vulgaris L. essential oils. Molecules 2015, 20, 12016–12028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morsy, N.F.S. Production of thymol rich extracts from ajwain (Carum copticum L.) and thyme (Thymus vulgaris L.) using supercritical CO2. Ind. Crops Prod. 2020, 145, 112072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tohidi, B.; Rahimmalek, M.; Arzani, A. Essential oil composition, total phenolic, flavonoid contents, and antioxidant activity of Thymus species collected from different regions of Iran. Food Chem. 2017, 220, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, M.A.; Rodrigues, A. Coupled extraction and dynamic headspace techniques for the characterization of essential oil and aroma fingerprint of Thymus species. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 9875–9882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendif, H.; Adouni, K.; Miara, M.D.; Baranauskienė, R.; Kraujalis, P.; Venskutonis, P.R.; Nabavi, S.M.; Maggi, F. Essential oils (EOs), pressurized liquid extracts (PLE) and carbon dioxide supercritical fluid extracts (SFE-CO2) from Algerian Thymus munbyanus as valuable sources of antioxidants to be used on an industrial level. Food Chem. 2018, 260, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coelho, J.P.; Cristino, A.F.; Matos, P.G.; Rauter, A.P.; Nobre, B.P.; Mendes, R.L.; Barroso, J.G.; Mainar, A.; Urieta, J.S.; Fareleira, J.M.N.A.; et al. Extraction of volatile oil from aromatic plants with supercritical carbon dioxide: Experiments and modeling. Molecules 2012, 17, 10550–10573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, P.; Gonçalves, S.; Grosso, C.; Andrade, P.B.; Valentão, P.; Bernardo-Gil, M.G.; Romano, A. Chemical profiling and biological screening of Thymus lotocephalus extracts obtained by supercritical fluid extraction and hydrodistillation. Ind. Crops Prod. 2012, 36, 246–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Risco, M.R.; Vicente, G.; Reglero, G.; Fornari, T. Fractionation of thyme (Thymus vulgaris L.) by supercritical fluid extraction and chromatography. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2011, 55, 949–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Rocha, B.C.A.; Kawase, K.Y.F.; Coelho, G.L.V. Comparison of SPME and SFE for the Determination of Volatile Constituents in Thymus vulgaris L. Lamiaceae. IJENS 2014, 14, 35–43. [Google Scholar]
- Grosso, C.; Figueiredo, A.C.; Burillo, J.; Mainar, A.M.; Urieta, J.S.; Barroso, J.G.; Coelho, J.A.; Palavra, A.M. Composition and antioxidant activity of Thymus vulgaris volatiles: Comparison between supercritical fluid extraction and hydrodistillation. J. Sep. Sci. 2010, 33, 2211–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrović, N.V.; Petrović, S.S.; Džamić, A.M.; Ćirić, A.D.; Ristić, M.S.; Milovanović, S.L.; Petrović, S.D. Chemical composition, antioxidant and antimicrobial activity of Thymus praecox supercritical extracts. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2016, 110, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šojić, B.; Tomović, V.; Kocić-Tanackov, S.; Kovačević, D.B.; Putnik, P.; Mrkonjić, Ž.; Đurović, S.; Jokanović, M.; Ivić, M.; Škaljac, S.; et al. Supercritical extracts of wild thyme (Thymus serpyllum L.) by-product as natural antioxidants in ground pork patties. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 130, 109661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miguel, M.G.; Duarte, F.L.; Venâncio, F.; Tavares, R. Comparison of the main components of the essential oils from flowers and leaves of Thymus mastichina (L.) L. ssp. mastichina collected at cifferent regions of Portugal. J. Essent. Oil Res. 2004, 16, 323–327. [Google Scholar]
- Miguel, M.G.; Simões, M.; Figueiredo, A.C.; Barroso, J.G.; Pedro, L.G.; Carvalho, L. Composition and antioxidant activities of the essential oils of Thymus caespititius, Thymus camphoratus and Thymus mastichina. Food Chem. 2004, 86, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miguel, M.G.; Guerrero, C.; Rodrigues, H.; Brito, J.C.; Duarte, F.; Venâncio, F.; Tavares, R. Main components of the essential oils from wild Portuguese Thymus mastichina (L.) L. ssp. mastichina in different developmental stages or under culture conditions. J. Essent. Oil Res. 2004, 16, 111–114. [Google Scholar]
- Miguel, M.G.; Simões, M.; Figueiredo, A.C.; Barroso, J.M.G.; Pedro, L.G.; Carvalho, L.M. Evaluation of antioxidant activity of Thymbra capitata, Thymus mastichina and Thymus camphoratus essential oils. J. Food Lipids 2005, 12, 181–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salgueiro, L.R.; Vila, R.; Tomàs, X.; Cañigueral, S.; da Cunha, A.P.; Adzet, T. Composition and variability of the essential oils of Thymus species from section Mastichina from Portugal. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 1997, 25, 659–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, T.; Marinero, P.; Asensio-S.-Manzanera, M.C.; Asensio, C.; Herrero, B.; Pereira, J.A.; Ramalhosa, E. Antioxidant activity of twenty wild Spanish Thymus mastichina L. populations and its relation with their chemical composition. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 57, 412–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grosso, C.; Coelho, J.A.; Urieta, J.S.; Palavra, A.M.F.; Barroso, J.G. Herbicidal activity of volatiles from Coriander, Winter Savory, Cotton Lavender, and Thyme isolated by hydrodistillation and supercritical fluid extraction. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 11007–11013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rassem, H.H.A.; Nour, A.H.; Yunus, R.M. Techniques for extraction of essential oils from plants: A review. Aust. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2016, 10, 117–127. [Google Scholar]
- COE. European Directorate for the Quality of Medicines, 6th ed.; European Pharmacopoeia: Strasbourg, France, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Gomes, P.B.; Mata, V.G.; Rodrigues, A.E. Production of rose geranium oil using supercritical fluid extraction. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2007, 41, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zellner, B.d.A.; Bicchi, C.; Dugo, P.; Rubiolo, P.; Dugo, G.; Mondello, L. Linear retention indices in gas chromatographic analysis: A review. Flavour Fragr. J. 2008, 23, 297–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Organization for Standardization. 8586:2012. Sensory Analysis—General Guidelines for the Selection, Training and Monitoring of Selected Assessors and Expert Sensory Assessors, 12th ed.; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012; p. 28. [Google Scholar]
- International Organization for Standardization. 13301:2018. Sensory Analysis—Methodology—General Guidance for Measuring Odour, Flavour and Taste Detection Thresholds by a Three-Alternative Forced-Choice (3-AFC) Procedure, 4th ed.; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018; p. 28. [Google Scholar]
- International Organization for Standardization. 11035:1994. Sensory Analysis—Identification and Selection of Descriptors for Establishing a Sensory Profile by a Multidimensional Approach, 12th ed.; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1994; p. 26. [Google Scholar]
- Barros, L.; Pereira, E.; Calhelha, R.C.; Dueñas, M.; Carvalho, A.M.; Santos-Buelga, C.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R. Bioactivity and chemical characterization in hydrophilic and lipophilic compounds of Chenopodium ambrosioides L. J. Funct. Foods 2013, 5, 1732–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, J.; Ortuño, C.; Benedito, J.; Bon, J. Optimization of the antioxidant capacity of thyme (Thymus vulgaris L.) extracts: Management of the drying process. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 46, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balachandran, S.; Kentish, S.E.; Mawson, R. The effects of both preparation method and season on the supercritical extraction of ginger. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2006, 48, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrés, M.F.; González-Coloma, A.; Muñoz, R.; De la Peña, F.; Julio, L.F.; Burillo, J. Nematicidal potential of hydrolates from the semi industrial vapor-pressure extraction of Spanish aromatic plants. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 29834–29840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Ma, S.; Niu, Y.; Chen, F.; Yu, D. Characterization of odour-active compounds of sweet orange essential oils of different regions by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry, gas chromatography-olfactometry and their correlation with sensory attributes. Flavour Fragr. J. 2016, 31, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Good Scents Company. Available online: https://www.thegoodscentscompany.com/ (accessed on 15 September 2021).
- Miyazaki, T.; Plotto, A.; Baldwin, E.A.; Reyes-De-Corcuera, J.I.; Gmitter, F.G., Jr. Aroma characterization of tangerine hybrids by gas-chromatography–olfactometry and sensory evaluation. J. Sci. Food. Agric. 2012, 92, 727–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, S.; Oestdal, H.; Skibsted, L.H.; Larsen, E.; Thybo, A.K. Chemical changes in wheat pan bread during storage and how it affects the sensory perception of aroma, flavour, and taste. J. Cereal Sci. 2011, 53, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birch, A.N.; Petersen, M.A.; Hansen, Å.S. The aroma profile of wheat bread crumb influenced by yeast concentration and fermentation temperature. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 50, 480–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Xu, F.; Wu, X.; Hu, W.; Chang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Chen, J.; Liu, C. GC-MS, GC-O and OAV analyses of key aroma compounds in Jiaozi Steamed Bread. GOST 2020, 3, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paravisini, L.; Sneddon, K.A.; Peterson, D.G. Comparison of the aroma profiles of intermediate wheatgrass and wheat bread crusts. Molecules 2019, 24, 2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Caputi, L.; Aprea, E. Use of terpenoids as natural flavouring compounds in food industry. Recent Pat. Food Nutr. Agric. 2011, 3, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelli, W.; Bahri, F.; Romane, A.; Höferl, M.; Wanner, J.; Schmidt, E.; Jirovetz, L. Chemical composition and anti-inflammatory activity of Algerian Thymus vulgaris essential oil. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2017, 12, 611–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shabnum, S.; Wagay, M.G. Essential oil composition of Thymus vulgaris L. and their uses. J. Res. Dev. 2011, 11, 83–94. [Google Scholar]
- Borugă, O.; Jianu, C.; Mişcă, C.; Goleţ, I.; Gruia, A.T.; Horhat, F.G. Thymus vulgaris essential oil: Chemical composition and antimicrobial activity. J. Med. Life 2014, 7, 56–60. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Crocoll, C.; Asbach, J.; Novak, J.; Gershenzon, J.; Degenhardt, J. Terpene synthases of oregano (Origanum vulgare L.) and their roles in the pathway and regulation of terpene biosynthesis. Plant Mol. Biol. 2010, 73, 587–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, A.S.; Schimmel, J.; Lukas, B.; Novak, J.; Barroso, J.G.; Figueiredo, A.C.; Pedro, L.G.; Degenhardt, J.; Trindade, H. Genomic characterization, molecular cloning and expression analysis of two terpene synthases from Thymus caespititius (Lamiaceae). Planta 2013, 238, 191–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolić, M.; Glamočlija, J.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R.; Calhelha, R.C.; Fernandes, Â.; Marković, T.; Marković, D.; Giweli, A.; Soković, M. Chemical composition, antimicrobial, antioxidant and antitumor activity of Thymus serpyllum L.; Thymus algeriensis Boiss. and Reut and Thymus vulgaris L. essential oils. Ind. Crops Prod. 2014, 52, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, M.A.; Rodríguez, O.; Mota, F.L.; Macedo, E.A.; Rodrigues, A.E. Evaluation of Group-Contribution Methods to Predict VLE and Odor Intensity of Fragrances. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 9390–9402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonmezdag, A.S.; Kelebek, H.; Selli, S. Characterization of aroma-active and phenolic profiles of wild thyme (Thymus serpyllum) by GC-MS-Olfactometry and LC-ESI-MS/MS. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 53, 1957–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benomari, F.Z.; Djabou, N.; Moumani, M.; Hassani, F.; Muselli, A.; Costa, J. Chemical variability of essential oils of three subspecies of Thymus munbyanus Boiss. & Reut. from Western Algeria. J. Essent. Oil Res. 2020, 32, 474–484. [Google Scholar]



| Species | Origin | Yields | Main Volatile Compounds | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HD | SFE-CO2 | ||||
| T. fontqueri, T. x. citriodorus and T. zygis subsp. gracilis | Portugal | HD (0.67 to 1.26%) and SFE-CO2 (<0.05 to 0.77%) | T. fontqueri: carvacrol (60.3%), γ-terpinene (25.8%) and p-cymene (6.3%); T. x. citriodorus: geraniol (76.1%), geranial (5.3%) and neral (3.7%) and T. zygis: thymol (41.0%), p-cymene (16.0%), and γ-terpinene (10.0%) | T. fontqueri: p-cymene (41.0%), γ-terpinene (25.8%) and carvacrol (2.6%); T. x. citriodorus: geraniol (66.5%), geranial (8.6%) and thymol (7.6%) and T. zygis: thymol (33.7%), p-cymene (10.5%) and carvacrol (8.7%) | [9] |
| T. munbyanus subsp. coloratus and T. munbyanus subsp. munyanus | Algeria | HD (0.09 to 0.11%) and SFE-CO2 (0.4%) | Camphor (11.7%), geranyl acetate (6.3%) and β-terpinyl acetate (5.1%) | E-nerolidol (2.0 to 13.7%), 4-terpineol (0.2 to 10.6%) and camphor (1.1. to 7.6%) | [10] |
| T. lotocephalus | Portugal | HD (0.30%) and SFE-CO2 (2.24 to 7.76%) | Linalool (10.4%), camphor (8.0%) and caryophyllene oxide (8.1%) | Camphor (1.2 to 7.9%), borneol (6.1 to 7.5%) and cis-linalool oxide (0.2 to 7.2%) | [12] |
| T. vulgaris L. | Egypt | HD (1.00%) and SFE-CO2 (0.32 to 1.28%) | p-cymene (35.7%), thymol (33.2 %), and γ-terpinene (9.5%) | Thymol (45.2 to 82.6%), fenipentol (n.d. to 8.48%) and phytol isomer (n.d. to 7.2%) | [7] |
| Portugal | ~0.023 kg/kg | Thymol (41.6%), p-cymene (28.9%) and γ-terpinene (5.1%) | Thymol (36.3%), p-cymene (24.4%) and thymoquinone (6.2%) | [11] | |
| Spain | 0.8 to 1.1% | Thymol (35.4 to 41.6%), p-cymene (28.9 to 34.8%) and γ-terpinene (5.1 to 7.0%) | Thymol (19.5 to 40.8%), p-cymene (10.0 to 42.6%) and γ-terpinene (0.8 to 6.9%) | [15] | |
| Spain | - | Thymol (35.4%), p-cymene (34.7%) and γ-terpinene (7.0%) | Thymol (36.8%), p-cymene (28.6%) and γ-terpinene (4.1%) | [24] | |
| No | Compound | LRI a | FR | DR | Sensory Descriptors | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RT (min) | EX | EO | HY | EX | EO | HY | ||||||||||
| 1 | α-Thujene | 926 | 5988 | tr | - | 1.8 | 0.2 | - | - | 2.0 | 0.1 | 2.0 | 0.1 | - | - | pine earthy, turpentine, fresh, sweet and woody [36,37] |
| 2 | α-Pinene | 933 | 6140 | 0.6 | 0.1 | 0.6 | 0.0 | - | - | 1.5 | 0.0 | 1.1 | 0.0 | - | - | herbaceous and green [9] |
| 3 | Camphene | 949 | 6480 | tr | - | tr | - | - | - | 0.3 | 0.0 | 0.4 | - | - | - | camphor, woody and herbal [36,37] |
| 4 | Sabinene | 972 | 6963 | tr | - | tr | - | - | - | - | - | tr | - | - | - | pine, turpentine, woody, terpenic, spicy and citrus [36,37] |
| 5 | β-Pinene | 977 | 7067 | - | - | tr | - | - | - | - | - | tr | - | - | - | green, piney, woody and green [37,38] |
| 6 | Amyl vinyl carbinol | 980 | 7128 | 0.9 | 0.1 | tr | - | - | - | 0.5 | 0.0 | 0.3 | 0.0 | - | - | mushroom, earthy, green and herbs [39,40,41,42] |
| 7 | β-Myrcene | 988 | 7313 | 1.0 | 0.1 | 1.8 | 0.0 | - | - | 2.0 | 0.0 | 2.7 | 0.2 | - | - | herbaceous, woody and floral [9] |
| 8 | 3-octanol | 997 | 7490 | - | - | tr | - | - | - | - | - | tr | - | - | - | earthy, mushroom and herbal [37] |
| 9 | α-Phellandrene | 1006 | 7681 | - | - | tr | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | citrus, herbaceous and terpenic [37] |
| 10 | 3-Carene | 1016 | 7908 | 1.3 | 0.5 | 2.8 | 0.0 | - | - | 2.5 | 0.1 | 4.14 | 0.3 | 8.7 | 0.1 | citrus and sweet [9,37] |
| 11 | p-Cymene | 1023 | 8067 | 4.6 | 0.5 | 10.3 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 6.5 | 0.2 | 17.6 | 1.1 | 34.2 | 0.9 | green, fresh, rubber, terpenic, woody and spicy [37,38] |
| 12 | d-Limonene | 1029 | 8180 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 0.4 | 0.1 | - | - | 0.2 | 0.0 | 0.4 | 0.0 | - | - | citrus, fresh and sweet [36,37] |
| 13 | Eucalyptol | 1031 | 8239 | 1.1 | 0.2 | 0.9 | 0.1 | - | - | 1.2 | 0.0 | 0.5 | 0.0 | - | - | woody, citrus, green, herbaceous and spicy [9,38,43] |
| 14 | β-cis-Ocimene | 1047 | 8580 | - | - | tr | - | - | - | - | - | tr | - | - | - | green and woody [9] |
| 15 | γ-Terpinene | 1058 | 8809 | 9.1 | 0.4 | 30.6 | 0.7 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 22.4 | 0.8 | 35.5 | 1.7 | 45.6 | 0.7 | herbaceous, woody, piney and fruity [37,38] |
| 16 | β-Terpineol | 1070 | 9062 | 1.8 | 0.4 | tr | - | - | - | 1.5 | 0.8 | 0.2 | 0.0 | - | - | woody, pungent and earthy [37] |
| 17 | Sabinene hydrate | 1071 | 9090 | - | - | tr | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | herbaceous, minty and oriental [9,37] |
| 18 | Terpinolene | 1086 | 9414 | - | - | tr | - | - | - | - | - | tr | - | - | - | herbaceous, woody and green [9] |
| 19 | β-Linalool | 1099 | 9695 | 1.0 | 0.2 | 1.3 | 0.0 | - | - | 1.0 | 0.1 | 1.9 | 0.2 | - | - | floral, lavender, citrus, woody and green [36,37,38] |
| 20 | Camphor | 1147 | 10.719 | 0.4 | 0.2 | - | - | - | - | 0.4 | 0.1 | - | - | - | - | camphoraceous and herbal [37] |
| 21 | Borneol | 1172 | 11.263 | 0.4 | 0.1 | tr | - | - | - | 0.7 | 0.0 | tr | - | - | - | herbaceous, oriental and woody [9] |
| 22 | 4-Terpineol | 1180 | 11.444 | 0.4 | 0.1 | 1.4 | 0.1 | - | - | 0.2 | 0.0 | 0.7 | 0.1 | - | - | spicy, woody and oriental [9,37] |
| 23 | α-Terpineol | 1194 | 11.743 | 0.1 | 0.0 | tr | - | - | - | - | - | tr | - | - | - | terpenic, pine and woody [37] |
| 24 | trans-Dihydrocarvone | 1201 | 11.900 | - | - | tr | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 25 | S-Verbenone | 1206 | 11.993 | 0.4 | 0.1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | camphoreous [37] |
| 26 | β-Citral | 1240 | 12.691 | - | - | tr | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | citrus [9,37] |
| 27 | Unknown | 1247 | 12.827 | 0.8 | 0.3 | - | - | - | - | 0.3 | 0.1 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 28 | Nerol | 1249 | 12.873 | - | - | tr | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | floral, citrus and green [9] |
| 29 | Unknown | 1264 | 13.168 | - | - | - | - | 0.3 | 0.0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 30 | α-Citral | 1277 | 13.440 | - | - | tr | - | - | - | - | - | tr | - | - | - | citrus [9,37] |
| 31 | Bornyl acetate | 1284 | 13.574 | 0.5 | 0.1 | - | - | - | - | 0.5 | 0.0 | - | - | - | - | camphor, woody, pine, balsamic, herbal and spicy [37] |
| 32 | Thymol | 1290 | 13.700 | 72.4 | 28.9 | 48.2 | 3.1 | 98.6 | 1.6 | 52.7 | 1.4 | 31.8 | 2.6 | - | - | herbaceous [9,37] |
| 33 | Carvacrol | 1298 | 13.857 | 1.0 | 0.6 | tr | - | 0.5 | 0.1 | 0.9 | 0.1 | tr | - | 11.5 | 1.3 | herbaceous and woody [9] |
| 34 | Elixene | 1334 | 14.546 | - | - | tr | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 35 | Thymol acetate | 1344 | 14.750 | 0.4 | 0.0 | tr | - | - | - | 0.5 | 0.1 | tr | - | - | - | thymol, sweet and balsamic [37] |
| 36 | β-Caryophyllene | 1422 | 16.220 | 0.8 | 0.2 | - | - | - | - | 2.1 | 0.1 | 0.7 | 0.1 | - | - | spicy, woody and sweet [9,37] |
| 37 | Copaene | 1433 | 16.410 | - | - | tr | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | woody, spicy and honey [37] |
| 38 | Citronellyl propionate | 1438 | 16.505 | - | - | tr | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | floral and green [37] |
| 39 | β-Farnesene | 1454 | 16.785 | - | - | tr | - | - | - | - | - | tr | - | - | - | woody, citrus and herbal [37] |
| 40 | α-Humulene | 1458 | 16.872 | - | - | tr | - | - | - | - | - | tr | - | - | - | woody [9,37] |
| 41 | Germacrene D | 1483 | 17.317 | 0.8 | 0.1 | tr | - | - | - | 0.2 | 0.0 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 42 | Germacrene B | 1498 | 17.595 | - | - | tr | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | woody, earthy and spicy [37] |
| 43 | Caryophylene oxide | 1585 | 19.088 | - | - | tr | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | woody and herbaceous [9] |
| 44 | γ-Eudesmol | 1612 | 19.725 | - | - | tr | - | - | - | - | - | tr | - | - | - | - |
| 45 | α-Cadinol | 1630 | 20.292 | - | - | tr | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | herbaceous and woody [9,37] | |
| 46 | Isopropyl myristate | 1723 | 22.850 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | tr | - | - | - | - |
| 47 | Isopropyl palmitate | 1927 | 26.102 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | tr | - | - | - | - |
| Identified total | 90.2 | 100.0 | 99.7 | 99.8 | 100.0 | 100.0 | ||||||||||
| Compound | Mass (μg Compound·g Plant−1 (DW)) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FR | DR | |||||
| EX | EO | HY | EX | EO | HY | |
| α-Pinene | 15.9 ± 2.7 b | 8.6 ± 0.0 c | - | 6.5 ± 0.0 c | 65.0 ± 0.0 a | - |
| Camphor | 23.8 ± 11.6 a | - | - | 4.8 ± 0.7 b | - | - |
| Eucalyptol | 34.3 ± 7.4 b | 18.6 ± 1.1 c | - | 7.0 ± 0.1 d | 123.8 ± 9.7 a | - |
| γ-Terpinene | 87.2 ± 3.8 b | 64.1 ± 1.4 c | 25.1 ± 9.9 d | 111.5 ± 3.9 b | 609.4 ± 28.3 a | 2.6 ± 0.0 e |
| p-Cymene | 49.5 ± 5.1 b | 29.0 ± 0.7 c | 14.8 ± 2.6 d | 55.6 ± 1.5 b | 337.0 ± 20.3 a | 1.7 ± 0.0 e |
| S-Verbenone | 61.8 ± 21.1 | - | - | - | - | - |
| Thymol | 1511.3 ± 62.3 b | 404.4 ± 25.9 c | 2389.2 ± 39.2 a | 282.1 ± 7.5 c | 2565.5 ± 28.7 a | - |
| Total | 1783.8 | 524.8 | 2429.1 | 467.4 | 3700.7 | 4.3 |
| Test | FR (µg·mL−1) | DR (µg·mL−1) | Commercial EO Standard | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EX | EO | HY | EX | EO | HY | (µg·mL−1) | |
| Vero cells (GI50) | 235 ± 7 b | 122 ± 12 c | >400 a | 271 ± 24 b | 65 ± 1 c | >400 a | 83.5 ± 0.1 c |
| ODT value | 6.3 × 10−4 a | - | - | 5.0 × 10−3 a | 3.0 × 10−4 a | - | 1.0 × 10−4 a |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kessler, J.C.; Vieira, V.A.; Martins, I.M.; Manrique, Y.A.; Afonso, A.; Ferreira, P.; Mandim, F.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R.; Barros, L.; Rodrigues, A.E.; et al. Obtaining Aromatic Extracts from Portuguese Thymus mastichina L. by Hydrodistillation and Supercritical Fluid Extraction with CO2 as Potential Flavouring Additives for Food Applications. Molecules 2022, 27, 694. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27030694
Kessler JC, Vieira VA, Martins IM, Manrique YA, Afonso A, Ferreira P, Mandim F, Ferreira ICFR, Barros L, Rodrigues AE, et al. Obtaining Aromatic Extracts from Portuguese Thymus mastichina L. by Hydrodistillation and Supercritical Fluid Extraction with CO2 as Potential Flavouring Additives for Food Applications. Molecules. 2022; 27(3):694. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27030694
Chicago/Turabian StyleKessler, Júlia C., Vanessa A. Vieira, Isabel M. Martins, Yaidelin A. Manrique, Andreia Afonso, Patrícia Ferreira, Filipa Mandim, Isabel C. F. R. Ferreira, Lillian Barros, Alírio E. Rodrigues, and et al. 2022. "Obtaining Aromatic Extracts from Portuguese Thymus mastichina L. by Hydrodistillation and Supercritical Fluid Extraction with CO2 as Potential Flavouring Additives for Food Applications" Molecules 27, no. 3: 694. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27030694
APA StyleKessler, J. C., Vieira, V. A., Martins, I. M., Manrique, Y. A., Afonso, A., Ferreira, P., Mandim, F., Ferreira, I. C. F. R., Barros, L., Rodrigues, A. E., & Dias, M. M. (2022). Obtaining Aromatic Extracts from Portuguese Thymus mastichina L. by Hydrodistillation and Supercritical Fluid Extraction with CO2 as Potential Flavouring Additives for Food Applications. Molecules, 27(3), 694. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27030694