Induction of Liver Size Reduction in Zebrafish Larvae by the Emerging Synthetic Cannabinoid 4F-MDMB-BINACA and Its Impact on Drug Metabolism
Abstract
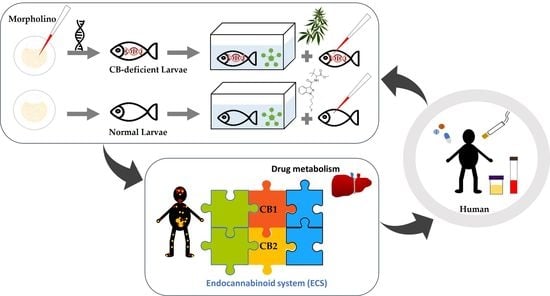
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Zebrafish Larvae Produce an Authentic Spectrum of 4F-MDMB-BINACA Metabolites
2.2. Spatial Distribution of 4F-MDMB-BINACA and Its Metabolites in Zebrafish Larvae
2.3. Differences in the Metabolism of 4F-MDMB-BINACA and 7′N-5F-ADB in Zebrafish Larvae and Influence of Cannabinoid Receptor Function on Drug Metabolism
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Other Materials
3.2. Zebrafish Maintenance and Embryo Collection
3.3. Drug Treatment of Zebrafish Larvae via Medium Exposure
3.4. Drug Treatment of Zebrafish Larvae via Microinjections into Different Compartments
3.5. Gene Knockdown of Cannabinoid Receptor Type 1 and Type 2 via Microinjection of Morpholino Oligonucleotides in Zebrafish Embryos
3.6. Measurement of the Fluorescent Liver Size in a Transgenic Zebrafish Larva
3.7. Zebrafish Sample Preparation and Metabolite Analysis by LC-HRMS/MS
3.8. Mass Spectrometry Image Analysis of Zebrafish Larva by MALDI-FT-ICR
4. Summary and Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Cassar, S.; Adatto, I.; Freeman, J.L.; Gamse, J.T.; Iturria, I.; Lawrence, C.; Muriana, A.; Peterson, R.T.; van Cruchten, S.; Zon, L.I. Use of Zebrafish in Drug Discovery Toxicology. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2020, 33, 95–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Waring, M.J.; Arrowsmith, J.; Leach, A.R.; Leeson, P.D.; Mandrell, S.; Owen, R.M.; Pairaudeau, G.; Pennie, W.D.; Pickett, S.D.; Wang, J.; et al. An analysis of the attrition of drug candidates from four major pharmaceutical companies. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2015, 14, 475–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blomme, E.A.G.; Will, Y. Toxicology Strategies for Drug Discovery: Present and Future. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2016, 29, 473–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swinney, D.C.; Anthony, J. How were new medicines discovered? Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2011, 10, 507–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacRae, C.A.; Peterson, R.T. Zebrafish as tools for drug discovery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2015, 14, 721–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellis, L. Zebrafish as a High-Throughput In Vivo Model for Testing the Bioactivity of Cannabinoids. In Recent Advances in Cannabinoid Research; Costain, W.J., Laprairie, R.B., Eds.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019; ISBN 978-1-83880-151-9. [Google Scholar]
- Katoch, S.; Patial, V. Zebrafish: An emerging model system to study liver diseases and related drug discovery. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2021, 41, 33–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goessling, W.; Sadler, K.C. Zebrafish: An important tool for liver disease research. Gastroenterology 2015, 149, 1361–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chakraborty, C.; Hsu, C.H.; Wen, Z.H.; Lin, C.S.; Agoramoorthy, G. Zebrafish: A Complete Animal Model for In Vivo Drug Discovery and Development. Curr. Drug Metab. 2009, 10, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hill, A. Zebrafish in Drug Discovery: Safety Assessment. In Drug Discovery and Evaluation: Safety and Pharmacokinetic Assays; Vogel, H.G., Maas, J., Hock, F.J., Mayer, D., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 605–629. ISBN 978-3-642-25239-6. [Google Scholar]
- Cutler, C.; Multani, P.; Robbins, D.; Kim, H.T.; Le, T.; Hoggatt, J.; Pelus, L.M.; Desponts, C.; Chen, Y.-B.; Rezner, B.; et al. Prostaglandin-modulated umbilical cord blood hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Blood 2013, 122, 3074–3081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; March, M.E.; Gutierrez-Uzquiza, A.; Kao, C.; Seiler, C.; Pinto, E.; Matsuoka, L.S.; Battig, M.R.; Bhoj, E.J.; Wenger, T.L.; et al. ARAF recurrent mutation causes central conducting lymphatic anomaly treatable with a MEK inhibitor. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1116–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandelbaum, J.; Shestopalov, I.A.; Henderson, R.E.; Chau, N.G.; Knoechel, B.; Wick, M.J.; Zon, L.I. Zebrafish blastomere screen identifies retinoic acid suppression of MYB in adenoid cystic carcinoma. J. Exp. Med. 2018, 215, 2673–2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- North, T.E.; Goessling, W.; Walkley, C.R.; Lengerke, C.; Kopani, K.R.; Lord, A.M.; Weber, G.J.; Bowman, T.V.; Jang, I.-H.; Grosser, T.; et al. Prostaglandin E2 regulates vertebrate haematopoietic stem cell homeostasis. Nature 2007, 447, 1007–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryals, M.; Morell, R.J.; Martin, D.; Boger, E.T.; Wu, P.; Raible, D.W.; Cunningham, L.L. The Inner Ear Heat Shock Transcriptional Signature Identifies Compounds That Protect Against Aminoglycoside Ototoxicity. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- White, R.M.; Cech, J.; Ratanasirintrawoot, S.; Lin, C.Y.; Rahl, P.B.; Burke, C.J.; Langdon, E.; Tomlinson, M.L.; Mosher, J.; Kaufman, C.; et al. DHODH modulates transcriptional elongation in the neural crest and melanoma. Nature 2011, 471, 518–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, P.B.; Hong, C.C.; Sachidanandan, C.; Babitt, J.L.; Deng, D.Y.; Hoyng, S.A.; Lin, H.Y.; Bloch, K.D.; Peterson, R.T. Dorsomorphin inhibits BMP signals required for embryogenesis and iron metabolism. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2008, 4, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poon, K.L.; Wang, X.; Ng, A.S.; Goh, W.H.; McGinnis, C.; Fowler, S.; Carney, T.J.; Wang, H.; Ingham, P.W. Humanizing the zebrafish liver shifts drug metabolic profiles and improves pharmacokinetics of CYP3A4 substrates. Arch. Toxicol. 2017, 91, 1187–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, X.; Huestis, M.A. New Synthetic Cannabinoids Metabolism and Strategies to Best Identify Optimal Marker Metabolites. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Wijk, R.C.; Krekels, E.H.J.; Hankemeier, T.; Spaink, H.P.; van der Graaf, P.H. Systems pharmacology of hepatic metabolism in zebrafish larvae. Drug Discov. Today Dis. Models 2016, 22, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza Anselmo, C.; Sardela, V.F.; Matias, B.F.; de Carvalho, A.R.; de Sousa, V.P.; Pereira, H.M.G.; de Aquino Neto, F.R. Is zebrafish (Danio rerio) a tool for human-like metabolism study? Drug Test. Anal. 2017, 9, 1685–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jones, H.S.; Trollope, H.T.; Hutchinson, T.H.; Panter, G.H.; Chipman, J.K. Metabolism of ibuprofen in zebrafish larvae. Xenobiotica 2012, 42, 1069–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brox, S.; Seiwert, B.; Haase, N.; Küster, E.; Reemtsma, T. Metabolism of clofibric acid in zebrafish embryos (Danio rerio) as determined by liquid chromatography-high resolution-mass spectrometry. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2016, 185–186, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantae, V.; Krekels, E.H.J.; Ordas, A.; González, O.; van Wijk, R.C.; Harms, A.C.; Racz, P.I.; van der Graaf, P.H.; Spaink, H.P.; Hankemeier, T. Pharmacokinetic Modeling of Paracetamol Uptake and Clearance in Zebrafish Larvae: Expanding the Allometric Scale in Vertebrates with Five Orders of Magnitude. Zebrafish 2016, 13, 504–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Richter, L.H.J.; Herrmann, J.; Andreas, A.; Park, Y.M.; Wagmann, L.; Flockerzi, V.; Müller, R.; Meyer, M.R. Tools for studying the metabolism of new psychoactive substances for toxicological screening purposes—A comparative study using pooled human liver S9, HepaRG cells, and zebrafish larvae. Toxicol. Lett. 2019, 305, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gampfer, T.M.; Wagmann, L.; Park, Y.M.; Cannaert, A.; Herrmann, J.; Fischmann, S.; Westphal, F.; Müller, R.; Stove, C.P.; Meyer, M.R. Toxicokinetics and toxicodynamics of the fentanyl homologs cyclopropanoyl-1-benzyl-4′-fluoro-4-anilinopiperidine and furanoyl-1-benzyl-4-anilinopiperidine. Arch. Toxicol. 2020, 94, 2009–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wagmann, L.; Frankenfeld, F.; Park, Y.M.; Herrmann, J.; Fischmann, S.; Westphal, F.; Müller, R.; Flockerzi, V.; Meyer, M.R. How to Study the Metabolism of New Psychoactive Substances for the Purpose of Toxicological Screenings—A Follow-Up Study Comparing Pooled Human Liver S9, HepaRG Cells, and Zebrafish Larvae. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.M.; Meyer, M.R.; Müller, R.; Herrmann, J. Drug Administration Routes Impact the Metabolism of a Synthetic Cannabinoid in the Zebrafish Larvae Model. Molecules 2020, 25, 4474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pertwee, R.G. Cannabinoid pharmacology: The first 66 years. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2006, 147 (Suppl. 1), S163–S171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Castaneto, M.S.; Gorelick, D.A.; Desrosiers, N.A.; Hartman, R.L.; Pirard, S.; Huestis, M.A. Synthetic cannabinoids: Epidemiology, pharmacodynamics, and clinical implications. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2014, 144, 12–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction. New Psychoactive Substances: Global Markets, Glocal Threats and the COVID-19 Pandemic; European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction: Lisbon, Portugal, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Krotulski, A.J.; Mohr, A.L.A.; Kacinko, S.L.; Fogarty, M.F.; Shuda, S.A.; Diamond, F.X.; Kinney, W.A.; Menendez, M.J.; Logan, B.K. 4F-MDMB-BINACA: A New Synthetic Cannabinoid Widely Implicated in Forensic Casework. J. Forensic Sci. 2019, 64, 1451–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction. 4F-MDMB-BICA: EMCDDA Initial Report on the New Psychoactive Substance Methyl 2-({[1-(4-Fluorobutyl)-1H-indol-3-yl]carbonyl}amino)-3,3-dimethylbutanoate (4F-MDMB-BICA); European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction: Lisbon, Portugal, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, H.S.; Watanabe, S.; Kuzhiumparambil, U.; Fong, C.Y.; Moy, H.Y.; Yao, Y.J.; Witting, P.K.; Fu, S. Monitoring metabolism of synthetic cannabinoid 4F-MDMB-BINACA via high-resolution mass spectrometry assessed in cultured hepatoma cell line, fungus, liver microsomes and confirmed using urine samples. Forensic Toxicol. 2021, 39, 198–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haschimi, B.; Mogler, L.; Halter, S.; Giorgetti, A.; Schwarze, B.; Westphal, F.; Fischmann, S.; Auwärter, V. Detection of the recently emerged synthetic cannabinoid 4F-MDMB-BINACA in “legal high” products and human urine specimens. Drug Test. Anal. 2019, 11, 1377–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shafi, A.; Berry, A.J.; Sumnall, H.; Wood, D.M.; Tracy, D.K. New psychoactive substances: A review and updates. Ther. Adv. Psychopharmacol. 2020, 10, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bazwinsky-Wutschke, I.; Zipprich, A.; Dehghani, F. Endocannabinoid System in Hepatic Glucose Metabolism, Fatty Liver Disease, and Cirrhosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, L.Y.; Alexa, K.; Cortes, M.; Schatzman-Bone, S.; Kim, A.J.; Mukhopadhyay, B.; Cinar, R.; Kunos, G.; North, T.E.; Goessling, W. Cannabinoid receptor signaling regulates liver development and metabolism. Development 2016, 143, 609–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- An, D.; Peigneur, S.; Hendrickx, L.A.; Tytgat, J. Targeting Cannabinoid Receptors: Current Status and Prospects of Natural Products. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stainier, D.Y.R.; Raz, E.; Lawson, N.D.; Ekker, S.C.; Burdine, R.D.; Eisen, J.S.; Ingham, P.W.; Schulte-Merker, S.; Yelon, D.; Weinstein, B.M.; et al. Guidelines for morpholino use in zebrafish. PLoS Genet. 2017, 13, e1007000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Phillips, J.B.; Westerfield, M. Zebrafish as a Model to Understand Human Genetic Diseases. In The Zebrafish in Biomedical Research; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 619–626. ISBN 9780128124314. [Google Scholar]
- Renninger, S.L.; Schonthaler, H.B.; Neuhauss, S.C.F.; Dahm, R. Investigating the genetics of visual processing, function and behaviour in zebrafish. Neurogenetics 2011, 12, 97–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johnson, J.; Sharick, J.T.; Skala, M.C.; Li, L. Sample preparation strategies for high-throughput mass spectrometry imaging of primary tumor organoids. J. Mass Spectrom. 2020, 55, e4452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeckel, A.M.; Matsumura, K.; Nishikawa, K.; Morimoto, Y.; Saporito, R.A.; Grant, T.; Ifa, D.R. Use of whole-body cryosectioning and desorption electrospray ionization mass spectrometry imaging to visualize alkaloid distribution in poison frogs. J. Mass Spectrom. 2020, 55, e4520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchberger, A.R.; DeLaney, K.; Johnson, J.; Li, L. Mass Spectrometry Imaging: A Review of Emerging Advancements and Future Insights. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 240–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addie, R.D.; Balluff, B.; Bovée, J.V.M.G.; Morreau, H.; McDonnell, L.A. Current State and Future Challenges of Mass Spectrometry Imaging for Clinical Research. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 6426–6433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asslan, M.; Lauzon, N.; Beus, M.; Maysinger, D.; Rousseau, S. Mass spectrometry imaging in zebrafish larvae for assessing drug safety and metabolism. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2021, 413, 5135–5146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janda, M.; Seah, B.K.B.; Jakob, D.; Beckmann, J.; Geier, B.; Liebeke, M. Determination of Abundant Metabolite Matrix Adducts Illuminates the Dark Metabolome of MALDI-Mass Spectrometry Imaging Datasets. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 8399–8407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, H.T.; Janfelt, C. Aspects of Quantitation in Mass Spectrometry Imaging Investigated on Cryo-Sections of Spiked Tissue Homogenates. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 11513–11520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulme, H.; Fridjonsdottir, E.; Gunnarsdottir, H.; Vallianatou, T.; Zhang, X.; Wadensten, H.; Shariatgorji, R.; Nilsson, A.; Bezard, E.; Svenningsson, P.; et al. Simultaneous mass spectrometry imaging of multiple neuropeptides in the brain and alterations induced by experimental parkinsonism and L-DOPA therapy. Neurobiol. Dis. 2020, 137, 104738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zecchi, R.; Franceschi, P.; Tigli, L.; Amidani, D.; Catozzi, C.; Ricci, F.; Salomone, F.; Pieraccini, G.; Pioselli, B.; Mileo, V. Sample preparation strategy for the detection of steroid-like compounds using MALDI mass spectrometry imaging: Pulmonary distribution of budesonide as a case study. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2021, 413, 4363–4371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goessling, W.; North, T.E.; Lord, A.M.; Ceol, C.; Lee, S.; Weidinger, G.; Bourque, C.; Strijbosch, R.; Haramis, A.-P.; Puder, M.; et al. APC mutant zebrafish uncover a changing temporal requirement for wnt signaling in liver development. Dev. Biol. 2008, 320, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Li, C.; Gong, Z. Development of a convenient in vivo hepatotoxin assay using a transgenic zebrafish line with liver-specific DsRed expression. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e91874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Korzh, S.; Pan, X.; Garcia-Lecea, M.; Winata, C.L.; Pan, X.; Wohland, T.; Korzh, V.; Gong, Z. Requirement of vasculogenesis and blood circulation in late stages of liver growth in zebrafish. BMC Dev. Biol. 2008, 8, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cannaert, A.; Sparkes, E.; Pike, E.; Luo, J.L.; Fang, A.; Kevin, R.C.; Ellison, R.; Gerona, R.; Banister, S.D.; Stove, C.P. Synthesis and in Vitro Cannabinoid Receptor 1 Activity of Recently Detected Synthetic Cannabinoids 4F-MDMB-BICA, 5F-MPP-PICA, MMB-4en-PICA, CUMYL-CBMICA, ADB-BINACA, APP-BINACA, 4F-MDMB-BINACA, MDMB-4en-PINACA, A-CHMINACA, 5F-AB-P7AICA, 5F-MDMB-P7AICA, and 5F-AP7AICA. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2020, 11, 4434–4446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Critical Review Report: 4F-MDMB-BINACA: Expert Committee on Drug Dependence, Forty-second Meeting Geneva. In Proceedings of the 42nd ECDD (2019): 4F-MDMB-BINACA, Geneva, Switzerland, 21–25 October 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Westerfield, M. The Zebrafish Book: A Guide for the Laboratory Use of Zebrafish (Danio rerio), 4th ed.; M. Westerfield: Eugene, OR, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Esain, V.; Kwan, W.; Carroll, K.J.; Cortes, M.; Liu, S.Y.; Frechette, G.M.; Sheward, L.M.V.; Nissim, S.; Goessling, W.; North, T.E. Cannabinoid Receptor-2 Regulates Embryonic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Development via Prostaglandin E2 and P-Selectin Activity. Stem Cells 2015, 33, 2596–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hoppstädter, J.; Valbuena Perez, J.V.; Linnenberger, R.; Dahlem, C.; Legroux, T.M.; Hecksteden, A.; Tse, W.K.F.; Flamini, S.; Andreas, A.; Herrmann, J.; et al. The glucocorticoid-induced leucine zipper mediates statin-induced muscle damage. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 4684–4701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, L.H.J.; Maurer, H.H.; Meyer, M.R. Metabolic fate of the new synthetic cannabinoid 7′N-5F-ADB in rat, human, and pooled human S9 studied by means of hyphenated high-resolution mass spectrometry. Drug Test. Anal. 2019, 11, 305–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Compounds | Metabolite ID | Integrated Human Screening Data * [27,32,34,35] | Data from Zebrafish Larvae | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aquatic Exposure, Published Data [27] | Microinjection | ||||||
| Blood | Urine | Caudal Vein | Heart Ventricle | Hindbrain | |||
| Parent compound | 4F-MDMB- BINACA | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | ||
| Phase I metabolites | M1 | ||||||
| M2 | + | + nq | + nq | ||||
| M3 | √√ | + nq | + nq | + nq | |||
| M4 | √√ | + | + | + | + | ||
| M5 | + | ||||||
| M6 | √ | √√ | ++ | + | + | + | |
| M7 | √ | + | |||||
| M8 | √ | √ | + | ||||
| M9 | + | ||||||
| M10 | √√ | + | + nq | + nq | + nq | ||
| M11 | √√ | + | + | + | + | ||
| M12 | + | + | + | + | |||
| M13 | √ | + | |||||
| M14 | √ | ||||||
| M15 | √√ | + | + | ++ | + | ||
| M16 | + | ||||||
| M17 | |||||||
| M18 | + | ||||||
| M19 | |||||||
| Total number of phase I metabolites | 3 | 9 | 14 | 8 | 7 | 8 | |
| Phase II metabolites | M20 | + | ++ | + | + | ||
| M21 | |||||||
| M22 | |||||||
| M23 | |||||||
| M24 | + | ||||||
| M25 | + | + nq | + | + | |||
| M26 | + | ||||||
| Total number of phase II metabolites | - | - | 4 | 2 | 2 | 2 | |
| Total number of detected Phase I/II metabolites | 3 | 9 | 18 | 10 | 9 | 10 | |
| 4F-MDMB-BINACA | 7′N-5F-ADB | |
|---|---|---|
| Log P 2 | 3.12 | 3.20 |
| Strongest acidic pKa 3 | 14.65 | 15.05 |
| Strongest basic pKa 3 | −0.76 | 3.11 |
| Log Intrinsic solubility (mol/L) 4 | −4.37 | −4.50 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, Y.M.; Dahlem, C.; Meyer, M.R.; Kiemer, A.K.; Müller, R.; Herrmann, J. Induction of Liver Size Reduction in Zebrafish Larvae by the Emerging Synthetic Cannabinoid 4F-MDMB-BINACA and Its Impact on Drug Metabolism. Molecules 2022, 27, 1290. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27041290
Park YM, Dahlem C, Meyer MR, Kiemer AK, Müller R, Herrmann J. Induction of Liver Size Reduction in Zebrafish Larvae by the Emerging Synthetic Cannabinoid 4F-MDMB-BINACA and Its Impact on Drug Metabolism. Molecules. 2022; 27(4):1290. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27041290
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Yu Mi, Charlotte Dahlem, Markus R. Meyer, Alexandra K. Kiemer, Rolf Müller, and Jennifer Herrmann. 2022. "Induction of Liver Size Reduction in Zebrafish Larvae by the Emerging Synthetic Cannabinoid 4F-MDMB-BINACA and Its Impact on Drug Metabolism" Molecules 27, no. 4: 1290. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27041290
APA StylePark, Y. M., Dahlem, C., Meyer, M. R., Kiemer, A. K., Müller, R., & Herrmann, J. (2022). Induction of Liver Size Reduction in Zebrafish Larvae by the Emerging Synthetic Cannabinoid 4F-MDMB-BINACA and Its Impact on Drug Metabolism. Molecules, 27(4), 1290. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27041290