Discovery of Leptulipin, a New Anticancer Protein from theIranian Scorpion, Hemiscorpius lepturus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Reagents, Media, Bacteria and Cells
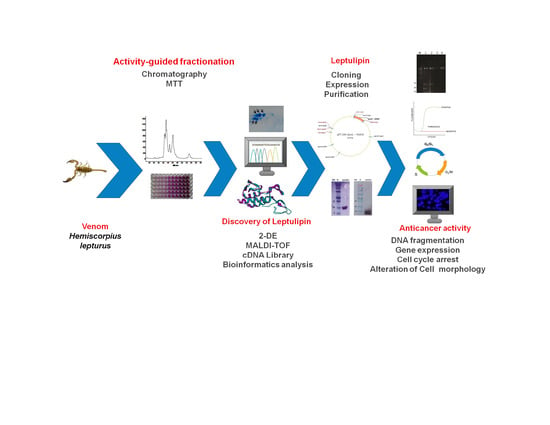
2.2. Graphical Representation of the Study
2.3. Venom Preparation
2.4. Venom Fractionation
2.5. Evaluation of the Anticancer Activity of Venom Fractions
2.6. Two-Dimensional Gel Electrophoresis
2.7. Mass Spectrometry
2.8. Bioinformatics Analyses
2.8.1. Similarity Analysis and Determination of the Mature Chain
2.8.2. Prediction of 3D Structure of the Protein
2.9. Construction of Plasmid, Expression and Purification of Leptulipin
2.10. Western Blotting
2.11. Evaluation of the Phospholipase Activity of Purified Leptulipin
2.12. Evaluation of Anticancer Activity of Leptulipin
2.12.1. MTT Assay
2.12.2. Lactate Dehydrogenase Release Assay
2.12.3. Analysis of Cell Morphology
2.13. Action Mechanism of Leptulipin
2.13.1. DNA Fragmentation Assay
2.13.2. Expression of Casp9, Bax, and Bcl-2 Genes
2.13.3. Cell Cycle Arrest by Flow cytometry
2.14. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Isolation of Anticancer Compound and Cytotoxicity Studies
3.2. Protein Identification
3.3. Bioinformatics Analysis
3.3.1. Similarity Analyses
3.3.2. Determination of the Mature Chain
3.3.3. Similarity Analyses
3.3.4. Prediction of 3D and Structural Alignment
3.4. Molecular Cloning, Purification, and Western Blotting of Leptulipin
3.5. Enzymatic Activity Assay for Leptulipin
3.6. Inhibition of Cell Proliferation
3.7. LDH Release Assay
3.8. Effect of Leptulipin on Cell Morphology
3.9. Analysis of Cell Cycle Arrest
3.10. DNA Fragmentation Analysis
3.11. Expression of Bax, Bcl-2 and Casp9
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padma, V.V. An overview of targeted cancer therapy. BioMedicine 2015, 5, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalapothakis, Y.; Miranda, K.; Pereira, A.H.; Witt, A.S.A.; Marani, C.; Martins, A.P.; Leal, H.G.; Campos-Júnior, E.; Pimenta, A.M.C.; Borges, A.; et al. Novel components of Tityus serrulatus venom: A transcriptomic approach. Toxicon 2021, 189, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolaou, M.; Pavlopoulou, A.; Georgakilas, A.G.; Kyrodimos, E. The challenge of drug resistance in cancer treatment: A current overview. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2018, 35, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, F.; Zafar, H.; You, X.; Khan, A.; Wu, J.; Ge, L. Cancer nanomedicine: Focus on recent developments and self-assembled peptide nanocarriers. J. Mater. Chem. B 2019, 7, 7639–7655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, F.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, L.; You, X.; Zhang, J.; Khan, A.; Khan, M.W.; Hasnat, M.; Zafar, H.; Wu, J.; et al. Paclitaxel-loaded pH responsive hydrogel based on self-assembled peptides for tumor targeting. Biomater. Sci. 2019, 7, 2023–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, H.; Raza, F.; Ma, S.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, J.; Shen, Q. Recent progress on nanomedicine-induced ferroptosis for cancer therapy. Biomater. Sci. 2021, 9, 5092–5115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M. Natural Products as Sources of New Drugs over the Nearly Four Decades from 01/1981 to 09/2019. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 770–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei, S.; Fekri, H.S.; Hashemi, F.; Hushmandi, K.; Mohammadinejad, R.; Ashrafizadeh, M.; Zarrabi, A.; Garg, M. Venom peptides in cancer therapy: An updated review on cellular and molecular aspects. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 164, 105327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srairi-Abid, N.; Othman, H.; Aissaoui, D.; BenAissa, R. Anti-tumoral effect of scorpion peptides: Emerging new cellular targets and signaling pathways. Cell Calcium 2019, 80, 160–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoodzadeh, A.; Zarrinnahad, H.; Pooshang, K.; Moradia, A. ScienceDirect First report on the isolation of melittin from Iranian honey bee venom and evaluation of its toxicity on gastric cancer AGS cells. J. Chin. Med. Assoc. 2015, 78, 574–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ghosh, A.; Roy, R.; Nandi, M.; Mukhopadhyay, A. Scorpion Venom-Toxins that Aid in Drug Development: A Review. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2019, 25, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmadi, S.; Knerr, J.M.; Argemi, L.; Bordon, K.C.F.; Pucca, M.B.; Cerni, F.A.; Arantes, E.C.; Çalişkan, F.; Laustsen, A.H. Scorpion venom: Detriments and benefits. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monge-Fuentes, V.; Gomes, F.M.M.; Campos, G.A.A.; de Castro Silva, J.; Biolchi, A.M.; dos Anjos, L.C.; Gonçalves, J.C.; Lopes, K.S.; Mortari, M.R. Neuroactive compounds obtained from arthropod venoms as new therapeutic platforms for the treatment of neurological disorders. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 21, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pal, P.; Roy, S.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Pal, T.K. Medicinal value of animal venom for treatment of Cancer in Humans—A Review. World Sci. News 2015, 22, 128–144. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Asmari, A.K.; Kunnathodi, F.; Al Saadon, K.; Idris, M.M. Elemental analysis of scorpion venoms. J. Venom Res. 2016, 7, 16–20. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, W.L.; Li, Z.J.; Li, J.B.; Liang, J. Research progress on medicinal values of scorpion venom components. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2017, 42, 3294–3304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaisakul, J.; Hodgson, W.C.; Kuruppu, S.; Prasongsook, N. Effects of animal venoms and toxins on hallmarks of cancer. J. Cancer 2016, 7, 1571–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Lyu, P.; Xi, X.; Ge, L.; Mahadevappa, R.; Shaw, C.; Kwok, H.F. Triggering of cancer cell cycle arrest by a novel scorpion venom-derived peptide—Gonearrestide. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2018, 22, 4460–4473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, R.; Liang, H.; Qin, Z.-h.; Liu, C.-y. Crotoxin induces apoptosis and autophagy in human lung carcinoma cells in vitro via activation of the p38MAPK signaling pathway. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2014, 35, 1323–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al Asmari, A.K.; Khan, A.Q. Investigation of in vivo potential of scorpion venom against skin tumorigenesis in mice via targeting markers associated with cancer development. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2016, 10, 3387–3397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Salem, M.L.; Shoukry, N.M.; Teleb, W.K.; Abdel-Daim, M.M.; Abdel-Rahman, M.A. In vitro and in vivo antitumor effects of the Egyptian scorpion Androctonus amoreuxi venom in an Ehrlich ascites tumor model. Springerplus 2016, 5, 570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Das Gupta, S.; Debnath, A.; Saha, A.; Giri, B.; Tripathi, G.; Vedasiromoni, J.R.; Gomes, A.; Gomes, A. Indian black scorpion (Heterometrus bengalensis Koch) venom induced antiproliferative and apoptogenic activity against human leukemic cell lines U937 and K562. Leuk. Res. 2007, 31, 817–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Cai, X.; Ye, T.; Huo, J.; Liu, C.; Zhang, S.; Cao, P. Analgesic-antitumor peptide inhibits proliferation and migration of SHG-44 human malignant glioma cells. J. Cell. Biochem. 2011, 112, 2424–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Suze, G.; Rosales, A.; Salazar, V.; Sevcik, C. Apoptogenic peptides from Tityus discrepans scorpion venom acting against the SKBR3 breast cancer cell line. Toxicon 2010, 56, 1497–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghani, R.; Kamiabi, F.; Mohammadi, M. Scorpionism by Hemiscorpius spp. in Iran: A review. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 24, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shahbazzadeh, D.; Srairi-abid, N.; Feng, W.; Ram, N.; Borchani, L.; Ronjat, M.; Akbari, A.; Pessah, I.N.; Waard, M.D.E.; Ayeb, M.E.L. Hemicalcin, a new toxin from the Iranian scorpion Hemiscorpius lepturus which is active on ryanodine-sensitive Ca2+ channels. Biochem. J. 2007, 96, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Srairi-abid, N.; Shahbazzadeh, D.; Chatti, I.; Mlayah-bellalouna, S. Hemitoxin, the first potassium channel toxin from the venom of the Iranian scorpion Hemiscorpius lepturus. FEBS J. 2008, 275, 4641–4650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri-Ziari, S.; Shahbazzadeh, D.; Sardari, S.; Sabatier, J.M.; Bagheri, K.P. Discovery of a new analgesic peptide, leptucin, from the iranian scorpion, Hemiscorpius lepturus. Molecules 2021, 26, 2580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jridi, I.; Catacchio, I.; Majdoub, H.; Shahbazeddah, D.; El Ayeb, M.; Frassanito, M.A.; Ribatti, D.; Vacca, A.; Borchani, L. Hemilipin, a novel Hemiscorpius lepturus venom heterodimeric phospholipase A2, which inhibits angiogenesis in vitro and in vivo. Toxicon 2015, 105, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krayem, N.; Parsiegla, G.; Gaussier, H.; Louati, H.; Jallouli, R.; Mansuelle, P.; Carrière, F.; Gargouri, Y. Functional characterization and FTIR-based 3D modeling of full length and truncated forms of Scorpio maurus venom phospholipase A 2. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Gen. Subj. 2018, 1862, 1247–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Incamnoi, P.; Patramanon, R.; Thammasirirak, S.; Chaveerach, A.; Uawonggul, N.; Sukprasert, S.; Rungsa, P.; Daduang, J.; Daduang, S. Heteromtoxin (HmTx), a novel heterodimeric phospholipase A2 from Heterometrus laoticus scorpion venom. Toxicon 2013, 61, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hariprasad; Singh, B.; Das, U.; Ethayathulla, A.S.; Kaur, P.; Singh, T.P.; Srinivasan, A. Cloning, sequence analysis and homology modeling of a novel phospholipase A2 from Heterometrus fulvipes (Indian black scorpion). DNA Seq. 2007, 18, 242–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazemi-Lomedasht, F.; Khalaj, V.; Pooshang Bagheri, K.; Behdani, M.; Shahbazzadeh, D. The first report on transcriptome analysis of the venom gland of Iranian scorpion, Hemiscorpius lepturus. Toxicon 2017, 1, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdez-Cruz, N.A.; Segovia, L.; Corona, M.; Possani, L.D. Sequence analysis and phylogenetic relationship of genes encoding heterodimeric phospholipases A2 from the venom of the scorpion Anuroctonus phaiodactylus. Gene 2007, 396, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdez-Cruz, N.A.; Batista, C.V.F.; Possani, L.D. Phaiodactylipin, a glycosylated heterodimeric phospholipase A2 from the venom of the scorpion Anuroctonus phaiodactylus. Eur. J. Biochem. 2004, 271, 1453–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conde, R.; Zamudio, F.Z.; Becerril, B.; Possani, L.D. Phospholipin, a novel heterodimeric phospholipase A2 from Pandinus imperator scorpion venom. FEBS Lett. 1999, 460, 447–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, J.; Yan, R.; Roy, A.; Xu, D.; Poisson, J.; Zhang, Y. The I-TASSER Suite: Protein structure and function prediction. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 7–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, C.C.; Meng, E.C.; Morris, J.H.; Pettersen, E.F.; Ferrin, T.E. Enhancing UCSF Chimera through web services. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, W478–W484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Memar, B.; Jamili, S.; Shahbazzadeh, D.; Bagheri, K.P. The first report on coagulation and phospholipase A2 activities of Persian Gulf lionfish, Pterois russelli, an Iranian venomous fish. Toxicon 2016, 113, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madeira, F.; Park, Y.M.; Lee, J.; Buso, N.; Gur, T.; Madhusoodanan, N.; Basutkar, P.; Tivey, A.R.N.; Potter, S.C.; Finn, R.D.; et al. The EMBL-EBI search and sequence analysis tools APIs in 2019. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W636–W641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cortes, J.; Perez-García, J.M.; Llombart-Cussac, A.; Curigliano, G.; El Saghir, N.S.; Cardoso, F.; Barrios, C.H.; Wagle, S.; Roman, J.; Harbeck, N.; et al. Enhancing global access to cancer medicines. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2020, 70, 105–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kant Upadhyay, R. Use of Animal Venom Peptides/Toxins in Cancer Therapeutics. Curr. Trends Biomed. Eng. Biosci. 2018, 16, 555945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gopalakrishnakone, P.; Possani, L.D.; Schwartz, E.F.; Rodríguez De La Vega, R.C. Scorpion venoms. In Scorpion Venoms; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 1–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-García, A.; Varela, D. Voltage-Gated K+/Na+ Channels and Scorpion Venom Toxins in Cancer. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pennington, M.W.; Czerwinski, A.; Norton, R.S. Peptide therapeutics from venom: Current status and potential. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2018, 26, 2738–2758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uzair, B.; Bint-e-Irshad, S.; Khan, B.A.; Azad, B.; Mahmood, T.; Rehman, M.U.; Braga, V.A. Scorpion Venom Peptides as a Potential Source for Human Drug Candidates. Protein Pept. Lett. 2018, 25, 702–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutertre, S.; Undheim, E.A.B.; Pineda, S.S.; Jin, A.H.; Lavergne, V.; Fry, B.G.; Lewis, R.J.; Alewood, P.F.; King, G.F. Venoms-based drug discovery: Proteomic and transcriptomic approaches. RSC Drug Discov. 2015, 11, 80–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prashanth, J.R.; Hasaballah, N.; Vetter, I. Pharmacological screening technologies for venom peptide discovery. Neuropharmacology 2017, 127, 4–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarfo-Poku, C.; Eshun, O.; Lee, K.H. Medical application of scorpion venom to breast cancer: A mini-review. Toxicon 2016, 122, 109–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.; Bharadvaja, N. Venom-Derived Bioactive Compounds as Potential Anticancer Agents: A Review. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2020, 27, 129–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akef, H.M. Anticancer and antimicrobial activities of scorpion venoms and their peptides. Toxin Rev. 2019, 38, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Ma, C.; Du, Q.; Wei, R.; Wang, L.; Zhou, M.; Chen, T.; Shaw, C. Two peptides, TsAP-1 and TsAP-2, from the venom of the Brazilian yellow scorpion, Tityus serrulatus: Evaluation of their antimicrobial and anticancer activities. Biochimie 2013, 95, 1784–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arpornsuwan, T.; Sriwai, W.; Jaresitthikunchai, J.; Phaonakrop, N.; Sritanaudomchai, H.; Roytrakul, S. Anticancer activities of antimicrobial BmKn2 peptides against oral and colon cancer cells. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2014, 20, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, R.S.Y. Apoptosis in cancer: From pathogenesis to treatment. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 30, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elmore, S. Apoptosis: A Review of Programmed Cell Death. Toxicol. Pathol. 2007, 35, 495–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benati, R.B.; Costa, T.R.; Da Costa Cacemiro, M.; Sampaio, S.V.; De Castro, F.A.; Burin, S.M. Cytotoxic and pro-apoptotic action of MjTX-I, a phospholipase A2 isolated from Bothrops moojeni snake venom, towards leukemic cells. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 23, 24–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Charris, E.; Lopes, D.S.; Gimenes, S.N.C.; Teixeira, S.C.; Montealegre-Sánchez, L.; Solano-Redondo, L.; Fierro-Pérez, L.; de MeloRodrigues Ávila, V. Antitumor potential of Pllans–II, an acidic Asp49–PLA2 from Porthidium lansbergii lansbergii snake venom on human cervical carcinoma HeLa cells. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 122, 1053–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medioni, J.; Brizard, M.; Elaidi, R.; Reid, P.F.; Benlhassan, K.; Bray, D. Innovative design for a phase 1 trial with intra-patient dose escalation: The Crotoxin study. Contemp. Clin. Trials Commun. 2017, 1, 186–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
















| HT-29 | MDA-MB-231 | |
|---|---|---|
| Casp 9 F | 5′-CCAGAGATTCGCAAACCAGAGG-3′ | 5′-CTGTCTACGGCACAGATGGAT-3′ |
| Casp 9 R | 5′-GGAGACCAAACGCTTAGAGACC-3′ | 5′-GGGACTCGTCTTCAGGGGAA-3′ |
| Bax F | 5′-AGGATGCGTCCACCAAGAAG-3′ | 5′-CCTGTGCACCAAGGTGCCGGAACT-3′ |
| Bax R | 5′-GGAAGAAGACCTCTCGGGG-3′ | 5′-CCACCCTGGTCTTGGATCCAGCCC-3′ |
| Bcl-2 F | 5′-GACTTCGCAGAGATGTCCAGT-3′ | 5′-TTGTGGCCTTCTTTGAGTTCGGTG-3′ |
| Bcl-2 R | 5′-CATCCCTGAAGAGTTCCTCCA-3′ | 5′-GGTGCCGGTTCAGGTACTCAGTCA-3′ |
| GAPDH F | 5′-GACCACAGTCCATGACATCACT | 5′-CGGAGTCAACGGATTTGGTCGTAT-3′ |
| GAPDH R | 5′-TCACTACAGTACCTGACACCAG-3′ | 5′-AGCCTTCTCCATGGTGGTGAAGAC-3′ |
| Spot No. | Protein Name | Mass (kDa) | Peptide Sequence |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Leptulipin | 12.81 | DHDHCDGILSGETK CEEALDNCFK |
| 2 | PLA2-2 | 12.09 | KWCGAGSEA DHDHCDNIGAGETK |
| 3 | PLA2-3 | 12.32 | CEDAFKQCLR THDHCDNIGSGETK |
| 4 | ND * | 7.46 | ND * |
| 5 | PLA2-4 | 7.38 | DHDHCDNIIPGETK |
| Similar Protein | Identity | Accession Number | Organism Name | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phaiodactylipin | 56.06% | Q6PXP0.2 | Anuroctonus phaiodactylus | [36] |
| Scorpio maurus PLA2 | 50.34% | MF347455.1 | Scorpio maurus | [31] |
| Phospholipin | 48.30% | P0DKU2.1 | Pandinus imperator | [37] |
| Hemilipin | 46.35% | A0A1L4BJ46.1 | Hemiscorpius lepturus | [30] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rezaei, A.; Asgari, S.; Komijani, S.; Sadat, S.N.; Sabatier, J.-M.; Nasrabadi, D.; Pooshang Bagheri, K.; Shahbazzadeh, D.; Akbari Eidgahi, M.R.; De Waard, M.; et al. Discovery of Leptulipin, a New Anticancer Protein from theIranian Scorpion, Hemiscorpius lepturus. Molecules 2022, 27, 2056. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27072056
Rezaei A, Asgari S, Komijani S, Sadat SN, Sabatier J-M, Nasrabadi D, Pooshang Bagheri K, Shahbazzadeh D, Akbari Eidgahi MR, De Waard M, et al. Discovery of Leptulipin, a New Anticancer Protein from theIranian Scorpion, Hemiscorpius lepturus. Molecules. 2022; 27(7):2056. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27072056
Chicago/Turabian StyleRezaei, Ali, Saeme Asgari, Samira Komijani, Seyedeh Narjes Sadat, Jean-Marc Sabatier, Davood Nasrabadi, Kamran Pooshang Bagheri, Delavar Shahbazzadeh, Mohammad Reza Akbari Eidgahi, Michel De Waard, and et al. 2022. "Discovery of Leptulipin, a New Anticancer Protein from theIranian Scorpion, Hemiscorpius lepturus" Molecules 27, no. 7: 2056. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27072056
APA StyleRezaei, A., Asgari, S., Komijani, S., Sadat, S. N., Sabatier, J.-M., Nasrabadi, D., Pooshang Bagheri, K., Shahbazzadeh, D., Akbari Eidgahi, M. R., De Waard, M., & Mirzahoseini, H. (2022). Discovery of Leptulipin, a New Anticancer Protein from theIranian Scorpion, Hemiscorpius lepturus. Molecules, 27(7), 2056. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27072056