International Comparison, Risk Assessment, and Prioritisation of 26 Endocrine Disrupting Compounds in Three European River Catchments in the UK, Ireland, and Spain
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Occurrence and Frequency
2.1.1. Steroid Hormones
2.1.2. Preservatives
2.1.3. Plasticizers
2.1.4. Alkylphenols
2.1.5. Flame Retardants
2.1.6. Other Compounds
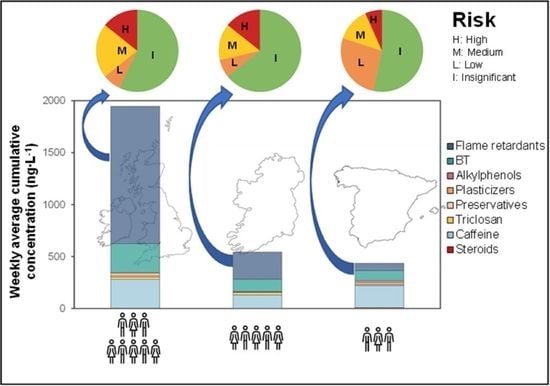
2.2. Identification of Geographical Patterns
2.3. Environmental Risk Assessment (ERA)
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Reagents, Chemicals, and Consumables
3.2. Site Locations
3.3. Sample Collection and Preparation
3.4. Instrumental Analysis
3.5. Method Performance
3.6. Environmental Risk Assessment (ERA)
3.7. Statistical and Data Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Wang, G.; Ma, P.; Zhang, Q.; Lewis, J.; Lacey, M.; Furukawa, Y.; O’Reilly, S.E.; Meaux, S.; McLachlan, J.; Zhang, S. Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals in New Orleans Surface Waters and Mississippi Sound Sediments. J. Environ. Monit. 2012, 14, 1353–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scholz, S.; Mayer, I. Molecular Biomarkers of Endocrine Disruption in Small Model Fish. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2008, 293, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vilela, C.L.S.; Bassin, J.P.; Peixoto, R.S. Water Contamination by Endocrine Disruptors: Impacts, Microbiological Aspects and Trends for Environmental Protection. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 235, 546–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Communication from the Commission to the European Parliament, the Council, the European Economic and Social Committee and the Committee of the Regions—Towards a Comprehensive European Union Framework on Endocrine Disruptors; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, M.; Sarma, D.K.; Shubham, S.; Kumawat, M.; Verma, V.; Prakash, A.; Tiwari, R. Environmental Endocrine-Disrupting Chemical Exposure: Role in Non-Communicable Diseases. Front. Public Health 2020, 8, 553850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porte, C.; Janer, G.; Lorusso, L.C.; Ortiz-Zarragoitia, M.; Cajaraville, M.P.; Fossi, M.C.; Canesi, L. Endocrine Disruptors in Marine Organisms: Approaches and Perspectives. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2006, 143, 303–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diamanti-Kandarakis, E.; Bourguignon, J.-P.; Giudice, L.C.; Hauser, R.; Prins, G.S.; Soto, A.M.; Zoeller, R.T.; Gore, A.C. Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals: An Endocrine Society Scientific Statement. Endocr. Rev. 2009, 30, 293–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteban, S.; Gorga, M.; Petrovic, M.; González-Alonso, S.; Barceló, D.; Valcárcel, Y. Analysis and Occurrence of Endocrine-Disrupting Compounds and Estrogenic Activity in the Surface Waters of Central Spain. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 466–467, 939–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rapp-Wright, H.; Regan, F.; White, B.; Barron, L.P. A Year-Long Study of the Occurrence and Risk of over 140 Contaminants of Emerging Concern in Wastewater Influent, Effluent and Receiving Waters in the Republic of Ireland. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 860, 160379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quynh, T.X.; Toan, V.D. Endocrine Disrupting Compounds (EDCs) in Surface Waters of the KimNguu River, Vietnam. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2019, 103, 734–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, L.; Lu, G.; Jiang, R.; Yan, Z.; Li, Y. Occurrence, Toxicity and Ecological Risk of Bisphenol A Analogues in Aquatic Environment—A Review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 208, 111481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Zhao, J.-L.; Yang, Y.-Y.; Jia, Y.-W.; Zhang, Q.-Q.; Chen, C.-E.; Liu, Y.-S.; Yang, B.; Xie, L.; Ying, G.-G. Occurrence, Mass Loads and Risks of Bisphenol Analogues in the Pearl River Delta Region, South China: Urban Rainfall Runoff as a Potential Source for Receiving Rivers. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 263, 114361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nipen, M.; Vogt, R.D.; Bohlin-Nizzetto, P.; Borgå, K.; Mwakalapa, E.B.; Borgen, A.R.; Schlabach, M.; Christensen, G.; Mmochi, A.J.; Breivik, K. Increasing Trends of Legacy and Emerging Organic Contaminants in a Dated Sediment Core From East-Africa. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 9, 805544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malnes, D.; Ahrens, L.; Köhler, S.; Forsberg, M.; Golovko, O. Occurrence and Mass Flows of Contaminants of Emerging Concern (CECs) in Sweden’s Three Largest Lakes and Associated Rivers. Chemosphere 2022, 294, 133825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riley, A.L.; Amezaga, J.; Burke, I.T.; Byrne, P.; Cooper, N.; Crane, R.A.; Comber, S.D.W.; Gandy, C.J.; Hudson-Edwards, K.A.; Jennings, E.; et al. Incorporating Conceptual Site Models into National-Scale Environmental Risk Assessments for Legacy Waste in the Coastal Zone. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 1045482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spurgeon, D.; Wilkinson, H.; Civil, W.; Hutt, L.; Armenise, E.; Kieboom, N.; Sims, K.; Besien, T. Worst-Case Ranking of Organic Chemicals Detected in Groundwaters and Surface Waters in England. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 835, 155101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasprzyk-Hordern, B.; Dinsdale, R.M.; Guwy, A.J. The Occurrence of Pharmaceuticals, Personal Care Products, Endocrine Disruptors and Illicit Drugs in Surface Water in South Wales, UK. Water Res. 2008, 42, 3498–3518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salimi, M.; Esrafili, A.; Gholami, M.; Jonidi Jafari, A.; Rezaei Kalantary, R.; Farzadkia, M.; Kermani, M.; Sobhi, H.R. Contaminants of Emerging Concern: A Review of New Approach in AOP Technologies. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 189, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyche, J.L.; Nourizadeh-Lillabadi, R.; Karlsson, C.; Stavik, B.; Berg, V.; Skåre, J.U.; Alestrøm, P.; Ropstad, E. Natural Mixtures of POPs Affected Body Weight Gain and Induced Transcription of Genes Involved in Weight Regulation and Insulin Signaling. Aquat. Toxicol. 2011, 102, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esperanza, M.; Seoane, M.; Servia, M.J.; Cid, Á. Effects of Bisphenol A on the Microalga Chlamydomonas Reinhardtii and the Clam Corbicula Fluminea. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 197, 110609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauretta, R.; Sansone, A.; Sansone, M.; Romanelli, F.; Appetecchia, M. Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals: Effects on Endocrine Glands. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chibwe, L.; Titaley, I.A.; Hoh, E.; Simonich, S.L.M. Integrated Framework for Identifying Toxic Transformation Products in Complex Environmental Mixtures. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2017, 4, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regulation (EC) No 1223/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 30 November 2009 on Cosmetic Products (Recast) (Text with EEA Relevance). 2009. Available online: http://data.europa.eu/eli/reg/2009/1223/oj (accessed on 4 August 2023).
- Regulation (EC) No 1107/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 21 October 2009 Concerning the Placing of Plant Protection Products on the Market and Repealing Council Directives 79/117/EEC and 91/414/EEC. 2009. Available online: http://data.europa.eu/eli/reg/2009/1107/oj (accessed on 4 August 2023).
- Vandenberg, L.N.; Colborn, T.; Hayes, T.B.; Heindel, J.J.; Jacobs, D.R.; Lee, D.-H.; Shioda, T.; Soto, A.M.; Vom Saal, F.S.; Welshons, W.V.; et al. Hormones and Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals: Low-Dose Effects and Nonmonotonic Dose Responses. Endocr. Rev. 2012, 33, 378–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergman, Å.; Heindel, J.J.; Jobling, S.; Kidd, K.A.; Zoeller, R.T. State of the Science of Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals-2012; United National Environment Programme: Nairobi, Kenya; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012; ISBN 978-92-4-150503-1. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission DG ENV. Towards the Establishment of a Priority List of Substances for Further Evaluation of Their Role in Endocrine Disruption; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Kasonga, T.K.; Coetzee, M.A.A.; Kamika, I.; Ngole-Jeme, V.M.; Benteke Momba, M.N. Endocrine-Disruptive Chemicals as Contaminants of Emerging Concern in Wastewater and Surface Water: A Review. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 277, 111485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, L.; Mackay, E.B.; Cardoso, A.C.; Baattrup-Pedersen, A.; Birk, S.; Blackstock, K.L.; Borics, G.; Borja, A.; Feld, C.K.; Ferreira, M.T.; et al. Protecting and Restoring Europe’s Waters: An Analysis of the Future Development Needs of the Water Framework Directive. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 658, 1228–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Environment Agency. European Waters—Assessment of Status and Pressures; European Environment Agency: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Environmental Protection Agency. Water Quality in Ireland 2016–2021; Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Ashfaq, M.; Sun, Q.; Ma, C.; Rashid, A.; Li, Y.; Mulla, S.I.; Yu, C.-P. Occurrence, Seasonal Variation and Risk Evaluation of Selected Endocrine Disrupting Compounds and Their Transformation Products in Jiulong River and Estuary, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 145, 370–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chafi, S.; Azzouz, A.; Ballesteros, E. Occurrence and Distribution of Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals and Pharmaceuticals in the River Bouregreg (Rabat, Morocco). Chemosphere 2022, 287, 132202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salgueiro-González, N.; Turnes-Carou, I.; Besada, V.; Muniategui-Lorenzo, S.; López-Mahía, P.; Prada-Rodríguez, D. Occurrence, Distribution and Bioaccumulation of Endocrine Disrupting Compounds in Water, Sediment and Biota Samples from a European River Basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 529, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cristale, J.; García Vázquez, A.; Barata, C.; Lacorte, S. Priority and Emerging Flame Retardants in Rivers: Occurrence in Water and Sediment, Daphnia Magna Toxicity and Risk Assessment. Environ. Int. 2013, 59, 232–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dishaw, L.V.; Macaulay, L.J.; Roberts, S.C.; Stapleton, H.M. Exposures, Mechanisms, and Impacts of Endocrine-Active Flame Retardants. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2014, 19, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Benijts, T.; Lambert, W.; De Leenheer, A. Analysis of Multiple Endocrine Disruptors in Environmental Waters via Wide-Spectrum Solid-Phase Extraction and Dual-Polarity Ionization LC-Ion Trap-MS/MS. Anal. Chem. 2004, 76, 704–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanderford, B.J.; Pearson, R.A.; Rexing, D.J.; Snyder, S.A. Analysis of Endocrine Disruptors, Pharmaceuticals, and Personal Care Products in Water Using Liquid Chromatography/Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 6265–6274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bai, X.; Lutz, A.; Carroll, R.; Keteles, K.; Dahlin, K.; Murphy, M.; Nguyen, D. Occurrence, Distribution, and Seasonality of Emerging Contaminants in Urban Watersheds. Chemosphere 2018, 200, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, L.B.; Murphy, S.F.; Verplanck, P.L.; Sandstrom, M.W.; Taylor, H.E.; Furlong, E.T. Chemical Loading into Surface Water along a Hydrological, Biogeochemical, and Land Use Gradient: A Holistic Watershed Approach. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 475–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boretti, A.; Rosa, L. Reassessing the Projections of the World Water Development Report. Npj Clean Water 2019, 2, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ying, G.-G.; Kookana, R.S.; Ru, Y.-J. Occurrence and Fate of Hormone Steroids in the Environment. Environ. Int. 2002, 28, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingues, J.T.; Orlando, R.M.; Almeida, M.R.; de Lemos, L.R.; Mageste, A.B.; Rodrigues, G.D. Extraction of Estrogen Hormones from Water Samples Using an Aqueous Two-Phase System: A New Approach for Sample Preparation in the Analysis of Emerging Contaminants. Microchem. J. 2021, 166, 106231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Céspedes, R.; Lacorte, S.; Raldúa, D.; Ginebreda, A.; Barceló, D.; Piña, B. Distribution of Endocrine Disruptors in the Llobregat River Basin (Catalonia, NE Spain). Chemosphere 2005, 61, 1710–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Roldán, R.; de Alda, M.L.; Gros, M.; Petrovic, M.; Martín-Alonso, J.; Barceló, D. Advanced Monitoring of Pharmaceuticals and Estrogens in the Llobregat River Basin (Spain) by Liquid Chromatography–Triple Quadrupole-Tandem Mass Spectrometry in Combination with Ultra Performance Liquid Chromatography–Time of Flight-Mass Spectrometry. Chemosphere 2010, 80, 1337–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, D.; Rodriguez-Mozaz, S.; Insa, S.; Schoevaart, R.; Barceló, D.; de Cazes, M.; Belleville, M.-P.; Sanchez-Marcano, J.; Misovic, A.; Oehlmann, J.; et al. Removal of Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals in Wastewater by Enzymatic Treatment with Fungal Laccases. Org. Process Res. Dev. 2017, 21, 480–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komori, K.; Tanaka, H.; Okayasu, Y.; Yasojima, M.; Sato, C. Analysis and Occurrence of Estrogen in Wastewater in Japan. Water Sci. Technol. 2004, 50, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonsioroski, A.; Mourikes, V.E.; Flaws, J.A. Endocrine Disruptors in Water and Their Effects on the Reproductive System. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hung, H.-S.; Yeh, K.-J.C.; Hsieh, C.-Y.; Chen, T.-C. Occurrence and Degradation of Free and Conjugated Estrogens in a River Receiving Feedlot Animal Discharge. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 11961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Zhou, X.; Xu, D.; Xiang, Y.; Ling, W.; Chen, M. Contamination and Risk Assessment of Estrogens in Livestock Manure: A Case Study in Jiangsu Province, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ministerio de Agricultura, Pesca y Alimentación. Encuestas Ganaderas 2021; Ministerio de Agricultura, Pesca y Alimentación: Madrid, Spain, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Rechsteiner, D.; Schrade, S.; Zähner, M.; Müller, M.; Hollender, J.; Bucheli, T.D. Occurrence and Fate of Natural Estrogens in Swiss Cattle and Pig Slurry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 5545–5554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vane, C.H.; Kim, A.W.; Lopes dos Santos, R.A.; Moss-Hayes, V. Contrasting Sewage, Emerging and Persistent Organic Pollutants in Sediment Cores from the River Thames Estuary, London, England, UK. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 175, 113340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Environment Agency. Catchment Risk Assessment of Steroid Oestrogens from Sewage Treatment Works; Environment Agency: Bristol, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, F.; Karu, K.; Campos, L.C. Simultaneous Measurement of Free and Conjugated Estrogens in Surface Water Using Capillary Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Analyst 2021, 146, 2689–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naldi, A.C.; Fayad, P.B.; Prévost, M.; Sauvé, S. Analysis of Steroid Hormones and Their Conjugated Forms in Water and Urine by On-Line Solid-Phase Extraction Coupled to Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Chem. Cent. J. 2016, 10, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Derisso, C.R.; Pompei, C.M.E.; Spadoto, M.; da Silva Pinto, T.; Vieira, E.M. Occurrence of Parabens in Surface Water, Wastewater Treatment Plant in Southeast of Brazil and Assessment of Their Environmental Risk. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2020, 231, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brausch, J.M.; Rand, G.M. A Review of Personal Care Products in the Aquatic Environment: Environmental Concentrations and Toxicity. Chemosphere 2011, 82, 1518–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorga, M.; Petrovic, M.; Barceló, D. Multi-Residue Analytical Method for the Determination of Endocrine Disruptors and Related Compounds in River and Waste Water Using Dual Column Liquid Chromatography Switching System Coupled to Mass Spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1295, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kung, T.A.; Lee, S.H.; Yang, T.C.; Wang, W.H. Survey of Selected Personal Care Products in Surface Water of Coral Reefs in Kenting National Park, Taiwan. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 635, 1302–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Ortiz, C.M.; Sentana-Gadea, I.; Varó-Galvañ, P.; Maestre-Pérez, S.E.; Prats-Rico, D. The Use of Combined Treatments for Reducing Parabens in Surface Waters: Ion-Exchange Resin and Nanofiltration. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 639, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Mariño, I.; Quintana, J.B.; Rodríguez, I.; Cela, R. Simultaneous Determination of Parabens, Triclosan and Triclocarban in Water by Liquid Chromatography/Electrospray Ionisation Tandem Mass Spectrometry: LC/MS/MS of Parabens, Triclosan and Triclocarban in Water. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2009, 23, 1756–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caban, M.; Stepnowski, P. The Quantification of Bisphenols and Their Analogues in Wastewaters and Surface Water by an Improved Solid-Phase Extraction Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry Method. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 28829–28839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loos, R.; Gawlik, B.M.; Locoro, G.; Rimaviciute, E.; Contini, S.; Bidoglio, G. EU Wide Monitoring Survey of Polar Persistent Pollutants in European River Waters; European Commission, Joint Research Centre, Institute for Environment and Sustainability: Luxembourg, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Yamazaki, E.; Yamashita, N.; Taniyasu, S.; Lam, J.; Lam, P.K.S.; Moon, H.-B.; Jeong, Y.; Kannan, P.; Achyuthan, H.; Munuswamy, N.; et al. Bisphenol A and Other Bisphenol Analogues Including BPS and BPF in Surface Water Samples from Japan, China, Korea and India. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 122, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Liu, J.; Ren, J.; Shen, J.; Fan, J.; Xi, R.; Chen, W.; Chen, Q. Occurrence, Distribution and Ecological Risk of Bisphenol Analogues in the Surface Water from a Water Diversion Project in Nanjing, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gil-Solsona, R.; Castaño-Ortiz, J.M.; Muñoz-Mas, R.; Insa, S.; Farré, M.; Ospina-Alvarez, N.; Santos, L.H.M.L.M.; García-Pimentel, M.; Barceló, D.; Rodríguez-Mozaz, S. A Holistic Assessment of the Sources, Prevalence, and Distribution of Bisphenol A and Analogues in Water, Sediments, Biota and Plastic Litter of the Ebro Delta (Spain). Environ. Pollut. 2022, 314, 120310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Y.; Ren, J.; You, Z.; Liu, J.; Lu, G.; Li, Y.; Li, J. The Sinking Behavior of Micro–Nano Particulate Matter for Bisphenol Analogues in the Surface Water of an Ecological Demonstration Zone, China. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2021, 23, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tišler, T.; Krel, A.; Gerželj, U.; Erjavec, B.; Dolenc, M.S.; Pintar, A. Hazard Identification and Risk Characterization of Bisphenols A, F and AF to Aquatic Organisms. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 212, 472–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamastra, L.; Suciu, N.A.; Trevisan, M. Sewage Sludge for Sustainable Agriculture: Contaminants’ Contents and Potential Use as Fertilizer. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 2018, 5, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ofwat. Appendix 1: Sludge treatment, transport and disposal—supporting evidence and design options. In Water 2020: Regulatory Framework for Wholesale Markets and the 2019 Price Review; Ofwat: Birmingham, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Roig, N.; Sierra, J.; Martí, E.; Nadal, M.; Schuhmacher, M.; Domingo, J.L. Long-Term Amendment of Spanish Soils with Sewage Sludge: Effects on Soil Functioning. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2012, 158, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, A.; Guieysse, B.; Jefferson, B.; Cartmell, E.; Lester, J.N. Nonylphenol in the Environment: A Critical Review on Occurrence, Fate, Toxicity and Treatment in Wastewaters. Environ. Int. 2008, 34, 1033–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Berg, P.; Huerta-Lwanga, E.; Corradini, F.; Geissen, V. ewage Sludge Application as a Vehicle for Microplastics in Eastern Spanish Agricultural Soils. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 261, 114198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez Cortes, L.; Marinov, D.; Sanseverino, I.; Navarro Cuenca, A.; Niegowska, M.; Porcel Rodriguez, E.; Lettieri, T. Selection of Substances for the 3rd Watch List under the Water Framework Directive; JRC Technical Report, European Commission: Luxembourg, 2020; p. 243. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, X.; Jiang, G.; Huang, G.; Liu, J.; Zhou, Q. Determination of 4-Tert-Octylphenol, 4-Nonylphenol and Bisphenol A in Surface Waters from the Haihe River in Tianjin by Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry with Selected Ion Monitoring. Chemosphere 2004, 56, 1113–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, K.-A.; Choi, K.-C. Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals with Estrogenicity Posing the Risk of Cancer Progression in Estrogen-Responsive Organs. In Advances in Molecular Toxicology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; Volume 9, pp. 1–33. ISBN 978-0-12-802229-0. [Google Scholar]
- Nagy, P.; Fekete, J.; Sharma, V.K. Octylphenol and Nonylphenol in Surface Water of Ráckevei-Soroksári Danube Branch, Hungary. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2005, 40, 1679–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Environment Agency. Nonylphenol Ethoxylates (NPE) in Imported Textiles; Environment Agency: Bristol, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Environmental Protection 2004 No. 1816. The Controls on Nonylphenol and Nonylphenol Ethoxylate Regulations 2004. 2004. Available online: https://www.legislation.gov.uk/uksi/2004/1816/contents/made (accessed on 4 August 2023).
- Peñalver, R.; Jacobs, M.R.; Hegarty, S.; Regan, F. Assessment of Anthropogenic Pollution by Monitoring Occurrence and Distribution of Chemicals in the River Liffey in Dublin. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 53754–53766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Céspedes, R.; Lacorte, S.; Ginebreda, A.; Barceló, D. Chemical Monitoring and Occurrence of Alkylphenols, Alkylphenol Ethoxylates, Alcohol Ethoxylates, Phthalates and Benzothiazoles in Sewage Treatment Plants and Receiving Waters along the Ter River Basin (Catalonia, N.E. Spain). Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2006, 385, 992–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, C.; Helm, P.A.; Morse, D.; Reiner, E.J. Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry Direct Injection Analysis of Organophosphorus Flame Retardants in Ontario Surface Water and Wastewater Effluent. Chemosphere 2018, 191, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Gao, L.; Li, W.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Cai, Y. Occurrence, Distribution and Seasonal Variation of Organophosphate Flame Retardants and Plasticizers in Urban Surface Water in Beijing, China. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 209, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barceló, D.; Porte, C.; Cid, J.; Albaigés, J. Determination of Organophosphorus Compounds in Mediterranean Coastal Waters and Biota Samples Using Gas Chromatography with Nitrogen-Phosphorus and Chemical Ionization Mass Spectrometric Detection. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 1990, 38, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quednow, K.; Püttmann, W. Temporal Concentration Changes of DEET, TCEP, Terbutryn, and Nonylphenols in Freshwater Streams of Hesse, Germany: Possible Influence of Mandatory Regulations and Voluntary Environmental Agreements. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2009, 16, 630–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristale, J.; Katsoyiannis, A.; Sweetman, A.J.; Jones, K.C.; Lacorte, S. Occurrence and Risk Assessment of Organophosphorus and Brominated Flame Retardants in the River Aire (UK). Environ. Pollut. 2013, 179, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yueh, M.-F.; Tukey, R.H. Triclosan: A Widespread Environmental Toxicant with Many Biological Effects. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2016, 56, 251–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barron, L.; Havel, J.; Purcell, M.; Szpak, M.; Kelleher, B.; Paull, B. Predicting Sorption of Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products onto Soil and Digested Sludge Using Artificial Neural Networks. Analyst 2009, 134, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunyoku, T.A.; Young, T.M. Removal of Triclocarban and Triclosan during Municipal Biosolid Production. Water Environ. Res. 2014, 86, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ma, X.; Wan, Y.; Wu, M.; Xu, Y.; Xu, Q.; He, Z.; Xia, W. Occurrence of Benzophenones, Parabens and Triclosan in the Yangtze River of China, and the Implications for Human Exposure. Chemosphere 2018, 213, 517–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishi, I.; Kawakami, T.; Onodera, S. Monitoring of Triclosan in the Surface Water of the Tone Canal, Japan. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2008, 80, 163–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ECHA Triclosan Substance Infocard. Available online: https://echa.europa.eu/substance-information/-/substanceinfo/100.020.167 (accessed on 4 August 2023).
- Commission Delegated Regulation (EU) No 357/2014 of 3 February 2014 Supplementing Directive 2001/83/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council and Regulation (EC) No 726/2004 of the European Parliament and of the Council as Regards Situations in Which Post-Authorisation Efficacy Studies May Be Required Text with EEA relevance. 2014. Available online: http://data.europa.eu/eli/reg_del/2014/357/oj (accessed on 9 February 2023).
- Marazuela, M.D.; Klaiber, M.; Moreno-Gordaliza, E.; Barata, A.; Gómez-Gómez, M.M. Safety Assessment of Commercial Antimicrobial Food Packaging: Triclosan and Microplastics, a Closer Look. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2022, 31, 100780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Zheng, G.; Wang, X.; Wang, M.; Chen, T. Biodegradation of triclosan and triclocarban in sewage sludge during composting under three ventilation strategies. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2019, 13, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alotaibi, M.D.; Patterson, B.M.; McKinley, A.J.; Reeder, A.Y.; Furness, A.J. Benzotriazole and 5-Methylbenzotriazole in recycled water, surface water and dishwashing detergents from perth, western australia: Analytical method development and application. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2015, 17, 448–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Careghini, A.; Mastorgio, A.F.; Saponaro, S.; Sezenna, E. Bisphenol A, Nonylphenols, Benzophenones, and Benzotriazoles in Soils, Groundwater, Surface Water, Sediments, and Food: A Review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 5711–5741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, Z.-Q.; Liu, Y.-S.; Xiong, Q.; Cai, W.-W.; Ying, G.-G. Occurrence, Toxicity and Transformation of Six Typical Benzotriazoles in the Environment: A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 661, 407–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nödler, K.; Licha, T.; Fischer, S.; Wagner, B.; Sauter, M. A Case Study on the Correlation of Micro-Contaminants and Potassium in the Leine River (Germany). Appl. Geochem. 2011, 26, 2172–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giger, W.; Schaffner, C.; Kohler, H.-P.E. Benzotriazole and Tolyltriazole as Aquatic Contaminants. 1. Input and Occurrence in Rivers and Lakes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 7186–7192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieduwilt, F.; Lenth, C.; Ctistis, G.; Plachetka, U.; Möller, M.; Wackerbarth, H. Evaluation of an On-Site Surface Enhanced Raman Scattering Sensor for Benzotriazole. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 8260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, Q.A.; Kulikov, S.M.; Garner-O’Neale, L.D. Caffeine in Surface and Wastewaters in Barbados, West Indies. SpringerPlus 2015, 4, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silva, C.P.; Lima, D.L.D.; Schneider, R.J.; Otero, M.; Esteves, V.I. Evaluation of the Anthropogenic Input of Caffeine in Surface Waters of the North and Center of Portugal by ELISA. . Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 479–480, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godoi, F.G.A.; Muñoz-Peñuela, M.; Gomes, A.D.O.; Tolussi, C.E.; Brambila-Souza, G.; Branco, G.S.; Lo Nostro, F.L.; Moreira, R.G. ndocrine Disruptive Action of Diclofenac and Caffeine on Astyanax Altiparanae Males (Teleostei: Characiformes: Characidae). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2020, 231, 108720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Lu, G.; Yang, X.; Wang, C. Single and Combined Effects of Selected Pharmaceuticals at Sublethal Concentrations on Multiple Biomarkers in Carassius Auratus. Ecotoxicology 2012, 21, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, M.T.; Greenway, S.L.; Farris, J.L.; Guerra, B. Assessing Caffeine as an Emerging Environmental Concern Using Conventional Approaches. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2008, 54, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buerge, I.J.; Poiger, T.; Müller, M.D.; Buser, H.-R. Caffeine, an Anthropogenic Marker for Wastewater Contamination of Surface Waters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 691–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munro, K.; Martins, C.P.B.; Loewenthal, M.; Comber, S.; Cowan, D.A.; Pereira, L.; Barron, L.P. Evaluation of Combined Sewer Overflow Impacts on Short-Term Pharmaceutical and Illicit Drug Occurrence in a Heavily Urbanised Tidal River Catchment (London, UK). Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 657, 1099–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paíga, P.; Ramos, S.; Jorge, S.; Silva, J.G.; Delerue-Matos, C. Monitoring Survey of Caffeine in Surface Waters (Lis River) and Wastewaters Located at Leiria Town in Portugal. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 33440–33450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagoda, A.; Żukowski, W.; Dąbrowska, B. Investigations of the Presence of Caffeine in the Rudawa River, Kraków, Poland. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- EMEA—European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products. Guideline on the Environmental Risk Assessment of Medicinal Products for Human Use—Committee for Medical Products for Human Use (CHMP). 2006. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/scientific-guideline/guideline-environmental-risk-assessment-medicinal-products-human-use-first-version_en.pdf (accessed on 4 August 2023).
- Liu, N.; Jin, X.; Feng, C.; Wang, Z.; Wu, F.; Johnson, A.C.; Xiao, H.; Hollert, H.; Giesy, J.P. Ecological Risk Assessment of Fifty Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products (PPCPs) in Chinese Surface Waters: A Proposed Multiple-Level System. Environ. Int. 2020, 136, 105454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, P.; Shappell, N.W.; Mukhopadhyay, M.; Onanong, S.; Rex, K.R.; Snow, D. Surveillance of Plasticizers, Bisphenol A, Steroids and Caffeine in Surface Water of River Ganga and Sundarban Wetland along the Bay of Bengal: Occurrence, Sources, Estrogenicity Screening and Ecotoxicological Risk Assessment. Water Res. 2021, 190, 116668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Central Statistics Office Census 2011 Population Classified by Area (Formerly Volume One). Available online: https://www.cso.ie/en/census/census2011reports/census2011populationclassifiedbyareaformerlyvolumeone/ (accessed on 6 January 2021).
- Central Statistics Office. Census 2016 Summary Results—Part 1; Central Statistics Office: Cork, Ireland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Uisce Éireann (Irish Water). Annual Environmental Report 2020; Uisce Éireann (Irish Water): Dublin, Ireland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Office for National Statistics Population Estimates. Available online: https://www.ons.gov.uk/peoplepopulationandcommunity (accessed on 6 January 2021).
- The Rivers Trust Raws Sewage in Our Rivers. Available online: https://theriverstrust.org/key-issues/sewage-in-rivers (accessed on 11 August 2022).
- Gencat Statistical Institute of Catalonia-Girona (Gironès). Available online: https://www.idescat.cat/emex/?id=170792&lang=en (accessed on 6 June 2023).
- Rodriguez-Mozaz, S.; Chamorro, S.; Marti, E.; Huerta, B.; Gros, M.; Sànchez-Melsió, A.; Borrego, C.M.; Barceló, D.; Balcázar, J.L. Occurrence of Antibiotics and Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Hospital and Urban Wastewaters and Their Impact on the Receiving River. Water Res. 2015, 69, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nejjari, F.; Khoury, B.; Puig, V.; Quevedo, J.; Pascual, J.; de Campos, S. Economic Linear Parameter Varying Model Predictive Control of the Aeration System of a Wastewater Treatment Plant. Sensors 2022, 22, 6008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, A.; Aceña, J.; Pérez, S.; López de Alda, M.; Barceló, D.; Gil, A.; Valcárcel, Y. Pharmaceuticals and Iodinated Contrast Media in a Hospital Wastewater: A Case Study to Analyse Their Presence and Characterise Their Environmental Risk and Hazard. Environ. Res. 2015, 140, 225–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloomfield, J.P.; Lewis, M.A.; Newell, A.J.; Loveless, S.E.; Stuart, M.E. Characterising Variations in the Salinity of Deep Groundwater Systems: A Case Study from Great Britain (GB). J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2020, 28, 100684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadhem, A.J. Assessment of Water Quality in Tigris River-Iraq by Using GIS Mapping. Nat. Resour. 2013, 04, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matsoukis, C.; Amoudry, L.O.; Bricheno, L.; Leonardi, N. Investigation of Spatial and Temporal Salinity Distribution in a River Dominated Delta through Idealized Numerical Modelling. Estuaries Coasts 2021, 44, 1790–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Council Directive 98/83/EC of 3 November 1998 on the Quality of Water Intended for Human Consumption. 2015. Available online: http://data.europa.eu/eli/dir/1998/83/oj (accessed on 4 August 2023).
- UK Goverment Lesgislations. The Water Supply (Water Quality) Regulations 2016. 2016. Available online: https://www.legislation.gov.uk/uksi/2016/614/contents/made (accessed on 4 August 2023).
- USGS Saline Water and Salinity. Available online: https://www.usgs.gov/special-topics/water-science-school/science/saline-water-and-salinity (accessed on 26 January 2023).
- Atekwana, E.A.; Ramatlapeng, G.J.; Ali, H.N.; Njilah, I.K.; Ndondo, G.R.N. Tide-Salinity Patterns Reveal Seawater-Freshwater Mixing Behavior at a River Mouth and Tidal Creeks in a Tropical Mangrove Estuary. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2022, 196, 104684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casila, J.C.; Azhikodan, G.; Yokoyama, K.; Fukushima, K.; Terajima, R. Effect of Rainfall on Saltwater and Suspended Sediment Dynamics in Multi-Branched Urban Tidal Estuaries. J. JSCE Ser. G 2017, 73, I_347–I_352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodriguez-Mozaz, S.; Vaz-Moreira, I.; Varela Della Giustina, S.; Llorca, M.; Barceló, D.; Schubert, S.; Berendonk, T.U.; Michael-Kordatou, I.; Fatta-Kassinos, D.; Martinez, J.L.; et al. Antibiotic Residues in Final Effluents of European Wastewater Treatment Plants and Their Impact on the Aquatic Environment. Environ. Int. 2020, 140, 105733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso, B.; Griffero, L.; Bentos Pereira, H.; Pareja, L.; Pérez Parada, A. Determination of glyphosate and AMPA in freshwater and soil from agroecosystems by 9-fluorenylmethoxycarbonyl chloride derivatization and liquid chromatography - fluorescence detection and tandem mass spectrometry. MethodsX 2022, 9, 101730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsohaimi, I.H.; Alothman, Z.A.; Khan, M.R.; Abdalla, M.A.; Busquets, R.; Alomary, A.K. Determination of bromate in drinking water by ultraperformance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry: Liquid Chromatography. J. Sep. Sci. 2012, 35, 2538–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boltner, A.; Schröder, W.; Grosse, S.; Schreiber, A.; Letzel, T. Simultaneous Characterization of Highly Polar, Polar and Nonpolar Compounds in River Water Using Serial Coupled RPLC and HILIC with a QTRAP® 5500 LC-MS/MS—Identification Using MRM Ratios and Enhanced Product Ion Scanning (EPI). 2016. Available online: https://www.sciex.com/content/dam/SCIEX/pdf/tech-notes/all/RP_and_HILIC_QTRAP_identification_of_compounds_in_river_water_QTRAP_5500_SCIEX_TUM.pdf (accessed on 4 August 2023).
- Carlson, M.; Thompson, R.D. Analyte Loss Due to Membrane Filter Adsorption as Determined by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2000, 38, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fuhrmann, M.; Fitts, J.P. Adsorption of Trace Metals on Glass Fiber Filters. J. Environ. Qual. 2004, 33, 1943–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidayati, N.V.; Syakti, A.D.; Asia, L.; Lebarillier, S.; Khabouchi, I.; Widowati, I.; Sabdono, A.; Piram, A.; Doumenq, P. Emerging contaminants detected in aquaculture sites in Java, Indonesia. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 773, 145057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jardim, W.F.; Montagner, C.C.; Pescara, I.C.; Umbuzeiro, G.A.; Di Dea Bergamasco, A.M.; Eldridge, M.L.; Sodré, F.F. An integrated approach to evaluate emerging contaminants in drinking water. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2012, 84, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana-Mayor, Á.; Socas-Rodríguez, B.; Rodríguez-Ramos, R.; Herrera-Herrera, A.V.; Rodríguez-Delgado, M.Á. Quality assessment of environmental water by a simple and fast non-ionic hydrophobic natural deep eutectic solvent-based extraction procedure combined with liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry for the determination of plastic migrants. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2021, 413, 1967–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Compounds | PNECfw (ng·L−1) | PNECmw (ng·L−1) | Liffey | Thames | Ter | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MEC (ng·L−1) | rRQfw | Riskfw | rRQmw | Riskmw | MEC (ng·L−1) | rRQfw | Riskfw | rRQmw | Riskmw | MEC (ng·L−1) | RQfw | Riskfw | |||
| Testosterone | 1.5 [113] | 0.15 | 3.63 | 2.42 | M | 24.2 | H | 0.900 | 0.6 | L | 6.00 | M | 0.459 a | 0.306 | L |
| Progesterone | 1000 b | 100 | 0.600 | 6 × 10−4 | I | 6 × 10−3 | I | - | - | - | - | - | 5.40 | 5 × 10−3 | I |
| E1 | 3.6 b | 0.36 | 2.46 a | 0.683 | L | 6.83 | M | 5.60 a | 1.56 | M | 15.6 | H | 30.6 | 8.50 | M |
| E1-3S | 20,500 b | 2050 | 1.95 a | 1 × 10−4 | I | 1 × 10−3 | I | 3.62 a | 2 × 10−4 | I | 2 × 10−3 | I | - | - | - |
| Caffeine | 1 [113] | 0.1 | 338 | 338 | H | 3380 | H | 432 | 432 | H | 4320 | H | 705 | 705 | H |
| Triclosan | 20 b | 2 | 35.1 a | 1.75 | M | 17.5 | H | 75.8 | 3.79 | M | 37.9 | H | 4.38 a | 0.219 | L |
| MeP | 5000 b | 500 | 8.41 a | 2 × 10−3 | I | 2 × 10−2 | I | 9.88 a | 2 × 10−3 | I | 2 × 10−2 | I | 39.2 | 8 × 10−3 | I |
| EtP | 2500 [58] | 250 | 3.69 | 1 × 10−3 | I | 1 × 10−2 | I | 19.5 | 8 × 10−3 | I | 8 × 10−2 | I | 9.53 | 4 × 10−3 | I |
| BPA | 1 [114] | 0.1 | 18.0 a | 18.0 | H | 180 | H | 15.9 a | 15.9 | H | 159 | H | 8.41 a | 8.41 | M |
| BPF | 840 [68] | 84 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 18.3 a | 2 × 10−2 | I |
| BPS | 6900 [66] | 690 | 13.0 | 2 × 10−3 | I | 2 × 10−2 | I | 79.3 | 1 × 10−2 | I | 0.11 | L | 79.3 | 1 × 10−2 | I |
| BPAF | 230 [66,68] | 23 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 36.9 | 0.160 | L |
| OP | 100 b | 10 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 54.1 | 0.541 | L |
| NP | 300 b | 30 | - | - | - | - | - | 12.3 a | 4 × 10−2 | I | 0.41 | L | - | - | - |
| BT | 7770 b | 777 | 218 | 2.8 × 10−2 | I | 0.3 | L | 357 | 5 × 10−2 | I | 0.46 | L | 136 | 2 × 10−2 | I |
| TCEP | 4000 b | 400 | 6.84 a | 2 × 10−3 | I | 2 × 10−2 | I | 4767 | 1.19 | M | 11.9 | H | - | - | - |
| TCPP | 30,000 [84] | 3000 | 524 | 2 × 10−2 | I | 0.2 | L | 1065 | 4 × 10−2 | I | 0.36 | L | 132 | 4 × 10−3 | I |
| TBEP | 13,000 [84] | 1300 | 25.6 | 2 × 10−3 | I | 2 × 10−2 | I | 79.2 | 6 × 10−3 | I | 6 × 10−2 | I | 20.8 | 2 × 10−3 | I |
| ΣRQsite | 361 | 455 | 723 | ||||||||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rapp-Wright, H.; Rodríguez-Mozaz, S.; Álvarez-Muñoz, D.; Barceló, D.; Regan, F.; Barron, L.P.; White, B. International Comparison, Risk Assessment, and Prioritisation of 26 Endocrine Disrupting Compounds in Three European River Catchments in the UK, Ireland, and Spain. Molecules 2023, 28, 5994. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28165994
Rapp-Wright H, Rodríguez-Mozaz S, Álvarez-Muñoz D, Barceló D, Regan F, Barron LP, White B. International Comparison, Risk Assessment, and Prioritisation of 26 Endocrine Disrupting Compounds in Three European River Catchments in the UK, Ireland, and Spain. Molecules. 2023; 28(16):5994. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28165994
Chicago/Turabian StyleRapp-Wright, Helena, Sara Rodríguez-Mozaz, Diana Álvarez-Muñoz, Damià Barceló, Fiona Regan, Leon P. Barron, and Blánaid White. 2023. "International Comparison, Risk Assessment, and Prioritisation of 26 Endocrine Disrupting Compounds in Three European River Catchments in the UK, Ireland, and Spain" Molecules 28, no. 16: 5994. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28165994
APA StyleRapp-Wright, H., Rodríguez-Mozaz, S., Álvarez-Muñoz, D., Barceló, D., Regan, F., Barron, L. P., & White, B. (2023). International Comparison, Risk Assessment, and Prioritisation of 26 Endocrine Disrupting Compounds in Three European River Catchments in the UK, Ireland, and Spain. Molecules, 28(16), 5994. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28165994