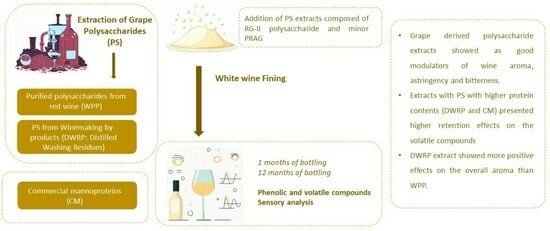
Grape-Derived Polysaccharide Extracts Rich in Rhamnogalacturonans-II as Potential Modulators of White Wine Flavor Compounds
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Oenological Parameters
2.2. Volatile Composition of Viura Wines Treated with PS extracts and CM
2.3. Phenolic Composition of Viura Wines Treated with PS Extracts and CM
2.4. Proanthocyanins of Viura Wines Treated with PS Extracts and CM
2.5. Sensory Characteristics of Viura Wines Treated with PS Extracts and CM
3. Material and Methods
3.1. Polysaccharide Extracts and Commercial Mannoproteins
3.2. Winemaking and Trials
3.3. Standard Oenological Parameters
3.4. Analysis of Volatile Compounds
3.5. Quantification of Monomeric and Polymeric Phenolic Compounds by HPLC-DAD
3.6. Sensory Analysis
3.7. Statistical Analyses
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
Abbreviations
| % Cat | % catechin terminal subunits |
| % Epi | % epicatechin terminal subunits |
| % Epi-gal | % epicatechin gallate terminal subunits |
| AG | ArabinoGalactan |
| AGP | ArabinoGalactan Protein |
| ANOVA | A one-way analysis of variance |
| CM | Commercial Mannoproteins |
| D.O.Ca | Rioja Qualified Denomination of Origin |
| DAD | Diode Array Detector |
| DWRP | Distilled Washing Residues Polysaccharides |
| GP | Glucosyl Polysaccharides |
| GPA | Generalized Procrustes Analysis |
| GPC | Gel Permeation Chromatography |
| HCl | Hydrochloric acid |
| HGs | HomoGalacturonans |
| HPLC | High-Performance Liquid Chromatography |
| IS | Internal Standards |
| mDP | mean Degree of Polymerization |
| MeOH | Methanol |
| MP | MannoProteins |
| Mw | Molecular weight |
| OAV | Odor Activity Values |
| PA | ProAnthocyanidin |
| PRAG | Polysaccharides Rich in Arabinose and Galactose |
| PS | PolySaccharides |
| RG-I | RhamnoGalacturonans type I |
| RG-II | RhamnoGalacturonans type II |
| T1 | One month aging |
| T12 | Twelve months aging |
| WPP | Wine-Purified Polysaccharides |
References
- Jackson, R.S. Wine Science: Principles and Applications, 3rd ed.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2008; pp. 435–441. [Google Scholar]
- Marangon, M.; Vincenzi, S.; Curioni, A. Wine fining with plant proteins. Molecules 2019, 24, 2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waterhouse, A.L.; Sacks, G.L.; Jeffery, D.W. Understanding Wine Chemistry, 1st ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comuzzo, P.; Tat, L.; Tonizzo, A.; Battistutta, F. Yeast derivatives (extracts and autolysates) in winemaking: Release of volatile compounds and effects on wine aroma volatility. Food Chem. 2006, 99, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones-Moore, H.R.; Jelley, R.E.; Marangon, M.; Fedrizzi, B. The interactions of wine polysaccharides with aroma compounds, tannins, and proteins, and their importance to winemaking. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 123, 107150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juega, M.; Carrascosa, A.V.; Martinez-Rodriguez, A.J. Effect of Short Ageing on Lees on the Mannoprotein Content, Aromatic Profile, and Sensorial Character of White Wines. J. Food Sci. 2015, 80, 384–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Magariño, S.; Martínez-Lapuente, L.; Bueno-Herrera, M.; Ortega-Heras, M.; Guadalupe, Z.; Ayestarán, B. Use of Commercial Dry Yeast Products Rich in Mannoproteins for White and Rosé Sparkling Wine Elaboration. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 5670–5681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinaldi, A.; Gonzalez, A.; Moio, L.; Gambuti, A. Commercial mannoproteins improve the mouthfeel and colour of wines obtained by excessive tannin extraction. Molecules 2021, 26, 4133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, S.; Francis, L.; Williams, P.; Kwiatkowski, M.; Gawel, R.; Cheynier, V.; Waters, E. The mouth-feel properties of polysaccharides and anthocyanins in a wine like medium. Food Chem. 2004, 85, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Ramos, D.; Cebollero, E.; Gonzalez, R. A recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain overproducing mannoproteins stabilizes wine against protein haze. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 5533–5540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandão, E.; Silva, M.S.; García-Estévez, I.; Williams, P.; Mateus, N.; Doco, T.; De Freitas, V.; Soares, S. Inhibition Mechanisms of Wine Polysaccharides on Salivary Protein Precipitation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 2955–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, H.H.; Cleary, M.T.; Dokoozlian, N.; Ford, C.M.; Fincher, G.B. Soluble cell wall carbohydrates and their relationship with sensory attributes in Cabernet Sauvignon wine. Food Chem. 2019, 298, 124745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufour, C.; Bayonove, C.L. Influence of wine structurally different polysaccharides on the volatility of aroma substances in a model system. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1999, 47, 671–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manjón, E.; Li, S.; Dueñas, M.; García-Estévez, I.; Escribano-Bailón, M.T. Effect of the addition of soluble polysaccharides from red and white grape skins on the polyphenolic composition and sensory properties of Tempranillo red wines. Food Chem. 2023, 400, 134110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitropoulou, A.; Hatzidimitriou, E.; Paraskevopoulou, A. Aroma release of a model wine solution as influenced by the presence of non-volatile components. Effect of commercial tannin extracts, polysaccharides and artificial saliva. Food Res. Int. 2011, 44, 1561–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Magariño, S.; Cano-Mozo, E.; Bueno-Herrera, M.; Canalejo, D.; Doco, T.; Ayestarán, B.; Guadalupe, Z. The effects of grape polysaccharides extracted from grape by-products on the chemical composition and sensory characteristics of white wines. Molecules 2022, 27, 4815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, H.-Y.; Li, S.-Y.; Zhao, X.; Lan, Y.-B.; Zhang, X.-K.; Shi, Y.; Duan, C.-Q. The compositional characteristics, influencing factors, effects on wine quality and relevant analytical methods of wine polysaccharides: A review. Food Chem. 2023, 403, 134467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, M.A.; York, W.S. The Composition and Structure of Plant Primary Cell Walls. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2003, 8, 1–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones-Moore, H.R.; Jelley, E.E.; Marangon, M.; Fedrizzi, B. The polysaccharides of winemaking: From grape to wine. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 111, 731–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanlin, R.L.; Hrmova, M.; Harbertson, J.F.; Downey, M.O. Review: Condensed tannin and grape cell wall interactions and their impact on tannin extractability into wine. Aust. J. Grape Wine Res. 2010, 16, 173–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrido-Banuelos, G.; Buica, A.; Schuckel, J.; Zietsman, A.J.; Willats, W.G.; Moore, J.P.; Du Toit, W.J. Investigating the relationship between cell wall polysaccharide composition and the extractibility of grape phenolic compounds into shiraz wines. part ii: Extractability during fermentation into wines made from grapes of different ripness levels. Food Chem. 2019, 278, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Fangel, J.U.; Willats, W.G.; Vivier, M.A.; Moore, J.P. Differences in berry skin and pulp cell wall polysaccharides from ripe and overripe shiraz grapes evaluated using glycan profiling reveals extension-rich flesh. Food Chem. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canalejo, D.; Guadalupe, Z.; Martínez-Lapuente, L.; Ayestarán, B.; Pérez-Magariño, S. Optimization of a method to extract polysaccharides from white grape pomace by-products. Food Chem. 2021, 365, 130445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canalejo, D.; Guadalupe, Z.; Martínez-Lapuente, L.; Ayestarán, B.; Pérez-Magariño, S.; Doco, T. Characterization of polysaccharide extracts recovered from different grape and winemaking products. Food Res. Int. 2022, 157, 111480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez, J.; Gonzalo-Diago, A.; Baroja, E.; García-Escudero, E. Características agronómicas y potencial enológico de las variedades de vid blancas autorizadas en la D.O.Ca. Rioja. Zubía Monográfico 2017, 29, 67–82. [Google Scholar]
- Vilanova, M.; Genisheva, Z.; Bescansa, L.; Masa, A.; Oliveira, J.M. Volatile composition of wines from cvs. Blanco lexítimo, Agudelo and Serradelo (Vitis vinifera) grown in Betanzos (NW Spain). J. Inst. Brew. 2009, 115, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.C.; Li, A.H.; Dizy, M.; Ullah, N.; Sun, W.X.; Tao, Y.S. Evaluation of aroma enhancement for “Ecolly” dry white wines by mixed inoculation of selected Rhodotorula mucilaginosa and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Food Chem. 2017, 228, 550–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, V.; López, R.; Cacho, J.F. Quantitative determination of the odorants of young red wines from different wines from different grape varieties. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2000, 80, 1659–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, I.L.; Newton, L. Determining wine aroma from compositional data. Aust. J. Grape Wine Res. 2005, 11, 114–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de-la-Fuente-Blanco, A.; Sáenz-Navajas, M.P.; Valentin, D.; Ferreira, V. Fourteen ethyl esters of wine can be replaced by simpler ester vectors without compromising quality but at the expense of increasing aroma concentration. Food Chem. 2020, 307, 125553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalier, P.; Angot, B.; Delteil, D.; Doco, T.; Gunata, Z. Interactions between aroma compounds and whole mannoprotein isolated from Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains. Food Chem. 2007, 100, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marassi, V.; Marangon, M.; Zattoni, A.; Vincenzi, S.; Versari, A.; Reschiglian, P.; Roda, B.; Curioni, A. Characterization of red wine native colloids by asymmetrical flow field-flow fractionation with online multidetection. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 110, 106204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteban-Fernández, A.; Muñoz-González, C.; Jiménez-Girón, A.; PérezJiménez, M.; Pozo-Bayón, M.Á. Aroma release in the oral cavity after wine intake is influenced by wine matrix composition. Food Chem. 2018, 243, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyu, J.; Chen, S.; Xu, Y.; Li, J.; Nie, Y.; Tang, K. Influence of tannins, human saliva, and the interaction between them on volatility of aroma compounds in a model wine. J. Food Sci. 2021, 86, 4466–4478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Zhai, H.; Ma, W.; Duan, C.; Yi, L. Yeast mannoproteins: Organoleptic modulating functions, mechanisms, and product development trends in winemaking. Food Front. 2023, 2023, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comuzzo, P.; Tat, L.; Fenzi, D.; Brotto, L.; Battistutta, F.; Zironi, R. Interactions between yeast autolysates and volatile compounds in wine and model solution. Food Chem. 2011, 127, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avram, V.; Floare, C.G.; Hosu, A.; Cimpoiu, C.; Măruţoiu, C.; Moldovan, Z. Characterization of Romanian Wines by Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Lett. 2015, 48, 1099–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loscos, N.; Hernandez-Orte, P.; Cacho, J.F.; Ferreira, V. Release and formation of varietal aroma compounds during alcoholic fermentation from nonfloral grape odorless flavor precursors fractions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 6674–6684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, T.; Fernandes, C.; Nunes, F.M.; Filipe-Ribeiro, L.; Cosme, F. Influence of the structural features of commercial mannoproteins in white wine protein stabilization and chemical and sensory properties. Food Chem. 2014, 159, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Sluyter, S.C.; McRae, J.M.; Falconer, R.J.; Smith, P.A.; Bacic, A.; Waters, E.J.; Marangon, M. Wine protein haze: Mechanisms of formation and advances in prevention. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 4020–4030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waters, E.J.; Pellerin, P.; Brillouet, J.M. A Saccharomyces mannoprotein that protects wine from protein haze. Carbohydr. Polym. 1994, 23, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Barrio-Galán, R.; Pérez-Magariño, S.; Ortega-Heras, M.; Guadalupe, Z.; Ayestarán, B. Polysaccharide characterization of commercial dry yeast preparations and their effect on white and red wine composition. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 48, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Barrio-Galán, R.; Medel-Marabolí, M.; Peña-Neira, Á. Effect of different aging techniques on the polysaccharide and phenolic composition and sensory characteristics of Syrah red wines fermented using different yeast strains. Food Chem. 2015, 179, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guadalupe, Z.; Palacios, A.; Ayestarán, B. Maceration enzymes and mannoproteins: A possible strategy to increase colloidal stability and color extraction in red wines. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 4854–4862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loira, I.; Vejarano, R.; Morata, A.; Ricardo-da-Silva, J.M.; Laureano, O.; González, M.C. Effect of Saccharomyces strains on the quality of red wines aged on lees. Food Chem. 2013, 139, 1044–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Lapuente, L.; Guadalupe, Z.; Ayestarán, B.; Ortega-Heras, M.; Pérez-Magariño, S. Sparkling Wines Produced from Alternative Varieties: Sensory Attributes and Evolution of Phenolics during Winemaking and Aging. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 2013, 64, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monagas, M.; Gómez-Cordovés, C.; Bartolomé, B.; Laureano, O.; Ricardo da Silva, J.M. Monomeric, oligomeric and polymeric flavan-3-ol composition of wines and grapes from Vitis vinífera L.cv. Graciano, Tempranillo, and Cabernet Sauvignon. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 6475–6481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidal, S.; Francis, L.; Guyot, S.; Marnet, N.; Kwiatkowski, M.; Gawel, R.; Cheynier, V.; Waters, E.J. The Mouth-Feel Properties of Grape and Apple Proanthocyanidins in a Wine-Like Medium. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2003, 83, 564–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjón, E.; Recio-Torrado, A.; Ramos-Pineda, A.M.; García-Estévez, I.; Escribano-Bailón, M.T. Effect of different yeast mannoproteins on the interaction between wine flavanols and salivary proteins. Food Res. Int. 2021, 143, 110279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poncet-Legrand, C.; Doco, T.; Williams, P.; Vernhet, A. Inhibition of grape seed tannin aggregation by wine mannoproteins: Effect of polysaccharide molecular weight. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 2007, 58, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, X.; Zhao, P.; Ma, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Cao, X.; Cheng, C.; Liu, H.; Du, G. Mannoproteins interfering wine astringency by modulating the reaction between phenolic fractions and protein in a model wine system. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 152, 112217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riou, V.; Vernhet, A.; Doco, T.; Moutounet, M. Aggregation of grape seed tannins in model wine—Effect of wine polysaccharides. Food Hydrocoll. 2002, 16, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laguna, L.; Sarkar, A. Oral tribology: Update on the relevance to study astringency in wines. Tribol. Mater. Surf. Interfaces 2017, 102, 478–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buffetto, F.; Ropartz, D.; Zhang, X.J.; Gilbert, H.J.; Guillon, F.; Ralet, M.C. Recovery and fine structure variability of RGII sub-domains in wine (Vitis vinifera Merlot). Ann. Bot. 2014, 114, 1327–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- OIV. International Organisation of Vine and Wine. In Compendium of International Methods of Wine and Must Analysis; International Organisation of Vine and Wine: Paris, France, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Magariño, S.; Martínez-Gil, A.; Bueno-Herrera, M.; Nevares, I.; del Alamo-Sanza, M. Kinetics of oxygen consumption, a key factor in the changes of young wines composition. LWT–Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 182, 114786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno, M.; Zapata, J.; Culleré, L.; Franco-Luesma, E.; de-la-Fuente-Blanco, A.; Ferreira, V. Optimization and Validation of a Method to Determine Enolones and Vanillin Derivatives in Wines—Occurrence in Spanish Red Wines and Mistelles. Molecules 2023, 28, 4228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Portu, J.; López, R.; Baroja, E.; Santamaría, P.; Garde-Cerdán, T. Improvement of grape and wine phenolic content by foliar application to grapevine of three different elicitors: Methyl jasmonate, chitosan, and yeast extract. Food Chem. 2016, 201, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guadalupe, Z.; Soldevilla, A.; Sáenz-Navajas, M.P.; Ayestarán, B. Analysis of polymeric phenolics in red wines using different techniques combined with gel permeation chromatography fractionation. J. Chromatogr. A 2006, 1112, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 4121:2003; Sensory Analysis—Guidelines for the Use of Quantitative Response Scales. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2003.


| T1 | T12 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compounds | C b | WPP b | DWRP b | CM b | F-Value | C b | WPP b | DWRP b | CM b | F-Value |
| 1-propanol | 33,643 (1522.0) b | 37,529 (1442.0) c | 32,195 (1180.8) a,b | 30,672 (200.4) a | 17.807 *** | 32,796 (1171.0) c | 27,407 (876.1) a | 29,552 (1246.6) b | 29,756 (154.1) b | 31.726 *** |
| Isobutanol | 1259.3 (39.6) b | 1040.9 (71.8) a | 1334.4 (62.6) b | 1324.7 (58.7) b | 15.938 *** | 22,424 (1125.7) c | 18,340 (1603.0) a | 20,079 (1068.4) b | 20,687 (543.8) b | 12.927 ** |
| 2-Methyl-1-butanol | 29,536 (2762.0) | 29,560 (1583.1) | 29,834 (1103.0) | 27,687 (831.9) | 0.972 (ns) | 27,447 (2124.9) b | 20,988 (4947.0) a | 24,600 (2307.3) a,b | 26,457 (639.9) b | 5.598 * |
| 3-Methyl-1-butanol | 28,933 (2015.0) | 25,780 (1510.9) | 26,576 (2295.3) | 28,253 (2114.2) | 3.073 (ns) | 158,137 (8747.6) b | 125,476 (20,626) a | 143,312 (8373.6) b | 149,973 (3206) b | 7.953 ** |
| 2-Phenylethanol | 17,197 (104.3) | 15,681 (866.3) | 18,104 (1736.7) | 15,847 (323.5) | 3.987 (ns) | 23,143 (1357.6) a | 24,122 (963.1) b | 22,406 (243.8) a | 24,360 (126.1) b | 20.059 *** |
| TOTAL HIGHER ALCOHOLS | 110,569 (6442.9) | 109,592 (4431.8) | 108,044 (5858.4) | 103,784 (3042.8) | 3.380 (ns) | 263,948 (14,526) c | 216,335 (25,337) a | 239,951 (13,239) b | 251,234 (4109.5) bc | 9.723 ** |
| 1-Hexanol | 444.9 (20.0) a | 481.3 (22.9) a | 986.7 (100.6) b | 1037.8 (134.3) b | 41.750 *** | 960.9 (22.2) | 952.4 (13.4) | 953.2 (15.7) | 960.9 (11.9) | 0.506 (ns) |
| €-3-Hexenol | 57.8 (4.2) a | 47.0 (2.8) a | 132.8 (8.7) c | 78.0 (6.8) b | 118.549 *** | 95.6 (6.9) | 94.1 (2.1) | 98.8 (0.4) | 97.7 (8.7) | 0.831 (ns) |
| (Z)-3-Hexenol | 181.2 (8.5) a | 149.2 (6.0) a | 416.2 (53.7) c | 244.3 (30.7) b | 43.235 *** | 485.8 (7.8) | 488.3 (1.3) | 491.4 (3.0) | 492.8 (6.0) | 2.080 (ns) |
| Benzyl alcohol | 198.5 (8.4) b | 198.5 (7.3) b | 213.3 (15.7) b | 107.4 (10.2) a | 59.554 *** | 153.2 (4.3) a | 167.8 (8.4) b | 177.3 (2.4) c | 173.3 (3.8) bc | 25.325 *** |
| TOTAL C6 ALCOHOLS | 882.4 (23.7) a | 876.0 (35.0) a | 1749.0 (178.7) c | 1467.5 (182.0) b | 33.611 *** | 1695.5 (18.8) | 1703.2 (18.6) | 1720.6 (21.6) | 1724.6 (5.3) | 3.691 (ns) |
| Ethyl butyrate | 54.0 (2.4) a | 54.0 (7.9) a | 110.3 (5.7) b | 62.6 (10.7) a | 40.579 *** | 213.9 (6.7) a | 254.5 (0.2) c | 232.8 (1.4) b | 263.4 (4.6) d | 175.091 *** |
| Ethyl hexanoate | 722.6 (88.1) a | 740.5 (31.8) a | 1474.6 (120.9) b | 861.0 (72.4) a | 52.911 *** | 353.4 (10.2) a | 374.9 (7.2) b | 354.8 (0.6) a | 403.4 (3.1) c | 79.376 *** |
| Ethyl octanoate | 1058.2 (89.8) a | 1003.7 (32.3) a | 2069.5 (422.9) b | 1373.3 (117.8) a | 14.281 *** | 266.5 (4.1) b | 256.3 (1.9) a | 252.0 (3.3) a | 293.9 (3.8) c | 188.401 *** |
| Ethyl decanoate | 237.8 (40.5) a | 210.4 (13.2) a | 579.1 (122.7) c | 388.0 (32.9) b | 19.152 *** | 32.2 (2.9) a | 33.5 (0.5) a | 32.0 (1.6) a | 38.4 (1.8) b | 14.596 *** |
| Ethyl-2-methylbutyrate | 10.6 (0.2) a | 10.1 (0.3) a | 12.2 (0.4) b | 10.1 (0.1) a | 38.058 *** | 7.2 (0.2) a | 7.0 (0.1) a | 8.0 (0.6) b | 7.3 (0.2) a | 10.679 ** |
| Ethyl isovalerate | 22.0 (2.1) | 23.6 (2.1) | 24.5 (1.3) | 21.1 (1.5) | 2.213 (ns) | 17.8 (2.3) | 17.6 (3.5) | 19.3 (0.2) | 16.5 (2.0) | 1.274 (ns) |
| Ethyl lactate | 1067.1 (40.2) a | 992.9 (30.5) a | 2522 (379.8) c | 1577.9 (247.2) b | 28.642 *** | 21,806.8 (211.9) a | 22,412.9 (217.2) b | 22,626.0 (126.8) b,c | 22,861.0 (96.4) c | 21.994 *** |
| TOTAL ETHYL ESTERS | 3172.3 (263.3) a | 3035.2 (100.8) a | 6792.1 (594.0) c | 4294.0 (285.3) b | 25.530 *** | 22,697.7 (212.3) a | 23,356.6 (217.2) b | 23,524.9 (126.8) b | 23,883.9 (96.1) c | 25.116 *** |
| Propyl acetate | 565.2 (2.0) a | 571.5 (31.1) a | 1131.6 (56.6) c | 712.0 (84.1) b | 75.742 *** | 34.9 (1.2) | 34.4 (0.5) | 32.8 (0.1) | 35.1 (1.4) | 3.771 (ns) |
| Isobutyl acetate | 367.0 (72.5) a,b | 334.8 (33.3) a | 754.9 (15.4) c | 412.4 (28.7) b | 155.111 *** | 27.4 (2.0) a | 28.6 (2.2) a | 25.8 (0.6) a | 35.8 (4.9) b | 7.058 * |
| Isoamyl acetate | 2554.5 (250.1) a,b | 2272.8 (66.0) a | 5156.1 (173.8) c | 3110.6 (522.5) b | 55.001 *** | 965.1 (22.3) a | 963.8 (5.6) a | 1011.6 (28.3) b | 1028.3 (40.3) b | 4.368 * |
| Hexyl acetate | 384.2 (53.0) a | 310.2 (16.7) a | 726.2 (86.8) b | 374.1 (61.1) a | 29.512 *** | 37.3 (1.9) a | 40.5 (0.3) c | 38.1 (0.1) a | 38.8 (0.4) b,c | 5.596 * |
| β-Phenylethyl acetate | 543.3 (1.4) a,b | 434.2 (48.2) a | 1081.7 (50.6) c | 625.9 (95.5) b | 69.424 *** | 69.8 (0.6) a | 78.0 (0.2) c | 78.4 (1.4) c | 77.5 (1.2) c | 52.655 *** |
| TOTAL ACETATES | 4414.2 (279.0) a | 3923.5 (98.8) a | 8850.4 (355.3) c | 5235 (716.2) b | 69.250 *** | 1134.5 (17.1) a | 1145.2 (6.9) a | 1186.6 (28.9) b | 1215.5 (48.1) b | 4.838 * |
| Isovaleric acid | 38.8 (0.1) a | 33.5 (2.4) a | 53.8 (8.7) b | 58.9 (9.6) b | 10.024 ** | 365.3 (5.0) | 362.5 (0.8) | 365.1 (7.2) | 376.1 (12.8) | 0.22 (ns) |
| Hexanoic acid | 1221.7 (17.5) a | 1071.0 (109.8) a | 1630.8 (176.2) b | 1610.2 (217.9) b | 10.403 ** | 4384.4 (17.1) b | 4342.0 (3.4) | 4318.0 (44.0) | 4302.1 (47.1) | 0.072 (ns) |
| Octanoic acid | 2574.9 (12.8) b | 1989.3 (267.2) a | 3062.8 (190.9) c | 3076.9 (306.5) c | 15.690 *** | 4.035.4 (10.0) a | 4140.3 (59.4) | 4040.2 (6.2) | 4131.6 (89.6) | 0.078 (ns) |
| Decanoic acid | 41.2 (10.2) a,b | 37.2 (3.1) a | 66.2 (6.4) c | 60.5 (19.4) b,c | 4.576 * | 301.7 (12.2) b | 297.3 (5.8) | 296.6 (1.9) | 304.8 (7.5) | 0.555 (ns) |
| TOTAL ACIDS | 3876.6 (40.6) b | 3131.0 (382.5) a | 4813.6 (382.2) c | 4806.5 (553.4) c | 13.222 ** | 9086.7 (34.3) | 9141.9 (69.4) | 9020.2 (59.3) | 9114.5 (141.9) | 0.403 (ns) |
| 4-vinylguaiacol | 332.5 (46.3) a | 299.0 (7.2) a | 662.8 (116.9) b | 345.7 (21.3) a | 21.176 *** | 121.4 (1.3) a | 128.3 (6.8) a | 141.3 (8.3) b | 126.7 (4.3) a | 23.578 *** |
| 4-vinylfenol | 267.5 (45.6) a | 262.7 (10.3) a | 664.1 (47.9) c | 373.4 (22.6) b | 85.457 *** | 46.9 (0.6) a | 47.0 (0.6) a | 56.7 (0.2) b | 49.2 (0.3) a | 7.189 *** |
| TOTAL PHENOLS | 600.0 (91.9) a | 561.7 (8.8) a | 1326.9 (158.9) b | 719.1 (43.9) a | 40.515 *** | 168.3 (1.4) a | 175.3 (6.8) a | 198.0 (8.3) b | 175.9 (4.3) a | 17.713 *** |
| Linalool | 37.1 (1.9) a | 45.9 (1.9) b | 42.8 (2.2) b | 44.5 (1.8) b | 11.642 *** | 27.5 (2.3) a | 35.1 (2.5) b | 34.4 (0.7) b | 34.3 (1.8) b | 19.486 *** |
| α-Terpineol | 6.2 (0.2) a | 6.5 (0.2) a | 6.9 (0.1) b | 6.3 (0.1) a | 11.500 ** | 2.8 (0.1) c | 2.6 (0.1) b | 3.8 (0.2) d | 2.3 (0.1) a | 163.189 *** |
| TOTAL TERPENES | 43.3 (1.9) a | 52.4 (1.9) b | 49.7 (2.3) b | 50.8 (1.8) b | 12.057 *** | 30.3 (2.3) a | 37.6 (2.6) b | 38.2 (0.8) b | 36.6 (1.8) b | 19.233 *** |
| T1 | T12 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compounds | Odor Descriptor | Odor Threshold (µg L−1) | Reference | C b | WPP b | DWRP b | CM b | F-Value | C b | WPP b | DWRP b | CM b | F-Value |
| Isobutanol | Alcohol, solvent, green, bitter | 75,000 | [25] | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 3.167 (ns) | |||||
| 2-Methyl-1-butanol | Alcohol | 30,000 | [25] | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 0.9 | 0.972 (ns) | 0.9 b | 0.7 a | 0.8 b | 0.9 b | 7.667 * |
| 3-Methyl-1-butanol | Alcohol | 7000 | [26] | 4.1 | 3.7 | 3.8 | 4.0 | 3.073 (ns) | 5.3 c | 4.2 a | 4.8 b | 5.0 b | 7.921 ** |
| 2-Phenylethanol | Roses, honey | 14,000 | [27] | 1.2 | 1.1 | 1.3 | 1.1 | 3.987 (ns) | 1.6 a | 1.7 b | 1.6 a | 1.7 b | 17.000 *** |
| (E)-3-Hexenol | Green, floral | 400 | [27] | 0.1 a | 0.1 a | 0.3 c | 0.2 b | 118.549 *** | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.667 (ns) |
| (Z)-3-Hexenol | Green, floral | 400 | [27] | 0.5 a | 0.4 a | 1.0 c | 0.6 b | 43.235 *** | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.383 (ns) |
| Ethyl butyrate | Papaya, apple | 20 | [26] | 2.7 a | 2.7 a | 5.5 b | 3.1 a | 40.579 *** | 10.7 a | 12.7 c | 11.6 b | 13.2 d | 219.933 *** |
| Ethyl hexanoate | Apple, fruity, sweetish | 14 | [26] | 51.6 a | 52.9 a | 105.3 b | 61.5 a | 52.911 *** | 25.2 a | 26.8 b | 25.3 a | 28.8 c | 74.772 *** |
| Ethyl octanoate | Apple, fruity, sweetish | 5 | [26] | 211.6 a | 200.7 a | 413.9 b | 274.7 a | 14.281 *** | 53.3 b | 51.3 a | 50.4 a | 58.8 c | 173.479 *** |
| Ethyl decanoate | Grape | 200 | [27] | 1.2 a | 1.1 a | 2.9 c | 1.9 b | 19.152 *** | |||||
| Ethyl 2-methylbutyrate | Fruity, strawberry, apple, blackberry | 2 | [30] | 5.3 a | 5.0 a | 6.1 b | 5.1 a | 38.058 *** | 3.6 a | 3.5 a | 4.0 b | 3.7 a | 10.563 ** |
| Ethyl isovalerate | Fruity | 3 | [28] | 7.3 | 7.9 | 8.2 | 7.0 | 2.213 (ns) | 5.9 | 5.9 | 6.4 | 5.5 | 1.275 (ns) |
| Isoamyl acetate | Banana, apple | 30 | [28] | 85.2 a,b | 75.8 a | 171.9 c | 103.7 b | 55.001 *** | 32.2 a | 32.1 a | 33.7 a | 34.3 b | 4.873 * |
| β-Phenylethyl acetate | Banana | 250 | [27] | 2.2 a,b | 1.7 a | 4.3 c | 2.5 b | 69.424 *** | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 1.036 (ns) |
| Isovaleric acid | Cheese | 33 | [27] | 1.2 a | 1.0 a | 1.6 b | 1.8 b | 10.024 ** | 10.9 | 10.9 | 10.9 | 11.3 | 0.221 (ns) |
| Hexanoic acid | Cheese, fatty | 3000 | [29] | 0.4 a | 0.4 a | 0.5 b | 0.5 b | 10.403 ** | 1.5 | 1.4 | 1.4 | 1.4 | 0.072 (ns) |
| Octanoic acid | Cheese, fatty, rancid | 1000 | [29] | 2.6 b | 2.0 a | 3.1 c | 3.1 c | 15.690 *** | 4.0 | 4.1 | 4.0 | 4.1 | 0.078 (ns) |
| 4-vinylguaiacol | Clove, curry | 40 | [28] | 8.3 a | 7.5 a | 16.6 b | 8.6 a | 21.176 *** | 3.0 a | 3.2 a | 3.5 b | 3.2 a | 23.578 *** |
| 4-vinylphenol | Smoky, almond | 180 | [28] | 1.5 a | 1.5 a | 3.7 c | 2.1 b | 85.457 *** | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.423 (ns) |
| Linalool | Floral, citrus | 25 | [25] | 1.5 | 1.8 | 1.7 | 1.8 | 1.833 (ns) | 1.1 | 1.4 | 1.4 | 1.4 | 1.129 (ns) |
| T1 | T12 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flavonoids c | C b | WPP b | DWRP b | CM b | F-Value | C b | WPP b | DWRP b | CM b | F-Value |
| Flavonols | ||||||||||
| Myricetin-3-gal | 1.30 (0.02) | nd | nd | nd | - | 0.91 (0.01) | nd | nd | nd | - |
| Myricetin-3-glcU | 1.92 (0.04) | 1.79 (0.19) | 1.50 (0.32) | 1.40 (0.42) | 2.559 (ns) | 1.34 (0.03) | 1.25 (0.12) | 1.05 (0.2) | 0.98 (0.27) | 3.095 (ns) |
| Myricetin-3-glc | 0.95 (0.01) b | 0.30 (0.02) a | 1.39 (0.01) d | 0.99 (0.10) c | 356.043 *** | 0.67 (0.01) b | 0.21 (0.01) a | 0.97 (0.01) c | 0.69 (0.06) b | 433.25 *** |
| Quercetin-3-glcU | 1.80 (0.04) b | 1.10 (0.32) a | 1.88 (0.21) b | 4.04 (0.52) c | 31.623 *** | 1.26 (0.03) b | 0.77 (0.2) a | 1.32 (0.13) b | 2.83 (0.33) c | 39.401 *** |
| Quercetin-3-glc | 1.73 (0.04) a | 3.33 (0.74) b | 1.24 (0.34) a | 1.06 (0.19) a | 18.696 *** | 1.21 (0.03) a | 2.33 (0.47) b | 0.87 (0.22) a | 0.74 (0.12) a | 22.619 *** |
| Free kaempferol | 1.86 (0.04) a | 5.48 (1.06) c | 2.86 (0.34) a,b | 4.60 (0.78) b | 14.731 *** | 1.30 (0.03) a | 3.84 (0.68) c | 2.00 (0.22) a | 3.22 (0.50) b | 17.796 *** |
| Free syringetin | 3.28 (0.91) | nd | nd | nd | - | 2.30 (0.58) | nd | nd | nd | - |
| Isorhamnetin | 1.63 (0.02) d | 0.28 (0.03) a | 0.36 (0.04) b | 0.41 (0.04) c | 1443.579 *** | 1.14 (0.01) d | 0.20 (0.02) a | 0.25 (0.03) b | 0.29 (0.03) c | 1483.778 *** |
| Total myricetin | 4.17 (0.05) c | 2.09 (0.19) a | 2.89 (0.32) b | 2.39 (0.43) b | 46.759 *** | 2.92 (0.03) c | 1.46 (0.12) a | 2.02 (0.2) b | 1.67 (0.28) b | 56.42 *** |
| Total quercetin | 3.53 (0.06) a,b | 4.43 (0.81) b | 3.12 (0.40) a | 5.10 (0.55) b | 4.190 * | 2.47 (0.04) a,b | 3.10 (0.51) b,c | 2.19 (0.26) a | 3.57 (0.35) c | 5.029 * |
| Total kaempferol | 1.86 (0.04) a | 5.48 (1.06) c | 2.86 (0.34) a,b | 4.60 (0.78) b | 14.731 *** | 1.30 (0.03) a | 3.84 (0.68) c | 2.00 (0.22) a | 3.22 (0.50) b | 17.796 *** |
| Total syringetin | 3.28 (0.91) | nd | nd | nd | - | 2.30 (0.58) | nd | nd | nd | - |
| Total Flavonols | 14.47 (0.91) c | 12.28 (1.35) b | 9.23 (0.62) a | 12.50 (1.05) b | 24.269 *** | 10.13 (0.58) c | 8.60 (0.86) b | 6.46 (0.39) a | 8.75 (0.67) b | 29.347 *** |
| Flavanols | ||||||||||
| Epigallocatechin | 7.08 (0.84) b | 3.85 (0.78) a | 3.54 (0.65) a | 4.44 (0.71) a | 17.396 *** | 3.03 (0.13) | 2.99 (0.09) | 2.99 (0.13) | 2.94 (0.08) | 0.078 (ns) |
| Catechin | 17.96 (1.32) | 17.79 (1.47) | 17.92 (1.67) | 18.98 (1.79) | 0.021 (ns) | 29.83 (2.34) | 29.86 (2.41) | 30.22 (2.22) | 29.52 (2.31) | 0.019 (ns) |
| Epicatechin | 14.38 (1.44) | 16.20 (1.09) | 16.54 (1.43) | 17.40 (2.01) | 1.440 (ns) | 16.58 (1.54) c | 2.48 (0.52) a | 4.24 (0.37) b | 4.14 (0.42) b | 172.286 *** |
| Total Flavanols | 39.42 (2.13) | 37.84 (1.99) | 38.00 (2.29) | 40.82 (2.79) | 0.871 (ns) | 49.44 (2.80) b | 35.33 (2.47) a | 37.45 (2.25) a | 36.60 (2.35) a | 11.553 ** |
| Hydroxybenzoic Acids (HBAs) | ||||||||||
| Gallic acid | 8.70 (1.02) | 7.70 (0.85) | 7.55 (0.67) | 7.98 (0.77) | 1.253 (ns) | 5.02 (0.76) a | 7.98 (0.45) b | 8.16 (0.76) b | 7.32 (0.61) b | 16.346 *** |
| Hydroxycinnamic acids (HCAs) | ||||||||||
| trans-Caftaric acid | 2.22 (0.19) a | 2.09 (0.31) a | 6.22 (0.87) b | 2.12 (0.13) a | 55.027 *** | 1.02 (0.12) | 1.02 (0.08) | 1.02 (0.07) | 1.01 (0.10) | 0.009 (ns) |
| trans-Coutaric acid | 16.79 (1.72) | 14.38 (1.65) | 13.56 (1.03) | 15.37 (1.28) | 2.886 (ns) | 2.32 (0.65) | 2.27 (0.31) | 2.32 (0.3) | 2.32 (0.13) | 0.014 (ns) |
| Caffeic acid | 1.15 (0.04) c | 1.00 (0.02) a,b | 0.96 (0.03) a | 1.13 (0.04) b,c | 18.200 *** | nd | nd | nd | nd | - |
| trans-fertaric acid | 0.14 (0.01) a | 0.17 (0.01) b | 0.22 (0.01) c | 0.27 (0.01) c | 46.75 *** | nd | nd | nd | nd | - |
| Ferulic acid | 0.43 (0.02) a | 0.42 (0.02) a | 0.49 (0.02) a | 0.60 (0.02) b | 10.688 ** | nd | nd | nd | nd | - |
| Total HCAs | 20.73 (1.73) b | 18.06 (1.68) a | 21.45 (1.35) b | 19.49 (1.29) a | 3.757 (ns) | 3.34 (0.66) | 3.29 (0.32) | 3.34 (0.31) | 3.33 (0.16) | 0.011 (ns) |
| Total monomeric phenolics | 83.32 (3.06) b | 75.88 (3.05) a | 76.23 (2.81) a | 80.79 (3.33) a,b | 4.480 * | 67.93 (3.04) c | 55.2 (2.67) a | 55.41 (2.43) a | 56.00 (2.52) a,b | 16.741 *** |
| T1 | T12 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polymeric Compounds b | C c | WPP c | DWRP c | CM c | F-Value | C c | WPP c | DWRP c | CM c | F-Value |
| PA | 60.47 (3.91) | 54.78 (3.33) | 55.45 (3.26) | 49.33 (2.89) | 3.660 (ns) | 45.2 (2.95) b | 35.74 (1.87) a | 34.80 (1.95) a | 32.69 (1.83) a | 6.986 * |
| % Cat | 10.40 (2.64) b | 7.23 (1.23) a | 13.07 (1.58) c | 11.07 (1.47) b,c | 10.695 ** | 9.5 (2.32) b | 7.02 (1.12) a | 12.10 (1.32) c | 11.02 (1.32) b,c | 11.538 ** |
| % Epi | 16.13 (2.09) a | 21.75 (2.97) b,c | 23.59 (2.79) c | 18.77 (2.36) a,b | 9.774 ** | 7.02 (0.95) a | 9.71 (1.39) b | 10.72 (1.24) b | 9.17 (1.13) b | 10.363 ** |
| % Epi-gal | 2.78 (0.31) | 2.69 (0.27) | 2.69 (0.37) | 3.26 (0.59) | 2.729 (ns) | 1.60 (0.11) a | 1.58 (0.10) a | 1.49 (0.13) a | 1.95 (0.23) b | 10.924 ** |
| mDP | 2.75 (0.35) c | 2.08 (0.23) b | 1.61 (0.15) a | 1.72 (0.17) a | 174.180 *** | 3.22 (0.47) c | 2.37 (0.24) b | 1.62 (0.14) a | 1.68 (0.15) a | 155.770 *** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Canalejo, D.; Martínez-Lapuente, L.; Ayestarán, B.; Pérez-Magariño, S.; Doco, T.; Guadalupe, Z. Grape-Derived Polysaccharide Extracts Rich in Rhamnogalacturonans-II as Potential Modulators of White Wine Flavor Compounds. Molecules 2023, 28, 6477. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28186477
Canalejo D, Martínez-Lapuente L, Ayestarán B, Pérez-Magariño S, Doco T, Guadalupe Z. Grape-Derived Polysaccharide Extracts Rich in Rhamnogalacturonans-II as Potential Modulators of White Wine Flavor Compounds. Molecules. 2023; 28(18):6477. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28186477
Chicago/Turabian StyleCanalejo, Diego, Leticia Martínez-Lapuente, Belén Ayestarán, Silvia Pérez-Magariño, Thierry Doco, and Zenaida Guadalupe. 2023. "Grape-Derived Polysaccharide Extracts Rich in Rhamnogalacturonans-II as Potential Modulators of White Wine Flavor Compounds" Molecules 28, no. 18: 6477. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28186477
APA StyleCanalejo, D., Martínez-Lapuente, L., Ayestarán, B., Pérez-Magariño, S., Doco, T., & Guadalupe, Z. (2023). Grape-Derived Polysaccharide Extracts Rich in Rhamnogalacturonans-II as Potential Modulators of White Wine Flavor Compounds. Molecules, 28(18), 6477. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28186477