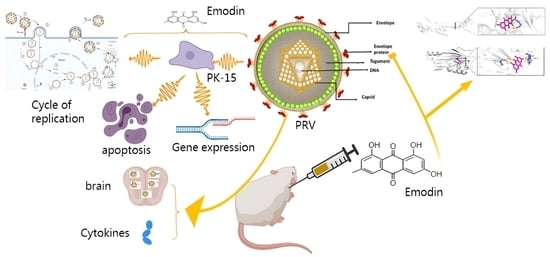
Emodin as an Inhibitor of PRV Infection In Vitro and In Vivo
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Emodin Inhibits the Proliferation of PRV in PK-15 Cells
2.2. Effect of Emodin on Stages of the PRV Life Cycle
2.3. Emodin Inhibits PRV Gene Expression
2.4. Effect of Emodin on PRV gB and gD Protein Expression
2.5. Emodin Alleviates PRV-Induced Apoptosis
2.6. Emodin Inhibits PRV Infection in Mice
2.7. Changes in Serum Cytokines
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Cells, Virus, and Reagents
3.2. Assays for Cytotoxicity and Inhibitory Activity
3.3. Inhibitory Action Assay
3.4. Gene Expression Assay
3.5. Western Blotting
3.6. Molecular Docking
3.7. Cell Apoptosis Assay
3.8. Mice Viral Challenge Protection Test
3.9. Statistical Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pomeranz, L.E.; Reynolds, A.E.; Hengartner, C.J. Molecular biology of pseudorabies virus: Impact on neurovirology and veterinary medicine. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2005, 69, 462–500. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sehl, J.; Teifke, J.P. Comparative Pathology of Pseudorabies in Different Naturally and Experimentally Infected Species—A Review. Pathogens 2020, 9, 633. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gu, Z.; Dong, J.; Wang, J.; Hou, C.; Sun, H.; Yang, W.; Bai, J.; Jiang, P. A novel inactivated gE/gI deleted pseudorabies virus (PRV) vaccine completely protects pigs from an emerged variant PRV challenge. Virus Res. 2015, 195, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zheng, H.H.; Fu, P.F.; Chen, H.Y.; Wang, Z.Y. Pseudorabies Virus: From Pathogenesis to Prevention Strategies. Viruses 2022, 14, 1638. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, X.; Xie, C.; Ding, S.; Yang, H.; Guo, S.; Li, J.; Qin, L.; Ban, F.; Wang, D.; et al. A novel human acute encephalitis caused by pseudorabies virus variant strain. Clin. Infect. Dis. Off. Publ. Infect. Dis. Soc. Am. 2020, 73, e3690–e3700. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, W.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, X.; Zhang, H. Case Report: Metagenomic Next-Generation Sequencing for Diagnosis of Human Encephalitis and Endophthalmitis Caused by Pseudorabies Virus. Front. Med. 2022, 8, 753988. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, Z.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, B.; Chen, H.; Wang, X. Cytopathic and Genomic Characteristics of a Human-Originated Pseudorabies Virus. Viruses 2023, 15, 170. [Google Scholar]
- Harvey, A. The role of natural products in drug discovery and development in the new millennium. Idrugs Investig. Drugs J. 2010, 13, 70–72. [Google Scholar]
- van Herwerden, E.F.; Süssmuth, R.D. Sources for Leads: Natural Products and Libraries. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2016, 232, 91–123. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, E.; Stewart, L.E.; Darley, B.A.; Pham, A.M.; Esteban, I.; Panda, S.S. Plant-Based Natural Products and Extracts: Potential Source to Develop New Antiviral Drug Candidates. Molecules 2021, 26, 6197. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.; Cui, Q.; Fu, Q.; Song, X.; Jia, R.; Yang, Y.; Zou, Y.; Li, L.; He, C.; Liang, X.; et al. Antiviral properties of resveratrol against pseudorabies virus are associated with the inhibition of IκB kinase activation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8782. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.; Tong, W.; Song, X.; Jia, R.; Li, L.; Zou, Y.; He, C.; Liang, X.; Lv, C.; Jing, B.; et al. Antiviral Effect of Resveratrol in Piglets Infected with Virulent Pseudorabies Virus. Viruses 2018, 10, 457. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Li, C.; Li, Z.; Shangguan, A.; Jiang, J.; Zeng, W.; Zhang, S.; He, Q. Quercetin as an antiviral agent inhibits the Pseudorabies virus in vitro and in vivo. Virus Res. 2021, 305, 198556. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Men, X.; Li, S.; Cai, X.; Fu, L.; Shao, Y.; Zhu, Y. Antiviral Activity of Luteolin against Pseudorabies Virus In Vitro and In Vivo. Animals 2023, 13, 761. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dong, X.; Fu, J.; Yin, X.; Cao, S.; Li, X.; Lin, L.; Ni, J. Emodin: A Review of its Pharmacology, Toxicity and Pharmacokinetics. Phytother. Res. 2016, 30, 1207–1218. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Gao, J.; Pang, X.; Chen, A.; Wang, Y. Molecular Mechanisms of Action of Emodin: As an Anti-Cardiovascular Disease Drug. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 559607. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, T.; Wu, S.; Chen, J.; Li, C.; Hsiang, C. Emodin blocks the SARS coronavirus spike protein and angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 interaction. Antivir. Res. 2007, 74, 92–101. [Google Scholar]
- Hsiang, C.; Ho, T. Emodin is a novel alkaline nuclease inhibitor that suppresses herpes simplex virus type 1 yields in cell cultures. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 155, 227–235. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, J.-P.; Wang, Q.-W.; Su, Y.; Gu, L.-M.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, X.-X.; Chen, C.; Li, W.-Z.; Wang, G.-F.; Li, K.-S. Emodin Inhibition of Influenza A Virus Replication and Influenza Viral Pneumonia via the Nrf2, TLR4, p38/JNK and NF-κB Pathways. Molecules 2017, 22, 1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Huang, M.; Xia, Y.; Peng, P.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, S.; Wang, X.; Xue, C.; Cao, Y. Emodin from Aloe Inhibits Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus via Toll-Like Receptor 3 Activation. Viruses 2021, 13, 1243. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, K.; Zhou, J.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, Y.; Ming, L.; Huang, D.; Yang, R.; Lin, Z.; Chen, D. pH-responsive and CD44-targeting polymer micelles based on CD44p-conjugated amphiphilic block copolymer PEG-b-HES-b-PLA for delivery of emodin to breast cancer cells. Nanotechnology 2022, 33, 275604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curanovic, D.; Enquist, L.W. Virion-incorporated glycoprotein B mediates transneuronal spread of pseudorabies virus. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 7796–7804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Lu, G.; Qi, J.; Wu, L.; Tian, K.; Luo, T.; Shi, Y.; Yan, J.; Gao, G.F. Structural basis of nectin-1 recognition by pseudorabies virus glycoprotein D. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, L.; Yao, J.; Yang, Y.; Luo, W.; Yuan, X.; Yang, L.; Wang, A. Current Status and Challenge of Pseudorabies Virus Infection in China. Virol. Sin. 2021, 36, 588–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Li, S.; Wang, X.; Zou, M.; Gao, S. Bartha-k61 vaccine protects growing pigs against challenge with an emerging variant pseudorabies virus. Vaccine 2017, 35, 1161–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, T.; Peng, J.; Tian, Z.; Zhao, H.; Li, N.; Liu, Y.; Chen, J.; Leng, C.; Sun, Y.; Chang, D.; et al. Pseudorabies virus variant in Bartha-K61-vaccinated pigs, China, 2012. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2013, 19, 1749–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Li, N.; Cong, X.; Wang, C.-H.; Du, M.; Li, L.; Zhao, B.; Yuan, J.; Liu, D.-D.; Li, S.; et al. Pathogenicity and genomic characterization of a pseudorabies virus variant isolated from Bartha-K61-vaccinated swine population in China. Vet. Microbiol. 2014, 174, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, W.; Liu, F.; Zheng, H.; Liang, C.; Zhou, Y.-J.; Jiang, Y.-F.; Shan, T.-L.; Gao, F.; Li, G.-X.; Tong, G.-Z. Emergence of a Pseudorabies virus variant with increased virulence to piglets. Vet. Microbiol. 2015, 181, 236–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Chen, X.-X.; Zhang, G. Human PRV Infection in China:An Alarm to Accelerate Eradication of PRV in Domestic Pigs. Virol. Sin. 2021, 36, 823–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, M.D.; Jafari, R.; Ignatushchenko, M.; Seki, T.; Larsson, E.A.; Dan, C.; Sreekumar, L.; Cao, Y.; Nordlund, P. Monitoring drug target engagement in cells and tissues using the cellular thermal shift assay. Science 2013, 341, 84–87. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Cai, X.; Ren, Z.; Shao, Y.; Xu, Y.; Fu, L.; Zhu, Y. Piceatannol as an Antiviral Inhibitor of PRV Infection In Vitro and In Vivo. Animals 2023, 13, 2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rue, C.A.; Ryan, P. Characterization of pseudorabies virus glycoprotein C attachment to heparan sulfate proteoglycans. J. Gen. Virol. 2002, 83, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroeter, C.; Vallbracht, M.; Altenschmidt, J.; Kargoll, S.; Fuchs, W.; Klupp, B.G.; Mettenleiter, T.C. Mutations in Pseudorabies Virus Glycoproteins gB, gD, and gH Functionally Compensate for the Absence of gL. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 2264–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cairns, T.M.; Atanasiu, D.; Saw, W.T.; Lou, H.; Whitbeck, J.C.; Ditto, N.T.; Bruun, B.; Browne, H.; Bennett, L.; Wu, C.; et al. Localization of the interaction site of herpes simplex virus glycoprotein D (gD) on the membrane fusion regulator, gH/gL. J. Virol. 2020, 94, e00983-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wang, R.; Hu, H.; Chen, X.; Yin, Z.; Liang, X.; He, C.; Yin, L.; Ye, G.; Zou, Y.; et al. The antiviral activity of kaempferol against pseudorabies virus in mice. BMC Vet. Res. 2021, 17, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallbracht, M.; Brun, D.; Tassinari, M.; Vaney, M.C.; Pehau, A.G.; Guardado, C.P.; Haouz, A.; Klupp, B.G.; Mettenleiter, T.C.; Rey, F.A.; et al. Structure-Function Dissection of Pseudorabies Virus Glycoprotein B Fusion Loops. J. Virol. 2017, 92, e01203-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, N.; Feng, W.; Fu, T.; Tang, D.; Zeng, Z.; Wang, B. Membrane fusion, potential threats, and natural antiviral drugs of pseudorabies virus. Vet. Res. 2023, 54, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, G.; Liu, H.; Zhou, Q.; Liu, X.; Huang, L.; Weng, C. A Tug of War: Pseudorabies Virus and Host Antiviral Innate Immunity. Viruses 2022, 14, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teodoro, J.G.; Branton, P.E. Regulation of apoptosis by viral gene products. J. Virol. 1997, 71, 1739–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, B.J. Viruses and apoptosis. Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 2001, 82, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megan, H.O.; Jonathan, C.K. Apoptosis and Necroptosis as Host Defense Strategies to Prevent Viral Infection. Trends Cell Biol. 2017, 27, 800–809. [Google Scholar]
- Deruelle, M.J.; De Corte, N.; Englebienne, J.; Nauwynck, H.J.; Favoreel, H.W. Pseudorabies virus US3-mediated inhibition of apoptosis does not affect infectious virus production. J. Gen. Virol. 2010, 91, 1127–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.D.; Lin, P.Y.; Liao, M.H.; Chang, C.I.; Hsu, J.L.; Yu, F.L.; Wu, H.Y.; Shih, W.L. Suppression of apoptosis by pseudorabies virus Us3 protein kinase through the activation of PI3-K/Akt and NF-κB pathways. Res. Vet. Sci. 2013, 95, 764–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, A.K.; Chen, Z.; Sun, Z.; McCullough, D. Pseudorabies virus induces apoptosis in tissue culture cells. Arch. Virol. 2000, 145, 2193–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.; Luo, G.; Zhang, C.; Feng, L.; Luo, X.; Gan, L. Curcumin protects rat hippocampal neurons against pseudorabies virus by regulating the BDNF/TrkB pathway. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 22204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wan, H.; Yin, Z.; Li, L.; Liang, X.; Zhao, X.; Yin, L.; Ye, G.; et al. Myricetin inhibits pseudorabies virus infection through direct inactivation and activating host antiviral defense. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 985108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wei, F.; Chen, L.-J.; Xiong, H.-R.; Liu, Y.-Y.; Luo, F.; Hou, W.; Xiao, H.; Yang, Z.-Q. In Vitro and in Vivo Studies of the Inhibitory Effects of Emodin Isolated from Polygonum cuspidatum on Coxsakievirus B4. Molecules 2013, 18, 11842–11858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Shao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Ren, Z.; Fu, L.; Zhu, Y. Antiviral activity of dandelion aqueous extract against pseudorabies virus both in vitro and in vivo. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 9, 1090398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brittle, E.E.; Reynolds, A.E.; Enquist, L.W. Two modes of pseudorabies virus neuroinvasion and lethality in mice. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 12951–12963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, P.M.; Wolcott, R.M.; Chervenak, R.; Jennings, S.R. Control of acute cutaneous herpes simplex virus infection: T cell-mediated viral clearance is dependent upon interferon-gamma (IFN-γ). Virology 1994, 202, 76–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trevejo, J.M.; Marino, M.W.; Philpott, N.; Josien, R.; Richards, E.C.; Elkon, K.B.; Falck-Pedersen, E. TNF-α-dependent maturation of local dendritic cells is critical for activating the adaptive immune response to virus infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 12162–12167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, T.; Narazaki, M.; Kishimoto, T. IL-6 in inflammation, immunity, and disease. Cold Spring Harbor Perspect. Biol. 2014, 6, a016295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feilong, W.; Song, Z.; Ryounghoon, J.; Ivan, V.; Xintong, J.; Amir, L.; Clifford, D.F.; Petras, D.D.; Joerg, H. Interferon Gamma Induces Reversible Metabolic Reprogramming of M1 Macrophages to Sustain Cell Viability and Pro-Inflammatory Activity. Ebiomedicine 2018, 30, 303–316. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, D.P.; Ramsay, A.J.; Maguire, D.J.; Rolph, M.S.; Ramshaw, I.A. Interleukin-4 mediates down regulation of antiviral cytokine expression and cytotoxic T-lymphocyte responses and exacerbates vaccinia virus infection in vivo. J. Virol. 1996, 70, 7103–7107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anupama, S.; Shradha, W.; Roza, N. T helper 2 and T follicular helper cells: Regulation and function of interleukin-4. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2016, 30, 29–37. [Google Scholar]







| Gene Name | Sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| UL44-F | CGTCAGGAATCGCATCA |
| UL44-R | CGCGTCACGTTCACCAC |
| IE180-F | CGCTCCACCAACAACC |
| IE180-R | TCGTCCTCGTCCCAGA |
| UL29-F | AGAAGCCGCACGCCATCACC |
| UL29-R | GGGAACCCGCAGACGGACAA |
| EP0-F | GGGCGTGGGTGTTT |
| EP0-R | GCTTTATGGGCAGGT |
| US6-F | AACATCCTCACCGACTTCA |
| US6-R | CGTCAGGAATCGCATCA |
| UL27-F | TCGTCCACGTCGTCCTCTTCG |
| UL27-R | CGGCATCGCCAACTTCTTCC |
| β-actin-F | TGCGGGACATCAAGGAGAA |
| β-actin-R | AGGAAGGAGGGCTGGAAGA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cai, X.; Wang, Z.; Li, X.; Zhang, J.; Ren, Z.; Shao, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhu, Y. Emodin as an Inhibitor of PRV Infection In Vitro and In Vivo. Molecules 2023, 28, 6567. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28186567
Cai X, Wang Z, Li X, Zhang J, Ren Z, Shao Y, Xu Y, Zhu Y. Emodin as an Inhibitor of PRV Infection In Vitro and In Vivo. Molecules. 2023; 28(18):6567. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28186567
Chicago/Turabian StyleCai, Xiaojing, Zhiying Wang, Xiaocheng Li, Jing Zhang, Zhiyuan Ren, Yi Shao, Yongkang Xu, and Yan Zhu. 2023. "Emodin as an Inhibitor of PRV Infection In Vitro and In Vivo" Molecules 28, no. 18: 6567. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28186567
APA StyleCai, X., Wang, Z., Li, X., Zhang, J., Ren, Z., Shao, Y., Xu, Y., & Zhu, Y. (2023). Emodin as an Inhibitor of PRV Infection In Vitro and In Vivo. Molecules, 28(18), 6567. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28186567