Electrochemical Epoxidation Catalyzed by Manganese Salen Complex and Carbonate with Boron-Doped Diamond Electrode
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
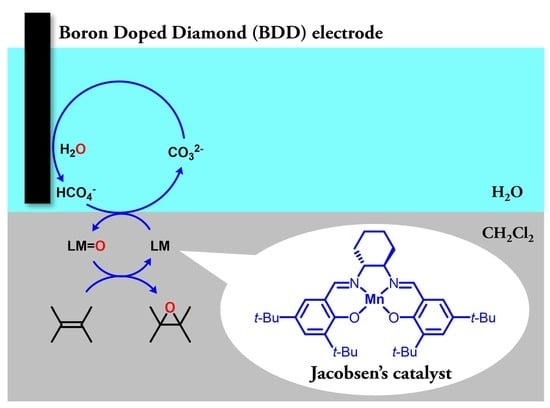
2.1. Electrochemical Epoxidation Using a BDD
2.2. Exploration of More Efficient Catalysts
2.3. Optimization of Manganese Salen Complexes
3. Experimental
3.1. Chemicals and Equipment
3.2. General Procedure for Electrochemical Epoxidation
3.3. General Procedure for Epoxidation with Hydrogen Peroxide
4. Conclusions
5. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Yan, M.; Kawamata, Y.; Baran, P.S. Synthetic Organic Electrochemical Methods since 2000: On the Verge of a Renaissance. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 13230–13319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Q.H.; Ge, H.Q.; Ye, C.P.; Liu, Z.M.; Su, K.X. Advances in homogeneous and heterogeneous catalytic asymmetric epoxidation. Chem. Rev. 2005, 105, 1603–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holm, R.H. Metal-Centered Oxygen Atom Transfer Reactions. Chem. Rev. 1987, 87, 1401–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Traylor, T.G.; Perrin, C.L. MCPBA epoxidation of alkenes: Reinvestigation of correlation between rate and ionization potential. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 9513–9516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dryuk, V.G. The mechanism of epoxidation of olefins by peracids. Tetrahedron 1976, 32, 2855–2866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, K.; Maalouf, J.H.; Lazouski, N.; Corbin, N.; Yang, D.; Manthiram, K. Epoxidation of Cyclooctene Using Water as the Oxygen Atom Source at Manganese Oxide Electrocatalysts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 6413–6418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatsumi, D.; Tsukamoto, T.; Honna, R.; Hoshino, S.; Shimada, T.; Takagi, S. Highly selective photochemical epoxidation of cyclohexene sensitized by Ru(II) porphyrinclay hybrid catalyst. Chem. Lett. 2017, 46, 1311–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, B.; Singh, K.K.; Gupta, S.S. Selective photocatalytic hydroxylation and epoxidation reactions by an iron complex using water as the oxygen source. Chem. Sci. 2017, 8, 7545–7551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, D.; Saracini, C.; Lee, Y.M.; Sun, W.; Fukuzumi, S.; Nam, W. Photocatalytic Asymmetric Epoxidation of Terminal Olefins Using Water as an Oxygen Source in the Presence of a Mononuclear Non-Heme Chiral Manganese Complex. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 15857–15860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funyu, S.; Isobe, T.; Takagi, S.; Tryk, D.A.; Inoue, H. Highly efficient and selective epoxidation of alkenes by photochemical oxygenation sensitized by a ruthenium(II) porphyrin with water as both electron and oxygen donor. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 5734–5740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishihara, H.; Pressprich, K.; Murray, R.W.; Collman, J.P. Electrochemical Olefin Epoxidation with Manganese meso-Tetraphenylporphyrin Catalyst and Hydrogen Peroxide Generation at Polymer-Coated Electrodes. Inorg. Chem. 1990, 29, 1000–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torii, S.; Uneyama, K.; Tanaka, H.; Yamanaka, T.; Yasuda, T.; Ono, M.; Kohmoto, Y. Efficient Conversion of Olefins into Epoxides, Bromohydrins, and Dibromides with Sodium Bromide in Water-Organic Solvent Electrolysis Systems. J. Org. Chem. 1981, 46, 3312–3315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torii, S.; Uneyama, K.; Ono, M.; Tazawa, H.; Matsunami, S. A regioselective ω-epoxidation of polyisoprenoids by the sodium bromide promoted electrochemical oxidation. Tetrahedron Lett. 1979, 20, 4661–4662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moutet, J.-C.; Ourari, A. Electrocatalytic epoxidation and oxidation with dioxygen using manganese(III) Schiff-base complexes. Electrochim. Acta 1997, 42, 2525–2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, P.; Wong, K.-Y. Enantioselective electrocatalytic epoxidation of olefins by chiral manganese Schiff-base complexes. Electrochem. Commun. 1999, 1, 559–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, A.; Sakaki, S. Theoretical study of photoinduced epoxidation of olefins catalyzed by ruthenium porphyrin. J. Phys. Chem. A 2011, 115, 4774–4785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, H.; Kuroboshi, M.; Takeda, H.; Kanda, H.; Torii, S. Electrochemical asymmetric epoxidation of olefins by using an optically active Mn-salen complex. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2001, 507, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsen, E.N.; Zhang, W.; Güler, M.L. Electronic Tuning of Asymmetric Catalysts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1991, 113, 6703–6704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourbaix, M. Atlas of Electrochemical Equilibria in Aqueous Solutions; National Association of Corrosion Engineers: Houston, TX, USA, 1974.
- Hincapie, B.; Llano, S.M.; Garces, H.F.; Espinal, D.; Suib, S.L.; Garces, L.J. Epoxidation of cyclopentene by a low cost and environmentally friendly bicarbonate/peroxide/manganese system. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2018, 36, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, A.M.; Moreno, V.; Delgado, S.X.; Ramírez, A.E.; Vargas, L.A.; Vicente, M.Á.; Gil, A.; Galeano, L.A. Encapsulation of SALEN- and SALHD-Mn(III) complexes in an Al-pillared clay for bicarbonate-assisted catalytic epoxidation of cyclohexene. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2016, 416, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monfared, H.H.; Aghapoor, V.; Ghorbanloo, M.; Mayer, P. Highly selective olefin epoxidation with the bicarbonate activation of hydrogen peroxide in the presence of manganese(III) meso-tetraphenylporphyrin complex: Optimization of effective parameters using the Taguchi method. Appl. Catal. A-Gen. 2010, 372, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Richardson, D.E. Epoxidation of alkenes with bicarbonate-activated hydrogen peroxide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 3220–3221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, B.S.; Vogt, M.; DeRose, V.J.; Burgess, K. Manganese-catalyzed epoxidations of alkenes in bicarbonate solutions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 11946–11954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drozd, V.A.; Ottenbacher, R.V.; Bryliakov, K.P. Asymmetric Epoxidation of Olefins with Sodium Percarbonate Catalyzed by Bis-amino-bis-pyridine Manganese Complexes. Molecules 2022, 27, 2538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escande, V.; Petit, E.; Garoux, L.; Boulanger, C.; Grison, C. Switchable Alkene Epoxidation/Oxidative Cleavage with H2O2/NaHCO3: Efficient Heterogeneous Catalysis Derived from Biosourced Eco-Mn. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 2704–2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, K.; Nagatomo, S.; Fujinami, S.; Furutachi, H.; Ogo, S.; Suzuki, M.; Uehara, A.; Maeda, Y.; Watanabe, Y.; Kitagawa, T. A New Mononuclear Iron(III) Complex Containing a Peroxocarbonate Ligand. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2002, 41, 1202–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, D.E.; Yao, H.; Frank, K.M.; Bennett, D.A. Equilibria, kinetics, and mechanism in the bicarbonate activation of hydrogen peroxide: Oxidation of sulfides by peroxymonocarbonate. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 1729–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Oloman, C.W. Electro-oxidation of carbonate in aqueous solution on a platinum rotating ring disk electrode. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2005, 35, 945–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoharan, G.; Muthu Mohamed, M.; Raghavendran, N.S.; Narasimham, K.C. Electrolytic preparation of sodium and potassium percarbonate. Trans. SAEST (Soc. Adv. Electrochem. Sci. Technol.) 2000, 35, 69–72. [Google Scholar]
- Wiel, P.; Janssen, L.J.J.; Hoogland, J.G. Electrolysis of a carbonate-borate solution with a platinum anode-I. Current efficiency at perborate concentration of zero. Electrochim. Acta 1971, 16, 1217–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irkham; Fiorani, A.; Valenti, G.; Kamoshida, N.; Paolucci, F.; Einaga, Y. Electrogenerated Chemiluminescence by in Situ Production of Coreactant Hydrogen Peroxide in Carbonate Aqueous Solution at a Boron-Doped Diamond Electrode. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 1518–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chardon, C.P.; Matthée, T.; Neuber, R.; Fryda, M.; Comninellis, C. Efficient Electrochemical Production of Peroxodicarbonate Applying DIACHEM® Diamond Electrodes. ChemistrySelect 2017, 2, 1037–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Ruiz, E.J.; Meas, Y.; Ortega-Borges, R.; Jurado Baizabal, J.L. Electrochemical production of peroxocarbonate at room temperature using conductive diamond anodes. Surf. Eng. Appl. Electrochem. 2014, 50, 478–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velazquez-Peña, S.; Sáez, C.; Cañizares, P.; Linares-Hernández, I.; Martínez-Miranda, V.; Barrera-Díaz, C.; Rodrigo, M.A. Production of oxidants via electrolysis of carbonate solutions with conductive-diamond anodes. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 230, 272–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, E.J.; Ortega-Borges, R.; Jurado, J.L.; Chapman, T.W.; Meas, Y. Simultaneous anodic and cathodic production of Sodium percarbonate in aqueous solution. Electrochem. Solid-State Lett. 2008, 12, E1–E4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, M.S.; Furuta, T.; Nishiki, Y. Conversion of carbon dioxide to peroxycarbonate at boron-doped diamond electrode. Electrochem. Commun. 2004, 6, 201–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, M.S.; Furuta, T.; Nishiki, Y. Electrochemical synthesis of sodium peroxycarbonate at boron-doped diamond electrodes. Electrochem. Solid-State Lett. 2003, 6, D5–D7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavrikis, S.; Göltz, M.; Rosiwal, S.; Wang, L.; Ponce de León, C. Boron-Doped Diamond Electrocatalyst for Enhanced Anodic H2O2 Production. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2020, 3, 3169–3173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einaga, Y. Development of Electrochemical Applications of Boron-Doped Diamond Electrodes. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2018, 91, 1752–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenderich, K.; Nieuweweme, B.A.M.; Mul, G.; Mei, B.T. Selective Electrochemical Oxidation of H2O to H2O2 Using Boron-Doped Diamond: An Experimental and Techno-Economic Evaluation. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 7803–7812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, M.; Shinde, V.S.; Rueping, M. A review of asymmetric synthetic organic electrochemistry and electrocatalysis: Concepts, applications, recent developments and future directions. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 2710–2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, C.; Fang, P.; Liu, Z.-R.; Xu, S.-S.; Xu, K.; Cheng, X.; Lei, A.; Xu, H.-C.; Zeng, C.; Mei, T.-S. Recent advances in organic electrosynthesis employing transition metal complexes as electrocatalysts. Sci. Bull. 2021, 66, 2412–2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novaes, L.F.T.; Liu, J.; Shen, Y.; Lu, L.; Meinhardt, J.M.; Lin, S. Electrocatalysis as an enabling technology for organic synthesis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 7941–8002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaeffer, N.; Leitner, W. Electrocatalysis with Molecular Transition-Metal Complexes for Reductive Organic Synthesis. JACS Au 2022, 2, 1266–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mavrikis, S.; Perry, S.C.; Leung, P.K.; Wang, L.; Ponce de León, C. Recent Advances in Electrochemical Water Oxidation to Produce Hydrogen Peroxide: A Mechanistic Perspective. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 76–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sainna, M.A.; Kumar, S.; Kumar, D.; Fornarini, S.; Crestoni, M.E.; de Visser, S.P. A comprehensive test set of epoxidation rate constants for iron(iv)–oxo porphyrin cation radical complexes. Chem. Sci. 2015, 6, 1516–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakhmutova-Albert, E.V.; Yao, H.; Denevan, D.E.; Richardson, D.E. Kinetics and Mechanism of Peroxymonocarbonate Formation. Inorg. Chem. 2010, 49, 11287–11296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Jacobsen, E.N. Asymmetric olefin epoxidation with sodium hypochlorite catalyzed by easily prepared chiral manganese(III) salen complexes. J. Org. Chem. 1991, 56, 2296–2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsen, E.N.; Zhang, W.; Muci, A.R.; Ecker, J.R.; Deng, L. Highly enantioselective epoxidation catalysts derived from 1,2-diaminocyclohexane. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1991, 113, 7063–7064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, B.S.; Burgess, K. A Cheap, Catalytic, Scalable, and Environmentally Benign Method for Alkene Epoxidations. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 2933–2934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, B.; Lou, L.-L.; Yu, K.; Bian, W.; Liu, S. Selective epoxidation of alkenes with hydrogen peroxide over efficient and recyclable manganese oxides. Catal. Commun. 2011, 15, 52–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dar, T.A.; Uprety, B.; Sankar, M.; Maurya, M.R. Robust and electron deficient oxidovanadium(iv) porphyrin catalysts for selective epoxidation and oxidative bromination reactions in aqueous media. Green Chem. 2019, 21, 1757–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurahashi, T.; Fujii, H. One-electron oxidation of electronically diverse manganese(III) and nickel(II) salen complexes: Transition from localized to delocalized mixed-valence ligand radicals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 8307–8316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGarrigle, E.M.; Gilheany, D.G. Chromium-and manganese-salen promoted epoxidation of alkenes. Chem. Rev. 2005, 105, 1563–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Anode (3 cm2) | Epoxide Yield (%) |
|---|---|
| BDD | 18.5 |
| glassy carbon | 2.2 |
| platinum | 1.8 |
| graphite | 1.8 |
| Substrate (Ionization Energy) | Epoxide Yield (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| Electrochemical Generation | H2O2/Na2CO3 2 | |
| trans-β-methylstyrene | 18.5 | 26.4 |
| (8.08 eV) | ||
| cis-β-methylstyrene | 19.8 (85:15) 3 | 22.3 (84:16) 3 |
| (8.48 eV) | ||
| cyclooctene | 5.6 | 1.4 |
| (9.02 eV) | ||
| trans-stilbene | 1.6 | 1.0 |
| (7.70 eV) | ||
| cyclohexene | 0.3 | 0.4 |
| (9.12 eV) | ||
| Catalyst | Epoxide Yield (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Electrochemical Generation | H2O2/Na2CO3 2 | NaOCl 3 | |
| Mn(L1-Ome) | 5.3 | 2.1 | 45.5 |
| Mn(L1-t-Bu) | 18.5 | 26.4 | 74.1 |
| Mn(L1-H) | 2.2 | 13.2 | 59.8 |
| Mn(L1-Cl) | 1.8 | 3.3 | 60.9 |
| Mn(L1-NO2) | 1.8 | 1.8 | 53.8 |
| Mn(L2-t-Bu) | 7.3 | 1.5 | – |
| Mn(L2-H) | 0.5 | 0.8 | – |
| none | 0.7 | 0.5 | 8.4 |
| Catalyst | Epoxide Yield (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| Electrochemical Generation | H2O2/Na2CO3 2 | |
| Mn(L1-Ome) | 6.8 | 8.6 |
| Mn(L1-t-Bu) | 9.9 | 9.3 |
| Mn(L1-H) | 7.7 | 8.1 |
| Mn(L1-Cl) | 8.0 | 7.6 |
| Mn(L1-NO2) | 8.1 | 6.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Roy, P.K.; Amanai, K.; Shimizu, R.; Kodera, M.; Kurahashi, T.; Kitayama, K.; Hitomi, Y. Electrochemical Epoxidation Catalyzed by Manganese Salen Complex and Carbonate with Boron-Doped Diamond Electrode. Molecules 2023, 28, 1797. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28041797
Roy PK, Amanai K, Shimizu R, Kodera M, Kurahashi T, Kitayama K, Hitomi Y. Electrochemical Epoxidation Catalyzed by Manganese Salen Complex and Carbonate with Boron-Doped Diamond Electrode. Molecules. 2023; 28(4):1797. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28041797
Chicago/Turabian StyleRoy, Pijush Kanti, Keisuke Amanai, Ryosuke Shimizu, Masahito Kodera, Takuya Kurahashi, Kenji Kitayama, and Yutaka Hitomi. 2023. "Electrochemical Epoxidation Catalyzed by Manganese Salen Complex and Carbonate with Boron-Doped Diamond Electrode" Molecules 28, no. 4: 1797. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28041797
APA StyleRoy, P. K., Amanai, K., Shimizu, R., Kodera, M., Kurahashi, T., Kitayama, K., & Hitomi, Y. (2023). Electrochemical Epoxidation Catalyzed by Manganese Salen Complex and Carbonate with Boron-Doped Diamond Electrode. Molecules, 28(4), 1797. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28041797