Vanadium-Containing Anionic Chelate for Spectrophotometric Determination of Hydroxyzine Hydrochloride in Pharmaceuticals
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Choice of Azo Dye
2.2. Absorption Spectrum
2.3. Effect of pH
2.4. Effects of Extraction Time
2.5. Choice of V(V) and HTAR Concentrations
2.6. HZH-to-V(V) Molar Ratio, and Formula of the Extracted Complex
2.7. Ground-State Equilibrium Geometries of the Ions, Calculated Energies, and Spectral Comparison
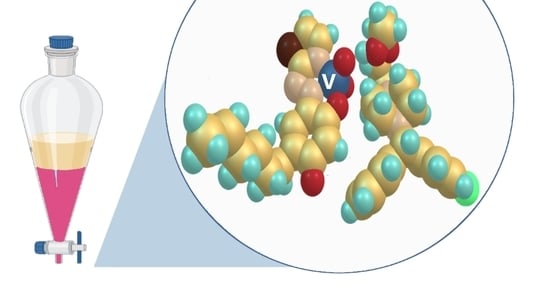
2.8. Optimized Ground-State Structures of the Ion-Association Complex
2.9. Chemical–Analytical Characteristics and Application
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Reagents and Chemicals
3.2. Instrumentation
3.3. Samples
3.4. Optimization Procedure
3.5. Procedure for the Determination of HZH
3.6. Theoretical
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Hydroxyzine Hydrochloride (Code C47559). Available online: https://ncit.nci.nih.gov/ncitbrowser/ConceptReport.jsp?dictionary=NCI_Thesaurus&ns=ncit&code=C47559 (accessed on 24 January 2023).
- Tsau, J.; DeAngelis, N. Hydroxyzine Dihydrochloride. In Analytical Profiles of Drug Substances; Florey, K., Ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1978; pp. 319–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammad, S.F.; Mokhtar, M.M.; Ahmed, H.; Hamed, E.; Naoya, K.; Kenichiro, N.; Naotaka, K. Precolumn fluorescence labeling method for simultaneous determination of hydroxyzine and cetirizine in human serum. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2007, 21, 1030–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krueger, J.A.; Kaduk, J.A.; Gindhart, A.M.; Blanton, T.N. Crystal structure of hydroxyzine dihydrochloride, C21H29ClN2O2Cl2. Powder Diffr. 2019, 34, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, R.; Siddaraju, C. A Selective PVC Matrix Assisted Potentiometric Sensor for the Determination of Hydroxyzine Hydrochloride (HDH). Port. Electrochim. Acta 2022, 40, 347–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, P.O.; Knoben, J.E.; Troutman, W.G. Handbook of Clinical Drug Data, 10th ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 794–796. [Google Scholar]
- High Risk Medications. NCQA’s HEDIS Measure: Use of High-Risk Medications in the Elderly. Available online: http://www.ncqa.org/Portals/0/Newsroom/SOHC/Drugs_Avoided_Elderly.pdf (accessed on 24 January 2023).
- Ackermann, H.; Kretzschmann, F.; Krüger, S.; Lexow, B. Dünnschichtchromatographisches Verfahren zur semiquantitativen Bestimmung von Hydroxyzinrückstanden in tierischem Material. Die Nahr. 1977, 21, 603–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sher, N.; Siddiqui, F.A.; Fatima, N.; Perveen, S.; Shafi, N. New Method Development for Hydroxyzine Determination: Application in Stability Studies, Pharmaceutical Formulations, and Humane Serum. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2015, 38, 911–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kintz, P.; Godelar, B.; Mangin, P. Gas chromatographic identification and quantification of hydroxyzine: Application in a fatal self-poisoning. Forensic Sci. Int. 1990, 48, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.-H.; Wu, H.-L.; Wu, S.-M.; Chen, S.-H.; Kou, H.-S. Quantitative enantiomeric analysis of chlorcyclizine, hydroxyzine, and meclizine by capillary electrophoresis. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2003, 376, 859–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendraprasad, N.; Basavaiah, K.; Vinay, B.K. Acid-base titrimetric assay of hydroxyzine dihydrochloride in pharmaceutical samples. Chem. Ind. Chem. Eng. Q. 2010, 16, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikulski, R.; Dembiński, B. Determination of colloidal electrolytes: Conductimetric titration of hydroxyzine hydrochloride with ammonium molybdate. Anal. Chim. Acta 1993, 272, 233–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zayed, S.I.; Al-Talhi, A.A.; Thagafi, A.E.A. Determination of hydroxyzine by differential pulse anodic voltammetry using carbon paste electrode. J. Chil. Chem. Soc. 2018, 63, 4064–4067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Budevski, O. Handbook of Practical Exercises in Analytical Chemistry for Pharmacy Students, 5th ed.; ARSO Medical Publishing House: Sofia, Bulgaria, 1999; pp. 270–271. [Google Scholar]
- Kurzawa, M.; Dembinski, B.; Szydiowska-Czerniak, A. Spectrophotometric determination of imipramine hydrochloride, doxepin hydrochloride, and hydroxyzine dihydrochloride with Reinecke salt. Acta Pol. Pharm. 1999, 56, 255–260. [Google Scholar]
- Basavaiah, K.; Charan, V.S. Titrimetric and spectrophotometric assay of some antihistamines through the determination of the chloride of their hydrochlorides. Farmaco 2002, 57, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basavaiah, K.; Charan, V. Spectrophotometric determination of two antihistamines by charge-transfer complex formation with chloranilic acid. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 2003, 65, 660–662. [Google Scholar]
- Rajendraprasad, N.; Basavaiah, K.; Vinay, K.B.; Revanasiddappa, H.D. Sensitive and selective extractive spectrophotometric method for the determination of hydroxyzine dihydrochloride in pharmaceuticals. J. Mex. Chem. Soc. 2010, 54, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendraprasad, N.; Basavaiah, K.; Vinay, K.B. Optimized and validated spectrophotometric methods for the determination of hydroxyzine hydrochloride in pharmaceuticals and urine using iodine and picric acid. J. Serb. Chem. Soc. 2011, 76, 1551–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naveed, S.; Qamar, F.; Zainab, S.; Sarwar, G.; Alam, M.T. Simple UV spectrophotometric assay of hydroxazine. World J. Pharm. Life Sci. 2015, 1, 65–70. [Google Scholar]
- Milcheva, N.P.; Genç, F.; Racheva, P.V.; Delchev, V.B.; Andruch, V.; Gavazov, K.B. An environmentally friendly cloud point extraction–spectrophotometric determination of trace vanadium using a novel reagent. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 334, 116086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racheva, P.V.; Milcheva, N.P.; Genc, F.; Gavazov, K.B. A centrifuge-less cloud point extraction-spectrophotometric determination of copper(II) using 6-hexyl-4-(2-thiazolylazo)resorcinol. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2021, 262, 120106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavazov, K.B.; Racheva, P.V.; Milcheva, N.P.; Divarova, V.V.; Kiradzhiyska, D.D.; Genç, F.; Saravanska, A.D. Use of a hydrophobic azo dye for the centrifuge-less cloud point extraction–spectrophotometric determination of cobalt. Molecules 2022, 27, 4725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hristov, D.; Milcheva, N.; Gavazov, K. Extraction-chromogenic systems for vanadium(V) based on azo dyes and xylometazoline hydrochloride. Acta Chim. Slov. 2019, 66, 987–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanocq, M.; Croisier, P.; Damme, M.V.; Aelvoet, C. Macro ionization constants of hydroxyzine, cetirizine and an analog. Anal. Lett. 1989, 22, 117–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tôei, K. Ion-association reagents. A review. Anal. Sci. 1987, 3, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Galesic, N.; Siroki, M. The structure of tetraphenylphosphonium dioxo [4-(2-pyridylazo)resorcinolato]vanadate(V), C24H20P+.C11H7N3O4V−. Acta Crystallogr. B 1979, 35, 2931–2937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galesic, N.; Siroki, M. Structure of tetraphenylphosphonium dioxo [4-(1,3-thiazol-2-ylazo)resorcinolato]vanadate(V) monohydrate, [P(C6H5)4][VO2(C9H5N3O2S)].H2O. Acta Crystallogr. C 1984, 40, 378–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yerramilli, A.; Kavipurapu, C.S.; Manda, R.R.; Pillutla, C.M. Extractive spectrophotometric method for the determination of vanadium(V) in steels and titanium base alloy. Anal. Chem. 1986, 58, 1451–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uslu, M.; Ulutürk, H.; Yartaşı, A.; Döker, S. A sensitive method for selective determination of vanadium species by dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction (DLLME) with spectrophotometric detection. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 2013, 95, 1638–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavazov, K.B.; Stefanova, T.S. Liquid-liquid extraction-spectrophotometric investigations of three ternary complexes of vanadium. Croat. Chem. Acta 2014, 87, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavazov, K.B.; Delchev, V.B.; Mileva, K.T.; Stefanova, T.S.; Toncheva, G.K. A 2:2:2 complex of vanadium(V) with 4-(2-thiazolylazo)orcinol and 2,3,5-triphenyl-2H-tetrazolium chloride. Acta Chim. Slov. 2016, 63, 392–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gavazov, K.B. Liquid-liquid extraction of ion-association complexes. In Advances in Chemistry Research; Taylor, J.C., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2019; Volume 50, pp. 203–238. [Google Scholar]
- Pilipenko, A.T.; Tananajko, M.M. Mixed Ligand and Mixed Metal Complexes and Their Use in Analytical Chemistry; Khimiya: Moscow, Russia, 1983; pp. 72–165. [Google Scholar]
- Gavazov, K.B.; Dimitrov, A.N.; Lekova, V.D. The use of tetrazolium salts in inorganic analysis. Russ. Chem. Rev. 2007, 76, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divarova, V.V.; Saravanska, A.D.; Toncheva, G.K.; Milcheva, N.; Delchev, V.B.; Gavazov, K.B. Spectrophotometric determination of molybdenum(VI) as a ternary complex with 4-nitrocatechol and benzalkonium chloride. Molecules 2022, 27, 1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanska, A.D.; Racheva, P.V.; Divarova, V.V.; Toncheva, G.K.; Milcheva, N.P.; Delchev, V.B.; Gavazov, K.B. Extraction-spectrophotometric and theoretical studies on a ternary complex obtained from vanadium(V) and 4-nitrocatechol. Russ. J. Inorg. Chem. 2021, 66, 1880–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konermann, L. Addressing a common misconception: Ammonium acetate as neutral pH “buffer” for native electrospray mass spectrometry. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2017, 28, 1827–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoe, J.H.; Jones, A.L. Colorimetric determination of iron with disodium-1,2-dihydroxybenzene-3,5-disulfonate. Ind. Eng. Chem. Anal. Ed. 1944, 16, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bent, H.E.; French, C.L. The structure of ferric thiocyanate and its dissociation in aqueous solution. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1941, 63, 568–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asmus, E. Eine neue Methode zur Ermittlung der Zusammensetzung schwacher Komplexe. Fresenius’ J. Anal. Chem. 1960, 178, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhiming, Z.; Dongsten, M.; Cunxiao, Y. Mobile equilibrium method for determining composition and stability constant of coordination compounds of the form MmRn. J. Rare Earths 1997, 15, 216–219. [Google Scholar]
- Holme, A.; Langmyhr, F.J. A modified and a new straight-line method for determining the composition of weak complexes of the form AmBn. Anal. Chim. Acta 1966, 36, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, A.E.; Manning, D.L. Spectrophotometric methods of establishing empirical formulas of colored complexes in solution. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1950, 72, 4488–4493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ATARAX Syrup 200 mL. Available online: https://apteka.framar.bg/01005291/ (accessed on 24 January 2023).
- Atarax™. Available online: https://www.e-lactancia.org/media/papers/Hydroxyzine-DS-Glaxo-SK2013.pdf (accessed on 24 January 2023).
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Petersson, G.A.; Nakatsuji, H.; et al. Gaussian 16; Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- ChemCraft. Available online: http://www.chemcraftprog.com (accessed on 1 February 2023).










| Reagent(s) | λmax, nm | Linear Range, μg mL−1 | ε, L mol−1 cm−1 | LOD | Comments | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Methyl orange | 510 | – | – | – | Includes both extraction and re-extraction. Chloroform consumption per sample: 20 mL | [15] |
| Reinecke salt | 525.5 | 30–520 | 1.27 × 105 | – | A slow and tedious procedure involving precipitation and drying of a Cr(III) complex for 6 h | [16] |
| Diphenylcarbazone + Hg(II) | 540 | Up to 60 | 6.62 × 103 | – | An indirect determination based on the decrease in the absorption of the Hg(II)–diphenylcarbazone complex | [17] |
| Chloranilic acid | 535 | 25–150 | 1.37 × 103 | 1.25 | A low-sensitivity procedure involving a charge-transfer complexation reaction in chloroform/acetonitrile | [18] |
| Orange II | 480 | 1.5–15 | 2.07 × 104 | 0.14 | Based on a chloroform-extracted ion pair. Chloroform consumption per sample: 20 mL | [19] |
| Picric acid | 400 | 3.75–45 | 8.06 × 103 | 0.62 | Based on a charge-transfer complexation reaction in chloroform | [20] |
| Iodine | 380 | 1.25–15 | 2.59 × 104 | 0.13 | Based on a charge-transfer complexation reaction in dichloromethane. Short shelf life of the used reagent solution | [20] |
| – | 230 | – | – | – | Not used for the analysis of real samples | [21] |
| HTAR + V(V) | 554 | Up to 12.2 | 3.50 × 104 | 0.13 | A sensitive, fast, and robust extraction–spectrophotometric procedure based on a ternary ion-association complex | This work |
| Excited State | Vertical Excitation Energy, nm | Oscillator Strength |
|---|---|---|
| 1ππ* | 504 | 0.0200 |
| 1ππ* | 475 | 0.5214 |
| 1nπ* | 452 | 0.0005 |
| Optimized Parameter | Scope of Optimization | Optimal Value |
|---|---|---|
| Wavelength, nm | 500–760 | 554 |
| Concentration of V(V), mol L−1 | – | 3.0 × 10−5 |
| Concentration of HTAR, mol L−1 | (2–3) × 10−4 | 2.4 × 10−4 |
| pH (ammonium acetate buffer) | 3.0–6.0 | 4.3 |
| Extraction time, s | 15–180 | 45 |
| Sample | HZH Spike, μg mL−1 | HZH Found, * μg mL−1 | RSD, % | Recovery, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Neurolax® tablets (Batch 1) | 0 | 3.04 ± 0.07 | 2.3 | – |
| 1.5 | 4.58 ± 0.11 | 2.4 | 103 | |
| 3.0 | 6.07 ± 0.09 | 1.5 | 101 | |
| 4.5 | 7.52 ± 0.14 | 1.9 | 99.6 | |
| Syrup | 0 | 2.99 ± 0.08 | 2.7 | – |
| 1.5 | 4.44 ± 0.08 | 1.8 | 96.7 | |
| 3.0 | 6.03 ± 0.12 | 2.0 | 101 | |
| 4.5 | 7.46 ± 0.13 | 1.7 | 99.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kirova, G.K.; Velkova, Z.Y.; Delchev, V.B.; Gavazov, K.B. Vanadium-Containing Anionic Chelate for Spectrophotometric Determination of Hydroxyzine Hydrochloride in Pharmaceuticals. Molecules 2023, 28, 2484. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062484
Kirova GK, Velkova ZY, Delchev VB, Gavazov KB. Vanadium-Containing Anionic Chelate for Spectrophotometric Determination of Hydroxyzine Hydrochloride in Pharmaceuticals. Molecules. 2023; 28(6):2484. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062484
Chicago/Turabian StyleKirova, Gergana Kirilova, Zdravka Yancheva Velkova, Vassil Borisov Delchev, and Kiril Blazhev Gavazov. 2023. "Vanadium-Containing Anionic Chelate for Spectrophotometric Determination of Hydroxyzine Hydrochloride in Pharmaceuticals" Molecules 28, no. 6: 2484. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062484
APA StyleKirova, G. K., Velkova, Z. Y., Delchev, V. B., & Gavazov, K. B. (2023). Vanadium-Containing Anionic Chelate for Spectrophotometric Determination of Hydroxyzine Hydrochloride in Pharmaceuticals. Molecules, 28(6), 2484. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062484