Cripowellins Pause Plasmodium falciparum Intraerythrocytic Development at the Ring Stage
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
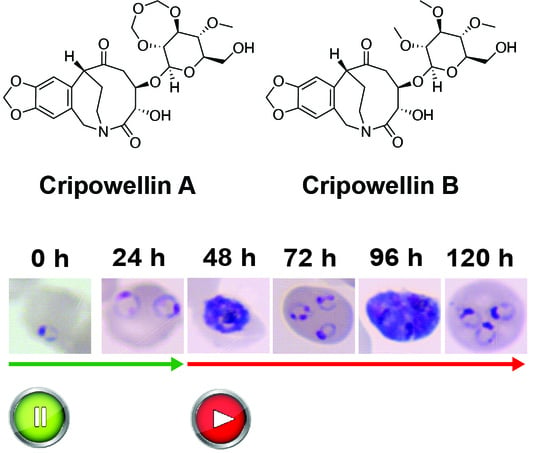
2.1. Cripowellins A and B Pause Parasites in Rings but Kill Trophozoite and Schizont Stages
2.2. Cripowellin B Is Cytostatic in Ring Stage Parasites
2.3. Cripowellin B Pauses Transcriptional Progression through the IDC
2.4. Cripowellin B Induced Cytostasis Is Not Reversed by Polyamine Supplementation
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals
3.2. Plasmodium falciparum Culture
3.3. Plasmodium falciparum Growth Inhibition Assays
3.4. Plasmodium falciparum Transcriptomics and Analysis
3.5. Reversal of P. falciparum Growth Inhibition by Polyamines Supplementation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. World Malaria Report 2022; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Murithi, J.M.; Owen, E.S.; Istvan, E.S.; Lee, M.C.S.; Ottilie, S.; Chibale, K.; Goldberg, D.E.; Winzeler, E.A.; Llinas, M.; Fidock, D.A.; et al. Combining stage specificity and metabolomic profiling to advance antimalarial drug discovery. Cell Chem. Biol. 2020, 27, 158–171.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilson, D.W.; Langer, C.; Goodman, C.D.; McFadden, G.I.; Beeson, J.G. Defining the timing of action of antimalarial drugs against Plasmodium falciparum. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 1455–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Portugaliza, H.P.; Miyazaki, S.; Geurten, F.J.; Pell, C.; Rosanas-Urgell, A.; Janse, C.J.; Cortes, A. Artemisinin exposure at the ring or trophozoite stage impacts Plasmodium falciparum sexual conversion differently. Elife 2020, 9, e60058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Pelt-Koops, J.C.; Pett, H.E.; Graumans, W.; van der Vegte-Bolmer, M.; van Gemert, G.J.; Rottmann, M.; Yeung, B.K.; Diagana, T.T.; Sauerwein, R.W. The spiroindolone drug candidate NITD609 potently inhibits gametocytogenesis and blocks Plasmodium falciparum transmission to anopheles mosquito vector. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 3544–3548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matthews, H.; Duffy, C.W.; Merrick, C.J. Checks and balances? DNA replication and the cell cycle in Plasmodium. Parasit. Vectors 2018, 11, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Babbitt, S.E.; Altenhofen, L.; Cobbold, S.A.; Istvan, E.S.; Fennell, C.; Doerig, C.; Llinás, M.; Goldberg, D.E. Plasmodium falciparum responds to amino acid starvation by entering into a hibernatory state. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, E3278–E3287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- van Biljon, R.; Niemand, J.; van Wyk, R.; Clark, K.; Verlinden, B.; Abrie, C.; von Grüning, H.; Smidt, W.; Smit, A.; Reader, J.; et al. Inducing controlled cell cycle arrest and re-entry during asexual proliferation of Plasmodium falciparum malaria parasites. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Assaraf, Y.G.; Abu-Elheiga, L.; Spira, D.T.; Desser, H.; Bachrach, U. Effect of polyamine depletion on macromolecular synthesis of the malarial parasite, Plasmodium falciparum, cultured in human erythrocytes. Biochem. J. 1987, 242, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van Brummelen, A.C.; Olszewski, K.L.; Wilinski, D.; Llinás, M.; Louw, A.I.; Birkholtz, L.-M. Co-inhibition of Plasmodium falciparum S-adenosylmethionine decarboxylase/ornithine decarboxylase reveals perturbation-specific compensatory mechanisms by transcriptome, proteome, and metabolome analyses. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 4635–4646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McLean, K.J.; Jacobs-Lorena, M. The response of Plasmodium falciparum to isoleucine withdrawal is dependent on the stage of progression through the intraerythrocytic cell cycle. Malar. J. 2020, 19, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hott, A.; Casandra, D.; Sparks, K.N.; Morton, L.C.; Castanares, G.-G.; Rutter, A.; Kyle, D.E. Artemisinin-resistant Plasmodium falciparum parasites exhibit altered patterns of development in infected erythrocytes. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 3156–3167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Codd, A.; Teuscher, F.; Kyle, D.E.; Cheng, Q.; Gatton, M.L. Artemisinin-induced parasite dormancy: A plausible mechanism for treatment failure. Malar. J. 2011, 10, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, T.; Yeoh, L.M.; Tutor, M.V.; Dixon, M.W.; McMillan, P.J.; Xie, S.C.; Bridgford, J.L.; Gillett, D.L.; Duffy, M.F.; Ralph, S.A.; et al. Decreased K13 abundance reduces hemoglobin catabolism and proteotoxic stress, underpinning artemisinin resistance. Cell Rep. 2019, 29, 2917–2928.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mok, S.; Stokes, B.H.; Gnadig, N.F.; Ross, L.S.; Yeo, T.; Amaratunga, C.; Allman, E.; Solyakov, L.; Bottrill, A.R.; Tripathi, J.; et al. Artemisinin-resistant K13 mutations rewire Plasmodium falciparum’s intra-erythrocytic metabolic program to enhance survival. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duvalsaint, M.; Kyle, D.E. Phytohormones, isoprenoids, and role of the apicoplast in recovery from dihydroartemisinin-induced dormancy of Plasmodium falciparum. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62, e01771-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hsu, E. The history of qing hao in the Chinese materia medica. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2006, 100, 505–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eastman, R.T.; Fidock, D.A. Artemisinin-based combination therapies: A vital tool in efforts to eliminate malaria. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2009, 7, 864–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tajuddeen, N.; Van Heerden, F.R. Antiplasmodial natural products: An update. Malar. J. 2019, 18, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Snijman, D.A.; Linder, H.P. Phylogenetic relationships, seed characters, and dispersal system evolution in Amaryllideae (Amaryllidaceae). Ann. Mo. Bot. Gard. 1996, 83, 362–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fennell, C.W.; van Staden, J. Crinum species in traditional and modern medicine. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2001, 78, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ka, S.; Koirala, M.; Merindol, N.; Desgagne-Penix, I. Biosynthesis and biological activities of newly discovered Amaryllidaceae alkaloids. Molecules 2020, 25, 4901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Presley, C.C.; Krai, P.; Dalal, S.; Su, Q.; Cassera, M.; Goetz, M.; Kingston, D.G.I. New potently bioactive alkaloids from Crinum erubescens. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2016, 24, 5418–5422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Velten, R.; Erdelen, C.; Gehling, M.; Gohrt, A.; Gondol, D.; Lenz, J.; Lockhoff, O.; Wachendorff, U.; Wendisch, D. Cripowellin A and B, a novel type of Amaryllidaceae alkaloid from Crinum powellii. Tetrahedron. Lett. 1998, 39, 1737–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enders, D.; Lenzen, A.; Backes, M.; Janeck, C.; Catlin, K.; Lannou, M.I.; Runsink, J.; Raabe, G. Asymmetric total synthesis of the 1-epi-aglycon of the cripowellins A and B. J. Org. Chem. 2005, 70, 10538–10551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enders, D.; Lenzen, A.; Raabe, G. Asymmetric synthesis of the 1-epi aglycon of the cripowellins A and B. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 3766–3769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.X.; Huo, J.M.; Hu, J.; Xu, Z.P.; Zhang, X. Amaryllidaceae alkaloids from Crinum latifolium with cytotoxic, antimicrobial, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory activities. Fitoterapia 2018, 130, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vossen, M.G.; Pferschy, S.; Chiba, P.; Noedl, H. The SYBR Green I malaria drug sensitivity assay: Performance in low parasitemia samples. Am. J. Trop. Med. 2010, 82, 398–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Roch, K.G.; Zhou, Y.; Blair, P.L.; Grainger, M.; Moch, J.K.; Haynes, J.D.; De La Vega, P.; Holder, A.A.; Batalov, S.; Carucci, D.J.; et al. Discovery of gene function by expression profiling of the malaria parasite life cycle. Science 2003, 301, 1503–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tarun, A.S.; Peng, X.; Dumpit, R.F.; Ogata, Y.; Silva-Rivera, H.; Camargo, N.; Daly, T.M.; Bergman, L.W.; Kappe, S.H. A combined transcriptome and proteome survey of malaria parasite liver stages. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lasonder, E.; Rijpma, S.R.; van Schaijk, B.C.; Hoeijmakers, W.A.; Kensche, P.R.; Gresnigt, M.S.; Italiaander, A.; Vos, M.W.; Woestenenk, R.; Bousema, T.; et al. Integrated transcriptomic and proteomic analyses of P. falciparum gametocytes: Molecular insight into sex-specific processes and translational repression. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 6087–6101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lopez-Barragan, M.J.; Lemieux, J.; Quinones, M.; Williamson, K.C.; Molina-Cruz, A.; Cui, K.; Barillas-Mury, C.; Zhao, K.; Su, X.Z. Directional gene expression and antisense transcripts in sexual and asexual stages of Plasmodium falciparum. BMC Genom. 2011, 12, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bozdech, Z.; Llinas, M.; Pulliam, B.L.; Wong, E.D.; Zhu, J.; DeRisi, J.L. The transcriptome of the intraerythrocytic developmental cycle of Plasmodium falciparum. PLoS Biol. 2003, 1, E5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Otto, T.D.; Wilinski, D.; Assefa, S.; Keane, T.M.; Sarry, L.R.; Bohme, U.; Lemieux, J.; Barrell, B.; Pain, A.; Berriman, M.; et al. New insights into the blood-stage transcriptome of Plasmodium falciparum using RNA-Seq. Mol. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chappell, L.; Ross, P.; Orchard, L.; Russell, T.J.; Otto, T.D.; Berriman, M.; Rayner, J.C.; Llinas, M. Refining the transcriptome of the human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum using amplification-free RNA-seq. BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kafsack, B.F.; Painter, H.J.; Llinas, M. New Agilent platform DNA microarrays for transcriptome analysis of Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium berghei for the malaria research community. Malar. J. 2012, 11, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Painter, H.J.; Chung, N.C.; Sebastian, A.; Albert, I.; Storey, J.D.; Llinas, M. Genome-wide real-time in vivo transcriptional dynamics during Plasmodium falciparum blood-stage development. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smilkstein, M.; Sriwilaijaroen, N.; Kelly, J.X.; Wilairat, P.; Riscoe, M. Simple and inexpensive fluorescence-based technique for high-throughput antimalarial drug screening. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 1803–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, T.; Simko, V. R package ‘corrplot’: Visualization of a Correlation Matrix. Open J. Anim. Sci. 2021, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Assaraf, Y.G.; Golenser, J.; Spira, D.T.; Messer, G.; Bachrach, U. Cytostatic effect of DL-alpha-difluoromethylornithine against Plasmodium falciparum and its reversal by diamines and spermidine. Parasitol. Res. 1987, 73, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Butler, J.H.; Painter, H.J.; Bremers, E.K.; Krai, P.; Llinás, M.; Cassera, M.B. Cripowellins Pause Plasmodium falciparum Intraerythrocytic Development at the Ring Stage. Molecules 2023, 28, 2600. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062600
Butler JH, Painter HJ, Bremers EK, Krai P, Llinás M, Cassera MB. Cripowellins Pause Plasmodium falciparum Intraerythrocytic Development at the Ring Stage. Molecules. 2023; 28(6):2600. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062600
Chicago/Turabian StyleButler, Joshua H., Heather J. Painter, Emily K. Bremers, Priscilla Krai, Manuel Llinás, and Maria B. Cassera. 2023. "Cripowellins Pause Plasmodium falciparum Intraerythrocytic Development at the Ring Stage" Molecules 28, no. 6: 2600. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062600
APA StyleButler, J. H., Painter, H. J., Bremers, E. K., Krai, P., Llinás, M., & Cassera, M. B. (2023). Cripowellins Pause Plasmodium falciparum Intraerythrocytic Development at the Ring Stage. Molecules, 28(6), 2600. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062600