Kinetics and Mechanism of In(III) Ions Electroreduction on Cyclically Renewable Liquid Silver Amalgam Film Electrode: Significance of the Active Complexes of In(III)—Acetazolamide
Abstract
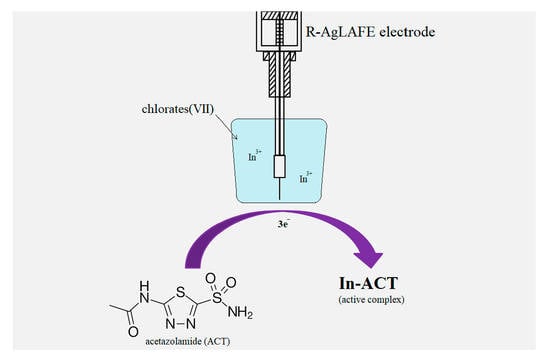
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals
3.2. Apparatus
- -
- The Ag/AgCl/3M KCl electrode as a reference;
- -
- A platinum wire as an auxiliary electrode;
- -
- A cyclically renewable liquid silver amalgam film electrode (R–AgLAFE) with the surface area of 17.25 mm2 as the working electrode (Figure 9).
3.3. Measurement Procedures
Kinetics and Thermodynamic Procedure
3.4. Experimental Operating Conditions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Grabarczyk, M.; Adamczyk, M. Simple, Responsive and Cost Effective Simultaneous Quantification of Ga(III) and In(III) in Environmental Water Samples. Int. Agrophys. 2019, 33, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prat, M.D.; Compano, R.; Granados, M.; Miralles, E. Liquid Chromatographic Determination of Gallium and indium with Fluorimetric Detection. J. Chromotogr. A 1996, 746, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uehara, N.; Jinno, K.; Hashimoto, M.; Shijo, Y. Selective Fluorometric Determination of Indium(III) by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography with 2-Methyl-8-Quinolinol Based on Aa Ligand-Exchange Reaction of Silanol Groups. J. Chromatogr. A 1997, 789, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.K.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, S.W.; Ko, J.; Bartsch, R.A.; Kim, J.S. Indium(III)-Induced Fluorescent Excimer Formation and Extinction in Calixarene−Fluor ionophores. Inorg. Chem. 2005, 44, 7866–7875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.C.; Li, H.J.; Yang, H.Z. A Sensitive and Highly Selective Fluorescent Sensor for In3+. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2010, 8, 3394–3397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.; Chae, J.B.; Kim, C. A Thiophene-Based Blue-Fluorescent Emitting Chemosensor for Detecting Indium (III) İon Author Links Open Overlay Panel. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2018, 97, 171–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, A.; Kang, J.H.; Jang, H.J.; Kim, C. Fluorescent Detection of Zn(II) and In(III) and Colorimetric Detection of Cu(II) and Co(II) by a Versatile Chemosensor. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2018, 65, 290–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.C.; Kim, C. A Thiourea-Naphthol Based Turn-On Fluorescent Sensor for Detecting In3+ and Its Application. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2020, 112, 107752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Lee, J.; Cheal, K. Sensitive Fluorescent Determination of İndium (III) by a Thiourea–Quinoline-Based. Instrum. Sci. Technol. 2022, 50, 481–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashibe, Y.; Kurosaki, M.; Takekawa, F.; Kuroda, R. Determination of Traces of Gallium and İndium in Ores by Electrothermal-Atomization Atomic Absorption Spectrometry with Matrix Modification. Microchim. Acta 1989, 98, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orians, K.J.; Boyle, E.A. Determination of Picomolar Concentrations of Titanium. Gallium and Indium in Sea Water by İnductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry Following an 8-Hydroxyquinoline Chelating Resin Preconcentration. Anal. Chim. Acta 1993, 282, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuzen, M.; Soylak, M. A Solid Phase Extraction Procedure for İndium Prior to Its Graphite Furnace Atomic Absorption Spectrometric Determination. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 129, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Połedniok, J. A Sensitive Spectrophotometric Method for Determination of Trace Quantities of Indium in Soil. Wat. Air Soil Poll. 2007, 186, 242–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslan, Y.; Kendüzler, E.; Ataman, O.Y. Indium Determination Using Slotted Quartz Tube-Atom Trap-Flame Atomic Absorption Spectrometry and Interference Studies. Talanta 2011, 85, 1786–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sereshti, H.; Entezari Heravi, Y.; Samadi, S. Optimized Ultrasound-Assisted emulsification Microextraction for Simultaneous Trace Multielement determination of Heavy Metals in Real Water Samples by ICP-OES. Talanta 2012, 97, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhrovčík, J.; Lesný, J. Determination of Indium in Liquid Crystal Displays by Flame Atomic Absorption Spectrometry. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 21, 163–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olıveır, L.C.; Sılva, I.S.; Pereıra, E.; Santana, E.S.; Iwaki, L.E.O.; Lopes, J.M.G.; Olıveıra, G.C. Validation Analysis Methodology to Determine the Cadmium. Indium and Impurities Concentration in Nuclear Grade Silver-indium-cadmium Alloys. Braz. J. Rad. Sci. 2022, 10, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Florence, T.M.; Batley, G.E.; Farrar, Y.J. The Determination of Indium by Anodic Stripping Voltammetry Application to Natural Waters. Electroanal. Chem. 1974, 56, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nosal-Wiercińska, A.; Martyna, M.; Grochowski, M.; Baś, B. First Electrochemical Studies on “CAP—PAIR” Effect for BI(III) Ion Electroreduction in the Presence of 2-Thiocytosine on Novel Cyclically Renewable Liquid Silver Amalgam Film Electrode (R-AgLAFE). J. Electrochem. Soc. 2021, 168, 066504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nosal-Wiercińska, A. The kinetics and mechanism of the electroreduction of Bi(III) ions from chlorates (VII) with varied water activity. Electrochim. Acta 2010, 55, 5917–5921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sykut, K.; Dalmata, G.; Marczewska, B.; Saba, J. Cognitive aspects of the cap-pair effect. Pol. J. Chem. 2004, 78, 1583–1596. [Google Scholar]
- Nosal–Wiercińska, A. Intermolecular Interactions in Systems Containing Bi(III)–ClO4−–H2O–Selected Amino Acids in the Aspect of Catalysis of Bi(III) Electroreduction. Electroanalysis 2014, 26, 1013–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engin, C.; Yilmaz, S.; Saglikoglu, G.; Yagmur, S.; Sadikoglu, M. Electroanalytical investigation of paracetamol on glassy carbon electrode by voltammetry. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2015, 10, 1916–1925. [Google Scholar]
- Martyna, M.; Pawlak, A.; Bazan-Woźniak, A.; Nosal-Wiercińska, A.; Pietrzak, R. The impact of acetazolamide-the ionic surfactant on the double layer parameters at the R-AgLAFe/chlorates (VII) interface. Adsorption 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nosal-Wiercińska, A. Catalytic activity of thiourea and its selected derivatives on electroreduction of In(III) in chlorates (VII). Cent. Eur. J. Chem. 2010, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nosal-Wiercińska, A.; Martyna, M.; Wiśniewska, M. Influence of mixed 2-thiocytosine–ionic surfactants adsorption layers on kinetics and mechanism of Bi (III) ions electro reduction: Use of the nanostructured R-AgLAFE. Appl. Nanosci. 2022, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieszporek, J.; Nieszporek, K. Experimental and theoretical studies of anionic surfactants activity at metal/solution interface: The influence of temperature and hydrocarbon chain length of surfactants on the zinc ions electroreduction rate. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2018, 91, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nazmutdinov, R.R.; Schmickler, W.; Kuznetsov, A.M. Microscopic modelling of the reduction of a Zn (II) aqua-complex on metal electrodes. Chem. Phys. 2005, 310, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazmutdinov, R.R.; Zinkicheva, T.T.; Tsirlina, G.A.; Kuz’minova Z., V. Why does the hydrolysis of In (III) aqua complexes make them electrochemically more active? Electrochim. Acta 2005, 50, 4888–4896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Pérez, G.; Andreu, A.; González-Arjona, D.; Calvente, J.J.; Molero, M. Influence of temperature on the reduction kinetics of Zn2+ at a mercury electrode. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2003, 552, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nosal-Wiercińska, A. Electrochemical and thermodynamic study of the electroreduction of Bi(III) ions in the presence of cysteine in solutions of different water activity. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2012, 681, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, E.; Galus, Z. Conditional Diffusion Coefficients of Ions and Molecules in Solution an Appraisal of the Conditions and Methods of Measurement. Pure Appl. Chem. 1979, 51, 1575–1582. [Google Scholar]
- Lasia, A. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy and Its Application. Modern Aspects of Electrochemistry; Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]











| 103 CIn(III) + 104 CACT /mol∙dm−3 | ∆E/V | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| v/mV·s−1 | ||||||||
| 5 | 10 | 20 | 50 | 100 | 200 | 500 | ||
| 0.00 | 0.0292 | 0.0313 | 0.0324 | 0.0333 | 0.0417 | 0.0504 | 0.0625 | 0.0645 |
| 0.10 | 0.0260 | 0.0265 | 0.0273 | 0.0321 | 0.0392 | 0.0468 | 0.0571 | 0.0592 |
| 0.30 | 0.0230 | 0.0232 | 0.0238 | 0.0310 | 0.0368 | 0.0440 | 0.0520 | 0.0558 |
| 0.50 | 0.0222 | 0.0226 | 0.0230 | 0.0297 | 0.0343 | 0.0381 | 0.0457 | 0.0501 |
| 1.00 | 0.0207 | 0.0211 | 0.0218 | 0.0281 | 0.0319 | 0.0340 | 0.0398 | 0.0472 |
| 3.00 | 0.0541 | 0.0547 | 0.0555 | 0.0613 | 0.0648 | 0.0710 | 0.0768 | 0.0910 |
| 5.00 | 0.0602 | 0.0608 | 0.0614 | 0.0690 | 0.0789 | 0.1141 | 0.1268 | 0.1373 |
| 10.0 | 0.0758 | 0.0762 | 0.0767 | 0.0878 | 0.0999 | 0.1257 | 0.1358 | 0.1411 |
| 103 CIn(III)+ 104 CACT /mol∙dm−3 | Slope | |
|---|---|---|
| Cathodic | Anodic | |
| 0.00 | 0.389 ± 0.029 | 0.485 ± 0.037 |
| 0.10 | 0.354 ± 0.027 | 0.500 ± 0.038 |
| 0.50 | 0.347 ± 0.027 | 0.479 ± 0.037 |
| 1.00 | 0.412 ± 0.031 | 0.479 ± 0.033 |
| 3.00 | 0.302 ± 0.023 | 0.483 ± 0.037 |
| 5.00 | 0.351 ± 0.027 | 0.431 ± 0.033 |
| 103 CIn(III) + 104 CACT /mol∙dm−3 | |
|---|---|
| 0.00 | 0.520 |
| 0.10 | 0.540 |
| 0.30 | 0.530 |
| 0.50 | 0.550 |
| 1.00 | 0.540 |
| 3.00 | 0.560 |
| 5.00 | 0.560 |
| 10.0 | 0.580 |
| 103 CIn(III)+ 104 CACT /mol∙dm−3 | ||
|---|---|---|
| 0.00 | 36 | 430 |
| 0.10 | 21.49 | 378 |
| 0.30 | 19.64 | 352 |
| 0.50 | 16.26 | 339 |
| 1.00 | 11.87 | 325 |
| 3.00 | 29.04 | 335 |
| 5.00 | 38.18 | 351 |
| 10.0 | 45.67 | 397 |
| 103 CIn(III)+ 104 CACT /mol∙dm−3 | α | ks 104/cm·s−1 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| CV | EIS | ||
| 0.00 | 0.40 | 0.53 | 0.35 |
| 0.10 | 0.44 | 0.89 | 1.03 |
| 0.30 | 0.48 | 1.23 | 1.55 |
| 0.50 | 0.51 | 3.29 | 4.33 |
| 1.00 | 0.59 | 6.23 | 7.12 |
| 3.00 | 0.49 | 6.17 | 6.96 |
| 5.00 | 0.35 | 5.93 | 6.48 |
| 10.0 | 0.27 | 5.72 | 6.23 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nosal-Wiercińska, A.; Martyna, M.; Pawlak, A.; Bazan-Woźniak, A.; Pietrzak, R.; Yilmaz, S.; Yağmur Kabaş, S.; Szabelska, A. Kinetics and Mechanism of In(III) Ions Electroreduction on Cyclically Renewable Liquid Silver Amalgam Film Electrode: Significance of the Active Complexes of In(III)—Acetazolamide. Molecules 2023, 28, 2942. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28072942
Nosal-Wiercińska A, Martyna M, Pawlak A, Bazan-Woźniak A, Pietrzak R, Yilmaz S, Yağmur Kabaş S, Szabelska A. Kinetics and Mechanism of In(III) Ions Electroreduction on Cyclically Renewable Liquid Silver Amalgam Film Electrode: Significance of the Active Complexes of In(III)—Acetazolamide. Molecules. 2023; 28(7):2942. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28072942
Chicago/Turabian StyleNosal-Wiercińska, Agnieszka, Marlena Martyna, Alicja Pawlak, Aleksandra Bazan-Woźniak, Robert Pietrzak, Selehatin Yilmaz, Sultan Yağmur Kabaş, and Anna Szabelska. 2023. "Kinetics and Mechanism of In(III) Ions Electroreduction on Cyclically Renewable Liquid Silver Amalgam Film Electrode: Significance of the Active Complexes of In(III)—Acetazolamide" Molecules 28, no. 7: 2942. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28072942
APA StyleNosal-Wiercińska, A., Martyna, M., Pawlak, A., Bazan-Woźniak, A., Pietrzak, R., Yilmaz, S., Yağmur Kabaş, S., & Szabelska, A. (2023). Kinetics and Mechanism of In(III) Ions Electroreduction on Cyclically Renewable Liquid Silver Amalgam Film Electrode: Significance of the Active Complexes of In(III)—Acetazolamide. Molecules, 28(7), 2942. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28072942