Divergence of Liver Lipidomes in Tibetan and Yorkshire Pigs Living at Different Altitudes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Liver Lipidomic Identification of Pig Breeds at Different Altitudes
2.2. Multivariate Statistical Analysis of the Pig Liver Lipidome According to Altitude and Breed
2.3. Changes in the Abundance of Major Lipid Classes in the Pig Liver According to Altitude and Breed
2.4. Differentially Abundant Lipids (DALs) in the Pig Liver According to Altitude and Breed
2.4.1. DALs in the Liver of Pigs of the Same Breed Raised at Different Altitudes
2.4.2. DALs in the Liver of Different Pig Breeds Raised at the Same Altitude
2.5. Kyoto Encyclopaedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) Annotation and Enrichment Analysis of Pig Liver DALs According to Altitude and Breed
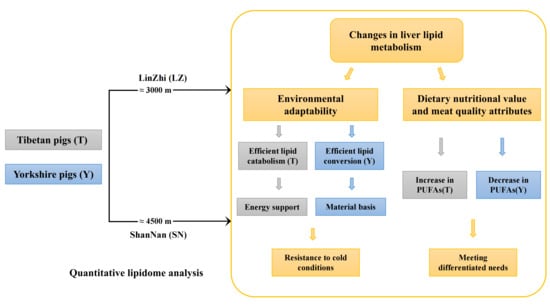
2.6. Complex Lipid Metabolism in the Liver of Tibetan and Yorkshire Pigs Reflects Adaptation to Environmental Changes
2.6.1. Efficient Lipid Catabolism Provides Energy Support for the Adaptive Survival of Tibetan Pigs in Cold Environments
2.6.2. Efficient Lipid Conversion and Accumulation Provide the Material Basis for the Adaptive Survival of Yorkshire Pigs in Cold Environments
2.7. Potential Effects of Adaptive Regulation of Liver Lipid Metabolism on Dietary Nutritional Value and Meat Quality Attributes
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Reagents
3.2. Sample Collection
3.3. Lipid Extraction
3.4. UPLC-MS/MS
3.5. Characterisation and Quantification of Lipid Molecular Species
3.6. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ma, Y.; Han, X.; Huang, C.; Zhong, L.; Adeola, A.C.; Irwin, D.M.; Xie, H.; Zhang, Y. Population Genomics Analysis Revealed Origin and High-altitude Adaptation of Tibetan Pigs. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 11463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Ban, D.; Gou, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, L.; Chamba, Y.; Zhang, H. Genome-wide DNA methylation profiles in Tibetan and Yorkshire pigs under high-altitude hypoxia. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2019, 10, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Zhang, C.-H.; Fauconnier, M.-L.; Mi, S. Characterization and differentiation of boiled pork from Tibetan, Sanmenxia and Duroc × (Landrac × Yorkshire) pigs by volatiles profiling and chemometrics analysis. Food Res. Int. 2020, 130, 108910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.; Zhou, L.; Huang, Y.; Zheng, M.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, C.; Peng, S.; Zeng, Q.; Zhong, L.; et al. A whole-genome sequence based association study on pork eating quality traits and cooking loss in a specially designed heterogeneous F6 pig population. Meat Sci. 2018, 146, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xiao, J.; Liu, X.; Gao, Y.; Luo, Z.; Gu, X.; Zhang, J.; Wu, D.; Geng, F. Tandem mass tag-labeled quantitative proteomic analysis of tenderloins between Tibetan and Yorkshire pigs. Meat Sci. 2021, 172, 108343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, M.; Shen, L.; Fan, Y.; Guo, Z.; Liu, B.; Chen, L.; Tang, G.; Jiang, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, S.; et al. High altitude adaptability and meat quality in tibetan pigs: A reference for local pork processing and genetic improvement. Animals 2019, 9, 1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Gao, C.; Yang, T.; Sha, Y.; Cai, Y.; Wang, X.; Yang, Q.; Liu, C.; Wang, B.; Zhao, S. Vascular characteristics and expression of hypoxia genes in Tibetan pigs’ hearts. Vet. Med. Sci. 2022, 8, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Guo, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhang, C.; Cui, T.; Ding, K.; Wang, P.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z. KLF4, a Key Regulator of a Transitive Triplet, Acts on the TGF-β Signaling Pathway and Contributes to High-Altitude Adaptation of Tibetan Pigs. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 628192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Li, Y.; Yang, Y.; Xu, K.; Yang, L.; Qiao, S.; Pan, H. Effect of a Plateau Environment on the Oxidation State of the Heart and Liver through AMPK/p38 MAPK/Nrf2-ARE Signaling Pathways in Tibetan and DLY Pigs. Animals 2022, 12, 1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, S.; Shang, K.; Jia, W.; Zhang, C.-H.; Liu, J.-Q.; Huang, D.-Q. Composition of chemical elements in the edible viscera of Tibetan pigs and its correlation with environment and feed. Food Res. Int. 2020, 129, 108832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, M.; Wang, Z.; Guo, X.; Wang, K.; Liu, S.; Zhang, B.; Shang, P. Integrated analysis of transcriptomic and proteomic analyses reveals different metabolic patterns in the livers of Tibetan and Yorkshire pigs. Anim Biosci 2021, 34, 922–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gluchowski, N.; Becuwe, M.; Walther, T.; Farese, R. Lipid droplets and liver disease: From basic biology to clinical implications. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 343–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Zheng, M.; Zhang, J.; Ye, Y.; Duan, M.; Chamba, Y.; Wang, Z.; Shang, P. Transcriptomics-Based Study of Differentially Expressed Genes Related to Fat Deposition in Tibetan and Yorkshire Pigs. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 919904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, H.; Xiao, Y.; Harlina, P.W.; Geng, F. Quantitative lipidomic analysis of chicken egg yolk during its formation. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2022. ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, M.A.; Lamichhane, S.; Dickens, A.; McGlinchey, A.; Ribeiro, H.C.; Sen, P.; Wei, F.; Hyötyläinen, T.; Orešič, M. Systems biology approaches to study lipidomes in health and disease. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2021, 1866, 158857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, S.; Shang, K.; Li, X.; Zhang, C.-H.; Liu, J.-Q.; Huang, D.-Q. Characterization and discrimination of selected China’s domestic pork using an LC-MS-based lipidomics approach. Food Control 2019, 100, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Lei, H.; Zhang, S.; Li, X.; Li, M.; Jiang, X.; Zhu, K.; Zhu, L. The comparison of energy metabolism and meat quality among three pig breeds. Anim. Sci. J. 2014, 85, 770–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Wang, J.; Sun, L.; Li, R.; Wu, D.; Tang, J.; Zhang, J.; Geng, F. Metabolome analysis shows that ultrasound enhances the lethality of chlorine dioxide against Salmonella Typhimurium by disrupting its material and energy metabolism. Food Res. Int. 2022, 162, 112135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thévenot, E.A.; Roux, A.; Xu, Y.; Ezan, E.; Junot, C. Analysis of the Human Adult Urinary Metabolome Variations with Age, Body Mass Index, and Gender by Implementing a Comprehensive Workflow for Univariate and OPLS Statistical Analyses. J. Proteome Res. 2015, 14, 3322–3335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Li, S.; Ye, H.; Luo, W.; Huang, Q.; Geng, F. Ovomucin may be the key protein involved in the early formation of egg-white thermal gel. Food Chem. 2022, 366, 130596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Shang, P.; Tao, Z.; Qiangba, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, H. Effect of a single nucleotide polymorphism in the growth hormone secretagogue receptor (GHSR) gene on growth rate in pigs. Gene 2017, 634, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauger, J.-F.; Chassé, É.; Mahat, B.; Lindon, C.; Bordenave, N.; Imbeault, P. The Effect of Acute Continuous Hypoxia on Triglyceride Levels in Constantly Fed Healthy Men. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Xing, L.; Zhang, J.; Wang, K.; Duan, M.; Wei, M.; Zhang, B.; Chang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Shang, P. Expression pattern of CRYAB and CTGF genes in two pig breeds at different altitudes. Arq. Bras. De Med. Veterinária E Zootec. 2022, 74, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheviron, Z.A.; Bachman, G.C.; Connaty, A.D.; McClelland, G.B.; Storz, J.F. Regulatory changes contribute to the adaptive enhancement of thermogenic capacity in high-altitude deer mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 8635–8640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Jin, M.; Fei, X.; Yuan, Z.; Wang, Y.; Quan, K.; Wang, T.; Yang, J.; He, M.; Wei, C. Transcriptome Comparison Reveals the Difference in Liver Fat Metabolism between Different Sheep Breeds. Animals 2022, 12, 1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Jia, Z.; Xu, Z.; Shi, J.; Zhao, X.; He, K.L. Transcriptional landscape in rat intestines under hypobaric hypoxia. PeerJ 2021, 9, e11823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuwata, H.; Hara, S. Role of acyl-CoA synthetase ACSL4 in arachidonic acid metabolism. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2019, 144, 106363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Qiao, L.; An, L.; Wang, W.; Liu, J.; Ren, Y.; Pan, Y.; Jing, J.; Liu, W. Transcriptome analysis of adipose tissues from two fat-tailed sheep breeds reveals key genes involved in fat deposition. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Li, M.; Li, X.; Shuai, S.; Liu, H.; Wang, J.; Jiang, A.; Gu, Y.; Zhang, K.; Teng, X.; et al. Distinct Expression Patterns of Genes Associated with Muscle Growth and Adipose Deposition in Tibetan Pigs: A Possible Adaptive Mechanism for High Altitude Conditions. High Alt. Med. Biol. 2009, 10, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abumrad, N.A. The Liver as a Hub in Thermogenesis. Cell Metab. 2017, 26, 454–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simcox, J.; Geoghegan, G.; Maschek, J.A.; Bensard, C.L.; Pasquali, M.; Miao, R.; Lee, S.; Jiang, L.; Huck, I.; Kershaw, E.E.; et al. Global Analysis of Plasma Lipids Identifies Liver-Derived Acylcarnitines as a Fuel Source for Brown Fat Thermogenesis. Cell Metab. 2017, 26, 509–522.e506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heeren, J.; Scheja, L. Brown adipose tissue and lipid metabolism. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2018, 29, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves-Bezerra, M.; Cohen, D. Triglyceride Metabolism in the Liver. Compr. Physiol. 2017, 8, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, S.; Siddiqi, S. Intracellular Trafficking and Secretion of VLDL. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2012, 32, 1079–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tapiero, H.; Nguyen Ba, G.; Couvreur, P.; Tew, K.D. Polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) and eicosanoids in human health and pathologies. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2002, 56, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doychev, V.; Mihaylova, G. Effect of flaxsee d and alpha tocopherol supplementation of pig diets on fatty acid content and lipid oxidation stability of m. Longissimus. Bulg. J. Agric. Sci. 2013, 19, 1416–1424. [Google Scholar]
- Mensink, R. Fatty acids: Health effects of saturated fatty acids. In Encyclopedia of Human Nutrition; Academic Press: Waltham, MA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Ngadi, M.O. Predicting intramuscular fat content of pork using hyperspectral imaging. J. Food Eng. 2014, 134, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starkey, C.P.; Geesink, G.H.; Collins, D.; Hutton Oddy, V.; Hopkins, D.L. Do sarcomere length, collagen content, pH, intramuscular fat and desmin degradation explain variation in the tenderness of three ovine muscles? Meat Sci. 2016, 113, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, W.; Wang, J.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, R.; Tang, J.; Geng, F. Quantitative proteomic analysis provides insight into the survival mechanism of Salmonella typhimurium under high-intensity ultrasound treatment. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2022, 5, 1740–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; Wang, J.; Wang, N.; Wu, D.; Li, H.; Geng, F. Ultrasound-assisted pH-shifting remodels egg-yolk low-density lipoprotein to enable construction of a stable aqueous solution of vitamin D3. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2022, 5, 964–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yin, D.; Liao, J.; Wang, Y.; Gou, R.; Tang, C.; Li, W.; Liu, Y.; Fu, J.; Shi, S.; et al. Regulation of protein corona on liposomes using albumin-binding peptide for targeted tumor therapy. J. Control. Release 2023, 355, 593–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, W.; Xu, Y.; Gu, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; Geng, F. Divergence of Liver Lipidomes in Tibetan and Yorkshire Pigs Living at Different Altitudes. Molecules 2023, 28, 2991. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28072991
Luo W, Xu Y, Gu X, Zhang J, Wang J, Geng F. Divergence of Liver Lipidomes in Tibetan and Yorkshire Pigs Living at Different Altitudes. Molecules. 2023; 28(7):2991. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28072991
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Wei, Yisha Xu, Xuedong Gu, Jiamin Zhang, Jinqiu Wang, and Fang Geng. 2023. "Divergence of Liver Lipidomes in Tibetan and Yorkshire Pigs Living at Different Altitudes" Molecules 28, no. 7: 2991. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28072991
APA StyleLuo, W., Xu, Y., Gu, X., Zhang, J., Wang, J., & Geng, F. (2023). Divergence of Liver Lipidomes in Tibetan and Yorkshire Pigs Living at Different Altitudes. Molecules, 28(7), 2991. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28072991