ZnO-CeO2 Hollow Nanospheres for Selective Determination of Dopamine and Uric Acid
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
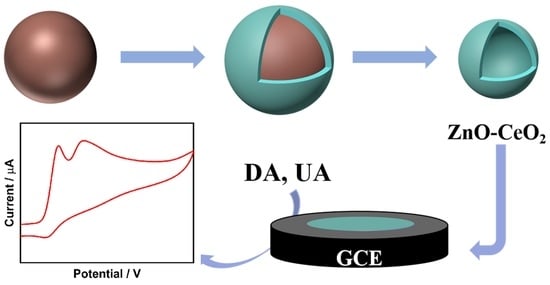
2.1. Morphological Characterization and Synthesis Mechanism of ZnO-CeO2 Hollow Nanospheres
2.2. Structural and Compositional Characterization of ZnO-CeO2 Hollow Nanospheres
2.3. Electrochemical Performance of ZnO-CeO2 Hollow Nanospheres
2.4. Determination of DA and UA on ZnO-CeO2/GCE
3. Experimental
3.1. Materials
3.2. Instruments
3.3. Synthesis of RF Resin Spheres
3.4. Synthesis of ZnO-CeO2 Hollow Nanospheres
3.5. Fabrication of the Modified Electrode
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liang, X.H.; Yu, A.X.; Bo, X.J.; Du, D.Y.; Su, Z.M. Metal/covalent-organic frameworks-based electrochemical sensors for the detection of ascorbic acid, dopamine and uric acid. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2023, 497, 215427. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, S.; Li, H.; Niu, W.; Xu, G. Simultaneous electrochemical determination of uric acid, dopamine, and ascorbic acid at single-walled carbon nanohorn modified glassy carbon electrode. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 25, 940–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Deng, P.; Tian, Y.; Feng, J.; Xiao, J.; Li, J.; Liu, J.; Li, G.; He, Q. Simultaneous and sensitive determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine and uric acid via an electrochemical sensor based on PVP-graphene composite. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2020, 18, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, G.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, K.; Yuan, Q.; Wang, X. One-pot synthesis of dendritic Pt3Ni nanoalloys as nonenzymatic electrochemical biosensors with high sensitivity and selectivity for dopamine detection. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 10998–11003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Wang, D.P.; Guo, C.; Liu, Y.; Rao, Q.; Lou, F.; Li, Q.; Dong, Y.; Li, Q.; Yang, H.B.; et al. Single-atom ruthenium biomimetic enzyme for simultaneous electrochemical detection of dopamine and Uuric acid. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 4916–4923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.C.; Ma, L.X. One-pot facile fabrication of graphene-zinc oxide composite and its enhanced sensitivity for simultaneous electrochemical detection of ascorbic acid, dopamine and uric acid. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 227, 488–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erden, P.E.; Kılıc, E. A review of enzymatic uric acid biosensors based on amperometric detection. Talanta 2013, 107, 312–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, C.; Yang, G.; Li, H.; Du, D.; Lin, Y. Electrochemical sensors and biosensors based on nanomaterials and nanostructures. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 230–249. [Google Scholar]
- Koventhan, C.; Vinothkumar, V.; Chen, S.M. Rational design of manganese oxide/tin oxide hybrid nanocomposite based electrochemical sensor for detection of prochlorperazine (antipsychotic drug). Microchem. J. 2022, 175, 107082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koventhan, C.; Vinothkumar, V.; Chen, S.M. Development of an electrochemical sensor based on a cobalt oxide/tin oxide composite for determination of antibiotic drug ornidazole. New J. Chem. 2021, 45, 12593–12605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ensafi, A.A.; Taei, M.; Khayamian, T. A differential pulse voltammetric method for simultaneous determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine, and uric acid using poly (3-(5-chloro-2-hydroxyphenylazo)-4,5-dihydroxynaphthalene-2,7-disulfonic acid) film modified glassy carbon electrode. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2009, 633, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Guo, H.; Wang, Z.; Long, Y.; Li, W.; Tu, Y. Au@Cu2O core-shell structure for high sensitive non-enzymatic glucose sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 255, 2510–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Wang, X.; Yang, T.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, P.; Feng, B.; Qing, T. Transition metal-doped germanium oxide nanozyme with enhanced enzyme-like activity for rapid detection of pesticide residues in water samples. Anal. Chim. Acta 2023, 1245, 340861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Chang, J.; Zhuang, X.; Li, H.; Hou, T.; Li, F. Two-dimensional cobalt-doped Ti3C2 MXene nanozyme-mediated homogeneous electrochemical strategy for pesticides assay based on in situ generation of electroactive substances. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 3669–3676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shetti, N.P.; Bukkitgar, S.D.; Reddy, K.R.; Reddy, C.V.; Aminabhavi, T.M. ZnO-based nanostructured electrodes for electrochemical sensors and biosensors in biomedical applications. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 141, 111417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganesamurthi, J.; Shanmugam, R.; Chen, T.W.; Chen, S.M.; Balamurugan, M.; Gan, Z.W.; Siddiqui, M.R.; Wabaidur, S.M.; Ali, M.A. NiO/ZnO binary metal oxide based electrochemical sensor for the evaluation of hazardous flavonoid in biological and vegetable samples. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 647, 129077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myndrul, V.; Coy, E.; Babayevska, N.; Zahorodna, V.; Balitskyi, V.; Baginskiy, I.; Gogotsi, O.; Bechelany, M.; Giardi, M.T.; Iatsunskyi, I. MXene nanoflakes decorating ZnO tetrapods for enhanced performance of skin-attachable stretchable enzymatic electrochemical glucose sensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 207, 114141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Zhang, W.; Wu, J.; Zhang, C.; Song, Y.; Zhao, Y. Programming a triple-shelled CuS@Ni(OH)2@CuS heterogeneous nanocage as robust electrocatalysts enabling long-term highly sensitive glucose detection. Electrochim. Acta 2023, 438, 141588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Zou, X.; Liu, Q.; Li, S.; Kang, C.; Xiang, W. A highly sensitive non-enzymatic glucose sensor based on CuS nanosheets modified Cu2O/CuO nanowire arrays. Electrochim. Acta 2020, 334, 135630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramanian, P.; Annalakshmi, M.; Chen, S.M.; Sathesh, T.; Peng, T.K.; Balamurugan, T.S.T. Facile solvothermal preparation of Mn2CuO4 microspheres: Excellent electrocatalyst for real-time detection of H2O2 released from live cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 43543–43551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Tang, J.; Huang, H.; Lin, T.; Luo, B.; Wang, L. Hollow structured cathode materials for rechargeable batteries. Sci. Bull. 2020, 65, 496–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivaraman, N.; Duraisamy, V.; Lucious, L.; Saraswathyamma, B.; Kumar, S.M.S.; Thangamuthu, R. In-situ construction of N and P doped hollow sphere carbon for electrochemical sensing of antibiotic drug from poultry sustenance. Electrochim. Acta 2023, 441, 141773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Huang, Y.; Wang, N.; Jiang, T.; Hu, S.; Zheng, B.; Yuan, H.; Xiao, D. Facile fabrication of Mn2O3 nanoparticle-assembled hierarchical hollow spheres and their sensing for hydrogen peroxide. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 9526–9533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Yan, X.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, D.; He, H.; Lei, Y.; Shen, X.; Luo, L. Mn3O4-CeO2 Hollow nanospheres for electrochemical determination of hydrogen peroxide. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2023, 6, 2116–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarjuna, Y.; Hsiao, Y.J. TeO2 doped ZnO nanostructure for the enhanced NO2 gas sensing on MEMS sensor device. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2024, 401, 134891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinothkumar, V.; Koventhan, C.; Chen, S.M. Facile one-step synthesis of Ni@CeO2 nanoparticles towards high performance voltammetric sensing of antipsychotic drug trifluoperazine. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 882, 160682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Guo, H.; Lu, A.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Chen, M.S.; Peng, D.L. Facile preparation of well-dispersed CeO2–ZnO composite hollow microspheres with enhanced catalytic activity for CO oxidation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, C.; Li, Y.; Chang, C.R.; He, C.; Lu, Q.; Yu, Y.; Duan, P.; Zhang, Z.; Luque, R. Hierarchically hollow MnO2@CeO2 heterostructures for NO oxidation: Remarkably promoted activity and SO2 tolerance. ACS Catal. 2021, 11, 10988–10996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Wang, Y.; Wei, Y.; Zhao, W.; Gao, D.; Yang, H.; Li, C. Successive interfacial reaction-directed synthesis of CeO2@Au@CeO2-MnO2 environmental catalyst with sandwich hollow structure. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 11595–11603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Li, Y.; Pan, X.; Cortie, D.; Huang, X.; Yi, Z. Photocatalytic oxidation of methane over silver decorated zinc oxide nanocatalysts. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Sheng, H.; Ross, R.D.; Han, J.; Wang, X.; Song, B.; Jin, S. Modifying redox properties and local bonding of Co3O4 by CeO2 enhances oxygen evolution catalysis in acid. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Feng, X.L.; Zhang, Z.; Jin, X.; Liu, D.P.; Zhang, Y. A controllable surface etching strategy for well-defined spiny yolk@shell CuO@CeO2 cubes and their catalytic performance boost. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1802559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, X.; Sheng, Z.; Yu, D.; Yang, L.; Xiao, X.; Wang, S. Influence of Mn/Ce ratio on the physicochemical properties and catalytic performance of graphene supported MnOx-CeO2 oxides for NH3-SCR at low temperature. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 423, 845–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogularasu, S.; Akilarasan, M.; Chen, S.M.; Chen, T.W.; Lou, B.S. Urea-based morphological engineering of ZnO; for the biosensing enhancement towards dopamine and uric acid in food and biological samples. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2019, 227, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wu, F.; Ouyang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Ji, Y. Zinc oxide nanoparticles decorated on graphene sheets@cerium oxide nanocomposites to sensitize gold electrode for the nonenzymatic hydrogenperoxide detection. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2016, 163, H834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Song, S.; Yue, H.; Gao, X.; Wang, B.; Guo, E. ZnO nanosheet balls anchored onto graphene foam for electrochemical determination of dopamine in the presence of uric acid. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 277, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Cui, G.; Dong, L.; Wang, X.; Zhen, Q.; Sun, Y.; Ma, S.; Zhang, C.; Pang, H. Synchronous electrochemical detection of dopamine and uric acid by a PMo12@MIL-100(Fe)@PVP nanocomposite. Anal. Biochem. 2022, 648, 114670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, C.; Zou, Z.; Liang, T.; Yuan, C.; Gao, J.; Tang, K.; Li, C.M. Methylene blue intercalated aptamer to amplify signals toward sensitively electrochemical detection of dopamine released from living Parkinson’s disease model cells. Sens. Actuators Rep. 2022, 4, 100080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.S.; Al-Ghurabi, E.H.; Asif, M.; Boumaza, M. Retrieving and morphological portrayal of Cu-nanoparticle impregnated reduced graphene oxide (CuNP@rGO) electrochemical bio-sensor. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2021, 329, 112826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, K.; Qiu, Y.; Li, J. Electro-catalytic behavior by polypyrrole-derived carbon supported iron for simultaneous electrochemical sensing of dopamine and uric acid. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2022, 910, 116188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Yu, L.; Yan, M.; Ye, J.; Huang, J.; Yang, X. Holey nitrogen-doped graphene aerogel for simultaneously electrochemical determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine and uric acid. Talanta 2021, 224, 121851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, R.; Lu, B.; Yuan, Y.; Gao, H.; Song, S.; Zhou, S.; Zang, J. Amorphous carbon film with self-modified carbon nanoparticles synthesized by low temperature carbonization of phenolic resin for simultaneous sensing of dopamine and uric acid. Electroanalysis 2021, 33, 2252–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaya, E.; Menendez, N.; Mazario, E.; Herrasti, P. Fe3O4-nanoparticle-modified sensor for the detection of dopamine, uric acid and ascorbic acid. Chemosensors 2023, 11, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, C.; Zeng, X.; Lei, J.; Hou, J.; Huo, D.; Hou, C. Co single-atom nanozymes for the simultaneous electrochemical detection of uric acid and dopamine in biofluids. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2024, 7, 6273–6283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Qiao, S.Z.; Liu, H.; Chen, J.; Orpe, A.; Zhao, D.; Lu, G.Q. Extension of the Stöber method to the preparation of monodisperse resorcinol–formaldehyde resin polymer and carbon spheres. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 5947–5951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Modified Material | Linear Range (μM) | Detection Limit (μM) | Reference | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DA | UA | DA | UA | ||
| CuNP a @rGO b | 20–1000 | 60–900 | 2.26 | 6.72 | [39] |
| N-doped carbon Supported iron | 5–900 | 4–300 | 3.21 | 3.348 | [40] |
| HNGA c | 0.6–75 | 0.4–50 | 0.22 | 0.12 | [41] |
| HNAC d | 2–10 | 20–100 | 0.401 | 2.800 | [42] |
| Fe3O4 | 10–100 | 20–160 | 4.5 | 14 | [43] |
| PPy e -Co-NNC f | 1–50 | 2–500 | 0.025 | 0.411 | [44] |
| PMo12 g @MIL-100(Fe) h @PVP i | 1–247 | 5–406 | 0.586 | 0.372 | [37] |
| ZnO-CeO2 | 5–800 | 10–1000 | 0.39 | 0.49 | This work |
| Serum Sample | Added (μM) | Found (μM) | Recovery (%) | RSD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 10 | 9.89 | 98.9 | 0.96 |
| 2 | 20 | 19.94 | 99.7 | 1.26 |
| 3 | 30 | 30.4 | 101.3 | 1.49 |
| Serum Sample | Added (μM) | Found (μM) | Recovery (%) | RSD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 20 | 19.57 | 97.9 | 1.29 |
| 2 | 30 | 30.45 | 101.5 | 1.23 |
| 3 | 40 | 40.2 | 100.5 | 1.47 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Yan, X.; Chen, Y.; Deng, D.; He, H.; Lei, Y.; Luo, L. ZnO-CeO2 Hollow Nanospheres for Selective Determination of Dopamine and Uric Acid. Molecules 2024, 29, 1786. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29081786
Zhang Y, Yan X, Chen Y, Deng D, He H, Lei Y, Luo L. ZnO-CeO2 Hollow Nanospheres for Selective Determination of Dopamine and Uric Acid. Molecules. 2024; 29(8):1786. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29081786
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yaru, Xiaoxia Yan, Yifan Chen, Dongmei Deng, Haibo He, Yunyi Lei, and Liqiang Luo. 2024. "ZnO-CeO2 Hollow Nanospheres for Selective Determination of Dopamine and Uric Acid" Molecules 29, no. 8: 1786. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29081786
APA StyleZhang, Y., Yan, X., Chen, Y., Deng, D., He, H., Lei, Y., & Luo, L. (2024). ZnO-CeO2 Hollow Nanospheres for Selective Determination of Dopamine and Uric Acid. Molecules, 29(8), 1786. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29081786