Size-Dependent Cytotoxicity of Nanocarbon Blacks
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
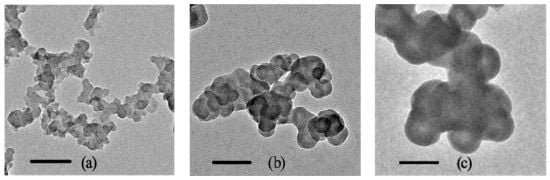
2.1. Characterization of NCBs
2.2. Cytotoxicity Determination of NCBs
2.3. Uptake of NCBs in RAW264.7 Cells
2.4. Mechanisms of NCBs-Induced Cytotoxicity
3. Discussion
4. Experimental Section
4.1. Characterization of NCBs
4.2. Cytotoxicity Assessments of NCBs
4.3. Observation for Cellular Uptake of NCBs by Optical Microscopy
4.4. 99mTc Labeling of NCBs
4.5. Measurement of Cellular Uptake of NCBs with Radiotracer Techniques
4.6. Determination of SOD Reactivity and MDA Production Induced by NCBs
4.7. Measurement of Intracellualr ROS Production
4.8. Observation of Nuclear Damage Induced by NCBs
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Information
ijms-14-22529-s001.pdf






| Incubated time/h | 14 nm NCBs | 51 nm NCBs | 95 nm NCBs |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 10.2 ± 2.2 | 13.4 ± 1.9 | 51.9 ± 3.8 |
| 24 | 32.3 ± 3.2 | 39.7 ± 2.9 | 78.4 ± 2.8 |
| 48 | 24.5 ± 3.4 | 31.4 ± 4.1 | 58.6 ± 3.4 |
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Service, R.F. American Chemical Society meeting: Nanomaterials show signs of toxicity. Science 2003, 300, 243. [Google Scholar]
- Brumfiel, G. Nanotechnology: A little knowledge. Nature 2003, 424, 246–248. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.; Tao, S.; Wang, W.T.; Liu, J.F.; Shen, H.Z.; Shen, G.F.; Wang, B.; Liu, X.P.; Li, W.; Huang, Y.; et al. Black carbon emissions in China from 1949 to 2050. Environ. Sci. Technol 2012, 46, 7595–7603. [Google Scholar]
- Levy, L.; Chaudhuri, I.S.; Krueger, N.; McCunney, R.J. Does carbon black disaggregate in lung fluid? A critical assessment. Chem. Res. Toxicol 2012, 25, 2001–2006. [Google Scholar]
- Belade, E.; Armand, L.; Martinon, L.; Kheuang, L.; Fleury-Feith, J.; Baeza-Squiban, A.; Lanone, S.; Billon-Galland, M.A.; Pairon, J.C.; Boczkowski, J. A comparative transmission electron microscopy study of titanium dioxide and carbon black nanoparticles uptake in human lung epithelial and fibroblast cell lines. Toxicol. In Vitro 2012, 26, 57–66. [Google Scholar]
- Bourdon, J.A.; Halappanavar, S.; Saber, A.T.; Jacobsen, N.R.; Williams, A.; Wallin, H.; Vogel, U.; Yauk, C.L. Hepatic and pulmonary toxicogenomic profiles in mice intratracheally instilled with carbon black nanoparticles reveal pulmonary inflammation, Acute phase response, and Alterations in lipid homeostasis. Toxicol. Sci 2012, 127, 474–484. [Google Scholar]
- Koike, E.; Kobayashi, T. Chemical and biological oxidative effects of carbon black nanoparticles. Chemosphere 2006, 65, 946–951. [Google Scholar]
- Stone, V.; Tuiman, M.; Vamvakopoulos, J.E.; Shaw, J.; Brown, D.; Petterson, S.; Faux, S.P.; Borm, P.; MacNee, W.; Michaelangeli, F.; et al. Increased calcium influx in a monocytic cell line on exposure to ultrafine carbon black. Eur. Respir. J 2000, 15, 297–303. [Google Scholar]
- Magrez, A.; Kasas, S.; Salicio, V.; Pasquier, N.; Seo, J.W.; Celio, M.; Catsicas, S.; Schwaller, B.; Forro, L. Cellular toxicity of carbon-based nanomaterials. Nano Lett 2006, 6, 1121–1125. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Li, W.X.; Li, Q.N.; Li, Y.G.; Li, Y.F.; Zhang, X.Y.; Huang, Q. Effects of serum proteins on intracellular uptake and cytotoxicity of carbon nanoparticles. Carbon 2009, 47, 1351–1358. [Google Scholar]
- Sanders, K.; Degn, L.L.; Mundy, W.R.; Zucker, R.M.; Dreher, K.; Zhao, B.Z.; Roberts, J.E.; Boyes, W.K. In vitro phototoxicity and hazard identification of nano-scale titanium dioxide. Toxicol. Appl. Pharm 2012, 258, 226–236. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, X.W.; Mattingly, C.A.; Tseng, M.T.; Cho, M.J.; Liu, Y.; Adams, V.R.; Mumper, R.J. Doxorubicin and paclitaxel-loaded lipid-based nanoparticles overcome multidrug resistance by inhibiting P-Glycoprotein and depleting ATP. Cancer Res 2009, 69, 3918–3926. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, M.; Huang, S.H.; Yu, K.J.; Clyne, A.M. Dextran and polymer polyethylene glycol (PEG) coating reduce both 5 and 30 nm iron oxide nanoparticle cytotoxicity in 2D and 3D cell culture. Int. J. Mol. Sci 2012, 13, 5554–5570. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, H.; Heller, D.A.; Strano, M.S. Single-particle tracking of endocytosis and exocytosis of single-walled carbon nanotubes in NIH-3T3 cells. Nano Lett 2008, 8, 1577–1585. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.X.; Zhang, X.; Li, Q.N.; Li, W.X. Biodistribution of functionalized multi-wall carbon nanotubes in mice. Nucl. Med. Biol 2007, 34, 579–583. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.G.; Zhang, X.D.; Li, Q.N.; Li, W.X. Radioodination of C60 derivative C60(OH)x(O)y. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem 2001, 250, 363–364. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.F.; Wang, J.; Deng, X.Y.; Sun, H.F.; Shi, Z.J.; Gu, Z.N.; Liu, Y.F.; Zhao, Y.L. Biodistribution of carbon single-wall carbon nanotubes in mice. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol 2004, 4, 1019–1024. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Cai, W.B.; He, L.N.; Nakayama, N.; Chen, K.; Sun, X.M.; Chen, X.Y.; Dai, H.J. In vivo biodistribution and highly efficient tumour targeting of carbon nanotubes in mice. Nat. Nanotechnol 2007, 2, 47–52. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, R.; Pantarotto, D.; Lacerda, L.; Pastorin, G.; Klumpp, C.; Prato, M.; Bianco, A.; Kostarelos, L. Tissue biodistribution and blood clearance rates of intravenously administered carbon nanotube radiotracers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 3357–3362. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Li, J.; Zhu, Y.; Qi, Y.J.; Zhu, Z.Y.; Li, W.X.; Huang, Q. Nanographene oxide labeling with 188Re. Nucl. Sci. Tech 2011, 22, 99–104. [Google Scholar]
- Gurr, J.R.; Wang, A.S.; Chen, C.H.; Jan, K.Y. Ultrafine titanium dioxide particles in the absence of photoactivation can induce oxidative damage to human bronchial epithelial cells. Toxicology 2005, 213, 66–73. [Google Scholar]
- Limbach, L.K.; Wick, P.; Manser, P.; Grass, R.N.; Bruinink, A.; Stark, W.J. Exposure of engineered nanoparticles to human lung epithelial cells, influence of chemical composition and catalytic activity on oxidative stress. Environ. Sci. Technol 2007, 41, 4158–4163. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.Y.; Wang, S.Y.; Yang, J.; Gu, X.M.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, Y.F.; Yang, J.; Xu, L.H.; Zhu, X.Q. Multiwall carbon nano-onions induce DNA damage and apoptosis in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Environ. Toxicol 2013, 8, 442–450. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.Y.; Song, W.H.; Guo, J.; Zhang, J.H.; Sun, Z.T.; Li, L.Y.; Ding, F.; Gao, M.L. Cytotoxicity of different sized TiO2 nanoparticles in mouse macrophages. Toxicol. Ind. Health 2013, 29, 523–533. [Google Scholar]
- Circu, M.L.; Aw, T.Y. Reactive oxygen species, cellular redox systems, and apoptosis. Free Radic. Biol. Med 2010, 48, 749–762. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, P.J.; Xu, J.; Liu, S.C.; Yang, Z. Nano copper induced apoptosis in podocytes via increasing oxidative stress. J. Hazard. Mater 2012, 241, 279–286. [Google Scholar]
- Ling, D.; Bae, B.C.; Park, W.; Na, K. Photodynamic efficacy of photosensitizers under an attenuated light dose via lipid nano-carrier-mediated nuclear targeting. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 5478–5486. [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe, M.; Yoneda, M.; Morohashi, A.; Hori, Y.; Okamoto, D.; Sato, A.; Kurioka, D.; Nittami, T.; Hirokawa, Y.; Shiraishi, T.; et al. Effects of Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles on A549 cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci 2013, 14, 15546–15560. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, M.R.; Lightbody, J.H.; Donaldson, K.; Sales, J.; Stone, V. Interactions between ultrafine particles and transition metals in vivo and in vitro. Toxicol. Appl. Pharm. 2002, 184, 172–179. [Google Scholar]
- Card, J.W.; Zeldin, D.C.; Bonner, J.C.; Nestman, E.R. Pulmonary applications and toxicity of engineered nanoparticles. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol 2008, 295, L400–L411. [Google Scholar]
- Stoeger, T.; Reinhard, C.; Takenaka, S.; Schroeppel, A.; Karg, E.; Ritter, B.; Heyder, J.; Schulz, H. Instillation of six different ultrafine carbon particles indicates a surface area threshold dose for acute lung inflammation in mice. Environ. Health Perspect 2006, 114, 328–333. [Google Scholar]
- Stone, V.; Shaw, J.; Brown, D.M.; Macnee, W.; Faux, S.P.; Donaldson, K. The role of oxidative stress in the prolonged inhibitory effect of ultrafine carbon black on epithelial cell function. Toxicol. In Vitro 1998, 12, 649–659. [Google Scholar]
- Gilmour, P.S.; Ziesenis, A.; Morrison, E.R.; Vickers, M.A.; Drost, E.M.; Ford, I.; Karg, E.; Mossa, C.; Schroeppel, A.; Ferron, G.A.; et al. Pulmonary and systemic effects of short-term inhalation exposure to ultrafine carbon black particles. Toxicol. Appl. Pharm 2004, 195, 35–44. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, S.; Boland, S.; Baeza-Squiban, A.; Hamel, R.; Thomassen, L.C.J.; Martens, J.A.; Billon-Galland, M.A.; Fleury-Feith, F.; Moisan, F.; Pairon, J.C.; et al. Oxidative stress and proinflammatory effects of carbon black and titanium dioxide nanoparticles: Role of particle surface area and internalized amount. Toxicology 2009, 260, 142–149. [Google Scholar]
- Rim, K.T.; Kim, S.J.; Han, J.H.; Kang, M.G.; Kim, J.K.; Yang, J.S. Effects of carbon black to inflammation and oxidative DNA damages in mouse macrophages. Mol. Cell. Toxicol 2011, 7, 415–423. [Google Scholar]
- Chithrni, B.D.; Ghazani, A.A.; Chan, W.C.W. Determining the size and shape dependence of gold nanoparticles uptake into mammalian cells. Nano Lett 2006, 6, 662–668. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.W.; Wu, Y.Y.; Jin, S.B.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, X.N.; Zhao, Y.L.; Yu, L.; Liang, X.J. Gold nanoparticles induce autophagosome accumulation through size-dependent nanoparticle uptake and lysosome impairment. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 8629–8639. [Google Scholar]
- Conner, S.D.; Schmid, S.L. Regulated portals of entry into the cell. Nature 2003, 422, 37–44. [Google Scholar]
- Stern, S.T.; Adiseshaiah, P.P.; Crist, R.M. Autophagy and lysosomal dysfunction as emerging mechanisms of nanomaterial toxicity. Part. Fibre Toxicol 2012, 9, 20. [Google Scholar]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Kong, H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Cui, Z.; Xia, K.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Zhu, Y. Size-Dependent Cytotoxicity of Nanocarbon Blacks. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 22529-22543. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms141122529
Kong H, Zhang Y, Li Y, Cui Z, Xia K, Sun Y, Zhao Q, Zhu Y. Size-Dependent Cytotoxicity of Nanocarbon Blacks. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2013; 14(11):22529-22543. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms141122529
Chicago/Turabian StyleKong, Huating, Yu Zhang, Yongjun Li, Zhifen Cui, Kai Xia, Yanhong Sun, Qunfen Zhao, and Ying Zhu. 2013. "Size-Dependent Cytotoxicity of Nanocarbon Blacks" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 14, no. 11: 22529-22543. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms141122529
APA StyleKong, H., Zhang, Y., Li, Y., Cui, Z., Xia, K., Sun, Y., Zhao, Q., & Zhu, Y. (2013). Size-Dependent Cytotoxicity of Nanocarbon Blacks. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 14(11), 22529-22543. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms141122529