Investigation of the Anti-Melanogenic and Antioxidant Characteristics of Eucalyptus camaldulensis Flower Essential Oil and Determination of Its Chemical Composition
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Chemical Compositions of E. camaldulensis Flower Essential Oil
| Consituents | K.I. (a) | K.I. (b) | Concentration (%) | Identification (c) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| α-Thujene | 925 | 930 | 0.6 | MS, K.I., ST |
| α-Pinene | 937 | 939 | 6.1 | MS, K.I., ST |
| β-Pinene | 976 | 979 | 0.3 | MS, K.I., ST |
| β-Myrcene | 989 | 990 | 0.3 | MS, K.I., ST |
| α-Phellandrene | 1002 | 1002 | 0.2 | MS, K.I., ST |
| α-Terpinene | 1015 | 1017 | 0.8 | MS, K.I., ST |
| p-Cymene | 1020 | 1024 | 4.9 | MS, K.I., ST |
| Limonene | 1025 | 1029 | 1.2 | MS, K.I., ST |
| 1,8-Cineole | 1027 | 1031 | 23.9 | MS, K.I., ST |
| cis-β-Ocimene | 1032 | 1037 | 0.1 | MS, K.I. |
| γ-Terpinene | 1055 | 1059 | 12.9 | MS, K.I., ST |
| Terpinolene | 1086 | 1088 | 1.3 | MS, K.I., ST |
| Linalool | 1095 | 1096 | 0.1 | MS, K.I., ST |
| 3-Methyl-3-butenyl 3-methylbutanoate | 1112 | 1114 | 0.5 | MS, K.I. |
| exo-Fenchol | 1120 | 1121 | 0.1 | MS, K.I. |
| 3-Methyl-2-butenyl 2-methylbutanoate | 1138 | 1141 | 0.2 | MS, K.I. |
| δ-Terpineol | 1163 | 1166 | 0.0 | MS, K.I. |
| Borneol | 1167 | 1169 | 0.0 | MS, K.I., ST |
| Terpinen-4-ol | 1175 | 1177 | 5.7 | MS, K.I., ST |
| α-Terpineol | 1187 | 1188 | 3.1 | MS, K.I., ST |
| Nerol | 1228 | 1229 | 0.2 | MS, K.I., ST |
| Methyl geranate | 1323 | 1324 | 0.3 | MS, K.I. |
| β-Elemene | 1389 | 1390 | 0.2 | MS, K.I., ST |
| ( Z)-Jasmone | 1392 | 1392 | 0.6 | MS, K.I. |
| α-Gurjunene | 1409 | 1409 | 0.1 | MS, K.I. |
| β-Caryophyllene | 1418 | 1419 | 0.9 | MS, K.I., ST |
| Aromadendrene | 1439 | 1441 | 0.1 | MS, K.I., ST |
| trans-Muurola-3,5-diene | 1452 | 1452 | 0.2 | MS, K.I. |
| α-Humulene | 1454 | 1454 | 0.2 | MS, K.I., ST |
| allo-Aromadendrene | 1458 | 1460 | 0.1 | MS, K.I. |
| cis-Cadina-1(6),4-diene | 1462 | 1463 | 0.3 | MS, K.I. |
| Viridiflorene | 1496 | 1496 | 0.5 | MS, K.I. |
| α-Muurolene | 1500 | 1500 | 0.3 | MS, K.I. |
| γ-Cadinene | 1512 | 1513 | 0.2 | MS, K.I. |
| δ-Cadinene | 1522 | 1523 | 0.6 | MS, K.I. |
| cis-Calamenene | 1528 | 1529 | 0.4 | MS, K.I. |
| trans-Cadina-1,4-diene | 1533 | 1534 | 0.2 | MS, K.I. |
| Elemol | 1549 | 1549 | 5.0 | MS, K.I., ST |
| epi-Globulol | 1555 | 1556 | 0.1 | MS, K.I. |
| Palustrol | 1567 | 1568 | 0.2 | MS, K.I. |
| Spathulenol | 1577 | 1578 | 0.2 | MS, K.I., ST |
| Caryophyllene oxide | 1582 | 1583 | 0.2 | MS, K.I., ST |
| Globulol | 1590 | 1590 | 1.0 | MS, K.I., ST |
| Guaiol | 1600 | 1600 | 0.7 | MS, K.I. |
| cis-Isolongifolanone | 1612 | 1613 | 0.5 | MS, K.I. |
| 1,10-di- epi-Cubenol | 1618 | 1619 | 0.2 | MS, K.I. |
| iso-Leptospermone | 1622 | 1622 | 0.2 | MS, K.I. |
| 10- epi-γ-Eudesmol | 1622 | 1623 | 0.5 | MS, K.I. |
| 1- epi-Cubenol | 1628 | 1628 | 0.3 | MS, K.I. |
| γ-Eudesmol | 1630 | 1630 | 8.0 | MS, K.I. |
| τ-Cadinol | 1640 | 1640 | 2.6 | MS, K.I. |
| α-Muurolol | 1645 | 1646 | 0.4 | MS, K.I. |
| α-Eudesmol | 1652 | 1653 | 11.6 | MS, K.I. |
| (2 z,6z)-Farnesol | 1698 | 1698 | 0.1 | MS, K.I. |
| Monoterpene hydrocarbons (%) | 29.0 | |||
| Oxygenated monoterpenes (%) | 34.9 | |||
| Sesquiterpene hydrocarbons (%) | 4.3 | |||
| Oxygenated sesquiterpenes (%) | 31.8 | |||
| Oil Yield (mL/100 g) | 2.68 ± 0.02 | |||
2.2. Cell Viability

2.3. Inhibitory Effects of E. camaldulensis Flower Essential Oil on Melanin Production

2.4. E. camaldulensis Flower Essential Oil Inhibited the Expression Levels of Melanogenesis-Related Proteins

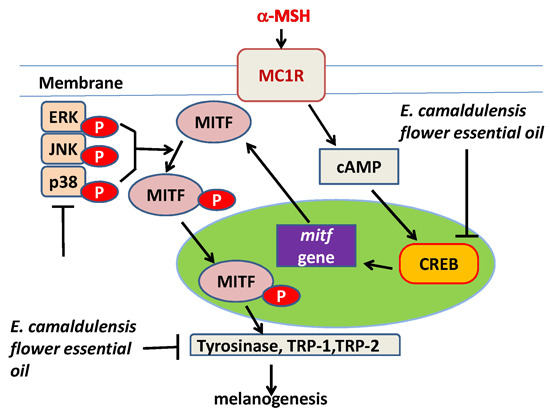
2.5. E. camaldulensis Flower Essential Oil Down-Regulated MAPK and PKA Signaling Pathways


2.6. Antioxidant Characteristics of E. camaldulensis Flower Essential Oil

3. Experimental Section
3.1. Chemicals and Reagents
3.2. Plant Materials and Extraction of Essential Oils
3.3. Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC/MS) Analysis of Essential Oil
3.4. Assay of Mushroom Tyrosinase Activity
3.5. Cell Culture and Cell Viability Assay
3.6. Measurement of Intracellular Melanin Content
3.7. Assay of Intracellular Tyrosinase Activity
3.8. Western Blotting Assay
3.9. Protein Kinase Regulators Assay
3.10. DPPH Scavenging Activity Assay
3.11. ABTS+ Scavenging Capacity Assay
3.12. Determination of Cellular ROS Level
3.13. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions

Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Panich, U.; Tangsupa-A-Nan, V.; Onkoksoong, T.; Kongtaphan, K.; Kasetsinsombat, K.; Akarasereenont, P.; Wongkajornsilp, A. Inhibition of UVA-mediated melanogenesis by ascorbic acid through modulation of antioxidant defense and nitric oxide system. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2011, 34, 811–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slominski, A.; Zmijewski, M.A.; Pawelek, J. l-Tyrosine and l-dihydroxyphenylalanine as hormone-like regulators of melanocyte functions. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2012, 25, 14–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briganti, S.; Camera, E.; Picardo, M. Chemical and instrumental approaches to treat hyperpigmentation. Pigment Cell Res. 2003, 16, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, A.; Fulton, J.E., Jr. The combination of glycolic acid and hydroquinone or kojic acid for the treatment of melasma and related conditions. Dermatol. Surg. 1996, 22, 443–447. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Virador, V.M.; Kobayashi, N.; Matsunaga, J.; Hearing, V.J. A standardized protocol for assessing regulators of pigmentation. Anal. Biochem. 1999, 270, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, R.; Bhalla, M.; Kanwar, A.J. A comparative study of 20% azelaic acid cream monotherapy vs. a sequential therapy in the treatment of melasma in dark-skinned patients. Dermatology. 2002, 205, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rendon, M.I.; Gaviria, J.I. Review of skin-lightening agents. Dermatol. Surg. 2005, 31, 886–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Gavín, J.; González-Vilas, D.; Fernández-Redondo, V.; Toribio, J. Pigmented contact dermatitis due to kojic acid. A paradoxical side effect of a skin lightener. Contact Dermat. 2010, 62, 63–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.L.; Liu, R.H.; Sheu, J.N.; Chen, S.T.; Sinchaikul, S.; Tsay, G.J. Toxicogenomics of A375 human malignant melanoma cells treated with arbutin. J. Biomed. Sci. 2007, 14, 87–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balina, L.M.; Graupe, K. The treatment of melasma: 20% Azelaic acid vs. 4% hydroquinone cream. Int. J. Dermatol. 1991, 30, 893–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halliwell, B. Free radicals, antioxidants, and human disease: Curiosity, cause, or consequence? Lancet 1994, 344, 721–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finkel, T.; Holbrook, N.J. Oxidants, oxidative stress and the biology of ageing. Nature 2000, 408, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wlaschek, M.; Briviba, K.; Stricklin, G.P.; Sies, H.; Scharffetter-Kochanek, K. Singlet oxygen may mediate the ultraviolet A-induced synthesis of interstitial collagenase. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1995, 104, 194–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sárdy, M. Role of matrix metalloproteinases in skin ageing. Connect. Tissue Res. 2009, 50, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Büyükokuroǧlu, M.E.; Gülçin, I.; Oktay, M.; Küfrevioǧlu, Ö.I. In vitro antioxidant properties of dantrolene sodium. Pharmacol. Res. 2001, 44, 491–494. [Google Scholar]
- Shahidul Alam, M.; Quader, M.A.; Rashid, M.A. HIV-inhibitory diterpenoid from Anisomeles indica. Fitoterapia 2000, 71, 574–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gülçin, I.; Oktay, M.; Küfrevioǧlu, Ö.I.; Aslan, A. Determination of antioxidant activity of lichen Cetraria islandica (L) Ach. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2002, 79, 325–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, C.H.; Liu, P.J.; Lin, K.P.; Chen, P.C. Nutritional supplement therapy improves oxidative stress, immune response, pulmonary function, and quality of life in allergic asthma patients: An open-label pilot study. Altern. Med. Rev. 2012, 17, 42–56. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dinis, T.C.P.; Madeira, V.M.C.; Almeida, L.M. Action of phenolic derivatives (acetaminophen, salicylate, and 5-aminosalicylate) as inhibitors of membrane lipid peroxidation and as peroxyl radical scavengers. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1994, 315, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roméro-Graillet, C.; Aberdam, E.; Clément, M.; Ortonne, J.P.; Ballotti, R. Nitric oxide produced by ultraviolet-irradiated keratinocytes stimulates melanogenesis. J. Clin. Investig. 1997, 99, 635–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, M.; Horikoshi, T.; Uchiwa, H.; Miyachi, Y. Up-regulation of tyrosinase gene by nitric oxide human melanocytes. Pigment Cell Res. 2000, 13, 248–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, A.K.; Funasaka, Y.; Slominski, A.; Ermak, G.; Hwang, J.; Pawelek, J.M.; Ichihashi, M. Production and release of proopiomelanocortin (POMC) derived peptides by human melanocytes and keratinocytes in culture: Regulation by ultraviolet B. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Mol. Cell Res. 1996, 1313, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasui, H.; Sakurai, H. Age-dependent generation of reactive oxygen species in the skin of live hairless rats exposed to UVA light. Exp. Dermatol. 2003, 12, 655–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Funasaka, Y.; Komoto, M.; Ichihashi, M. Depigmenting effect of α-tocopheryl ferulate on normal human melanocytes. Pigment Cell Res. 2000, 13, 170–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ormancey, X.; Sisalli, S.; Coutiere, P. Formulation of essential oils in functional perfumery. Parfums Cosmet. Actual. 2001, 157, 30–40. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.C.; Wang, H.F.; Yih, K.H.; Chang, L.Z.; Chang, T.M. Dual bioactivities of essential oil extracted from the leaves of Artemisia argyi as an antimelanogenic vs. antioxidant agent and chemical composition analysis by GC/MS. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 14679–14697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.C.; Chang, T.Y.; Chang, L.Z.; Wang, H.F.; Yih, K.H.; Hsieh, W.Y.; Chang, T.M. Inhibition of melanogenesis versus antioxidant properties of essential oil extracted from leaves of vitex negundo linn and chemical composition analysis by GC-MS. Molecules 2012, 17, 3902–3916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.C.; Wang, H.F.; Yih, K.H.; Chang, L.Z.; Chang, T.M. The dual antimelanogenic and antioxidant activities of the essential oil extracted from the leaves of Acorus macrospadiceus (Yamamoto) F. N. Wei et Y. K. Li. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 2012, 781280. [Google Scholar]
- Woolf, A. Essential oil poisoning. J. Toxicol.-Clin. Toxicol. 1999, 37, 721–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomson, K.F.; Wilkinson, S.M. Allergic contact dermatitis to plant extracts in patients with cosmetic dermatitis. Br. J. Dermatol. 2000, 142, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghisalberti, E.L. Bioactive acylphloroglucinol derivatives from Eucalyptus species. Phytochemistry 1996, 41, 7–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, A.Y.; Foster, S. Encyclopedia of Common Natural Ingredients Used in Food, Drugs, and Cosmetics, 2nd ed.; John Willey & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Cimanga, K.; Kambu, K.; Tona, L.; Apers, S.; de Bruyne, T.; Hermans, N.; Totté, J.; Pieters, L.; Vlietinck, A.J. Correlation between chemical composition and antibacterial activity of essential oils of some aromatic medicinal plants growing in the Democratic Republic of Congo. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2002, 79, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, J.; Abebe, W.; Sousa, S.M.; Duarte, V.G.; Machado, M.I.L.; Matos, F.J.A. Analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects of essential oils of Eucalyptus. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2003, 89, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siramon, P.; Ohtani, Y.; Ichiura, H. Biological performance of Eucalyptus camaldulensis leaf oils from Thailand against the subterranean termite Coptotermes formosanus Shiraki. J. Wood Sci. 2009, 55, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.S.; Huang, C.G.; Chen, Y.J.; Yu, J.J.; Chen, W.J.; Chang, S.T. Chemical compositions and larvicidal activities of leaf essential oils from two Eucalyptus species. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 452–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, K.; Shono, Y.; Kakimizu, A.; Okada, A.; Matsuo, N.; Satoh, A.; Nishimura, H. New mosquito repellent from Eucalyptus camaldulensis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1993, 41, 2164–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siramon, P.; Ohtani, Y. Antioxidative and antiradical activities of Eucalyptus camaldulensis leaf oils from Thailand. J. Wood Sci. 2007, 53, 498–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francisco, J.D.C.; Järvenpää, E.P.; Huopalahti, R.; Sivik, B. Comparison of Eucalyptus camaldulensis Dehn. oils from Mozambique as obtained by hydrodistillation and supercritical carbon dioxide extraction. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 2339–2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciftci, O.; Ozdemir, I.; Tanyildizi, S.; Yildiz, S.; Oguzturk, H. Antioxidative effects of curcumin, β-myrcene and 1,8-cineole against 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin-induced oxidative stress in rats liver. Toxicol. Ind. Health 2011, 27, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fadel, H.; Marx, F.; el-Sawy, A.; el-Ghorab, A. Effect of extraction techniques on the chemical composition and antioxidant activity of Eucalyptus camaldulensis var. brevirostris leaf oils. Zeitschrift fur Lebensmittel -Untersuchung und -Forschung 1999, 208, 212–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, A.I.; Anwar, F.; Chatha, S.A.S.; Jabbar, A.; Mahboob, S.; Nigam, P.S. Rosmarinus officinalis essential oil: Antiproliferative, antioxidant and antibacterial activities. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2010, 41, 1070–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abad, M.J.; Bedoya, L.M.; Apaza, L.; Bermejo, P. The Artemisia L. genus: A review of bioactive essential oils. Molecules 2012, 17, 2542–2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buscà, R.; Ballotti, R. Cyclic AMP a key messenger in the regulation of skin pigmentation. Pigment Cell Res. 2000, 13, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Malek, Z.; Swope, V.; Collins, C.; Boissy, R.; Zhao, H.; Nordlund, J. Contribution of melanogenic proteins to the heterogeneous pigmentation of human melanocytes. J. Cell Sci. 1993, 106, 1323–1331. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kameyama, K.; Sakai, C.; Kuge, S.; Nishiyama, S.; Tomita, Y.; Ito, S.; Wakamatsu, K.; Hearing, V.J. The expression of tyrosinase, tyrosinase-related proteins 1 and 2 (TRP1 and TRP2), the silver protein, and a melanogenic inhibitor in human melanoma cells of differing melanogenic activities. Pigment Cell Res./Spons. Eur. Soc. Pigment Cell Res. Int. Pigment Cell Soc. 1995, 8, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, C.; Khaled, M.; Fisher, D.E. MITF: Master regulator of melanocyte development and melanoma oncogene. Trends Mol. Med. 2006, 12, 406–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirobe, T. Basic fibroblast growth factor stimulates the sustained proliferation of mouse epidermal melanoblasts in a serum-free medium in the presence of dibutyryl cyclic AMP and keratinocytes. Development 1992, 114, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Galibert, M.D.; Carreira, S.; Goding, C.R. The Usf-1 transcription factor is a novel target for the stress-responsive p38 kinase and mediates UV-induced Tyrosinase expression. EMBO J. 2001, 20, 5022–5031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.K.; Sarkar, C.; Mallick, S.; Saha, B.; Bera, R.; Bhadra, R. Human placental lipid induces melanogenesis through p38 MAPK in B16F10 mouse melanoma. Pigment Cell Res. 2005, 18, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oyaizu, M. Studies on products of browing reaction: Antioxidative activity of product of browing reaction preapared from glucosamine. Jpn. J. Nutr. 1986, 44, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Haley, S.; Perret, J.; Harris, M.; Wilson, J.; Qian, M. Free radical scavenging properties of wheat extracts. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 1619–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emerit, I. Free radicals and aging of the skin. In Free Radicals and Aging; Birkhäuser: Basel, Switzerland, 1992; pp. 328–341. [Google Scholar]
- Adama, R.P. Identification of Essential Oil Components by Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectroscopy; Allured Publishing Co.: Carol Stream, IL, USA, 1995; pp. 57–322. [Google Scholar]
- Van den Dool, H.; Dec. Kratz, P. A generalization of the retention index system including linear temperature programmed gas—Liquid partition chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 1963, 11, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilodeau, M.L.; Greulich, J.D.; Hullinger, R.L.; Bertolotto, C.; Ballotti, R.; Andrisani, O.M. BMP-2 stimulates tyrosinase gene expression and melanogenesis in differentiated melanocytes. Pigment Cell Res. 2001, 14, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tada, H.; Shiho, O.; Kuroshima, K.-I.; Koyama, M.; Tsukamoto, K. An improved colorimetric assay for interleukin 2. J. Immunol. Methods 1986, 93, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuboi, T.; Kondoh, H.; Hiratsuka, J.; Mishima, Y. Enhanced melanogenesis induced by tyrosinase gene-transfer increases boron-uptake and killing effect of boron neutron capture therapy for amelanotic melanoma. Pigment Cell Res. 1998, 11, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.Y.; Koo, J.H.; Song, Y.G.; Kwon, K.B.; Lee, J.H.; Sohn, H.S.; Park, B.H.; Jhee, E.C.; Park, J.W. Stimulation of melanogenesis by scoparone in B16 melanoma cells. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2006, 27, 1467–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brand-Williams, W.; Cuvelier, M.E.; Berset, C. Use of a free radical method to evaluate antioxidant activity. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 1995, 28, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Re, R.; Pellegrini, N.; Proteggente, A.; Pannala, A.; Yang, M.; Rice-Evans, C. Antioxidant activity applying an improved ABTS radical cation decolorization assay. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1999, 26, 1231–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murrant, C.L.; Reid, M.B. Detection of reactive oxygen and reactive nitrogen species in skeletal muscle. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2001, 55, 236–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, H.-C.; Ho, Y.-C.; Lim, J.-M.; Chang, T.-Y.; Ho, C.-L.; Chang, T.-M. Investigation of the Anti-Melanogenic and Antioxidant Characteristics of Eucalyptus camaldulensis Flower Essential Oil and Determination of Its Chemical Composition. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 10470-10490. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160510470
Huang H-C, Ho Y-C, Lim J-M, Chang T-Y, Ho C-L, Chang T-M. Investigation of the Anti-Melanogenic and Antioxidant Characteristics of Eucalyptus camaldulensis Flower Essential Oil and Determination of Its Chemical Composition. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2015; 16(5):10470-10490. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160510470
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Huey-Chun, Ya-Chi Ho, Jia-Min Lim, Tzu-Yun Chang, Chen-Lung Ho, and Tsong-Min Chang. 2015. "Investigation of the Anti-Melanogenic and Antioxidant Characteristics of Eucalyptus camaldulensis Flower Essential Oil and Determination of Its Chemical Composition" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 16, no. 5: 10470-10490. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160510470
APA StyleHuang, H. -C., Ho, Y. -C., Lim, J. -M., Chang, T. -Y., Ho, C. -L., & Chang, T. -M. (2015). Investigation of the Anti-Melanogenic and Antioxidant Characteristics of Eucalyptus camaldulensis Flower Essential Oil and Determination of Its Chemical Composition. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 16(5), 10470-10490. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160510470