In Vivo Molecular MRI Imaging of Prostate Cancer by Targeting PSMA with Polypeptide-Labeled Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Characterization of Polypeptide-SPIONs

2.2. In Vitro MRI of Polypeptide-SPIONs

2.3. In Vitro Binding Assay
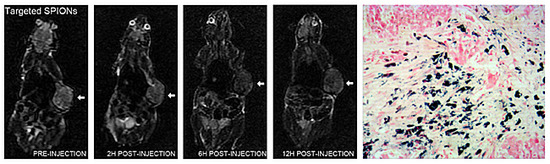
2.4. In Vivo MRI



| Post Injection Time | LNCaP + Polypeptide-SPIONs (Fe3O4 0.240 mg/mL) | LNCaP + Polypeptide-SPIONs (Fe3O4 0.120 mg/mL) | LNCaP + Polypeptide-SPIONs (Fe3O4 0.060 mg/mL) | LNCaP + Polypeptide-SPIONs (Fe3O4 0.030 mg/mL) | LNCaP + Non-Targeted SPIONs (Fe3O4 0.240 mg/mL) | PC3 + Polypeptide-SPIONs (Fe3O4 0.240 mg/mL) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 h | 19.9 ± 3.4 * | 15.7 ± 2.7 * | 11.8 ± 1.6 | 11.3 ± 1.4 | 9.5 ± 2.0 | 8.7 ± 2.2 | 0.000 |
| 6 h | 34.3 ± 3.6 * | 31.1 ± 2.7 * | 23.5 ± 1.4 * | 19.6 ± 0.9 * | 11.9 ± 3.9 | 11.1 ± 3.1 | 0.000 |
| 12 h | 30.9 ± 1.4 * | 30.0 ± 1.4 * | 22.8 ± 1.8 * | 18.5 ± 1.5 * | 12.0 ± 2.0 | 10.4 ± 2.6 | 0.000 |
| p-Value | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.304 | 0.179 |
2.5. Histologic Analysis
| Histologic Results | Fe3O4 0.240 mg/mL | Fe3O4 0.120 mg/mL | Fe3O4 0.060 mg/mL | Fe3O4 0.030 mg/mL | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prussian blue labeling density | 11.2 ± 2.1 | 9.7 ± 1.4 | 8.0 ± 1.3 | 6.9 ± 1.0 | 0.002 |

2.6. Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Preparation of Polypeptide-PLGA
3.3. Preparation of Polypeptide-SPIONs
3.4. Characterization of Polypeptide-SPIONs
3.5. In Vitro MRI of Polypeptide-SPIONs
3.6. Cell Lines
3.7. In Vitro Binding Assay
3.8. Animal Model
3.9. In Vivo MRI Study
3.10. In Vivo MRI Image Analysis
3.11. Histological Analysis
3.12. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Abbreviations
| PSMA | prostate specific membrane antigen |
| PCa | prostate cancer |
| MRI | magnetic resonance imaging |
| SPIONs | superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles |
| PVA | Poly (vinyl alcohol) was used as stabilizing agent |
| PLGA | poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) was used for the preparation of SPIONs |
| NHS | N-Hydroxysuccinimide was used as condensation agent |
| EDC | N-Hydroxysuccinimide; N-(3-Dimethylaminopropyl)-N'-ethylcarbodiimide hydrochloride was used as condensation agent |
| VSM | vibrating sample magnetometer was used for the characterization of the magnetization property of SPIONs |
| PBS | phosphate-buffered saline |
| RSE | relative signal enhancement was used for quantitative evaluation of negative contrast of MRI images following SPIONs injection |
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.; Ma, J.; Zou, Z.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2014, 64, 9–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ukimura, O.; Faber, K.; Gill, I.S. Intraprostatic targeting. Curr. Opin. Urol. 2012, 22, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turkbey, B.; Albert, P.S.; Kurdziel, K.; Choyke, P.L. Imaging localized prostate cancer: Current approaches and new developments. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2009, 192, 1471–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Nunzio, C.; Kramer, G.; Marberger, M.; Montironi, R.; Nelson, W.; Schroder, F.; Sciarra, A.; Tubaro, A. The controversial relationship between benign prostatic hyperplasia and prostate cancer: The role of inflammation. Eur. Urol. 2010, 60, 106–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blomqvist, L.; Carlsson, S.; Gjertsson, P.; Heintz, E.; Hultcrantz, M.; Mejare, I.; Andren, O. Limited evidence for the use of imaging to detect prostate cancer: A systematic review. Eur. J. Radiol. 2014, 83, 1601–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tilki, D.; Seitz, M.; Singer, B.B.; Irmak, S.; Stief, C.G.; Reich, O.; Ergun, S. Molecular imaging of tumor blood vessels in prostate cancer. Anticancer Res. 2009, 29, 1823–1829. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, A.; Heston, W.D. Tumor target prostate specific membrane antigen (PSMA) and its regulation in prostate cancer. J. Cell. Biochem. 2004, 91, 528–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmittgen, T.D.; Teske, S.; Vessella, R.L.; True, L.D.; Zakrajsek, B.A. Expression of prostate specific membrane antigen and three alternatively spliced variants of PSMA in prostate cancer patients. Int. J. Cancer 2003, 107, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajasekaran, S.A.; Anilkumar, G.; Oshima, E.; Bowie, J.U.; Liu, H.; Heston, W.; Bander, N.H.; Rajasekaran, A.K. A novel cytoplasmic tail MXXXL motif mediates the internalization of prostate-specific membrane antigen. Mol. Biol. Cell 2003, 14, 4835–4845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, F.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wei, G.; Yang, A.; Zhang, R.; Huan, Y.; Cui, Y.; et al. MRI of prostate stem cell antigen expression in prostate tumors. Nanomedicine 2012, 7, 691–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Cuschieri, A. Tumour cell labelling by magnetic nanoparticles with determination of intracellular iron content and spatial distribution of the intracellular iron. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 9111–9125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Taylor, R.M.; Huber, D.L.; Monson, T.C.; Ali, A.M.; Bisoffi, M.; Sillerud, L.O. Multifunctional iron platinum stealth immunomicelles: Targeted detection of human prostate cancer cells using both fluorescence and magnetic resonance imaging. J. Nanopart. Res. 2011, 13, 4717–4729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, T.; Josephson, L. Current state and future applications of active targeting in malignancies using superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. Cancer Biomark. 2009, 5, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bates, D.; Abraham, S.; Campbell, M.; Zehbe, I.; Curiel, L. Development and characterization of an antibody-labeled super-paramagnetic iron oxide contrast agent targeting prostate cancer cells for magnetic resonance imaging. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e97220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdolahi, M.; Shahbazi-Gahrouei, D.; Laurent, S.; Sermeus, C.; Firozian, F.; Allen, B.J.; Boutry, S.; Muller, R.N. Synthesis and in vitro evaluation of MR molecular imaging probes using J591 mAb-conjugated SPIONs for specific detection of prostate cancer. Contrast Media Mol. Imaging 2013, 8, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasten, B.B.; Liu, T.; Nedrow-Byers, J.R.; Benny, P.D.; Berkman, C.E. Targeting prostate cancer cells with PSMA inhibitor-guided gold nanoparticles. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 565–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tagawa, S.T.; Beltran, H.; Vallabhajosula, S.; Goldsmith, S.J.; Osborne, J.; Matulich, D.; Petrillo, K.; Parmar, S.; Nanus, D.M.; Bander, N.H. Anti-prostate-specific membrane antigen-based radioimmunotherapy for prostate cancer. Cancer 2010, 116, 1075–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frigerio, B.; Fracasso, G.; Luison, E.; Cingarlini, S.; Mortarino, M.; Coliva, A.; Seregni, E.; Bombardieri, E.; Zuccolotto, G.; Rosato, A.; et al. A single-chain fragment against prostate specific membrane antigen as a tool to build theranostic reagents for prostate cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 2013, 49, 2223–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Yu, G.; Lindner, D.; Brady-Kalnay, S.M.; Zhang, Q.; Lu, Z.R. Peptide targeted high-resolution molecular imaging of prostate cancer with MRI. Am. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2014, 4, 525–536. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tan, M.; Burden-Gulley, S.M.; Li, W.; Wu, X.; Lindner, D.; Brady-Kalnay, S.M.; Gulani, V.; Lu, Z.R. MR molecular imaging of prostate cancer with a peptide-targeted contrast agent in a mouse orthotopic prostate cancer model. Pharm. Res. 2012, 29, 953–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lupold, S.E.; Rodriguez, R. Disulfide-constrained peptides that bind to the extracellular portion of the prostate-specific membrane antigen. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2004, 3, 597–603. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tse, B.W.; Cowin, G.J.; Soekmadji, C.; Jovanovic, L.; Vasireddy, R.S.; Ling, M.T.; Khatri, A.; Liu, T.; Thierry, B.; Russell, P.J. PSMA-targeting iron oxide magnetic nanoparticles enhance MRI of preclinical prostate cancer. Nanomedicine 2014, 19, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Ittrich, H.; Peldschus, K.; Raabe, N.; Kaul, M.; Adam, G. Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles in biomedicine: Applications and developments in diagnostics and therapy. Rofo 2013, 185, 1149–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Kaminski, M.D.; Chen, H.; Torno, M.; Taylor, L.; Rosengart, A.J. Synthesis and characterization of highly-magnetic biodegradable poly(d,l-lactide-co-glycolide) nanospheres. J. Control. Release 2007, 119, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, M.K.; Kim, D.; Lee, I.H.; So, J.S.; Jeong, Y.Y.; Jon, S. Image-guided prostate cancer therapy using aptamer-functionalized thermally cross-linked superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. Small 2011, 7, 2241–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, W.; Jiang, J.; Guan, W.; Zhang, Z.; Duan, Y. In Vivo Molecular MRI Imaging of Prostate Cancer by Targeting PSMA with Polypeptide-Labeled Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 9573-9587. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms16059573
Zhu Y, Sun Y, Chen Y, Liu W, Jiang J, Guan W, Zhang Z, Duan Y. In Vivo Molecular MRI Imaging of Prostate Cancer by Targeting PSMA with Polypeptide-Labeled Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2015; 16(5):9573-9587. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms16059573
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Yunkai, Ying Sun, Yaqing Chen, Weiyong Liu, Jun Jiang, Wenbin Guan, Zhongyang Zhang, and Yourong Duan. 2015. "In Vivo Molecular MRI Imaging of Prostate Cancer by Targeting PSMA with Polypeptide-Labeled Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 16, no. 5: 9573-9587. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms16059573
APA StyleZhu, Y., Sun, Y., Chen, Y., Liu, W., Jiang, J., Guan, W., Zhang, Z., & Duan, Y. (2015). In Vivo Molecular MRI Imaging of Prostate Cancer by Targeting PSMA with Polypeptide-Labeled Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 16(5), 9573-9587. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms16059573