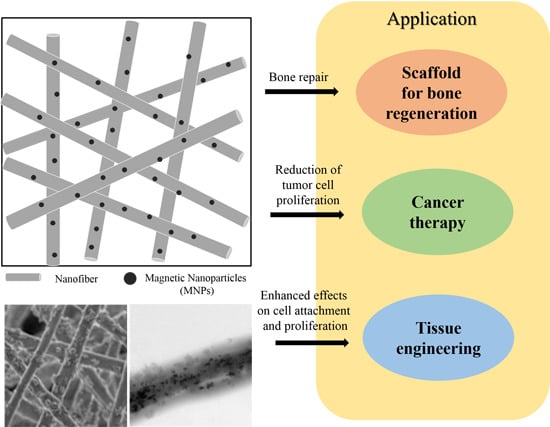
Biomedical Applications of Magnetically Functionalized Organic/Inorganic Hybrid Nanofibers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Nanofibers
1.2. Hybrid Nanofiber System
| Hybrid Nanofiber | Precursor and Polymer/Dopant | Potential Application | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| CO3O4 | 1. Cobalt acetate; 2. PVA/ H2O | Biomarker | [16] |
| Fe3O4 | 1. Iron (II) chloride; 2. Graft copolymer, poly(ethylene oxide) (PEO) or PVA | Drug carrier | [19] |
| CeO2 | 1. Cerium nitrate; 2. PVA/H2O | Catalyst | [27] |
| SiO2 | 1. Tetraethylorthosilicate; 2. HCl | Drug carrier | [28] |
| Ca10(PO4)6(OH, F)2 | 1. Ca(NO3)2; 2. P(C2H5O)3 | Artificial bone | [29] |
| Ta2O5 | 1. Tantalum isopropyl oxide; 2. PVAC/DMF (or acetic acid) | Implant | [30] |

2. Methods to Prepare MNPs (Magnetic Nanoparticles)
2.1. Precipitation
2.2. Reverse Micelle Formation
2.3. Thermal Decomposition
2.4. Liquid Phase Reduction
3. Preparation of MNP-Functionalized Nanofibers

4. Biomedical Applications of MNP-Functionalized Nanofibers
| Source of Nanofiber | Kind of MNPs | Technology | Application | In Vitro and in Vivo | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chitosan / poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA) | Fe3O4 | ES | Bone regeneration | MG63 human osteoblast–like cells | [83] |
| Hydroxyapatite (HA) nanoparticles and poly(lactic acid) (PLA) | Super-paramagnetic Fe2O3 nanoparticles | ES | Bone tissue formation and remodeling in rabbit defects | White rabbit model of lumbar transverse defects | [32] |
| Poly(ε-caprolactone) (PCL) | MNPs | ES | Bone regeneration | Osteoblastic cells and subcutaneously implanted in rats | [73] |
| Hydroxyapatite (HA) | MNPs | Immersion of MNPs into HA scaffold | Bone repair | ROS 17/2.8 and MC3T3-E1 cells | [84] |
| Magnetic poly(l-lactic acid) (PLLA) | Fe3O4 | ES | Enhanced effects on cell attachment and proliferation | MC3T3-E1 | [85] |
| Poly(d,l-lactic acid) (PDLLA) | Superpara-magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs) | ES | Cell proliferation and induction of the cell orientation | Osteoblast cells | [86] |
| Chitosan | E-CHS-Fe3O4 | ES | Hyperthermia treatment of tumor cells | HFL1 and caco-2 cells | [87] |
| Cross-linked chitosan | Fe3O4 | ES by iminodiacetic acid (IDA) | Reduction of tumor cell proliferation | Tumor cells | [88] |
| Polystyrene (PS) and poly(styrene-co-maleic anhydride) (PSMA) | Magnetic NP-nanofibers (NF) | ES with surface-embedded T cell receptor ligand | Isolation and activation of primary CD3+ T lymphocytes | Lymph nodes harvested from C57BL/6 mice | [89] |
| Porous hydroxyapatite composite | Up-conversion of luminescent and MNPs | ES | Indomethacin, T1 magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) contrast agents, and luminescent nanoparticles | MC 3T3-E1 cells | [90] |
| Hydroxyapatite nanocrystals within PCL | Doped with gadolinium (Gd) | ES | In situ monitoring of bone tissue regeneration by MR | Human mesenchymal stem cells | [91] |
| Amphiphilic peptide | Macrocyclic Gd (III) | β-sheet amino acid sequence | MRI | Tibialis anterior muscle of a murine model | [92] |
4.1. Scaffold for Bone Regeneration

4.2. Cancer Therapy
4.3. Tissue Engineering
5. Conclusions and Future Prospects
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- MacDiarmid, A.G.; Jones, W.E.; Norris, I.D.; Gao, J.; Johnson, A.T.; Pinto, N.J.; Hone, J.; Han, B.; Ko, F.K.; Okuzaki, H.; et al. Electrostatically-generated nanofibers of electronic polymers. Synth. Met. 2001, 119, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, C.; Hsiao, B.S.; Chu, B. Nanofibrous materials and their applications. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 2006, 36, 333–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doshi, J.; Reneker, D.H. Electrospinning process and applications of electrospun fibers. J. Electrost. 1995, 35, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frenot, A.; Chronakis, I.S. Polymer nanofibers assembled by electrospinning. Curr. Opin. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2003, 8, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Nagapudi, K.; Apkarian, R.P.; Chaikof, E.L. Engineered collagen-PEO nanofibers and fabrics. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2001, 12, 979–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, W.; Yong, T.; Teo, W.E.; Ma, Z.W.; Ramakrishna, S. Fabrication and endothelialization of collagen-blended biodegradable polymer nanofibers: Potential vascular graft for blood vessel tissue engineering. Tissue Eng. 2005, 11, 1574–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subbiah, T.; Bhat, G.; Tock, R.; Parameswaran, S.; Ramkumar, S. Electrospinning of nanofibers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2005, 96, 557–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Zhang, N.; Nichols, H.L.; Shi, D.; Wen, X. Modification of nanostructured materials for biomedical applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2007, 27, 579–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Reneker, D.H. Mechanical properties of composites using ultrafine electrospun fibers. Polym. Compos. 1999, 20, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Z.; Lim, C.T.; Ramakrishna, S.; Huang, Z.M. Recent development of polymer nanofibers for biomedical and biotechnological applications. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2005, 16, 933–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Babel, A.; Jenekhe, S.A.; Xia, Y.N. Nanofibers of conjugated polymers prepared by electrospinning with a two-capillary spinneret. Adv. Mater. 2004, 16, 2062–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.M.; Liu, D.S.; Shuang, S.M.; Choi, M.M.F. A homocysteine biosensor with eggshell membrane as an enzyme immobilization platform. Sens. Actuators B 2006, 114, 936–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.M.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Kotaki, M.; Ramakrishna, S. A review on polymer nanofibers by electrospinning and their applications in nanocomposites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2003, 63, 2223–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Zhang, G.; Min, J.Z.; Ding, J.Q.; Jiang, X.M. Synthesis and antibacterial testing of silver/poly (ether amide) composite nanofibers with ultralow silver content. J. Nanomater. 2014, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, M.; Singh, D.; Saraf, S.; Saraf, S. Lipid carriers: A versatile delivery vehicle for proteins and peptides. Yakugaku Zasshi 2008, 128, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahoo, S.K.; Diinawaz, F.; Krishnakumar, S. Nanotechnology in ocular drug delivery. Drug Discov. Today 2008, 13, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandamme, T.F. Microemulsions as ocular drug delivery systems: Recent developments and future challenges. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2002, 21, 15–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaysinsky, S.; Davidson, P.M.; Bruce, B.D.; Weiss, J. Stability and antimicrobial efficiency of eugenol encapsulated in surfactant micelles as affected by temperature and ph. J. Food Prot. 2005, 68, 1359–1366. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gaysinsky, S.; Davidson, P.M.; McClements, D.J.; Weiss, J. Formulation and characterization of phytophenol-carrying antimicrobial microemulsions. Food Biophys. 2008, 3, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaysinsky, S.; Taylor, T.M.; Davidson, P.M.; Bruce, B.D.; Weiss, J. Antimicrobial efficacy of eugenol microemulsions in milk against Listeria monocytogenes and Escherichia coli O157: H7. J. Food Prot. 2007, 70, 2631–2637. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, X.; Yuan, X.Y. Synthesis of poly(ethylene glycol)-b-poly (l-lactic acid) diblock copolymers and formation of their electrospun fibers. Acta Polym. Sin. 2008, 405–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellenberger, C.R.; Luechinger, N.A.; Stark, W.J. Porous Polymer Membranes. U.S. Patent US 13/943,058, 14 Novemeber 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Nirmala, R.; Kalpana, D.; Navamathavan, R.; Lee, Y.S.; Kim, H.Y. Preparation and characterizations of silver incorporated polyurethane composite nanofibers via electrospinning for biomedical applications. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2013, 13, 4686–4693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demir, M.M.; Gulgun, M.A.; Menceloglu, Y.Z.; Erman, B.; Abramchuk, S.S.; Makhaeva, E.E.; Khokhlov, A.R.; Matveeva, V.G.; Sulman, M.G. Palladium nanoparticles by electrospinning from poly(acrylonitrile-co-acrylic acid)-PdCl2 solutions. Relations between preparation conditions, particle size, and catalytic activity. Macromolecules 2004, 37, 1787–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.Z.; Li, Y.X.; Sun, G.; Zhang, G.L.; Liu, H.; Du, J.S.; Yang, S.A.; Bai, J.; Yang, Q.B. Fabrication of Au/PVP by electrospinning nanofiber composites by electrospinning. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2007, 105, 3618–3622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Wang, Y.; Xia, Y.N. Electrospining of polymeric and cermic nanofibers as uniaxially aligned arrays. Nano Lett. 2003, 3, 1167–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Shao, C.; Liu, Y.; Mu, R.; Guan, H. Nanofibers of CeO2 via an electrospinning technique. Thin Solid Films 2005, 478, 228–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.I.; Ko, E.K.; Yum, J.; Jung, C.H.; Lee, Y.M.; Shin, H. Nanofibrous poly(lactic acid)/hydroxyapatite composite scaffolds for guided tissue regeneration. Macromol. Biosci. 2008, 8, 328–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Cushing, B.L.; O’Connor, C.J. Synthesis and characterization of monodisperse ultra-thin silica-coated magnetic nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 2008, 19, 085601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, A.; Patra, M.K.; Mathew, M.; Songara, S.; Singh, V.K.; Gowd, G.S.; Vadera, S.R.; Kumar, N. Preparation and characterization of biocompatible and water-dispersible superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs). Adv. Sci. Lett. 2010, 3, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Lu, B.; Zhao, Y.; Jiang, X. Fabrication of aligned fibrous arrays by magnetic electrospinning. Adv. Mater. 2007, 19, 3702–3706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Xiao, B.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Xue, H.D.; Lei, J.; Kong, H.; Huang, Y.G.; Jin, Z.Y.; Gu, N.; et al. Super-paramagnetic responsive nanofibrous scaffolds under static magnetic field enhance osteogenesis for bone repair in vivo. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takenaka, S.; Ishida, M.; Serizawa, M.; Tanabe, E.; Otsuka, K. Formation of carbon nanofibers and carbon nanotubes through methane decomposition over supported cobalt catalysts. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 11464–11472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Fan, M.; Brown, R.C.; van Leeuwen, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, W.; Song, Y.; Zhang, P. Synthesis, properties, and environmental applications of nanoscale iron-based materials: A review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 36, 405–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, A.H.; Salabas, E.L.; Schüth, F. Magnetic nanoparticles: Synthesis, protection, functionalization, and application. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 1222–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corot, C.; Robert, P.; Idee, J.M.; Port, M. Recent advances in iron oxide nanocrystal technology for medical imaging. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2006, 58, 1471–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basti, H.; Tahar, L.B.; Smiri, L.S.; Herbst, F.; Vaulay, M.J.; Chau, F.; Ammar, S.; Benderbous, S. Catechol derivatives-coated Fe3O4 and γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticles as potential MRI contrast agents. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 341, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laurent, S.; Forge, D.; Port, M.; Roch, A.; Robic, C.; Elst, L.V.; Muller, R.N. Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: Synthesis, stabilization, vectorization, physicochemical characterizations, and biological applications. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 2064–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennard, R.; DeSisto, W.J.; Giririjan, T.P.; Mason, M.D. Intrinsic property measurement of surfactant-templated mesoporous silica films using time-resolved single-molecule imaging. J. Chem. Phys. 2008, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellusci, M.; La Barbera, A.; Seralessandri, L.; Padella, F.; Piozzi, A.; Varsano, F. Preparation of albumin-ferrite superparamagnetic nanoparticles using reverse micelles. Polym. Int. 2009, 58, 1142–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, E.L.; Itri, R.; Lima, E.; Baptista, M.S.; Berquo, T.S.; Goya, G.F. Large magnetic anisotropy in ferrihydrite nanoparticles synthesized from reverse micelles. Nanotechnology 2006, 17, 5549–5555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seip, C.T.; Carpenter, E.E.; O’Connor, C.J.; John, V.T.; Li, S.C. Magnetic properties of a series of ferrite nanoparticles synthesized in reverse micelles. Magn. IEEE Trans. 1998, 34, 1111–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, C.J.; Seip, C.T.; Carpenter, E.E.; Li, S.C.; John, V.T. Synthesis and reactivity of nanophase ferrites in reverse micellar solutions. Nanostruct. Mater. 1999, 12, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewandowska-Lancucka, J.; Staszewska, M.; Szuwarzynski, M.; Kepczynski, M.; Romek, M.; Tokarz, W.; Szpak, A.; Kania, G.; Nowakowska, M. Synthesis and characterization of the superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles modified with cationic chitosan and coated with silica shell. J. Alloy. Compd. 2014, 586, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.M.; Li, L.; Leung, C.W.; Lai, P.T.; Pong, P.W.T. Synthesis and characterization of silica-encapsulated iron oxide nanoparticles. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2014, 50, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sadjadi, M.S.; Fathi, F.; Farhadyar, N.; Zare, K. Synthesize and characterization of multifunctional silica coated magnetic nanoparticles using polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) as a mediator. J. Nano Res. 2011, 16, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohapatra, S.; Pal, D.; Ghosh, S.K.; Pramanik, P. Design of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticle for purification of recombinant proteins. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2007, 7, 3193–3199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santra, S.; Tapec, R.; Theodoropoulou, N.; Dobson, J.; Hebard, A.; Tan, W.H. Synthesis and characterization of silica-coated iron oxide nanoparticles in microemulsion: The effect of nonionic surfactants. Langmuir 2001, 17, 2900–2906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namdeo, M.; Saxena, S.; Tankhiwale, R.; Bajpai, M.; Mohan, Y.M.; Bajpai, S.K. Magnetic nanoparticles for drug delivery applications. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2008, 8, 3247–3271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McBain, S.C.; Yiu, H.H.P.; Dobson, J. Magnetic nanoparticles for gene and drug delivery. Int. J. Nanomed. 2008, 3, 169–180. [Google Scholar]
- Arruebo, M.; Fernandez-Pacheco, R.; Ibarra, M.R.; Santamaria, J. Magnetic nanoparticles for drug delivery. Nano Today 2007, 2, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.D.; Shin, D.M.; Simons, J.W.; Nie, S.M. Nanotechnology for targeted cancer therapy. Expert Rev. Anticancer Therapy 2007, 7, 833–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, S.M.; Xing, Y.; Kim, G.J.; Simons, J.W. Nanotechnology applications in cancer. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2007, 9, 257–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scherer, F.; Anton, M.; Schillinger, U.; Henkel, J.; Bergemann, C.; Kruger, A.; Gansbacher, B.; Plank, C. Magnetofection: Enhancing and targeting gene delivery by magnetic force in vitro and in vivo. Gene Ther. 2002, 9, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, M.M.; Kim, H.-H.; Kim, H.; Muhammed, M.; Kim, D.K. Iron oxide-based nanomagnets in nanomedicine: Fabrication and applications. Nano Rev. 2010, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.H.; Li, Y.J.; Li, Y.L. Architecture of low dimensional nanostructures based on conjugated polymers. Polym. Chem. 2013, 4, 5162–5180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Gao, J.H.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, X.X.; Xu, B. Colloidosome-based synthesis of a multifunctional nanostructure of silver and hollow iron oxide nanoparticles. Langmuir 2010, 26, 4184–4187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senthil, M.; Ramesh, C. Biogenic synthesis of Fe3O4 nanoparticles using tridax procumbens leaf extract and its antibacterial activity on pseudomonas aeruginosa. Dig. J. Nanomater. Biostruct. 2012, 7, 1655–1660. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, S.Y.; Shi, Y.G.; Zhang, S.X.; Jiang, K.; Yang, S.X.; Li, Z.D.; Takayama-Muromachi, E. Biopolymer-assisted green synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles and their magnetic properties. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 10398–10401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Bakar, M.; Tan, W.L.; Abu Bakar, N.H.H. A simple synthesis of size-reduce magnetite nano-crystals via aqueous to toluene phase-transfer method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2007, 314, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, W.; Wright, E.; Mottelay, P.F. William Gilbert of Colchester, Physician of London, on the Loadstone and Magnetic Bodies and on the Great Magnet the Earth. A New Physiology, Demonstrated with Many Arguments and Experiments; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1893; p. 368. [Google Scholar]
- Anton, F. Process and Apparatus for Preparing Artificial Threads. U.S. Patent US1975504 A, 2 October 1934. [Google Scholar]
- Anton, F. Method and Apparatus for Spinning. U.S. Patent US2349950 A, 30 May 1944. [Google Scholar]
- Tucker, N.; Stanger, J.J.; Staiger, M.P.; Razzaq, H.; Hofman, K. The history of the science and technology of electrospinning from 1600 to 1995. J. Eng. Fabr. Fibers 2012, 7, 63–73. [Google Scholar]
- Larsen, G.; Velarde-Ortiz, R.; Minchow, K.; Barrero, A.; Loscertales, I.G. A method for making inorganic and hybrid (organic/inorganic) fibers and vesicles with diameters in the submicrometer and micrometer range via sol-gel chemistry and electrically forced liquid jets. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 1154–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, C.P.; Sell, S.A.; Boland, E.D.; Simpson, D.G.; Bowlin, G.L. Nanofiber technology: Designing the next generation of tissue engineering scaffolds. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2007, 59, 1413–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasita, R.; Katti, D.S. Nanofibers and their applications in tissue engineering. Int. J. Nanomed. 2006, 1, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraf, A.; Lozier, G.; Haesslein, A.; Kasper, F.K.; Raphael, R.M.; Baggett, L.S.; Mikos, A.G. Fabrication of nonwoven coaxial fiber meshes by electrospinning. Tissue Eng. Part C 2009, 15, 333–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.Z.; Wang, X.; Feng, Y.; Li, J.; Lim, C.T.; Ramakrishna, S. Coaxial electrospinning of (fluorescein isothiocyanate-conjugated bovine serum albumin)-encapsulated poly(epsilon-caprolactone) nanofibers for sustained release. Biomacromolecules 2006, 7, 1049–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.M.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Ramakrishna, S.; Lim, C.T. Electrospinning and mechanical characterization of gelatin nanofibers. Polymer 2004, 45, 5361–5368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.I.; Krebs, M.D.; Bonino, C.A.; Samorezov, J.E.; Khan, S.A.; Alsberg, E. Electrospun chitosan–alginate nanofibers with in situ polyelectrolyte complexation for use as tissue engineering scaffolds. Tissue Eng. Part A 2010, 17, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luong-Van, E.; Grøndahl, L.; Chua, K.N.; Leong, K.W.; Nurcombe, V.; Cool, S.M. Controlled release of heparin from poly(ε-caprolactone) electrospun fibers. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 2042–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.K.; Patel, K.D.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, E.J.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, T.H.; Kim, H.W. Potential of magnetic nanofiber scaffolds with mechanical and biological properties applicable for bone regeneration. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e91584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selvakumar, M.; Jaganathan, S.K.; Nando, G.B.; Chattopadhyay, S. Synthesis and characterization of novel polycarbonate based polyurethane/polymer wrapped hydroxyapatite nanocomposites: Mechanical properties, osteoconductivity and biocompatibility. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2015, 11, 291–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.H.; Liao, H.C.; Hsu, S.H.; Chen, R.S.; Wu, M.C.; Yang, Y.F.; Wu, C.C.; Chen, M.H.; Su, W.F. A novel polyurethane/cellulose fibrous scaffold for cardiac tissue engineering. Rsc. Adv. 2015, 5, 6932–6939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.K.; Aguilar, L.E.; Kim, D.K.; Lee, K.M.; Park, C.H.; Kim, C.S. Development of polyurethane/non-woven fabric composite as a protective device for filtering ultrafine particles in air and absorption of CO2. Dig. J. Nanomater. Biostruct. 2014, 9, 1547–1553. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, H.J.; Kim, S.B.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, M.H. Preparation of electrospun polyurethane filter media and their collection mechanisms for ultrafine particles. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2014, 64, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Zheng, W.; Huang, H.-M.; Li, Z.-Y.; Zhang, H.-N.; Wang, W.; Wang, C. Decoration of electrospun nanofibers with magnetic nanoparticles via electrospinning and sol-gel process. Chem. Res. Chin. Univ. 2010, 26, 847–850. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.-R.; Tsai, T.-C.; Chung, M.; Lu, S.-Z. Synthesis and characterization of magnetic nanoparticles embedded in polyvinyl pyrrolidone nanofiber film by electrospinning method. J. Appl. Phys. 2009, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaer, M.; Crittin, M.; Kasmi, L.; Pierzchala, K.; Calderone, C.; Digigow, R.G.; Fink, A.; Forró, L.; Sienkiewicz, A. Multi-functional magnetic photoluminescent photocatalytic polystyrene-based micro-and nano-fibers obtained by electrospinning. Fibers 2014, 2, 75–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexiou, C.; Arnold, W.; Klein, R.J.; Parak, F.G.; Hulin, P.; Bergemann, C.; Erhardt, W.; Wagenpfeil, S.; Lubbe, A.S. Locoregional cancer treatment with magnetic drug targeting. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 6641–6648. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ahn, B.W.; Kang, T.J. Preparation and characterization of magnetic nanofibers with iron oxide nanoparticles and poly(ethylene terephthalate). J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 125, 1567–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Zhang, X.; Song, Y.; Han, B.; Hu, X.; Wang, X.; Lin, Y.; Deng, X. Magnetic biodegradable Fe3O4/CS/PVA nanofibrous membranes for bone regeneration. Biomed. Mater. 2011, 6, 055008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, X.B.; Hu, H.; Xie, L.Q.; Lan, F.; Jiang, W.; Wu, Y.; Gu, Z.W. Magnetic responsive hydroxyapatite composite scaffolds construction for bone defect reparation. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 3365–3378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, D.; Shi, Y.; Duan, S.; Wei, Y.; Cai, Q.; Yang, X. Electrospun magnetic poly(l-lactide) (PLLA) nanofibers by incorporating PLLA-stabilized Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2013, 33, 3498–3505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Yang, G.; Li, J.; Ding, S.; Zhou, S. Cell behaviors on magnetic electrospun poly-d,l-lactide nanofibers. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2014, 34, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, T.C.; Lin, F.H.; Lin, J.C. In vitro feasibility study of the use of a magnetic electrospun chitosan nanofiber composite for hyperthermia treatment of tumor cells. Acta Biomater. 2012, 8, 2704–2711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, T.C.; Lin, F.H.; Lin, J.C. In vitro characterization of magnetic electrospun ida-grafted chitosan nanofiber composite for hyperthermic tumor cell treatment. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2013, 24, 1152–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.; An, H.J.; Jun, S.H.; Kim, T.J.; Lim, S.A.; Park, G.; Na, H.B.; Park, Y.I.; Hyeon, T.; Yee, C.; et al. Single step isolation and activation of primary CD3+ T lymphocytes using alcohol-dispersed electrospun magnetic nanofibers. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 4018–4024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Liu, H.; Sun, S.; Li, X.; Zhou, Y.; Hou, Z.; Lin, J. Multifunctional hydroxyapatite/Na(Y/Gd)F4:Yb3+, Er3+ composite fibers for drug delivery and dual modal imaging. Langmuir 2014, 30, 1176–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganesh, N.; Ashokan, A.; Rajeshkannan, R.; Chennazhi, K.; Koyakutty, M.; Nair, S.V. Magnetic resonance functional nano-hydroxyapatite incorporated poly(caprolactone) composite scaffolds for in situ monitoring of bone tissue regeneration by MRI. Tissue Eng. Part A 2014, 20, 2783–2794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preslar, A.T.; Parigi, G.; McClendon, M.T.; Sefick, S.S.; Moyer, T.J.; Haney, C.R.; Waters, E.A.; MacRenaris, K.W.; Luchinat, C.; Stupp, S.I.; et al. Gd(III)-labeled peptide nanofibers for reporting on biomaterial localization in vivo. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 7325–7332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasoju, N.; Bora, U. Silk fibroin in tissue engineering. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2012, 1, 393–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bueno, E.M.; Glowacki, J. Cell-free and cell-based approaches for bone regeneration. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2009, 5, 685–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gloria, A.; de Santis, R.; Ambrosio, L. Polymer-based composite scaffolds for tissue engineering. J. Appl. Biomater. Biomech. 2010, 8, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, H.-J.; Lee, S.J.; Uthaman, S.; Thomas, R.G.; Hyun, H.; Jeong, Y.Y.; Cho, C.-S.; Park, I.-K. Biomedical Applications of Magnetically Functionalized Organic/Inorganic Hybrid Nanofibers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 13661-13677. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160613661
Lee H-J, Lee SJ, Uthaman S, Thomas RG, Hyun H, Jeong YY, Cho C-S, Park I-K. Biomedical Applications of Magnetically Functionalized Organic/Inorganic Hybrid Nanofibers. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2015; 16(6):13661-13677. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160613661
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Hwa-Jeong, Sang Joon Lee, Saji Uthaman, Reju George Thomas, Hoon Hyun, Yong Yeon Jeong, Chong-Su Cho, and In-Kyu Park. 2015. "Biomedical Applications of Magnetically Functionalized Organic/Inorganic Hybrid Nanofibers" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 16, no. 6: 13661-13677. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160613661
APA StyleLee, H. -J., Lee, S. J., Uthaman, S., Thomas, R. G., Hyun, H., Jeong, Y. Y., Cho, C. -S., & Park, I. -K. (2015). Biomedical Applications of Magnetically Functionalized Organic/Inorganic Hybrid Nanofibers. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 16(6), 13661-13677. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160613661