Molecularly Imprinted Composite Membranes for Selective Detection of 2-Deoxyadenosine in Urine Samples
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Preparation of Molecularly Imprinted Membranes
2.2. Characterization of the Membranes



2.3. Adsorption Kinetic

2.4. Binding Capacities of the MIMs



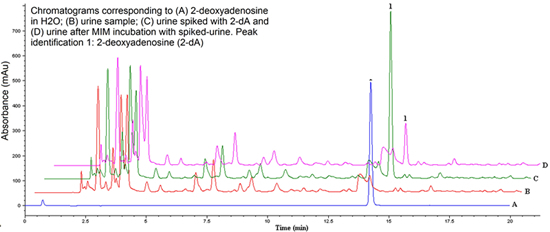
2.5. Urine Sample Analysis

3. Experimental Section
3.1. Reagents and Apparatus
3.2. Preparation of Molecularly Imprinted Membrane
3.3. Kinetic Adsorption Test
3.4. Binding Experiments of 2-dA on Membranes
3.5. Extraction of 2-dA from Spiked Human Urine
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rios, G.M.; Belleville, M.P.; Paolucci-Jeanjean, D. Membrane engineering in biotechnology: Quo vamos? Trends Biotechnol. 2007, 25, 242–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Gayakwad, A.; Das Nagale, B. A review: Nanomembrane and application. Int. J. Innov. Res. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2014, 3, 8373–8381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pendergast, M.-T.M.; Hoek, E.M.V. A review of water treatment membrane nanotechnology. Energy Environ. Sci. 2011, 4, 1946–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pabby, A.K.; Rizvi, S.S.H.; Sastre, A.M. Handbook of Membrane Separations: Chemical, Pharmaceutical, Food, and Biotechnological Applications, 2nd ed.; Taylor and Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015; pp. 3–825. [Google Scholar]
- Baker, R.W. Membrane Technology and Applications, 2nd ed.; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 2004; p. 287. [Google Scholar]
- Trotta, F.; Biasizzo, M.; Caldera, F. Molecularly imprinted membranes. Membranes 2012, 2, 440–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Algieri, C.; Drioli, E.; Guzzo, L.; Donato, L. Bio-mimetic sensors based on molecularly imprinted membranes. Sensors 2014, 14, 13863–13912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wulff, G. Enzyme-like catalysis by molecularly imprinted polymers. Chem. Rev. 2002, 102, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasapollo, G.; del Sole, R.; Mergola, L.; Lazzoi, M.R.; Scardino, A.; Scorrano, S.; Mele, G. Molecularly imprinted polymers: Presente and future prospective. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 112, 5908–5945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piletsky, S.A.; Piletskaya, E.V.; Panasyuk, T.L.; El’skaya, A.V.; Levi, R.; Karube, I.; Wulff, G. Imprinted membranes for sensor technology: Opposite behaviour of covalently and noncovalently imprinted membranes. Macromolecules 1998, 31, 2137–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.N.; Kane, R.; Goto, M.; Belfort, G. Discriminate surface molecular recognition sites on a microporous substrate: A new approach. Macromolecules 2003, 36, 4472–4477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piletsky, S.A.; Panasyuk, T.L.; Piletskaya, E.V.; Nichols, I.A.; Ulbricht, M. Receptor and transport properties of imprinted membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 1999, 157, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kielczynski, R.; Bryjak, M. Molecularly imprinted membranes for chinchona alkaloids separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2005, 41, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.J.; Xu, Z.L.; Feng, J.L.; Bing, N.C.; Yang, Z.G. Molecularly imprinted membranes for the recognition of lovastatin acid in aqueous medium by a template analogue imprinting strategy. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 313, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piletsky, S.A.; Dubei, I.Y.; Fedroyak, D.M.; Kukhar, V.P. Substrate-selective polymeric membranes. Selective transfer of nucleic acid components. Biopolym. Kletka 1990, 6, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew-Krotz, J.; Shea, K.J. Imprinted polymer membranes for the selective transport of targeted neutral molecules. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1996, 118, 8154–8155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sergeyeva, T.A.; Piletsky, S.A.; Piletska, E.V.; Brovko, O.O.; Karabanova, L.V.; Sergeyeva, L.M.; El'skaya, A.V.; Turner, A.P.F. In situ formation of porous molecularly imprinted polymer membranes. Macromolecules 2003, 36, 7352–7357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.Y.; Kobayashi, T.; Fujii, N. Surface molecular imprinting on photosensitive dithiocarbamoyl polyacrylonitrile membranes using photograft polymerization. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 1997, 70, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzgoev, A.; Haupt, K. Molecularly imprinted polymer membranes for chiral separation. Chirality 1999, 11, 465–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, M.; Izumi, J.; Kitao, T.; Sakamoto, S. Molecularly imprinted polymeric membranes containing DIDE derivatives for optical resolution of amino-acids. Macromolecules 1996, 29, 8197–8203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, T.; Wang, H.Y.; Fuji, N. Molecular imprint membranes of polyacrylonitrile copolymers with different acrylic acid segments. Anal. Chim. Acta 1998, 365, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvestri, D.; Borrelli, C.; Giusti, P.; Cristallini, C.; Ciardelli, G. Polymeric devices containing imprinted nanospheres: A novel approach to improve recognition in water for clinical uses. Anal. Chim. Acta 2005, 542, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, M.; Brunner, H.; Tovar, G.E.M. Selective separations and hydrodynamic studies: A new approach using molecularly imprinted nanosphere composite membranes. Desalination 2002, 149, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scorrano, S.; Longo, L.; Vasapollo, G. Molecularly imprinted polymer for solid-phase extraction of 1-methyladenosine from human urine. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 659, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mergola, L.; Scorrano, S.; del Sole, R.; Lazzoi, M.R.; Vasapollo, G. Developments in the synthesis of a water compatible molecularly imprinted polymer as artificial receptor for detection of 3-nitro-l-tyrosine in neurological diseases. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 40, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limbach, P.A.; Crain, P.F.; McCloskey, J.A. Summary: The modified nucleosides of RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994, 22, 2183–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schram, K.H. Urinary nucleosides. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 1998, 17, 131–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, G.A.; Goodenough-Lashua, D.M. Mechanisms of RNA-modifying and -editing enzymes. In Modification and Editing of RNA; Grosjean, H., Benne, R., Eds.; American Society for Microbiology: Washington, DC, USA, 1998; pp. 135–168. [Google Scholar]
- Seidel, A.; Brunner, S.; Seidel, P.; Fritz, G.I.; Herbarth, O. Modified nucleosides: An accurate tumour marker for clinical diagnosis of cancer, early detection and therapy control. Br. J. Cancer 2006, 94, 1726–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walters, D.L.; Jacobs, D.L.; Tomaszewski, J.E.; Graves, S. Analysis of various nucleosides in plasma using solid phase extraction and high-performance liquid chromatography with UV detection. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 1999, 19, 955–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymańska, E.; Markuszewski, M.J.; Bodzioch, K.; Kaliszan, R. Development and validation of urinary nucleosides and creatinine assay by capillary electrophoresis with solid-phase extraction. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2007, 44, 1118–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrofoglio, L.A.; Bezy, V.; Chaimbault, P.; Delépée, R.; Rhourri, B.; Morin, P. Mass spectrometry based methods for analysis of nucleosides as antiviral drugs and potential tumor biomarkers. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids 2007, 26, 1523–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Ambrosio, S.M.; Gibson-D’Ambrosio, R.E.; Trewyn, R.W. An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for the detection and quantitation of the tumor marker 1-methylinosine in human urine. Clin. Chim. Acta 1991, 199, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishiwata, S.; Itoh, K.; Yamaguchi, T.; Ishida, N.; Mizugaki, M. Comparison of serum and urinary levels of modified nucleoside, 1-methyladenosine, in cancer patients using a monoclonal antibody-based inhibition ELISA. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 1995, 176, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.-Y.; Xu, Z.-L.; Wu, P.; Yin, S.-J. Binding constant and transport property of S-naproxen molecularly imprinted composite membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 331, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bing, N.-C.; Xu, Z.-L.; Wang, X.-J.; Yang, Z.-G.; Yang, H. Recognition properties of poly(vinylidene fluoride) Hollow-Fiber membranes modified by Levofloxacin-imprinted polymers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2007, 106, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulbricht, M. Membrane separations using molecularly imprinted polymers. J. Chromatogr. B 2004, 804, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smuleac, V.; Bachas, L.; Bhattacharyy, D. Aqueous-phase synthesis of PAA in PVDF membrane pores for nanoparticle synthesis and dichlorobiphenyl degradation. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 346, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steuck, M.J. Porous Membrane Having Hydrophilic Surface and Process. US Patent 4618533, 21 October 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Asman, Z.; Yusof, N.A.; Abdullah, A.H.; Haron, M.J. Synthesis and characterization of Hybrid molecularly imprinted polymer (MIP) membranes for removal of methylene blue (MB). Molecules 2012, 17, 1916–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yusof, N.A.; Zakaria, N.D.; Maamor, N.A.M.; Abdullah, N.A.M.; Abdullah, A.H.; Haron, M.J. Synthesis and characterization of molecularly imprinted polymer membrane for the removal of 2,4-dinitrophenol. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 3993–4004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Scorrano, S.; Mergola, L.; Di Bello, M.P.; Lazzoi, M.R.; Vasapollo, G.; Del Sole, R. Molecularly Imprinted Composite Membranes for Selective Detection of 2-Deoxyadenosine in Urine Samples. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 13746-13759. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160613746
Scorrano S, Mergola L, Di Bello MP, Lazzoi MR, Vasapollo G, Del Sole R. Molecularly Imprinted Composite Membranes for Selective Detection of 2-Deoxyadenosine in Urine Samples. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2015; 16(6):13746-13759. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160613746
Chicago/Turabian StyleScorrano, Sonia, Lucia Mergola, Maria Pia Di Bello, Maria Rosaria Lazzoi, Giuseppe Vasapollo, and Roberta Del Sole. 2015. "Molecularly Imprinted Composite Membranes for Selective Detection of 2-Deoxyadenosine in Urine Samples" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 16, no. 6: 13746-13759. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160613746
APA StyleScorrano, S., Mergola, L., Di Bello, M. P., Lazzoi, M. R., Vasapollo, G., & Del Sole, R. (2015). Molecularly Imprinted Composite Membranes for Selective Detection of 2-Deoxyadenosine in Urine Samples. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 16(6), 13746-13759. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160613746