Pharmacogenomics of Methotrexate Membrane Transport Pathway: Can Clinical Response to Methotrexate in Rheumatoid Arthritis Be Predicted?
Abstract
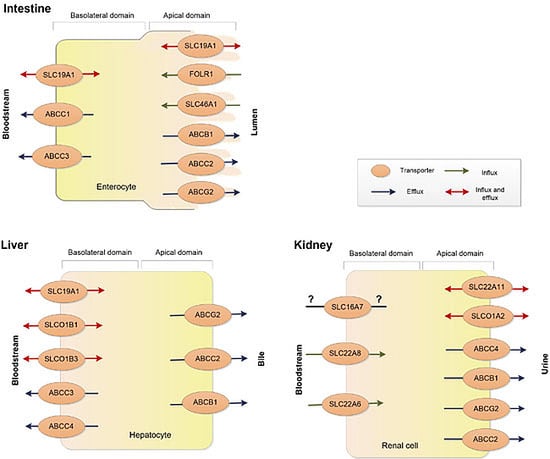
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Studied Population
2.2. Genotypes and Haplotypes Characteristics
2.3. Genotype Approach and Clinical Response to Methotrexate (MTX)
2.4. Haplotype Approach and Clinical Response to MTX
| SLCs | Alleles | Response | Non-Response | p | OR (95% CI) | ABCs | Alleles | Response | Non-Response | p | OR (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SLC16A7 A>T (rs3763980) | A carriers | 96 (45.5) | 115 (54.5) | 0.061 | Reference | ABCB1 C>T (rs1045642) | C carriers | 79 (45.9) | 93 (54.1) | 0.255 | Reference |
| TT | 9 (40.9) | 13 (59.1) | 0.26 (0.06–1.06) | TT | 26 (42.6) | 35 (57.4) | 1.88 (0.63–5.55) | ||||
| AA | 53 (44.5) | 66 (55.5) | 0.890 | Reference | CC | 29 (46.0) | 34 (54.0) | 0.622 | Reference | ||
| T carriers | 52 (45.6) | 62 (54.4) | 0.94 (0.38–2.32) | T carriers | 76 (44.7) | 94 (55.3) | 1.29 (0.47–3.50) | ||||
| SLC16A7 T>G (rs10877333) | T carriers | 104 (45.4) | 125 (54.6) | 0.999 | Reference | ABCB1 C>T (rs1128503) | C carriers | 81 (44.0) | 103 (56.0) | 0.496 | Reference |
| GG | 1 (25.0) | 3 (75.0) | 1.00 (0.00–0.00) | TT | 24 (49.0) | 25 (51.0) | 1.56 (0.43–5.57) | ||||
| TT | 72 (44.7) | 89 (55.3) | 0.738 | Reference | CC | 35 (45.5) | 42 (54.5) | 0.244 | Reference | ||
| G carriers | 33 (45.8) | 39 (54.2) | 1.19 (0.43–3.33) | T carriers | 70 (44.9) | 86 (55.1) | 1.80 (0.67–4.87) | ||||
| SLC19A1 G>A (rs7499) | G carriers | 94 (48.2) | 101 (51.8) | 0.851 | Reference | ABCB1 G>A/T (rs2032582) | G carriers | 80 (44.4) | 100 (55.6) | 0.706 | Reference |
| AA | 11 (28.9) | 27 (71.1) | 1.14 (0.28–4.58) | TT | 23 (48.9) | 24 (51.1) | 1.27 (0.36–4.47) | ||||
| GG | 47 (51.6) | 44 (48.4) | 0.613 | Reference | GG | 36 (44.4) | 45 (55.6) | 0.349 | Reference | ||
| A carriers | 58 (40.8) | 84 (59.2) | 1.28 (0.49-3.30) | T carriers | 67 (45.9) | 79 (54.1) | 1.62 (0.59–4.44) | ||||
| SLC19A1 G>A (rs1051266) | G carriers | 80 (46.8) | 91 (53.2) | 0.924 | Reference | ABCC1 T>C (rs35592) | T carriers | 95 (45.2) | 115 (54.8) | 0.630 | Reference |
| AA | 25 (40.3) | 37 (59.7) | 1.05 (0.36–3.09) | CC | 10 (43.5) | 13 (56.5) | 1.47 (0.31–7.09) | ||||
| GG | 37 (46.2) | 43 (53.8) | 0.672 | Reference | TT | 56 (45.2) | 68 (54.8) | 0.130 | Reference | ||
| A carriers | 68 (44.4) | 85 (55.6) | 1.23 (0.47–3.18) | C carriers | 49 (45.0) | 60 (55.0) | 2.12 (0.80–5.58) | ||||
| SLC19A1 A>G (rs2838956) | A carriers | 91 (47.6) | 100 (52.4) | 0.512 | Reference | ABCC1 A>G (rs246240) | A carriers | 102 (45.3) | 123 (54.7) | 0.846 | Reference |
| GG | 14 (33.3) | 28 (66.7) | 1.61 (0.39–6.66) | GG | 3 (37.5) | 5 (62.5) | 0.76 (0.05–11.46) | ||||
| AA | 39 (47.6) | 43 (52.4) | 0.813 | Reference | AA | 73 (45.9) | 86 (54.1) | 0.008 * | Reference | ||
| G carriers | 66 (43.7) | 85 (56.3) | 0.89 (0.33–2.39) | G carriers | 32 (43.2) | 42 (56.8) | 5.47 (1.56–19.25) | ||||
| SLC19A1 G>A (rs3788200) | G carriers | 90 (47.1) | 101 (52.9) | 0.504 | Reference | ABCC1 G>C (rs2074087) | G carriers | 101 (45.5) | 121 (54.5) | 0.419 | Reference |
| AA | 15 (35.7) | 27 (64.3) | 1.62 (0.39–6.68) | CC | 4 (36.4) | 7 (63.6) | 0.42 (0.05–3.42) | ||||
| GG | 41 (50.0) | 41 (50.0) | 0.285 | Reference | GG | 62 (42.5) | 84 (57.5) | 0.104 | Reference | ||
| A carriers | 64 (42.4) | 87 (57.6) | 1.69 (0.65–4.42) | C carriers | 43 (49.4) | 44 (50.6) | 0.46 (0.18–1.18) | ||||
| SLC22A11 T>A (rs11231809) | T carriers | 86 (43.0) | 114 (57.0) | 0.031 * | Reference | ABCC1 G>A (rs3784864) | G carriers | 76 (42.7) | 102 (57.3) | 0.015 * | Reference |
| AA | 19 (57.6) | 14 (42.4) | 0.19 (0.04–0.86) (a) | AA | 29 (52.7) | 26 (47.3) | 0.24 (0.07–0.76) (b) | ||||
| TT | 29 (36.2) | 51 (63.8) | 0.116 | Reference | GG | 31 (46.3) | 36 (53.7) | 0.402 | Reference | ||
| A carriers | 76 (49.7) | 77 (50.3) | 0.44 (0.16–1.22) | A carriers | 74 (44.6) | 92 (55.4) | 0.64 (0.23–1.80) | ||||
| SLC46A1 G>A (rs2239907) | G carriers | 89 (47.8) | 97 (52.2) | 0.429 | Reference | ABCC2 G>A (rs717620) | G carriers | 102 (45.1) | 124 (54.9) | 0.486 | Reference |
| AA | 16 (34.0) | 31 (66.0) | 1.61 (0.49–5.28) | AA | 3 (42.9) | 4 (57.1) | 0.30 (0.01–8.89) | ||||
| GG | 42 (48.3) | 45 (51.7) | 0.986 | Reference | GG | 59 (43.7) | 76 (56.3) | 0.576 | Reference | ||
| A carriers | 63 (43.2) | 83 (56.8) | 1.01 (0.39–2.61) | A carriers | 46 (46.9) | 52 (53.1) | 0.77 (0.31–1.91) | ||||
| SLCO1B1 T>C (rs4149056) | T carriers | 86 (46.5) | 99 (53.5) | 0.812 | Reference | ABCC2 C>T (rs4148396) | C carriers | 81 (44.0) | 103 (56.0) | 0.677 | Reference |
| CC | 19 (39.6) | 29 (60.4) | 0.87 (0.28–2.69) | TT | 24 (49.0) | 25 (51.0) | 0.78 (0.25–2.45) | ||||
| TT | 82 (48.5) | 87 (51.5) | 0.935 | Reference | CC | 29 (38.7) | 46 (61.3) | 0.265 | Reference | ||
| C carriers | 23 (35.9) | 41 (64.1) | 1.05 (0.36–3.07) | T carriers | 76 (48.1) | 82 (51.9) | 0.55 (0.20-1.56) | ||||
| ABCG2 T>C (rs13120400) | T carriers | 95 (44.8) | 117 (55.2) | 0.188 | Reference | ||||||
| CC | 10 (47.6) | 11 (52.4) | 0.36 (0.08–1.65) | ||||||||
| TT | 52 (44.8) | 64 (55.2) | 0.226 | Reference | |||||||
| C carriers | 53 (45.3) | 64 (54.7) | 1.84 (0.68–4.96) | ||||||||
| ABCG2 G>A (rs17731538) | G carriers | 101 (45.1) | 123 (54.9) | 0.898 | Reference | ||||||
| AA | 4 (44.4) | 5 (55.6) | 1.16 (0.13–10.55) | ||||||||
| GG | 63 (46.0) | 74 (54.0) | 0.994 | Reference | |||||||
| A carriers | 42 (43.8) | 54 (56.2) | 1.00 (0.39–2.55) |
| Haplotype | Estimated Frequency (%) | p | OR (95% CI) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SLC16A7 A>T (rs3763980) | SLC16A7 T>G (rs10877333) | |||||
| A | T | 54.5 | Reference | |||
| T | T | 29.2 | 0.360 | 0.72 (0.36–1.44) | ||
| A | G | 16.3 | 0.890 | 1.11 (0.38–3.06) | ||
| SLC19A1 G>A (rs7499) | SLC19A1 G>A (rs1051266) | SLC19A1 A>G (rs2838956) | SLC19A1 G>A (rs3788200) | |||
| G | G | A | G | 48.7 | Reference | |
| A | A | G | A | 33.6 | 0.430 | 1.38 (0.62–3.03) |
| G | A | A | G | 5.8 | 0.860 | 0.88 (0.21–3.66) |
| G | A | G | A | 4.4 | 0.830 | 1.22 (0.19–7.70) |
| A | G | A | G | 2.0 | 0.330 | 3.80 (0.26–55.41) |
| ABCB1 C>T (rs1045642) | ABCB1 C>T (rs1128503) | ABCB1 G>A/T (rs2032582) | ||||
| C | C | G | 43.7 | Reference | ||
| T | T | T | 37.5 | 0.470 | 1.32 (0.63–2.76) | |
| T | C | G | 10.7 | 0.720 | 0.82 (0.28–2.44) | |
| C | T | T | 3.9 | 0.530 | 0.49 (0.05–4.55) | |
| C | T | G | 2.7 | 0.820 | 0.77 (0.08–7.56) | |
| ABCC1 T>C (rs35592) | ABCC1 G>C (rs2074087) | ABCC1 G>A (rs3784864) | ||||
| T | G | A | 42.6 | Reference | ||
| C | G | G | 18.1 | 0.025 * | 4.12 (1.20–14.09) | |
| T | G | G | 17.7 | 0.061 | 3.60 (0.95–13.65) | |
| C | C | G | 9.4 | 0.700 | 0.77 (0.21–2.86) | |
| T | C | G | 7.4 | 0.690 | 0.72 (0.15–3.54) | |
| ABCC1 T>C (rs35592) | ABCC1 A>G (rs246240) | ABCC1 G>A (rs3784864) | ||||
| T | A | A | 46.3 | Reference | ||
| T | A | G | 18.9 | 0.150 | 2.05 (0.78–5.38) | |
| C | A | G | 16.4 | 0.620 | 1.26 (0.50–3.16) | |
| C | G | G | 11.1 | 0.010 * | 7.26 (1.64–32.14) | |
| T | G | G | 6.2 | 0.370 | 2.24 (0.39–12.83) | |
| ABCC2 G>A (rs717620) | ABCC2 C>T (rs4148396) | |||||
| G | C | 55.3 | Reference | |||
| A | T | 22.2 | 0.370 | 0.66 (0.26–1.64) | ||
| G | T | 22.2 | 0.390 | 0.72 (0.34–1.52) | ||
| ABCG2 T>C (rs13120400) | ABCG2 G>A (rs17731538) | |||||
| T | G | 48.6 | Reference | |||
| C | G | 28.7 | 0.730 | 1.15 (0.53–2.49) | ||
| T | A | 21.7 | 0.870 | 1.07 (0.46-2.51) | ||
2.5. Genetic Risk Index and Clinical Response to MTX

3. Discussion
4. Experimental Section
4.1. Patients and Study Design
4.2. Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms Selection and Genotyping
4.3. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Abbreviations
| A | adenine |
| ACR | American College of Rheumatology |
| ABC | ATP-binding cassette |
| C | cytosine |
| CI | confidence interval |
| DAS28 | Disease Activity Score in 28 joints |
| DMARD | disease modifying antirheumatic drug |
| eGFR | estimated glomerular filtration rate |
| EULAR | European League Against Rheumatism |
| FPGS | folylpolyglutamate synthetase |
| G | guanine |
| GGH | gamma-glutamyl hydrolase |
| GRI | genetic risk index |
| HWE | Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium |
| MRP1 | multidrug resistance-associated protein 1 |
| MTX | methotrexate |
| NSAIDs | non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs |
| OAT4 | organic anion transporter 4 |
| OR | odds ratio |
| PD | pharmacodynamics |
| PGx | pharmacogenomics |
| PK | pharmacokinetics |
| RA | rheumatoid arthritis |
| SLC | solute carrier |
| SLCO | solute carrier organic anion transporter |
| SCr | serum creatinine concentration |
| SNP | single nucleotide polymorphism |
| T | thymine |
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smith, H.S.; Smith, A.R.; Seidner, P. Painful rheumatoid arthritis. Pain Phys. 2011, 14, E427–E458. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, L.K.; Chhabra, S.R. The chemistry of methotrexate and its analogues. Med. Res. Rev. 1988, 8, 95–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasim, N.A.; Whitehouse, M.; Ramachandran, C.; Bermejo, M.; Lennernas, H.; Hussain, A.S.; Junginger, H.E.; Stavchansky, S.A.; Midha, K.K.; Shah, V.P.; et al. Molecular properties of WHO essential drugs and provisional biopharmaceutical classification. Mol. Pharm. 2004, 1, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korell, J.; Stamp, L.K.; Barclay, M.L.; Dalrymple, J.M.; Drake, J.; Zhang, M.; Duffull, S.B. A population pharmacokinetic model for low-dose methotrexate and its polyglutamated metabolites in red blood cells. Clin. Pharm. 2013, 52, 475–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalliokoski, A.; Niemi, M. Impact of OATP transporters on pharmacokinetics. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 158, 693–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rindfleisch, J.A.; Muller, D. Diagnosis and management of rheumatoid arthritis. Am. Fam. Phys. 2005, 72, 1037–1047. [Google Scholar]
- Lima, A.; Azevedo, R.; Sousa, H.; Seabra, V.; Medeiros, R. Current approaches for TYMS polymorphisms and their importance in molecular epidemiology and pharmacogenetics. Pharmacogenomics 2013, 14, 1337–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, A.; Monteiro, J.; Bernardes, M.; Sousa, H.; Azevedo, R.; Seabra, V.; Medeiros, R. Prediction of methotrexate clinical response in Portuguese rheumatoid arthritis patients: Implication of MTHFR rs1801133 and ATIC rs4673993 polymorphisms. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, A.; Bernardes, M.; Azevedo, R.; Monteiro, J.; Sousa, H.; Medeiros, R.; Seabra, V. SLC19A1, SLC46A1 and SLCO1B1 polymorphisms as predictors of methotrexate-related toxicity in Portuguese rheumatoid arthritis patients. Toxicol. Sci. 2014, 142, 196–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benucci, M.; Saviola, G.; Manfredi, M.; Sarzi-Puttini, P.; Atzeni, F. Cost effectiveness analysis of disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs in rheumatoid arthritis. A systematic review literature. Int. J. Rheumatol. 2011, 2011, 845496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kremer, J.M.; Lee, J.K. The safety and efficacy of the use of methotrexate in long-term therapy for rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1986, 29, 822–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinblatt, M.E.; Kaplan, H.; Germain, B.F.; Block, S.; Solomon, S.D.; Merriman, R.C.; Wolfe, F.; Wall, B.; Anderson, L.; Gall, E.; et al. Methotrexate in rheumatoid arthritis. A five-year prospective multicenter study. Arthritis Rheum. 1994, 37, 1492–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, H.; Cronstein, B.N. Understanding the mechanisms of action of methotrexate: Implications for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Bull. NYU Hosp. Jt. Dis. 2007, 65, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dervieux, T.; Greenstein, N.; Kremer, J. Pharmacogenomic and metabolic biomarkers in the folate pathway and their association with methotrexate effects during dosage escalation in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2006, 54, 3095–3103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swierkot, J.; Szechinski, J. Methotrexate in rheumatoid arthritis. Pharmacol. Rep. 2006, 58, 473–492. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chan, E.S.; Cronstein, B.N. Molecular action of methotrexate in inflammatory diseases. Arthritis Res. 2002, 4, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silman, A.; Pearson, J. Epidemiology and genetics of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. 2002, 4, S265–S272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Branco, J.C.; Canhao, H. Epidemiological study of rheumatic diseases in Portugal—EpiReumaPt. Acta Reumatol. Port. 2011, 36, 203–204. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dias, A. Terapêutica anti-inflamatória em reumatologia: Coxibes—parte I: (b) Epidemiologia da osteoartrose e da artrite reumatóide. Anamnesis 2001, 10, 16–19. [Google Scholar]
- Mikkelsen, T.S.; Thorn, C.F.; Yang, J.J.; Ulrich, C.M.; French, D.; Zaza, G.; Dunnenberger, H.M.; Marsh, S.; McLeod, H.L.; Giacomini, K.; et al. PharmGKB summary: Methotrexate pathway. Pharm. Genomics 2011, 21, 679–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Transporter Consortium; Giacomini, K.M.; Huang, S.M.; Tweedie, D.J.; Benet, L.Z.; Brouwer, K.L.; Chu, X.; Dahlin, A.; Evers, R.; Fischer, V.; et al. Membrane transporters in drug development. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2010, 9, 215–236. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, A.; Jansen, M.; Sakaris, A.; Min, S.H.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Tsai, E.; Sandoval, C.; Zhao, R.; Akabas, M.H.; Goldman, I.D. Identification of an intestinal folate transporter and the molecular basis for hereditary folate malabsorption. Cell 2006, 127, 917–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kremer, J.M. Toward a better understanding of methotrexate. Arthritis Rheum. 2004, 50, 1370–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alamanos, Y.; Drosos, A.A. Epidemiology of adult rheumatoid arthritis. Autoimmun Rev. 2005, 4, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romao, V.C.; Canhao, H.; Fonseca, J.E. Old drugs, old problems: Where do we stand in prediction of rheumatoid arthritis responsiveness to methotrexate and other synthetic DMARDs? BMC Med. 2013, 11, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siva, C.; Yokoyama, W.M.; McLeod, H.L. Pharmacogenetics in rheumatology: The prospects and limitations of an emerging field. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2002, 41, 1273–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, F.; Ranganathan, P. Methotrexate pharmacogenetics in rheumatoid arthritis: A status report. Pharmacogenomics 2013, 14, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowland, M.; Tozer, T.N. Clinical Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics: Concepts and Applications, 4th ed.; Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott William & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Kroot, E.J.A.; van Leeuwen, M.A.; van Rijswijk, M.H.; Prevoo, M.L.L.; vanʼt Hof, M.A.; van de Putte, L.B.A.; van Riel, P.L.C.M. No increased mortality in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: Up to 10 years of follow up from disease onset. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2000, 59, 954–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjornadal, L.; Baecklund, E.; Yin, L.; Granath, F.; Klareskog, L.; Ekbom, A. Decreasing mortality in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: Results from a large population based cohort in Sweden, 1964–1995. J. Rheumatol. 2002, 29, 906–912. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Deng, F.Y.; Mo, X.B.; Qiu, Y.H.; Lei, S.F. Pharmacogenetics and pharmacogenomics for rheumatoid arthritis responsiveness to methotrexate treatment: The 2013 update. Pharmacogenomics 2014, 15, 551–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibofsky, A. Overview of epidemiology, pathophysiology, and diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis. Am. J. Manag. Care 2012, 18, S295–S302. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Klareskog, L.; van der Heijde, D.; de Jager, J.P.; Gough, A.; Kalden, J.; Malaise, M.; Martin Mola, E.; Pavelka, K.; Sany, J.; Settas, L.; et al. Therapeutic effect of the combination of etanercept and methotrexate compared with each treatment alone in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: Double-blind randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2004, 363, 675–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moncrieffe, H.; Hinks, A.; Ursu, S.; Kassoumeri, L.; Etheridge, A.; Hubank, M.; Martin, P.; Weiler, T.; Glass, D.N.; Thompson, S.D.; et al. Generation of novel pharmacogenomic candidates in response to methotrexate in juvenile idiopathic arthritis: Correlation between gene expression and genotype. Pharm. Genomics 2010, 20, 665–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Rotte, M.C.; Bulatovic, M.; Heijstek, M.W.; Jansen, G.; Heil, S.G.; van Schaik, R.H.; Wulffraat, N.M.; de Jonge, R. ABCB1 and ABCC3 gene polymorphisms are associated with first-year response to methotrexate in juvenile idiopathic arthritis. J. Rheumatol. 2012, 39, 2032–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekaratanawong, S.; Anzai, N.; Jutabha, P.; Miyazaki, H.; Noshiro, R.; Takeda, M.; Kanai, Y.; Sophasan, S.; Endou, H. Human organic anion transporter 4 is a renal apical organic anion/dicarboxylate exchanger in the proximal tubules. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2004, 94, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Aubel, R.A.; Smeets, P.H.; Peters, J.G.; Bindels, R.J.; Russel, F.G. The MRP4/ABCC4 gene encodes a novel apical organic anion transporter in human kidney proximal tubules: Putative efflux pump for urinary cAMP and cGMP. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2002, 13, 595–603. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Koepsell, H.; Endou, H. The SLC22 drug transporter family. Pflugers Arch. 2004, 447, 666–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyazaki, H.; Sekine, T.; Endou, H. The multispecific organic anion transporter family: Properties and pharmacological significance. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2004, 25, 654–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burckhardt, B.C.; Burckhardt, G. Transport of organic anions across the basolateral membrane of proximal tubule cells. Rev. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2003, 146, 95–158. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Haga, S.B.; Burke, W. Using pharmacogenetics to improve drug safety and efficacy. JAMA 2004, 291, 2869–2871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vormfelde, S.V.; Schirmer, M.; Hagos, Y.; Toliat, M.R.; Engelhardt, S.; Meineke, I.; Burckhardt, G.; Nurnberg, P.; Brockmoller, J. Torsemide renal clearance and genetic variation in luminal and basolateral organic anion transporters. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2006, 62, 323–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirmohamed, M.; Park, B.K. Genetic susceptibility to adverse drug reactions. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2001, 22, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berggren, S.; Gall, C.; Wollnitz, N.; Ekelund, M.; Karlbom, U.; Hoogstraate, J.; Schrenk, D.; Lennernas, H. Gene and protein expression of P-glycoprotein, MRP1, MRP2, and CYP3A4 in the small and large human intestine. Mol. Pharm. 2007, 4, 252–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drozdzik, M.; Rudas, T.; Pawlik, A.; Kurzawski, M.; Czerny, B.; Gornik, W.; Herczynska, M. The effect of 3435C>T MDR1 gene polymorphism on rheumatoid arthritis treatment with disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2006, 62, 933–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takano, M.; Yumoto, R.; Murakami, T. Expression and function of efflux drug transporters in the intestine. Pharmacol. Ther. 2006, 109, 137–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bland, J.M.; Altman, D.G. Multiple significance tests: The Bonferroni method. BMJ 1995, 310, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perneger, T.V. Whatʼs wrong with Bonferroni adjustments. BMJ 1998, 316, 1236–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warren, R.D.; Nichols, A.P.; Bender, R.A. Membrane transport of methotrexate in human lymphoblastoid cells. Cancer Res. 1978, 38, 668–671. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Van der Heijde, D.; Klareskog, L.; Rodriguez-Valverde, V.; Codreanu, C.; Bolosiu, H.; Melo-Gomes, J.; Tornero-Molina, J.; Wajdula, J.; Pedersen, R.; Fatenejad, S.; et al. Comparison of etanercept and methotrexate, alone and combined, in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: Two-year clinical and radiographic results from the TEMPO study, a double-blind, randomized trial. Arthritis Rheum. 2006, 54, 1063–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capell, H.A.; Madhok, R.; Porter, D.R.; Munro, R.A.; McInnes, I.B.; Hunter, J.A.; Steven, M.; Zoma, A.; Morrison, E.; Sambrook, M.; et al. Combination therapy with sulfasalazine and methotrexate is more effective than either drug alone in patients with rheumatoid arthritis with a suboptimal response to sulfasalazine: Results from the double-blind placebo-controlled MASCOT study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2007, 66, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aletaha, D.; Neogi, T.; Silman, A.J.; Funovits, J.; Felson, D.T.; Bingham, C.O., 3rd; Birnbaum, N.S.; Burmester, G.R.; Bykerk, V.P.; Cohen, M.D.; et al. 2010 rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: An American College of Rheumatology/European League against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2010, 69, 1580–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prevoo, M.L.; vanʼt Hof, M.A.; Kuper, H.H.; van Leeuwen, M.A.; van de Putte, L.B.; van Riel, P.L. Modified disease activity scores that include twenty-eight-joint counts. Development and validation in a prospective longitudinal study of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1995, 38, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinken, M.; Halwachs, S.; Kneuer, C.; Honscha, W. Subcellular localization and distribution of the reduced folate carrier in normal rat tissues. Eur. J. Histochem. 2011, 55, e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owen, S.A.; Hider, S.L.; Martin, P.; Bruce, I.N.; Barton, A.; Thomson, W. Genetic polymorphisms in key methotrexate pathway genes are associated with response to treatment in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Pharm. J. 2013, 13, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baslund, B.; Gregers, J.; Nielsen, C.H. Reduced folate carrier polymorphism determines methotrexate uptake by B cells and CD4+ T cells. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2008, 47, 451–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohanec Grabar, P.; Logar, D.; Lestan, B.; Dolzan, V. Genetic determinants of methotrexate toxicity in rheumatoid arthritis patients: A study of polymorphisms affecting methotrexate transport and folate metabolism. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2008, 64, 1057–1068. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Drozdzik, M.; Rudas, T.; Pawlik, A.; Gornik, W.; Kurzawski, M.; Herczynska, M. Reduced folate carrier-1 80G>A polymorphism affects methotrexate treatment outcome in rheumatoid arthritis. Pharm. J. 2007, 7, 404–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, H.M.; Gillis, D.; Hissaria, P.; Lester, S.; Somogyi, A.A.; Cleland, L.G.; Proudman, S.M. Common polymorphisms in the folate pathway predict efficacy of combination regimens containing methotrexate and sulfasalazine in early rheumatoid arthritis. J. Rheumatol 2008, 35, 562–571. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Konig, J.; Cui, Y.; Nies, A.T.; Keppler, D. A novel human organic anion transporting polypeptide localized to the basolateral hepatocyte membrane. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2000, 278, G156–G164. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tirona, R.G.; Leake, B.F.; Merino, G.; Kim, R.B. Polymorphisms in OATP-C: Identification of multiple allelic variants associated with altered transport activity among European- and African-Americans. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 35669–35675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trevino, L.R.; Shimasaki, N.; Yang, W.; Panetta, J.C.; Cheng, C.; Pei, D.; Chan, D.; Sparreboom, A.; Giacomini, K.M.; Pui, C.H.; et al. Germline genetic variation in an organic anion transporter polypeptide associated with methotrexate pharmacokinetics and clinical effects. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 5972–5978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arceci, R.J.; Stieglitz, K.; Bras, J.; Schinkel, A.; Baas, F.; Croop, J. Monoclonal antibody to an external epitope of the human mdr1 P-glycoprotein. Cancer Res. 1993, 53, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Takatori, R.; Takahashi, K.A.; Tokunaga, D.; Hojo, T.; Fujioka, M.; Asano, T.; Hirata, T.; Kawahito, Y.; Satomi, Y.; Nishino, H.; et al. ABCB1 C3435T polymorphism influences methotrexate sensitivity in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2006, 24, 546–554. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kooloos, W.M.; Wessels, J.A.; van der Straaten, T.; Allaart, C.F.; Huizinga, T.W.; Guchelaar, H.J. Functional polymorphisms and methotrexate treatment outcome in recent-onset rheumatoid arthritis. Pharmacogenomics 2010, 11, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fromm, M.F.; Kauffmann, H.M.; Fritz, P.; Burk, O.; Kroemer, H.K.; Warzok, R.W.; Eichelbaum, M.; Siegmund, W.; Schrenk, D. The effect of rifampin treatment on intestinal expression of human MRP transporters. Am. J. Pathol. 2000, 157, 1575–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keppler, D.; Kartenbeck, J. The canalicular conjugate export pump encoded by the cmrp/cmoat gene. Prog. Liver Dis. 1996, 14, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Simon, N.; Marsot, A.; Villard, E.; Choquet, S.; Khe, H.X.; Zahr, N.; Lechat, P.; Leblond, V.; Hulot, J.S. Impact of ABCC2 polymorphisms on high-dose methotrexate pharmacokinetics in patients with lymphoid malignancy. Pharmacogenomics J. 2013, 13, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranganathan, P.; Culverhouse, R.; Marsh, S.; Mody, A.; Scott-Horton, T.J.; Brasington, R.; Joseph, A.; Reddy, V.; Eisen, S.; McLeod, H.L. Methotrexate (MTX) pathway gene polymorphisms and their effects on MTX toxicity in Caucasian and African American patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J. Rheumatol. 2008, 35, 572–579. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Maliepaard, M.; van Gastelen, M.A.; Tohgo, A.; Hausheer, F.H.; van Waardenburg, R.C.; de Jong, L.A.; Pluim, D.; Beijnen, J.H.; Schellens, J.H. Circumvention of breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP)-mediated resistance to camptothecins in vitro using non-substrate drugs or the BCRP inhibitor GF120918. Clin. Cancer Res. 2001, 7, 935–941. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Spencer, K.L.; Voruganti, V.S.; Jorgensen, N.W.; Fornage, M.; Best, L.G.; Brown-Gentry, K.D.; Cole, S.A.; Crawford, D.C.; Deelman, E.; et al. Association of functional polymorphism rs2231142 (Q141K) in the ABCG2 gene with serum uric acid and gout in 4 US populations: The PAGE study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2013, 177, 923–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.H.; Lee, M.S.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, S.W.; Kang, R.H.; Choi, M.J.; Park, S.J.; Kim, S.J.; Lee, J.M.; Cole, S.P.; et al. MRP1 polymorphisms associated with citalopram response in patients with major depression. J. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2010, 30, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leschziner, G.D.; Andrew, T.; Pirmohamed, M.; Johnson, M.R. ABCB1 genotype and PGP expression, function and therapeutic drug response: A critical review and recommendations for future research. Pharm. J. 2007, 7, 154–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, A.; Bernardes, M.; Sousa, H.; Azevedo, R.; Costa, L.; Ventura, F.; Seabra, V.; Medeiros, R. SLC19A1 80G allele as a biomarker of methotrexate-related gastrointestinal toxicity in Portuguese rheumatoid arthritis patients. Pharmacogenomics 2014, 15, 807–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradic, M.; Costa, J.; Chelo, I.M. Genotyping with sequenom. Methods Mol. Biol. 2011, 772, 193–210. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sole, X.; Guino, E.; Valls, J.; Iniesta, R.; Moreno, V. SNPStats: A web tool for the analysis of association studies. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 1928–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halilova, K.I.; Brown, E.E.; Morgan, S.L.; Bridges, S.L., Jr.; Hwang, M.H.; Arnett, D.K.; Danila, M.I. Markers of treatment response to methotrexate in rheumatoid arthritis: Where do we stand? Int. J. Rheumatol. 2012, 2012, 978396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronnelid, J.; Wick, M.C.; Lampa, J.; Lindblad, S.; Nordmark, B.; Klareskog, L.; van Vollenhoven, R.F. Longitudinal analysis of citrullinated protein/peptide antibodies (anti-CP) during 5 year follow up in early rheumatoid arthritis: Anti-CP status predicts worse disease activity and greater radiological progression. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2005, 64, 1744–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morel, J.; Combe, B. How to predict prognosis in early rheumatoid arthritis. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2005, 19, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dervieux, T.; Furst, D.; Lein, D.O.; Capps, R.; Smith, K.; Walsh, M.; Kremer, J. Polyglutamation of methotrexate with common polymorphisms in reduced folate carrier, aminoimidazole carboxamide ribonucleotide transformylase, and thymidylate synthase are associated with methotrexate effects in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2004, 50, 2766–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, J.J.; Wells, G.; Verhoeven, A.C.; Felson, D.T. Factors predicting response to treatment in rheumatoid arthritis: the importance of disease duration. Arthritis Rheum. 2000, 43, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swierkot, J.; Slezak, R.; Karpinski, P.; Pawlowska, J.; Noga, L.; Szechinski, J.; Wiland, P. Associations between single-nucleotide polymorphisms of RFC-1, GGH, MTHFR, TYMS and TCII genes and the efficacy and toxicity of methotrexate treatment in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Pol. Arch. Med. Wewn. 2015, 125, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Muralidharan, N.; Mariaselvam, C.M.; Cb, M.; Negi, V.S. Reduced folate carrier-1 80G>A gene polymorphism is not associated with methotrexate treatment response in South Indian Tamils with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plaza-Plaza, J.C.; Aguilera, M.; Canadas-Garre, M.; Chemello, C.; Gonzalez-Utrilla, A.; Faus Dader, M.J.; Calleja, M.A. Pharmacogenetic polymorphisms contributing to toxicity induced by methotrexate in the southern Spanish population with rheumatoid arthritis. OMICS 2012, 16, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, T.; Hamada, A.; Mori, S.; Saito, H. Genetic polymorphisms in metabolic and cellular transport pathway of methotrexate impact clinical outcome of methotrexate monotherapy in Japanese patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Drug Metab. Pharm. 2012, 27, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohanec Grabar, P.; Leandro-García, L.J.; Inglada-Pérez, L.; Logar, D.; Rodríguez-Antona, C.; Dolžan, V. Genetic variation in the SLC19A1 gene and methotrexate toxicity in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Pharmacogenomics 2012, 13, 1583–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatzikyriakidou, A.; Georgiou, I.; Voulgari, P.V.; Papadopoulos, C.G.; Tzavaras, T.; Drosos, A.A. Transcription regulatory polymorphism −43T>C in the 5′-flanking region of SLC19A1 gene could affect rheumatoid arthritis patient response to methotrexate therapy. Rheumatol. Int. 2007, 27, 1057–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilgendorf, C.; Ahlin, G.; Seithel, A.; Artursson, P.; Ungell, A.L.; Karlsson, J. Expression of thirty-six drug transporter genes in human intestine, liver, kidney, and organotypic cell lines. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2007, 35, 1333–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bleasby, K.; Hall, L.A.; Perry, J.L.; Mohrenweiser, H.W.; Pritchard, J.B. Functional consequences of single nucleotide polymorphisms in the human organic anion transporter hOAT1 (SLC22A6). J. Pharm. Exp. Ther. 2005, 314, 923–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erdman, A.R.; Mangravite, L.M.; Urban, T.J.; Lagpacan, L.L.; Castro, R.A.; de la Cruz, M.; Chan, W.; Huang, C.C.; Johns, S.J.; Kawamoto, M.; et al. The human organic anion transporter 3 (OAT3; SLC22A8): Genetic variation and functional genomics. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2006, 290, F905–F912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goricar, K.; Kovač, V.; Jazbec, J.; Zakotnik, B.; Lamovec, J.; Dolžan, V. Influence of the folate pathway and transporter polymorphisms on methotrexate treatment outcome in osteosarcoma. Pharm. Genomics 2014, 24, 514–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramsey, L.B.; Bruun, G.H.; Yang, W.; Treviño, L.R.; Vattathil, S.; Scheet, P.; Cheng, C.; Rosner, G.L.; Giacomini, K.M.; Fan, Y.; et al. Rare versus common variants in pharmacogenetics: SLCO1B1 variation and methotrexate disposition. Genome Res. 2012, 22, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radtke, S.; Zolk, O.; Renner, B.; Paulides, M.; Zimmermann, M.; Möricke, A.; Stanulla, M.; Schrappe, M.; Langer, T. Germline genetic variations in methotrexate candidate genes are associated with pharmacokinetics, toxicity, and outcome in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 2013, 121, 5145–5153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.N.; He, X.L.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.J.; Li, J.X.; Niu, C.H.; Gao, P. Impact of SLCO1B1 521T>C variant on leucovorin rescue and risk of relapse in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia treated with high-dose methotrexate. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2014, 61, 2203–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niemi, M.; Pasanen, M.K.; Neuvonen, P.J. Organic anion transporting polypeptide 1B1: A genetically polymorphic transporter of major importance for hepatic drug uptake. Pharmacol. Rev. 2011, 63, 157–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spinella, M.J.; Brigle, K.E.; Sierra, E.E.; Goldman, I.D. Distinguishing between folate receptor-alpha-mediated transport and reduced folate carrier-mediated transport in L1210 leukemia cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 7842–7849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Johnson, A.D.; Papp, A.C.; Kroetz, D.L.; Sadée, W. Multidrug resistance polypeptide 1 (MDR1, ABCB1) variant 3435C>T affects mRNA stability. Pharm. Genomics 2005, 15, 693–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamp, L.K.; Chapman, P.T.; OʼDonnell, J.L.; Zhang, M.; James, J.; Frampton, C.; Barclay, M.L.; Kennedy, M.A.; Roberts, R.L. Polymorphisms within the folate pathway predict folate concentrations but are not associated with disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis patients on methotrexate. Pharm. Genomics 2010, 20, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanabe, M.; Ieiri, L.; Nagata, N.; Inoue, K.; Ito, S.; Kanamori, Y.; Takahashi, M.; Kurata, Y.; Kigawa, J.; Higuchi, S.; et al. Expression of P-glycoprotein in human placenta: Relation to genetic polymorphism of the multidrug resistance (MDR)-1 gene. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2001, 297, 1137–1143. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Warren, R.B.; Smith, R.L.; Campalani, E.; Eyre, S.; Smith, C.H.; Barker, J.N.; Worthington, J.; Griffiths, C.E. Genetic variation in efflux transporters influences outcome to methotrexate therapy in patients with psoriasis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2008, 128, 1925–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.D.; Markova, S.; Liu, W.; Gow, J.M.; Baldwin, R.M.; Habashian, M.; Relling, M.V.; Ratain, M.J.; Kroetz, D.L. Functional characterization of ABCC2 promoter polymorphisms and allele-specific expression. Pharm. J. 2013, 13, 396–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deo, A.K.; Prasad, B.; Balogh, L.; Lai, Y.; Unadkat, J.D. Interindividual variability in hepatic expression of the multidrug resistance-associated protein 2 (MRP2/ABCC2): Quantification by liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2012, 40, 852–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lima, A.; Bernardes, M.; Azevedo, R.; Medeiros, R.; Seabra, V. Pharmacogenomics of Methotrexate Membrane Transport Pathway: Can Clinical Response to Methotrexate in Rheumatoid Arthritis Be Predicted? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 13760-13780. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160613760
Lima A, Bernardes M, Azevedo R, Medeiros R, Seabra V. Pharmacogenomics of Methotrexate Membrane Transport Pathway: Can Clinical Response to Methotrexate in Rheumatoid Arthritis Be Predicted? International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2015; 16(6):13760-13780. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160613760
Chicago/Turabian StyleLima, Aurea, Miguel Bernardes, Rita Azevedo, Rui Medeiros, and Vítor Seabra. 2015. "Pharmacogenomics of Methotrexate Membrane Transport Pathway: Can Clinical Response to Methotrexate in Rheumatoid Arthritis Be Predicted?" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 16, no. 6: 13760-13780. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160613760
APA StyleLima, A., Bernardes, M., Azevedo, R., Medeiros, R., & Seabra, V. (2015). Pharmacogenomics of Methotrexate Membrane Transport Pathway: Can Clinical Response to Methotrexate in Rheumatoid Arthritis Be Predicted? International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 16(6), 13760-13780. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160613760