Personalized Medicine in Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor (GIST): Clinical Implications of the Somatic and Germline DNA Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
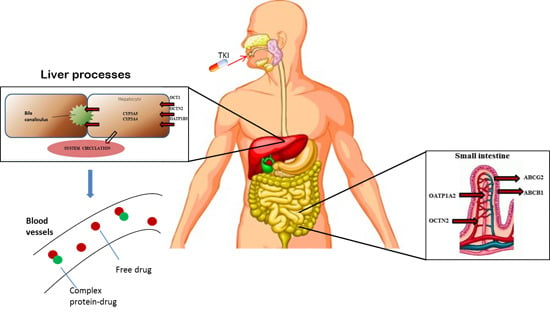
2. Pharmacogenetic Approaches in GIST: State of the Art

| Authors | Year | #n of the Evaluated SNPs and Pathway | Gene/Reference Sequence (rs) * | #n of Cases | Aim | Significant SNPs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| O’Brien et al [13]. | 2013 | 208 SNVs in 39 candidate genes related to DNA repair and dioxin metabolism or response | CYP1A2, CYP1B1, HIF1A, NQO1, G6PC/G6PT, ADH1A, ADH1B, ADH1C, ALDH18A1, ALDH1A1, ALDH1A2, ALDH1A3, ALDH1B1, ALDH1L1, ALDH1L2, ALDH2, CYP2B6, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2D6, CYP2E1, CYP3A4, GSTM1, GSTT1, GSTP1, HNF4A, NAT2, NFE2L2, NOS2A, PTGS2/COX2, SULT1A1, TP53, MDM2. | 279 GIST from a clinical trial of adjuvant imatinib mesylate | To test the association between germline SNVs and somatic mutations and to evaluate the hypothesis of environmental related origin for GIST | CYP1B1 rs2855658 and rs1056836 were associated with KIT exon 11 codon 557-8 del; ERCC2 rs50871 was associated with WT GIST; ERCC2 rs50871 was associated with KIT exon 11 insertion (no codon 557-8); GSTM1 deletion was associated with KIT exon 11 codon 557-8 del; RAD23B rs1805329 and rs7041137 were associated with other KIT mutations (none in exon 11) |
| Angelini et al [18]. | 2013 | 27 SNVs in 9 transporters genes; 4 SNVs in 4 metabolizing genes | SLC22A1 (rs12208357, rs683369, rs4646277, rs4646278, rs2282143, rs72552763); SLC22A4 (rs1050152); SLC22A5 (rs2631367, rs2631370, rs2631372); SLCO1A2 (rs11568563); SLCO1B3 (rs4149157, rs4149158, rs4149117, rs7311358); ABCA3 (rs323040, rs4146825); ABCB1 (rs10245483, rs3213619, rs1128501, , rs60023214, ); ABCC4 (rs3765534, rs9561765); ABCG2 (, ); CYP3A4 (rs2740574, rs28371759); CYP3A5 (, rs28365083). | 54 GIST patients receiving imatinib 400 mg | To evaluate the correlation among SNPs and clinical outcome | TTP improved by C allele in SLC22A4 (rs1050152; p = 0.013), and by G alleles in SLC22A5 (s2631367; p = 0.042) and (rs2631372; p = 0.045) |
| Koo et al [19]. | 2015 | 5 SNVs in 2 transporters genes; 1 SNVs in 1 metabolizing genes | ABCB1 (, rs1045642, ); ABCG2 (, ); CYP3A5 (). | 209 GIST patients receiving imatinib 400 mg | To evaluate the correlation among SNPs and clinical outcome | The 5-year PFS rate in patients with the AA variant of ABCG2 rs2032582 was superior compared with patients with CC/CA genotypes (p = 0.047) |
| Angelini et al [23]. | 2015 | 13 SNVs in 8 folate pathway genes | RFC (rs1051266); FOLR (rs2071010); DHFR (rs70991108); TS (rs45445694, rs34489327); SHMT (rs1979277); MTHFR (rs1801131, rs1801133); MTR (rs1805087); MTRR (rs10380). | 60 GIST patients receiving imatinib 400 mg and 153 controls | To evaluate the correlation among SNPs and clinical outcome | In 54 patients, presence of WT allele in RFC rs1051266, (AA/AG) was associated with reduced TTP (p = 0.028) |
| Rutkowski et al [28]. | 2012 | 6 SNVs in 2 VEGF pathway genes | VEGFA (rs699947, rs3025039,rs2010963, rs833061); VEGFR2 (1531289, rs1870377). | 39 GIST patients receiving sunitinib 2nd line treatment 50 mg | To evaluate the correlation among SNPs and adverse reactions or toxicity | Presence C-allele in VEGFA rs833061 and the T-allele in rs3025039 were associated with higher risk of hypothyroidism (p = 0.041 and p = 0.015, respectively) |
3. Analysis in Somatic DNA
3.1. KIT/PDGFRA Mutant GIST
3.2. Wild-Type GIST
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Antonescu, C.R. The gist paradigm: Lessons for other kinase-driven cancers. J. Pathol. 2011, 223, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demetri, G.D.; von Mehren, M.; Blanke, C.D.; van den Abbeele, A.D.; Eisenberg, B.; Roberts, P.J.; Heinrich, M.C.; Tuveson, D.A.; Singer, S.; Janicek, M.; et al. Efficacy and safety of imatinib mesylate in advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumors. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 347, 472–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demetri, G.D.; van Oosterom, A.T.; Garrett, C.R.; Blackstein, M.E.; Shah, M.H.; Verweij, J.; McArthur, G.; Judson, I.R.; Heinrich, M.C.; Morgan, J.A.; et al. Efficacy and safety of sunitinib in patients with advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumour after failure of imatinib: A randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2006, 368, 1329–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demetri, G.D.; Reichardt, P.; Kang, Y.K.; Blay, J.Y.; Rutkowski, P.; Gelderblom, H.; Hohenberger, P.; Leahy, M.; von Mehren, M.; Joensuu, H.; et al. Efficacy and safety of regorafenib for advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumours after failure of imatinib and sunitinib (grid): An international, multicentre, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2013, 381, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, R.; Dei Tos, A.P.; Rindi, G. Gistogram: A graphic presentation of the growing gist complexity. Virchows Arch. 2013, 463, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corless, C.L.; Barnett, C.M.; Heinrich, M.C. Gastrointestinal stromal tumours: Origin and molecular oncology. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 11, 865–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lourenço, N.; Hélias-Rodzewicz, Z.; Bachet, J.B.; Brahimi-Adouane, S.; Jardin, F.; Tran van Nhieu, J.; Peschaud, F.; Martin, E.; Beauchet, A.; Chibon, F.; et al. Copy-neutral loss of heterozygosity and chromosome gains and losses are frequent in gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Mol. Cancer 2014, 13, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Astolfi, A.; Nannini, M.; Pantaleo, M.A.; di Battista, M.; Heinrich, M.C.; Santini, D.; Catena, F.; Corless, C.L.; Maleddu, A.; Saponara, M.; et al. A molecular portrait of gastrointestinal stromal tumors: An integrative analysis of gene expression profiling and high-resolution genomic copy number. Lab. Investig. 2010, 90, 1285–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nannini, M.; Astolfi, A.; Urbini, M.; Indio, V.; Santini, D.; Heinrich, M.C.; Corless, C.L.; Ceccarelli, C.; Saponara, M.; Mandrioli, A.; et al. Integrated genomic study of quadruple-wt gist (kit/pdgfra/sdh/ras pathway wild-type gist). BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angelini, S.; Ravegnini, G.; Fletcher, J.A.; Maffei, F.; Hrelia, P. Clinical relevance of pharmacogenetics in gastrointestinal stromal tumor treatment in the era of personalized therapy. Pharmacogenomics 2013, 14, 941–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liegl, B.; Kepten, I.; Le, C.; Zhu, M.; Demetri, G.D.; Heinrich, M.C.; Fletcher, C.D.; Corless, C.L.; Fletcher, J.A. Heterogeneity of kinase inhibitor resistance mechanisms in gist. J. Pathol. 2008, 216, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hertz, D.L.; McLeod, H.L. Use of pharmacogenetics for predicting cancer prognosis and treatment exposure, response and toxicity. J. Hum. Genet. 2013, 58, 346–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brien, K.M.; Orlow, I.; Antonescu, C.R.; Ballman, K.; McCall, L.; DeMatteo, R.; Engel, L.S. Gastrointestinal stromal tumors, somatic mutations and candidate genetic risk variants. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinrich, M.C.; Corless, C.L.; Demetri, G.D.; Blanke, C.D.; von Mehren, M.; Joensuu, H.; McGreevey, L.S.; Chen, C.J.; van den Abbeele, A.D.; Druker, B.J.; et al. Kinase mutations and imatinib response in patients with metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumor. J. Clin. Oncol. 2003, 21, 4342–4349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eechoute, K.; Sparreboom, A.; Burger, H.; Franke, R.M.; Schiavon, G.; Verweij, J.; Loos, W.J.; Wiemer, E.A.; Mathijssen, R.H. Drug transporters and imatinib treatment: Implications for clinical practice. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 406–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, B.; Dutreix, C.; Mehring, G.; Hayes, M.J.; Ben-Am, M.; Seiberling, M.; Pokorny, R.; Capdeville, R.; Lloyd, P. Absolute bioavailability of imatinib (glivec) orally versus intravenous infusion. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2004, 44, 158–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angelini, S.; Soverini, S.; Ravegnini, G.; Barnett, M.; Turrini, E.; Thornquist, M.; Pane, F.; Hughes, T.P.; White, D.L.; Radich, J.; et al. Association between imatinib transporters and metabolizing enzymes genotype and response in newly diagnosed chronic myeloid leukemia patients receiving imatinib therapy. Haematologica 2013, 98, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angelini, S.; Pantaleo, M.A.; Ravegnini, G.; Zenesini, C.; Cavrini, G.; Nannini, M.; Fumagalli, E.; Palassini, E.; Saponara, M.; di Battista, M.; et al. Polymorphisms in OCTN1 and OCTN2 transporters genes are associated with prolonged time to progression in unresectable gastrointestinal stromal tumours treated with imatinib therapy. Pharmacol. Res. 2013, 68, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koo, D.H.; Ryu, M.H.; Ryoo, B.Y.; Beck, M.Y.; Na, Y.S.; Shin, J.G.; Lee, S.S.; Kim, E.Y.; Kang, Y.K. Association of ABCG2 polymorphism with clinical efficacy of imatinib in patients with gastrointestinal stromal tumor. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2015, 75, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.J.; Ward, R.L. Folate and one-carbon metabolism and its impact on aberrant dna methylation in cancer. Adv. Genet. 2010, 71, 79–121. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fuso, A. The “golden age” of DNA methylation in neurodegenerative diseases. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2013, 51, 523–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okamoto, Y.; Sawaki, A.; Ito, S.; Nishida, T.; Takahashi, T.; Toyota, M.; Suzuki, H.; Shinomura, Y.; Takeuchi, I.; Shinjo, K.; et al. Aberrant DNA methylation associated with aggressiveness of gastrointestinal stromal tumour. Gut 2012, 61, 392–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angelini, S.; Ravegnini, G.; Nannini, M.; Bermejo, J.L.; Musti, M.; Pantaleo, M.A.; Fumagalli, E.; Venturoli, N.; Palassini, E.; Consolini, N.; et al. Folate-related polymorphisms in gastrointestinal stromal tumours: Susceptibility and correlation with tumour characteristics and clinical outcome. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2015, 23, 817–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, C.; Ryu, M.H.; Kang, B.W.; Yoon, S.K.; Ryoo, B.Y.; Chang, H.M.; Lee, J.L.; Beck, M.Y.; Kim, T.W.; Kang, Y.K. Cross-sectional study of imatinib plasma trough levels in patients with advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumors: Impact of gastrointestinal resection on exposure to imatinib. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 1554–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eechoute, K.; Fransson, M.N.; Reyners, A.K.; de Jong, F.A.; Sparreboom, A.; van der Graaf, W.T.; Friberg, L.E.; Schiavon, G.; Wiemer, E.A.; Verweij, J.; et al. A long-term prospective population pharmacokinetic study on imatinib plasma concentrations in gist patients. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 5780–5787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, S.; Ryu, M.H.; Yoo, C.; Beck, M.Y.; Ryoo, B.Y.; Kang, Y.K. Imatinib plasma monitoring-guided dose modification for managing imatinib-related toxicities in gastrointestinal stromal tumor patients. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2013, 28, 1248–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Paolo, A.; Polillo, M.; Capecchi, M.; Cervetti, G.; Baratè, C.; Angelini, S.; Guerrini, F.; Fontanelli, G.; Arici, R.; Ciabatti, E.; et al. The c.480c>g polymorphism of hoct1 influences imatinib clearance in patients affected by chronic myeloid leukemia. Pharmacogenomics J. 2014, 14, 328–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutkowski, P.; Bylina, E.; Klimczak, A.; Switaj, T.; Falkowski, S.; Kroc, J.; Lugowska, I.; Brzeskwiniewicz, M.; Melerowicz, W.; Osuch, C.; et al. The outcome and predictive factors of sunitinib therapy in advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST) after imatinib failure-one institution study. BMC Cancer 2012, 12, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 2004, 116, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croce, C.M. Causes and consequences of microRNA dysregulation in cancer. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2009, 10, 704–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nannini, M.; Ravegnini, G.; Angelini, S.; Astolfi, A.; Biasco, G.; Pantaleo, M.A. MicroRNA profiling in gastrointestinal stromal tumors: Implication as diagnostic and prognostic markers. Epigenomics 2015, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Gits, C.M.; van Kuijk, P.F.; Jonkers, M.B.; Boersma, A.W.; van Ijcken, W.F.; Wozniak, A.; Sciot, R.; Rutkowski, P.; Schöffski, P.; Taguchi, T.; et al. MiR-17-92 and miR-221/222 cluster members target KIT and ETV1 in human gastrointestinal stromal tumours. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 109, 1625–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haller, F.; von Heydebreck, A.; Zhang, J.D.; Gunawan, B.; Langer, C.; Ramadori, G.; Wiemann, S.; Sahin, O. Localization- and mutation-dependent microRNA (miRNA) expression signatures in gastrointestinal stromal tumours (GISTs), with a cluster of co-expressed miRNAs located at 14q32.31. J. Pathol. 2010, 220, 71–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koelz, M.; Lense, J.; Wrba, F.; Scheffler, M.; Dienes, H.P.; Odenthal, M. Down-regulation of miR-221 and miR-222 correlates with pronounced KIT expression in gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Int. J. Oncol. 2011, 38, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramanian, S.; Lui, W.O.; Lee, C.H.; Espinosa, I.; Nielsen, T.O.; Heinrich, M.C.; Corless, C.L.; Fire, A.Z.; van de Rijn, M. MicroRNA expression signature of human sarcomas. Oncogene 2008, 27, 2015–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirota, S.; Isozaki, K.; Moriyama, Y.; Hashimoto, K.; Nishida, T.; Ishiguro, S.; Kawano, K.; Hanada, M.; Kurata, A.; Takeda, M.; et al. Gain-of-function mutations of c-KIT in human gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Science 1998, 279, 577–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinrich, M.C.; Corless, C.L.; Duensing, A.; McGreevey, L.; Chen, C.J.; Joseph, N.; Singer, S.; Griffith, D.J.; Haley, A.; Town, A.; et al. PDGFRA activating mutations in gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Science 2003, 299, 708–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liegl-Atzwanger, B.; Fletcher, J.A.; Fletcher, C.D. Gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Virchows Arch. 2010, 456, 111–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinrich, M.C.; Maki, R.G.; Corless, C.L.; Antonescu, C.R.; Harlow, A.; Griffith, D.; Town, A.; McKinley, A.; Ou, W.B.; Fletcher, J.A.; et al. Primary and secondary kinase genotypes correlate with the biological and clinical activity of sunitinib in imatinib-resistant gastrointestinal stromal tumor. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 5352–5359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maleddu, A.; Pantaleo, M.A.; Nannini, M.; di Battista, M.; Saponara, M.; Lolli, C.; Biasco, G. Mechanisms of secondary resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibitors in gastrointestinal stromal tumours (review). Oncol. Rep. 2009, 21, 1359–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, S.; Gasparotto, D.; Toffolatti, L.; Pastrello, C.; Gallina, G.; Marzotto, A.; Sartor, C.; Barbareschi, M.; Cantaloni, C.; Messerini, L.; et al. Molecular and clinicopathologic characterization of gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs) of small size. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2010, 34, 1480–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assämäki, R.; Sarlomo-Rikala, M.; Lopez-Guerrero, J.A.; Lasota, J.; Andersson, L.C.; Llombart-Bosch, A.; Miettinen, M.; Knuutila, S. Array comparative genomic hybridization analysis of chromosomal imbalances and their target genes in gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2007, 46, 564–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wozniak, A.; Sciot, R.; Guillou, L.; Pauwels, P.; Wasag, B.; Stul, M.; Vermeesch, J.R.; Vandenberghe, P.; Limon, J.; Debiec-Rychter, M. Array CGH analysis in primary gastrointestinal stromal tumors: Cytogenetic profile correlates with anatomic site and tumor aggressiveness, irrespective of mutational status. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2007, 46, 261–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, P.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, L.; Guo, X.; Wongvipat, J.; Shamu, T.; Fletcher, J.A.; Dewell, S.; Maki, R.G.; Zheng, D.; et al. ETV1 is a lineage survival factor that cooperates with KIT in gastrointestinal stromal tumours. Nature 2010, 467, 849–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ran, L.; Sirota, I.; Cao, Z.; Murphy, D.; Chen, Y.; Shukla, S.; Xie, Y.; Kaufmann, M.C.; Gao, D.; Zhu, S.; et al. Combined inhibition of map kinase and KIT signaling synergistically destabilizes ETV1 and suppresses GIST tumor growth. Cancer Discov. 2015, 5, 304–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nannini, M.; Biasco, G.; Astolfi, A.; Pantaleo, M.A. An overview on molecular biology of KIT/PDGFRA wild type (WT) gastrointestinal stromal tumours (GIST). J. Med. Genet. 2013, 50, 653–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniels, M.; Lurkin, I.; Pauli, R.; Erbstösser, E.; Hildebrandt, U.; Hellwig, K.; Zschille, U.; Lüders, P.; Krüger, G.; Knolle, J.; et al. Spectrum of KIT/PDGFRA/BRAF mutations and phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase pathway gene alterations in gastrointestinal stromal tumors (gist). Cancer Lett 2011, 312, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falchook, G.; Long, G.; Kurzrock, R.; Kim, F.K.; Arkenau, T.; Brown, M.; Hamid, O.; Infante, J.R.; Millward, M.; Pavlick, A.C.; et al. Dabrafenib in patients with melanoma, untreated brain metastases, and other solid tumours: A phase 1 dose-escalation trial. Lancet 2012, 379, 1893–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falchook, G.; Trent, J.; Heinrich, M.; Beadling, C.; Patterson, J.; Bastida, C.; Blackman, S.; Kurzrock, R. BRAF mutant gastrointestinal stromal tumor: First report of regression with BRAF inhibitor dabrafenib (GSK2118436) and whole exomic sequencing for analysis of acquired resistance. Oncotarget 2013, 4, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nannini, M.; Astolfi, A.; Paterini, P.; Urbini, M.; Santini, D.; Catena, F.; Indio, V.; Casadio, R.; Pinna, A.D.; Biasco, G.; et al. Expression of IGF-1 receptor in KIT/PDGF receptor-α wild-type gastrointestinal stromal tumors with succinate dehydrogenase complex dysfunction. Future Oncol. 2013, 9, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belinsky, M.G.; Rink, L.; Flieder, D.B.; Jahromi, M.S.; Schiffman, J.D.; Godwin, A.K.; Mehren, M. Overexpression of insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor and frequent mutational inactivation of SDHA in wild-type SDHB-negative gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2013, 52, 214–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miettinen, M.; Wang, Z.F.; Sarlomo-Rikala, M.; Osuch, C.; Rutkowski, P.; Lasota, J. Succinate dehydrogenase-deficient GISTs: A clinicopathologic, immunohistochemical, and molecular genetic study of 66 gastric GISTs with predilection to young age. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2011, 35, 1712–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janeway, K.A.; Kim, S.Y.; Lodish, M.; Nosé, V.; Rustin, P.; Gaal, J.; Dahia, P.L.; Liegl, B.; Ball, E.R.; Raygada, M.; et al. Defects in succinate dehydrogenase in gastrointestinal stromal tumors lacking KIT and PDGFRA mutations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 314–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pantaleo, M.A.; Astolfi, A.; Urbini, M.; Nannini, M.; Paterini, P.; Indio, V.; Saponara, M.; Formica, S.; Ceccarelli, C.; Casadio, R.; et al. Analysis of all subunits, SDHA, SDHB, SDHC, SDHD, of the succinate dehydrogenase complex in KIT/PDGFRA wild-type GIST. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2014, 22, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Killian, J.K.; Kim, S.Y.; Miettinen, M.; Smith, C.; Merino, M.; Tsokos, M.; Quezado, M.; Smith, W.I., Jr.; Jahromi, M.S.; Xekouki, P.; et al. Succinate dehydrogenase mutation underlies global epigenomic divergence in gastrointestinal stromal tumor. Cancer Discov. 2013, 3, 648–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Killian, J.K.; Miettinen, M.; Walker, R.L.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, Y.J.; Waterfall, J.J.; Noyes, N.; Retnakumar, P.; Yang, Z.; Smith, W.I.; et al. Recurrent epimutation of SDHC in gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Sci. Transl. Med. 2014, 6, 268ra177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pantaleo, M.A.; Nannini, M.; Corless, C.L.; Heinrich, M.C. Quadruple wild-type (WT) GIST: Defining the subset of gist that lacks abnormalities of KIT, PDGFRA, SDH, or RAS signaling pathways. Cancer Med. 2015, 4, 101–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedegaard, J.; Thorsen, K.; Lund, M.K.; Hein, A.M.; Hamilton-Dutoit, S.J.; Vang, S.; Nordentoft, I.; Birkenkamp-Demtröder, K.; Kruhøffer, M.; Hager, H.; et al. Next-generation sequencing of RNA and DNA isolated from paired fresh-frozen and formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded samples of human cancer and normal tissue. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Allen, E.M.; Wagle, N.; Stojanov, P.; Perrin, D.L.; Cibulskis, K.; Marlow, S.; Jane-Valbuena, J.; Friedrich, D.C.; Kryukov, G.; Carter, S.L.; et al. Whole-exome sequencing and clinical interpretation of formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tumor samples to guide precision cancer medicine. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 682–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nannini, M.; Astolfi, A.; Urbini, M.; Biasco, G.; Pantaleo, M.A. Liquid biopsy in gastrointestinal stromal tumors: A novel approach. J. Transl. Med. 2014, 12, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ravegnini, G.; Nannini, M.; Sammarini, G.; Astolfi, A.; Biasco, G.; Pantaleo, M.A.; Hrelia, P.; Angelini, S. Personalized Medicine in Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor (GIST): Clinical Implications of the Somatic and Germline DNA Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 15592-15608. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160715592
Ravegnini G, Nannini M, Sammarini G, Astolfi A, Biasco G, Pantaleo MA, Hrelia P, Angelini S. Personalized Medicine in Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor (GIST): Clinical Implications of the Somatic and Germline DNA Analysis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2015; 16(7):15592-15608. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160715592
Chicago/Turabian StyleRavegnini, Gloria, Margherita Nannini, Giulia Sammarini, Annalisa Astolfi, Guido Biasco, Maria A. Pantaleo, Patrizia Hrelia, and Sabrina Angelini. 2015. "Personalized Medicine in Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor (GIST): Clinical Implications of the Somatic and Germline DNA Analysis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 16, no. 7: 15592-15608. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160715592
APA StyleRavegnini, G., Nannini, M., Sammarini, G., Astolfi, A., Biasco, G., Pantaleo, M. A., Hrelia, P., & Angelini, S. (2015). Personalized Medicine in Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor (GIST): Clinical Implications of the Somatic and Germline DNA Analysis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 16(7), 15592-15608. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160715592