Sinulariolide Suppresses Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cell Migration and Invasion by Inhibiting Matrix Metalloproteinase-2/-9 through MAPKs and PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathways
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Sinulariolide Inhibited Migration and Invasion of HA22T Cells



2.2. Sinulariolide Reduced the Matrix Metalloproteinase (MMP)-2/-9 Activities of HA22T Cells

2.3. Sinulariolide Down-Regulated Protein Levels of MMP-2, MMP-9, and uPA, but Increased Protein Levels of TIMP-1
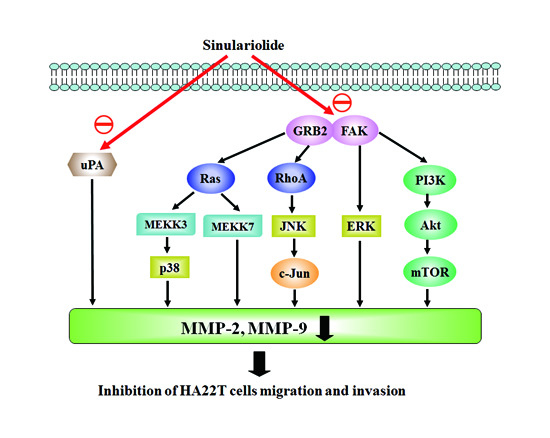
2.4. Sinulariolide Inhibited MAPKs and PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway Related Molecules

2.5. Sinulariolide Inhibited GRB2 and FAK Signaling Pathways

3. Discussion
3.1. Sinulariolide Inhibits Hepatocarcinoma Cell Metastasis and Induces Apoptosis
3.2. Sinulariolide Inhibits Multiple Signaling Pathways in HCC
3.3. Sinulariolide Inhibits Hepatocarcinoma Cell Metastasis through Multiple Signaling Pathways
3.4. Both Sinulariolide and 11-epi-Sinulariolide Acetate Inhibits Hepatocellular Carcinoma
4. Experimental Section
4.1. Materials and Chemical Reagents
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. Cell Migration Assay
4.4. Wound Healing Assay
4.5. Gelatin Zymography Assay
4.6. Cell Invasion Assay
4.7. Western Blot Analysis
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions

Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.; Ma, J.; Zou, Z.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2014, 64, 9–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davar, D.; Tarhini, A.A.; Kirkwood, J.M. Adjuvant therapy for melanoma. Cancer J. 2012, 18, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Serag, H.B.; Rudolph, K.L. Hepatocellular carcinoma: Epidemiology and molecular carcinogenesis. Gastroenterology 2007, 132, 2557–2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montalto, G.; Cervello, M.; Giannitrapani, L.; Dantona, F.; Terranova, A.; Castagnetta, L.A. Epidemiology, risk factors, and natural history of hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2002, 963, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czaja, A.J. Current management strategies for hepatocellular carcinoma. Minerva Gastroenterol. Dietol. 2013, 59, 143–159. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Arii, S.; Mise, M.; Harada, T.; Furutani, M.; Ishigami, S.; Niwano, M.; Mizumoto, M.; Fukumoto, M.; Imamura, M. Overexpression of matrix metalloproteinase 9 gene in hepatocellular carcinoma with invasive potential. Hepatology 1996, 24, 316–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terada, T.; Okada, Y.; Nakanuma, Y. Expression of immunoreactive matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of matrix metalloproteinases in human normal livers and primary liver tumors. Hepatology 1996, 23, 1341–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, K.B.; Nabha, S.M.; Atanaskova, N. Role of MAP kinase in tumor progression and invasion. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2003, 22, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vivanco, I.; Sawyers, C.L. The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase Akt pathway in human cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 489–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osaki, M.; Oshimura, M.; Ito, H. Pi3k-Akt pathway: Its functions and alterations in human cancer. Apoptosis 2004, 9, 667–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.K.; Soto, D.E.; Feldman, M.D.; Goldsmith, J.D.; Mick, R.; Hahn, S.M.; Machtay, M.; Muschel, R.J.; McKenna, W.G. Signaling pathways in NSCLC as a predictor of outcome and response to therapy. Lung 2004, 182, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shih, Y.W.; Chen, P.S.; Wu, C.H.; Jeng, F.Y.; Wang, C.J. α-Chaconine-reduced metastasis involves a PI3K/Akt signaling pathway with downregulation of NF-κB in human lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 11035–11043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faulkner, D.J. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2001, 18, 1–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faulkner, D.J. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2002, 19, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, P.W.; Chang, F.R.; McPhail, A.T.; Lee, K.H.; Wu, Y.C. New cembranolide analogues from the formosan soft coral Sinularia flexibilis and their cytotoxicity. Nat. Prod. Res. 2003, 17, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ojika, M.; Islam, M.K.; Shintani, T.; Zhang, Y.; Okamoto, T.; Sakagami, Y. Three new cytotoxic acylspermidines from the soft coral, Sinularia sp. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2003, 67, 1410–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aceret, T.L.; Coll, J.C.; Uchio, Y.; Sammarco, P.W. Antimicrobial activity of the diterpenes flexibilide and sinulariolide derived from Sinularia flexibilis quoy and gaimard 1833 (coelenterata: alcyonacea, octocorallia). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C 1998, 120, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, H.M.; Khanfar, M.A.; Elnagar, A.Y.; Mohammed, R.; Shaala, L.A.; Youssef, D.T.; Hifnawy, M.S.; el Sayed, K.A. Pachycladins A–E, prostate cancer invasion and migration inhibitory eunicellin-based diterpenoids from the red sea soft coral cladiella pachyclados. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 848–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, C.C.; Su, J.H.; Lin, J.J.; Chen, C.C.; Hwang, W.I.; Huang, H.H.; Wu, Y.J. An investigation into the cytotoxic effects of 13-acetoxysarcocrassolide from the soft coral sarcophyton crassocaule on bladder cancer cells. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 2622–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.I.; Chen, C.C.; Chen, J.C.; Su, J.H.; Huang, H.H.; Chen, J.Y.; Wu, Y.J. Proteomic analysis of anti-tumor effects of 11-dehydrosinulariolide on Cal-27 cells. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 1254–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, T.R.; Lin, J.J.; Chiu, C.C.; Chen, J.Y.; Su, J.H.; Cheng, Z.J.; Hwang, W.I.; Huang, H.H.; Wu, Y.J. Proteomic investigation of anti-tumor activities exerted by sinularin against A2058 melanoma cells. Electrophoresis 2012, 33, 1139–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neoh, C.A.; Wang, R.Y.; Din, Z.H.; Su, J.H.; Chen, Y.K.; Tsai, F.J.; Weng, S.H.; Wu, Y.J. Induction of apoptosis by sinulariolide from soft coral through mitochondrial-related and p38MAPK pathways on human bladder carcinoma cells. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 2893–2911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabelo, L.; Monteiro, N.; Serquiz, R.; Santos, P.; Oliveira, R.; Oliveira, A.; Rocha, H.; Morais, A.H.; Uchoa, A.; Santos, E. A lactose-binding lectin from the marine sponge Cinachyrella apion (Cal) induces cell death in human cervical adenocarcinoma cells. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 727–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maoka, T.; Tokuda, H.; Suzuki, N.; Kato, H.; Etoh, H. Anti-oxidative, anti-tumor-promoting, and anti-carcinogensis activities of nitroastaxanthin and nitrolutein, the reaction products of astaxanthin and lutein with peroxynitrite. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 1391–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.I.; Wang, R.Y.; Lin, J.J.; Su, J.H.; Chiu, C.C.; Chen, J.C.; Chen, J.Y.; Wu, Y.J. Proteomic profiling of the 11-dehydrosinulariolide-treated oral carcinoma cells Ca9–22: Effects on the cell apoptosis through mitochondrial-related and ER stress pathway. J. Proteomics 2012, 75, 5578–5589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondratyuk, T.P.; Park, E.J.; Yu, R.; van Breemen, R.B.; Asolkar, R.N.; Murphy, B.T.; Fenical, W.; Pezzuto, J.M. Novel marine phenazines as potential cancer chemopreventive and anti-inflammatory agents. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 451–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, K.J.; Chen, Y.C.; el-Shazly, M.; Du, Y.C.; Su, J.H.; Tsao, C.W.; Yen, W.H.; Chang, W.B.; Su, Y.D.; Yeh, Y.T.; et al. 5-episinuleptolide acetate, a norcembranoidal diterpene from the formosan soft coral Sinularia sp., induces leukemia cell apoptosis through Hsp90 inhibition. Molecules 2013, 18, 2924–2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, J.H.; Lin, Y.F.; Lu, Y.; Yeh, H.C.; Wang, W.H.; Fan, T.Y.; Sheu, J.H. Oxygenated cembranoids from the cultured and wild-type soft corals Sinularia flexibilis. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2009, 57, 1189–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.J.; Su, J.H.; Tsao, C.Y.; Hung, C.T.; Chao, H.H.; Lin, J.J.; Liao, M.H.; Yang, Z.Y.; Huang, H.H.; Tsai, F.J.; et al. Sinulariolide induced hepatocellular carcinoma apoptosis through activation of mitochondrial-related apoptotic and PERK/eIF2α/ATF4/CHOP pathway. Molecules 2013, 18, 10146–10161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.H.; Su, J.H.; Chiu, C.C.; Lin, J.J.; Yang, Z.Y.; Hwang, W.I.; Chen, Y.K.; Lo, Y.H.; Wu, Y.J. Proteomic investigation of the sinulariolide-treated melanoma cells A375: Effects on the cell apoptosis through mitochondrial-related pathway and activation of caspase cascade. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 2625–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Q.; Tang, Z.Y.; Xue, Q.; Shi, D.R.; Song, H.Y.; Tang, H.B. Invasion and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma in relation to urokinase-type plasminogen activator, its receptor and inhibitor. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2000, 126, 641–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Guan, J.L. Signal transduction by focal adhesion kinase in cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2009, 28, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giubellino, A.; Burke, T.R., Jr.; Bottaro, D.P. GRB2 signaling in cell motility and cancer. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2008, 12, 1021–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Young, J.; Prabhala, H.; Pan, E.; Mestdagh, P.; Muth, D.; Teruya-Feldstein, J.; Reinhardt, F.; Onder, T.T.; Valastyan, S.; et al. miR-9, a MYC/MYCN-activated microRNA, regulates E-cadherin and cancer metastasis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2010, 12, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Egeblad, M.; Werb, Z. New functions for the matrix metalloproteinases in cancer progression. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, T.W.; Moon, S.K.; Chang, Y.C.; Ko, J.H.; Lee, Y.C.; Cho, G.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, J.G.; Kim, C.H. Novel and therapeutic effect of caffeic acid and caffeic acid phenyl ester on hepatocarcinoma cells: Complete regression of hepatoma growth and metastasis by dual mechanism. FASEB J. 2004, 18, 1670–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, N.; Arteaga, M.; Zaidi, A.; Stauffer, J.; Cotler, S.J.; Zeleznik-Le, N.; Zhang, J.; Qiu, W. FAK is required for c-Met/β-catenin-driven hepatocarcinogenesis. Hepatology 2014, 61, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Yang, M.; Wang, D.; Yu, L.; Guo, C.; Guo, X.; Lin, N. Identification of GRB2 and GAB1 coexpression as an unfavorable prognostic factor for hepatocellular carcinoma by a combination of expression profile and network analysis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e85170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, W.H.; Chen, C.N.; Huang, H.I.; Lai, Y.L.; Teng, C.Y.; Kuo, W.H. Urokinase induces stromal cell-derived factor-1 expression in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 2012, 227, 697–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itoh, T.; Hayashi, Y.; Kanamaru, T.; Morita, Y.; Suzuki, S.; Wang, W.; Zhou, L.; Rui, J.A.; Yamamoto, M.; Kuroda, Y.; et al. Clinical significance of urokinase-type plasminogen activator activity in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2000, 15, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, C.D.; Neal, C.P.; Garcea, G.; Manson, M.M.; Dennison, A.R.; Berry, D.P. Prognostic molecular markers in hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review. Eur. J. Cancer 2007, 43, 979–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.J.; Su, J.H.; Tsai, C.C.; Chen, Y.J.; Liao, M.H.; Wu, Y.J. 11-epi-Sinulariolide scetate reduces cell migration andiInvasion of human hepatocellular carcinoma by reducing the activation of ERK1/2, p38MAPK and FAK/PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathways. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 4783–4798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, Y.-J.; Neoh, C.-A.; Tsao, C.-Y.; Su, J.-H.; Li, H.-H. Sinulariolide Suppresses Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cell Migration and Invasion by Inhibiting Matrix Metalloproteinase-2/-9 through MAPKs and PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 16469-16482. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160716469
Wu Y-J, Neoh C-A, Tsao C-Y, Su J-H, Li H-H. Sinulariolide Suppresses Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cell Migration and Invasion by Inhibiting Matrix Metalloproteinase-2/-9 through MAPKs and PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathways. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2015; 16(7):16469-16482. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160716469
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Yu-Jen, Choo-Aun Neoh, Chia-Yu Tsao, Jui-Hsin Su, and Hsing-Hui Li. 2015. "Sinulariolide Suppresses Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cell Migration and Invasion by Inhibiting Matrix Metalloproteinase-2/-9 through MAPKs and PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathways" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 16, no. 7: 16469-16482. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160716469
APA StyleWu, Y. -J., Neoh, C. -A., Tsao, C. -Y., Su, J. -H., & Li, H. -H. (2015). Sinulariolide Suppresses Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cell Migration and Invasion by Inhibiting Matrix Metalloproteinase-2/-9 through MAPKs and PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathways. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 16(7), 16469-16482. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160716469