High Genetic Diversity of Microbial Cellulase and Hemicellulase Genes in the Hindgut of Holotrichia parallela Larvae
Abstract
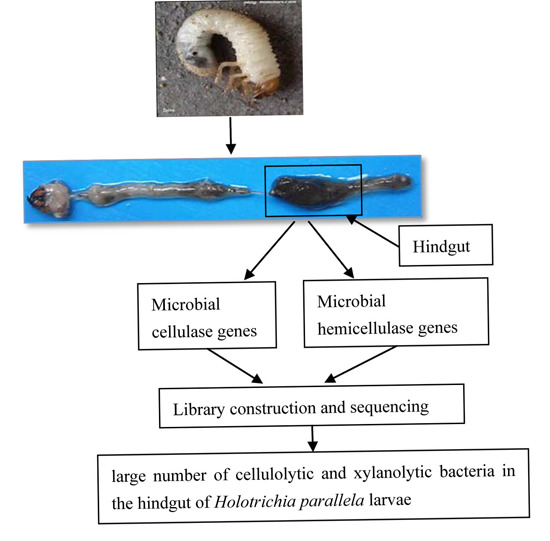
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Cellulase and Hemicellulase Gene Cloning and Diversity Analysis



2.2. Phylogenetic Analysis of GH8 Endoglucanase Gene Fragments
2.3. Phylogenetic Analysis of GH2 and GH36 Galactosidase Gene Fragments



2.4. Phylogenetic Analysis of GH10 and GH11 Endo-Xylanase Gene Fragments

2.5. Gene Cloning, Expression, and Characterization of Endo-Xylanase


3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Ethics Statement
4.2. Insect Samples
4.3. Insect Dissection and Total Bacterial DNA Extraction
4.4. PCR Amplification, Library Construction and Sequencing
| Pfam Family | Enzyme | EC Number | Primer (5ʹ–3ʹ) | Length bp |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GH2 | β-Galactosidase | EC3.2.1.23 | GH2F: GTGCGYACSWSBCAYTAYCC | 204–219 |
| GH2R: CCAAATRAYRAYGCTYGGRTGRTT | ||||
| GH3 | β-Glucosidase | EC3.2.1.21 | GH3F: GTKAAYCCRWSYGGIMRIYT | 183–200 |
| GH3R: TAISWYAKICCRTRVCCRAA | ||||
| GH5 | β-1,4-Endoglucanase | EC3.2.1.4 | GH5F: TWYGARYTIYTIAAYGARC | 195–258 |
| GH5R: NGGRTTRTARWARTGRAA | ||||
| GH8 | β-1,4-Endoglucanase | EC3.2.1.4 | GH8F: GAAGGYCWGGGYTWYGSVATG | 183–207 |
| GH8R: AATMWSYWSATCRCCATCGSTSGC | ||||
| GH10 | Endo-xylanase | EC3.2.1.8 | GH10F: GGYCAYACBCTNRTNTGGCA | 138–186 |
| GH10R: YTCRTTNACNACRTCCCA | ||||
| GH11 | Endo-xylanase | EC3.2.1.8 | GH11F: TAYMTGDSNSTBTAYGGBTGG | 336 |
| GH11R: TRCCVCTVCTYTKRTAVCCYTC | ||||
| GH36 | α-Galactosidase | EC3.2.1.22 | GH36F: GACATGTTCGTGATGGACGAYGGNTGGTT | 193 |
| GH36R: CGGACTCTGGGTTCACCATYTCNGGYTC | ||||
| GH39 | β-Xylosidase | EC3.2.1.37 | GH39F: TTYGARGTNTGGAAYGARCC | 223–230 |
| GH39R: GCRTGNCKISWIACRAARTC | ||||
| GH45 | β-1,4-Endoglucanase | EC3.2.1.4 | GH45F: ACCMGITAYTGGGAYTGYTG | 377–413 |
| GH45R: AAGRYICCNAVICCNCCICCNGG | ||||
| GH48 | Cellobio-Hydrolase | EC3.2.1.91 | GH48F: GARGCNCCNGAYYAYGGICA | 420 |
| GH48R: CCNCGYTGRWAIGTRTTDA | ||||
| GH52 | β-Xylosidase | EC3.2.1.37 | GH52F: GARGGNGARTAYMGIATGATGAAYAC | 197–200 |
| GH52R: GCVACNCCCATRTCRTGNGT |
| Standard | Touchdown PCR Settings | |
|---|---|---|
| 94 °C 5 min | ||
| 94 °C 30 s, X °C 30 s (−0.5 °C/cycle), 72 °C 30 s; 30 cycles | ||
| 94 °C 30 s, Y °C 30 s, 72 °C 30 s; 20 cycles | ||
| 72 °C 10 min | ||
| 4 °C infinity | ||
| Pfam Family | The following PCR settings are same as the Standard: | |
| GH2 (PF02836) | X = 62 | Y = 52 |
| GH3 (PF01915) | X = 65 | Y = 50 |
| GH5 (PF00150) | X = 58 | Y = 52 |
| GH8 (PF01270) | X = 65 | Y = 55 |
| GH10 (PF00331) | X = 60 | Y = 48 |
| GH11 (PF00457) | X = 60 | Y = 48 |
| GH36 (PF02065) | X = 65 | Y = 58 |
| GH39 (PF01229) | X = 65 | Y = 50 |
| GH45 (PF02015) | X = 68 | Y = 55 |
| GH48 (PF02011) | X = 65 | Y = 50 |
| GH52 (PF03512) | X = 68 | Y = 57 |
4.5. Phylogenetic Analysis of Cellulase and Hemicellulase Gene Sequences
4.6. Gene Cloning, Expression, and Characterization of Endo-Xylanase
4.7. Nucleotide Sequence Accession Numbers
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, S.W.; Zhang, H.Y.; Marshall, S.; Jackson, T.A. The scarab gut: A potential bioreactor for bio-fuel production. Insect Sci. 2010, 17, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.Y.; Jackson, T.A. Autochthonous bacterial flora indicated by PCR-DGGE of 16S rRNA gene fragments from the alimentary tract of Costelytra zealandica (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae). J. Appl. Microbiol. 2008, 105, 1277–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.T.; Xu, X.D.; Deloach, C.J. Biological control of white grubs (Coleopera: Scarabaeidae) by larvae of Promachus yesonicus (Diptera: Asilidae) in China. Biol. Control 1995, 5, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazemier, A.E.; Hackstein, J.H.P.; Op den Camp, H.J.M.; Rosenberg, J.; van der Drift, C. Bacteria in the intestinal tract of different species of arthropods. Microb. Ecol. 1997, 33, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayon, C. Volatile fatty acids and methane production in relation to anaerobic carbohydrate fermentation in Oryctes nasicornis larvae (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae). J. Insect Physiol. 1980, 26, 819–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.W.; Sheng, P.; Zhang, H.Y. Isolation and identification of cellulolytic bacteria from the gut of Holotrichia parallela larvae (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 2563–2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, P.; Huang, S.W.; Wang, Q.; Wang, A.L.; Zhang, H.Y. Isolation, screening, and optimization of the fermentation conditions of highly cellulolytic bacteria from the hindgut of Holotrichia parallela larvae (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae). Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2012, 167, 270–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKendry, P. Energy production from biomass (part 1): Overview of biomass. Bioresour. Technol. 2002, 83, 27–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badger, P.C. Ethanol from cellulose: A general review. In Trends in New Crops and New Uses; Janick, J., Whipkey, A., Eds.; ASHS Press: Alexandria, VA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Collins, T.; Gerday, C.; Feller, G. Xylanases, xylanase families and extremophilic xylanases. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2006, 29, 3–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henrissat, B.; Claeyssens, M.; Tomme, P.; Lemesle, L.; Mornon, J.P. Cellulase families revealed by hydrophobic cluster analysis. Gene 1989, 81, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.Z.; Luo, H.Y.; Wang, Y.R.; Huang, H.Q.; Shi, P.J.; Yang, P.L.; Meng, K.; Bai, Y.G.; Yao, B. A novel cold-active xylanase gene from the environmental DNA of goat rumen contents: Direct cloning, expression and enzyme characterization. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 3330–3336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warnecke, F.; Luginbühl, P.; Ivanova, N.; Ghassemian, M.; Richardson, T.H.; Stege, J.T.; Cayouette, M.; McHardy, A.C.; Djordjevic, G.; Aboushadi, N.; et al. Metagenomic and functional analysis of hindgut microbiota of a wood-feeding higher termite. Nature 2007, 450, 560–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cazemier, A.E.; Verdoes, J.C.; Reubsaet, F.A.; Hackstein, J.H.; van der Drift, C.; Op den Camp, H.J. Promicromonospora pachnodae sp. nov., a member of the (hemi)cellulolytic hindgut flora of larvae of the scarab beetle Pachnoda marginata. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2003, 83, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokuda, G.; Watanabe, H. Hidden cellulases in termites: Revision of an old hypothesis. Biol. Lett. 2007, 3, 336–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scharf, M.E.; Tartar, A. Termite digestomes as sources for novel lignocellulases. Biofuel Bioprod. Biorefin. 2008, 2, 540–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.W.; Zhang, H.Y. The impact of environmental heterogeneity and life stage on the hindgut microbiota of Holotrichia parallela larvae (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae). PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elifantz, H.; Waidner, LA.; Michelou, V.K.; Cottrell, M.T.; Kirchman, D.L. Diversity and abundance of glycosyl hydrolase family 5 in the North Atlantic Ocean. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2008, 63, 316–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behar, A.; Yuval, B.; Jurkevitch, E. Gut bacterial communities in the Mediterranean fruit fly (Ceratitis capitata) and their impact on host longevity. J. Insect Physiol. 2008, 54, 1377–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leser, T.D.; Lindecrona, R.H.; Jensen, T.K.; Jensen, B.B.; Moller, K. Changes in bacterial community structure in the colon of pigs fed different experimental diets and after infection with Brachyspira hyodysenteriae. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 3290–3296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, P.J.; Meng, K.; Zhou, Z.G.; Wang, Y.R.; Diao, Q.Y.; Yao, B. The host species affects the microbial community in the goat rumen. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 132–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.Z.; Wang, Y.R.; Yang, P.L.; Luo, H.Y.; Huang, H.Q.; Shi, P.J.; Meng, K.; Yao, B. Molecular detection and diversity of xylanase genes in alpine tundra soil. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 87, 1383–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hess, M.; Sczyrba, A.; Egan, R.; Kim, T.W.; Chokhawala, H.; Schroth, G.; Luo, S.J.; Clark, D.S.; Chen, F.; Zhang, T.; et al. Metagenomic discovery of biomass-degrading genes and genomes from cow rumen. Science 2011, 331, 463–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biely, P.; Kluepfel, D.; Morosoli, R.; Shareck, F. Mode of action of three endo-β-1,4-endo-xylanases of Streptomyces lividans. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1993, 1162, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biely, P.; Vrsanska, M.; Tenkanen, M.; Kluepfel, D. Endo-β-1,4-endo-xylanase families: Differences in catalytic properties. J. Biotechnol. 1997, 57, 151–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georis, J.; Giannotta, F.; de Buyl, E.; Granier, B.; Frere, J.M. Purification and properties of three endo-β-1,4-xylanases produced by Streptomyces sp. strain S38 which diver in their ability to enhance the bleaching of kraft pulps. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2000, 26, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, H.W.; Heo, S.Y.; Kim, D.Y.; Park, D.S.; Bae, K.S.; Park, H.Y. Biochemical characterization and sequence analysis of a xylanase produced by an exo-symbiotic bacterium of Gryllotalpa orientalis, Cellulosimicrobium sp. HY-12. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 2008, 93, 437–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.Y.; Shin, D.H.; Jung, S.; Lee, J.S.; Cho, H.Y.; Bae, K.S.; Sung, C.K.; Rhee, Y.H.; Son, K.H.; Park, H.Y. Biocatalytic properties and substrate-binding ability of a modular GH10 β-1,4-xylanase from an insect-symbiotic bacterium, Streptomyces mexicanus HY-14. J. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 863–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.P.; Huang, H.Q.; Meng, K.; Shi, P.J.; Wang, Y.R.; Luo, H.Y.; Yang, P.L.; Bai, Y.G.; Zhou, Z.G.; Yao, B. Molecular and biochemical characterization of a novel xylanase from the symbiotic Sphingobacterium sp. TN19. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 85, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.Z.; Godzik, A. Cd-hit: A fast program for clustering and comparing large sets of protein or nucleotide sequences. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 1658–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schloss, P.D.; Handelsman, J. Introducing DOTUR, a computer program for defining operational taxonomic units and estimating species richness. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 1501–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Retief, J.D. Phylogenetic analysis using PHYLIP. Bioinform. Methods Protoc. 1999, 132, 243–258. [Google Scholar]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sheng, P.; Li, Y.; Marshall, S.D.G.; Zhang, H. High Genetic Diversity of Microbial Cellulase and Hemicellulase Genes in the Hindgut of Holotrichia parallela Larvae. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 16545-16559. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160716545
Sheng P, Li Y, Marshall SDG, Zhang H. High Genetic Diversity of Microbial Cellulase and Hemicellulase Genes in the Hindgut of Holotrichia parallela Larvae. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2015; 16(7):16545-16559. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160716545
Chicago/Turabian StyleSheng, Ping, Yushan Li, Sean D. G. Marshall, and Hongyu Zhang. 2015. "High Genetic Diversity of Microbial Cellulase and Hemicellulase Genes in the Hindgut of Holotrichia parallela Larvae" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 16, no. 7: 16545-16559. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160716545
APA StyleSheng, P., Li, Y., Marshall, S. D. G., & Zhang, H. (2015). High Genetic Diversity of Microbial Cellulase and Hemicellulase Genes in the Hindgut of Holotrichia parallela Larvae. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 16(7), 16545-16559. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160716545