Differentiation Effects of Platelet-Rich Plasma Concentrations on Synovial Fluid Mesenchymal Stem Cells from Pigs Cultivated in Alginate Complex Hydrogel
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Results
2.1.1. Phenotype of Autologous Synovial Fluid Mesenchymal Stem Cells (SF-MSCs) from Pigs

2.1.2. Identification of Autologous SF-MSCs from Pigs

2.1.3. Potential of SF-MSCs to Differentiate



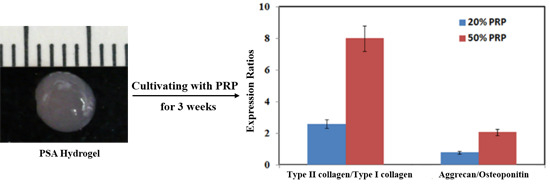
2.1.4. Effects of Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Concentrations on SF-MSCs


| Growth Factors in PRP | TGF-β1 (ng/mL) | bFGF (pg/mL) | PDGF (ng/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Before activation | 2.34 ± 0.76 | 26.62 ± 3.13 | 11.56 ± 2.21 |
| After activation (20%) | 5.14 ± 0.36 | 30.91 ± 1.57 | 26.16 ± 1.91 |
| After activation (50%) | 10.12 ± 5.28 | 37.64 ± 5.33 | 34.53 ± 1.44 |
| After activation (100%) | 20.38 ± 7.08 | 51.32 ± 9.63 | 50.75 ± 2.76 |
2.2. Discussion
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Isolation of Autologous SF-MSCs from Pigs
3.2. Isolation of Autologous BM-MSCs from Pigs
3.3. Identification of Autologous SF-MSCs from Pigs
3.4. Autologous PRP Preparation
3.5. Multipotent Differentiation
3.6. Preparation of the PRP-SF-MSCs-Alginate (PSA) Hydrogel System

3.7. Analysis of Gene Expression by Real-Time PCR
| Gene Symbol | Primer Sequences (3′→5′) | Size (bps) |
|---|---|---|
| GAPDH | AAGGGCATCCTGGGCTACAC GGTCCAGGGGCTCTTACTCC | 230 |
| Type I Collagen | AGAGGAGGGCCAAGAAGAAG ACGTCATCGCACAACACATT | 174 |
| Type II Collagen | TCTTCCTGGACCCGCCGGAC GCCACGCTCCCCTGGGAAAC | 199 |
| Osteocalcin | AACCCCGACTGCGACGAGCT ACACTTGCCGGGCAGGGAAG | 174 |
| Osteopontin | ACTCCGATGAATCCGATGAG TCCGTCTCCTCACTTTCCAC | 220 |
| Aggrecan | TGGCCACACATCGGGGTTGG GGCACTCGTCAAAGTCTGCCGT | 239 |
| aP2 | AGGTTACGGCTTCTTTCTCACCTTG TTGGCCATGCCAGCCACCTT | 214 |
| PPAγ2 | GCGCCCTGGCAAAGCACT TCCACGGAGCGAAACTGACAC | 221 |
3.8. 3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay (MTT) Assay
3.9. Evaluation of Concentrations of Growth Factors in PRP
3.10. Histological Staining and Immunofluorescence Staining
3.11. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dominici, M.; le Blanc, K.; Mueller, I.; Slaper-Cortenbach, I.; Marini, F.; Krause, D.; Deans, R.; Keating, A.; Prockop, Dj.; Horwitz, E. Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy 2006, 8, 315–317. [Google Scholar]
- Barry, F.P.; Murphy, J.M. Mesenchymal stem cells: Clinical applications and biological characterization. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2004, 36, 568–584. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Solchaga, L.A.; Gao, J.; Dennis, J.E.; Awadallah, A.; Lundberg, M.; Caplan, A.I.; Goldberg, V.M. Treatment of osteochondral defects with autologous bone marrow in a hyaluronan-based delivery vehicle. Tissue Eng. 2002, 8, 333–347. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kanaya, A.; Deie, M.; Adachi, N.; Nishimori, M.; Yanada, S.; Ochi, M. Intra-articular injection of mesenchymal stromal cells in partially torn anterior cruciate ligaments in a rat model. Arthroscopy 2007, 23, 610–617. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Young, R.G.; Butler, D.L.; Weber, W.; Caplan, A.I.; Gordon, S.L.; Fink, D.J. Use of mesenchymal stem cells in a collagen matrix for Achilles tendon repair. J. Orthop. Res. 1998, 16, 406–413. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Murphy, J.M.; Fink, D.J.; Hunziker, E.B.; Barry, F.P. Stem cell therapy in a caprine model of osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2003, 48, 3464–3474. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jones, E.A.; Crawford, A.; English, A.; Henshaw, K.; Mundy, J.; Corscadden, D.; Chapman, T.; Emery, P.; Hatton, P.; McGonagle, D. Synovial fluid mesenchymal stem cells in health and early osteoarthritis: Detection and functional evaluation at the single-cell level. Arthritis Rheum. 2008, 58, 1731–1740. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sekiya, I.; Ojima, M.; Suzuki, S.; Yamaga, M.; Horie, M.; Koga, H.; Tsuji, K.; Miyaguchi, K.; Ogishima, S.; Tanaka, H.; et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells in synovial fluid increase in the knee with degenerated cartilage and osteoarthritis. J. Orthop. Res. 2012, 30, 943–949. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Morito, T.; Muneta, T.; Hara, K.; Ju, Y.J.; Mochizuki, T.; Makino, H.; Umezawa, A.; Sekiya, I. Synovial fluid-derived mesenchymal stem cells increase after intra-articular ligament injury in humans. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2008, 47, 1137–1143. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Matsukura, Y.; Muneta, T.; Tsuji, K.; Koga, H.; Sekiya, I. Mesenchymal stem cells in synovial fluid increase after meniscus injury. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2014, 472, 1357–1364. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Eppley, B.L.; Woodell, J.E.; Higgins, J. Platelet quantification and growth factor analysis from platelet-rich plasma: Implications for wound healing. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2004, 114, 1502–1508. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Okuda, K.; Kawase, T.; Momose, M.; Murata, M.; Saito, Y.; Suzuki, H.; Wolff, L.F.; Yoshie, H. Platelet-rich plasma contains high levels of platelet-derived growth factor and transforming growth factor-β and modulates the proliferation of periodontally related cells in vitro. J. Periodontol. 2003, 74, 849–857. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- El-Sharkawy, H.; Kantarci, A.; Deady, J.; Hasturk, H.; Liu, H.; Alshahat, M.; van Dyke, T.E. Platelet-rich plasma: Growth factors and pro- and anti-inflammatory properties. J. Periodontol. 2007, 78, 661–669. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Molloy, T.; Wang, Y.; Murrell, G. The roles of growth factors in tendon and ligament healing. Sports Med. 2003, 33, 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gosens, T.; Peerbooms, J.C.; van Laar, W.; den Oudsten, B.L. Ongoing positive effect of platelet-rich plasma versus corticosteroid injection in lateral epicondylitis: A double-blind randomized controlled trial with 2-year follow-up. Am. J. Sports Med. 2011, 39, 1200–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, A.; Pavelko, T. Treatment of chronic elbow tendinosis with buffered platelet-rich plasma. Am. J. Sports Med. 2006, 34, 1774–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragab, E.M.; Othman, A.M. Platelets rich plasma for treatment of chronic plantar fasciitis. Arch. Orthop. Trauma Surg. 2012, 132, 1065–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orrego, M.; Larrain, C.; Rosales, J.; Valenzuela, L.; Matas, J.; Durruty, J.; Sudy, H.; Mardones, R. Effects of platelet concentrate and a bone plug on the healing of hamstring tendons in a bone tunnel. Arthroscopy 2008, 24, 1373–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogrin, M.; Rupreht, M.; Crnjac, A.; Dinevski, D.; Krajnc, Z.; Recnik, G. The effect of platelet-derived growth factors on knee stability after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: A prospective randomized clinical study. Wien. Klin. Wochenschr. 2010, 122 (Suppl. 2), 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez, M.; Guadilla, J.; Fiz, N.; Andia, I. Ultrasound-guided platelet-rich plasma injections for the treatment of osteoarthritis of the hip. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2012, 51, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spaková, T.; Rosocha, J.; Lacko, M.; Harvanová, D.; Gharaibeh, A. Treatment of knee joint osteoarthritis with autologous platelet-rich plasma in comparison with hyaluronic acid. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2012, 91, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, A.; Tummala, P.; King, A.; Lee, B.; Kraus, M.; Tse, V.; Jacobs, C.R. Buffered platelet-rich plasma enhances mesenchymal stem cell proliferation and chondrogenic differentiation. Tissue Eng. Part C Methods 2009, 15, 431–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Textor, J.A.; Tablin, F. Activation of equine platelet-rich plasma: Comparison of methods and characterization of equine autologous thrombin. Vet. Surg. 2012, 41, 784–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amable, P.R.; Carias, R.B.; Teixeira, M.V.; da Cruz Pacheco, I.; Corrêa do Amaral, R.J.; Granjeiro, J.M.; Borojevic, R. Platelet-rich plasma preparation for regenerative medicine: Optimization and quantification of cytokines and growth factors. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2013, 4, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodan, S.B.; Wesolowski, G.; Thomas, K.A.; Yoon, K.; Rodan, G.A. Effects of acidic and basic fibroblast growth factors on osteoblastic cells. Connect. Tissue Res. 1989, 20, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awad, H.A.; Halvorsen, Y.D.; Gimble, J.M.; Guilak, F. Effects of transforming growth factor beta1 and dexamethasone on the growth and chondrogenic differentiation of adipose-derived stromal cells. Tissue Eng. 2003, 9, 1301–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunziker, E.B.; Rosenberg, L.C. Repair of partial-thickness defects in articular cartilage: Cell recruitment from the synovial membrane. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 1996, 78, 721–733. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, H.B.; Giannoudis, P.V.; Boxall, S.A.; McGonagle, D.; Jones, E. The systemic influence of platelet-derived growth factors on bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in fracture patients. BMC Med. 2015, 13, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Bari, C.; Dell’Accio, F.; Tylzanowski, P.; Luyten, F.P. Multipotent mesenchymal stem cells from adult human synovial membrane. Arthritis Rheum. 2001, 44, 1928–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakaguchi, Y.; Sekiya, I.; Yagishita, K.; Muneta, T. Comparison of human stem cells derived from various mesenchymal tissues: Superiority of synovium as a cell source. Arthritis Rheum. 2005, 52, 2521–2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horie, M.; Sekiya, I.; Muneta, T.; Ichinose, S.; Matsumoto, K.; Saito, H.; Murakami, T.; Kobayashi, E. Intra-articular Injected synovial stem cells differentiate into meniscal cells directly and promote meniscal regeneration without mobilization to distant organs in rat massive meniscal defect. Stem Cells 2009, 27, 878–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koga, H.; Shimaya, M.; Muneta, T.; Nimura, A.; Morito, T.; Hayashi, M.; Suzuki, S.; Ju, Y.J.; Mochizuki, T.; Sekiya, I. Local adherent technique for transplanting mesenchymal stem cells as a potential treatment of cartilage defect. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2008, 10, R84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, D.R.; Park, G.Y.; Lee, S.U. The effects of intra-articular platelet-rich plasma injection according to the severity of collagenase-induced knee osteoarthritis in a rabbit model. Ann. Rehabil. Med. 2012, 36, 458–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, C.Q.; Chen, S.B.; Cheng, X.G. The regenerative effect of platelet-rich plasma on healing in large osteochondral defects. Int. Orthop. 2010, 34, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, C.W.; Chen, W.C.; Liu, H.W.; Chen, C.H. Application of synovial fluid mesenchymal stem cells: Platelet-rich plasma hydrogel for focal cartilage defect. J. Exp. Clin. Med. 2014, 6, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuan, R.S.; Boland, G.; Tuli, R. Adult mesenchymal stem cells and cell-based tissue engineering. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2003, 5, 32–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, H.-C.; Chen, W.-C.; Chiang, C.-W.; Chen, L.-Y.; Chang, Y.-C.; Chen, C.-H. Differentiation Effects of Platelet-Rich Plasma Concentrations on Synovial Fluid Mesenchymal Stem Cells from Pigs Cultivated in Alginate Complex Hydrogel. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 18507-18521. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160818507
Tang H-C, Chen W-C, Chiang C-W, Chen L-Y, Chang Y-C, Chen C-H. Differentiation Effects of Platelet-Rich Plasma Concentrations on Synovial Fluid Mesenchymal Stem Cells from Pigs Cultivated in Alginate Complex Hydrogel. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2015; 16(8):18507-18521. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160818507
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Hao-Che, Wei-Chuan Chen, Chih-Wei Chiang, Lei-Yen Chen, Yu-Ching Chang, and Chih-Hwa Chen. 2015. "Differentiation Effects of Platelet-Rich Plasma Concentrations on Synovial Fluid Mesenchymal Stem Cells from Pigs Cultivated in Alginate Complex Hydrogel" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 16, no. 8: 18507-18521. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160818507
APA StyleTang, H.-C., Chen, W.-C., Chiang, C.-W., Chen, L.-Y., Chang, Y.-C., & Chen, C.-H. (2015). Differentiation Effects of Platelet-Rich Plasma Concentrations on Synovial Fluid Mesenchymal Stem Cells from Pigs Cultivated in Alginate Complex Hydrogel. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 16(8), 18507-18521. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160818507