Earthworm Lumbricus rubellus MT-2: Metal Binding and Protein Folding of a True Cadmium-MT
Abstract
:1. Introduction

2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Production of Untagged Recombinant Zinc- and Cadmium-Bound wMT-2

2.2. Proton-Driven Metal Loss

| Metals Bound (n) | Neutral Masses for CdnwMT-2 | Neutral Masses for ZnnwMT-2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Observed | Theoretical | Observed | Theoretical | |
| 8 | 8678.0 | 8681.1 | 8303.5 | 8305.1 |
| 7 | 8570.5 | 8570.8 | 8240.0 | 8241.7 |
| 6 | – | – | 8175.0 | 8178.3 |
| 5 | – | – | 8112.0 | 8114.9 |
| 4 | 8239.9 | 8239.6 | 8050.5 | 8051.5 |
| 3 | – | – | 7984.0 | 7988.1 |
| 2 | – | – | 7916.0 | 7924.7 |
| 1 | 7908.5 | 7908.3 | 7856.5 | 7861.3 |
| 0 (apo) | 7798.0 | 7797.9 | 7796.0 | 7797.9 |
2.3. Affinities of wMT-2 for Cadmium and Zinc

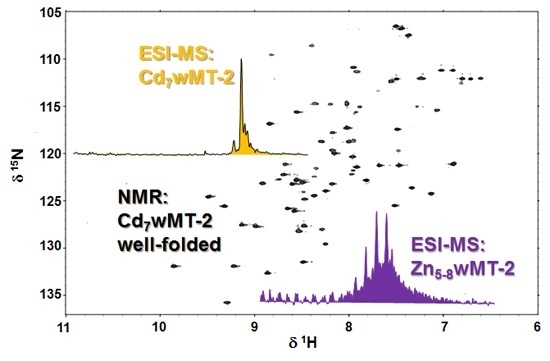
2.4. Folding Behaviour of Zn- and Cd-wMT-2


3. Experimental Section
3.1. Materials
3.2. Protein Expression and Purification
3.3. Determination of Protein Concentration and Metal-Protein Stoichiometries by ICP-OES
3.4. Mass Spectrometry
3.5. Affinity Measurements by 19F NMR Spectroscopy
3.6. 1H NMR Spectroscopy
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Foster, A.W.; Robinson, N.J. Promiscuity and preferences of metallothioneins: The cell rules. BMC Biol. 2011, 9, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blindauer, C.A.; Leszczyszyn, O.I. Metallothioneins: Unparalleled diversity in structures and functions for metal ion homeostasis and more. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2010, 27, 720–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blindauer, C.A. Metallothioneins. In Binding, Transport and Storage of Metal Ions in Biological Cells; Maret, W., Wedd, A.G., Eds.; The Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, UK, 2014; pp. 606–665. [Google Scholar]
- Capdevila, M.; Bofill, R.; Palacios, O.; Atrian, S. State-of-the-art of metallothioneins at the beginning of the 21st century. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2012, 256, 46–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margoshes, M.; Vallee, B.L. A cadmium protein from equine kidney cortex. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1957, 79, 4813–4814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maret, W. Redox biochemistry of mammalian metallothioneins. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2011, 16, 1079–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klaassen, C.D.; Liu, J.; Diwan, B.A. Metallothionein protection of cadmium toxicity. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2009, 238, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallee, B.L. Implications and inferences of metallothionein structure. Exp. Suppl. 1987, 52, 5–16. [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter, R.D. The elusive function of metallothioneins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 8428–8430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blindauer, C.A.; Schmid, R. Cytosolic metal handling in plants: Determinants for zinc specificity in metal transporters and metallothioneins. Metallomics 2010, 2, 510–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dallinger, R.; Berger, B.; Gruber, C.; Hunziker, P.; Stürzenbaum, S. Metallothioneins in terrestrial invertebrates: Structural aspects, biological significance and implications for their use as biomarkers. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2000, 46, 331–346. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Janssens, T.K.S.; Roelofs, D.; van Straalen, N.M. Molecular mechanisms of heavy metal tolerance and evolution in invertebrates. Insect Sci. 2009, 16, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, A.J.; Kille, P.; Stürzenbaum, S.R. Microevolution and ecotoxicology of metals in invertebrates. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 1085–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, J.; Plant, J.A.; Voulvoulis, N.; Oates, C.J.; Ihlenfeld, C. Cadmium levels in Europe: Implications for human health. Environ. Geochem. Health 2010, 32, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- 2015 International Year of Soils. Available online: http://www.fao.org/soils-2015/ (accessed on 30 November 2015).
- Dominguez, J.; Gomez-Brandon, M. The influence of earthworms on nutrient dynamics during the process of vermicomposting. Waste Manag. Res. 2013, 31, 859–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stürzenbaum, S.R.; Andre, J.; Kille, P.; Morgan, A.J. Earthworm genomes, genes and proteins: The (re)discovery of Darwin’s worms. Proc. R. Soc. B 2009, 276, 789–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stürzenbaum, S.R.; Kille, P.; Morgan, A.J. The identification, cloning and characterization of earthworm metallothionein. FEBS Lett. 1998, 431, 437–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeitoun-Ghandour, S.; Charnock, J.M.; Hodson, M.E.; Leszczyszyn, O.I.; Blindauer, C.A.; Stürzenbaum, S.R. The two Caenorhabditis elegans metallothioneins (CeMT-1 and CeMT-2) discriminate between essential zinc and toxic cadmium. FEBS J. 2010, 277, 2531–2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leszczyszyn, O.I.; Zeitoun-Ghandour, S.; Stürzenbaum, S.R.; Blindauer, C.A. Tools for metal ion sorting: In vitro evidence for partitioning of zinc and cadmium in C. elegans metallothionein isoforms. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 448–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, S.L.; Bundy, J.G.; Want, E.J.; Kille, P.; Stürzenbaum, S.R. The metabolomic responses of Caenorhabditis elegans to cadmium are largely independent of metallothionein status, but dominated by changes in cystathionine and phytochelatins. J. Proteome Res. 2009, 8, 3512–3519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dallinger, R.; Berger, B.; Hunziker, P.; Kägi, J.H.R. Metallothionein in snail Cd and Cu Metabolism. Nature 1997, 388, 237–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palacios, O.; Pagani, A.; Perez-Rafael, S.; Egg, M.; Höckner, M.; Brandstätter, A.; Capdevila, M.; Atrian, S.; Dallinger, R. Shaping mechanisms of metal specificity in a family of metazoan metallothioneins: Evolutionary differentiation of mollusc metallothioneins. BMC Biol. 2011, 9, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palacios, O.; Perez-Rafael, S.; Pagani, A.; Dallinger, R.; Atrian, S.; Capdevila, M. Cognate and noncognate metal ion coordination in metal-specific metallothioneins: The Helix pomatia system as a model. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2014, 19, 923–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mustonen, M.; Haimi, J.; Vaisanen, A.; Knott, K.E. Metallothionein gene expression differs in earthworm populations with different exposure history. Ecotoxicology 2014, 23, 1732–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisker, K.V.; Holmstrup, M.; Sørensen, J.G. Variation in metallothionein gene expression is associated with adaptation to copper in the earthworm Dendrobaena octaedra. Comp. Biochem. Phys. C 2013, 157, 220–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Homa, J.; Rorat, A.; Kruk, J.; Cocquerelle, C.; Plytycz, B.; Vandenbulcke, F. Dermal exposure of Eisenia andrei earthworms: Effects of heavy metals on metallothionein and phytochelatin synthase gene expressions in coelomocytes. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2015, 34, 1397–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irizar, A.; Rodriguez, M.P.; Izquierdo, A.; Cancio, I.; Marigomez, I.; Soto, M. Effects of soil organic matter content on cadmium toxicity in Eisenia fetida: Implications for the use of biomarkers and standard toxicity tests. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2015, 68, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stürzenbaum, S.R.; Georgiev, O.; Morgan, A.J.; Kille, P. Cadmium detoxification in earthworms: From genes to cells. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 6283–6289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galay-Burgos, M.; Spurgeon, D.J.; Weeks, J.M.; Stürzenbaum, S.R.; Morgan, A.J.; Kille, P. Developing a new method for soil pollution monitoring using molecular genetic biomarkers. Biomarkers 2003, 8, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stürzenbaum, S.R.; Winters, C.; Galay, M.; Morgan, A.J.; Kille, P. Metal ion trafficking in earthworms—Identification of a cadmium-specific metallothionein. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 34013–34018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owen, J.; Hedley, B.A.; Svendsen, C.; Wren, J.; Jonker, M.J.; Hankard, P.K.; Lister, L.J.; Stürzenbaum, S.R.; Morgan, A.J.; Spurgeon, D.J.; et al. Transcriptome profiling of developmental and xenobiotic responses in a keystone soil animal, the oligochaete annelid Lumbricus rubellus. BMC Genom. 2008, 9, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Günther, V.; Lindert, U.; Schaffner, W. The taste of heavy metals: Gene regulation by MTF-1. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1823, 1416–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Höckner, M.; Dallinger, R.; Stürzenbaum, S.R. Metallothionein gene activation in the earthworm (Lumbricus rubellus). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 460, 537–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, A.J.; Stürzenbaum, S.R.; Winters, C.; Grime, G.W.; Abd Aziz, N.A.; Kille, P. Differential metallothionein expression in earthworm (Lumbricus rubellus) tissues. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2004, 57, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marino, F.; Stürzenbaum, S.R.; Kille, P.; Morgan, A.J. Cu–Cd interactions in earthworms maintained in laboratory microcosms: The examination of a putative copper paradox. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C 1998, 120, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bundy, J.G.; Sidhu, J.K.; Rana, F.; Spurgeon, D.J.; Svendsen, C.; Wren, J.F.; Stürzenbaum, S.R.; Morgan, A.J.; Kille, P. “Systems toxicology” approach identifies coordinated metabolic responses to copper in a terrestrial non-model invertebrate, the earthworm Lumbricus rubellus. BMC Biol. 2008, 6, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruber, C.; Stürzenbaum, S.; Gehrig, P.; Sack, R.; Hunziker, P.; Berger, B.; Dallinger, R. Isolation and characterization of a self-sufficient one-domain protein—(Cd)-metallothionein from Eisenia foetida. Eur. J. Biochem. 2000, 267, 573–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngu, T.T.; Stürzenbaum, S.R.; Stillman, M.J. Cadmium binding studies to the earthworm Lumbricus rubellus metallothionein by electrospray mass spectrometry and circular dichroism spectroscopy. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 351, 229–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loo, J.A. Electrospray ionization mass spectrometry: A technology for studying noncovalent macromolecular complexes. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2000, 200, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehrig, P.M.; You, C.H.; Dallinger, R.; Gruber, C.; Brouwer, M.; Kägi, J.H.R.; Hunziker, P.E. Electrospray ionization mass spectrometry of zinc, cadmium, and copper metallothioneins: Evidence for metal-binding cooperativity. Protein Sci. 2000, 9, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaia, J.; Fabris, D.; Wei, D.; Karpel, R.L.; Fenselau, C. Monitoring metal ion flux in reactions of metallothionein and drug-modified metallothionein by electrospray mass spectrometry. Protein Sci. 1998, 7, 2398–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palumaa, P.; Tammiste, I.; Kruusel, K.; Kangur, L.; Jornvall, H.; Sillard, R. Metal binding of metallothionein-3 versus metallothionein-2: Lower affinity and higher plasticity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Proteins Proteom. 2005, 1747, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leszczyszyn, O.I.; Blindauer, C.A. Zinc transfer from the embryo-specific metallothionein EC from wheat: A case study. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2010, 12, 13408–13418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutherland, D.E. K.; Willans, M.J.; Stillman, M.J. Single domain metallothioneins: Supermetalation of human MT 1A. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 3290–3299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palacios, O.; Espart, A.; Espin, J.; Ding, C.; Thiele, D.J.; Atrian, S.; Capdevila, M. Full characterization of the Cu-, Zn-, and Cd-binding properties of CnMT1 and CnMT2, two metallothioneins of the pathogenic fungus Cryptococcus neoformans acting as virulence factors. Metallomics 2014, 6, 279–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kebarle, P.; Verkerk, U.H. Electrospray: From ions in solution to ions in the gas phase, what we know now. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2009, 28, 898–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Rafael, S.; Atrian, S.; Capdevila, M.; Palacios, O. Differential ESI-MS behaviour of highly similar metallothioneins. Talanta 2011, 83, 1057–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.L.; Wojciechowski, M.; Fenselau, C. Assessment of metals in reconstituted metallothioneins by electrospray mass-spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 1993, 65, 1355–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braun, W.; Wagner, G.; Wörgötter, E.; Vašák, M.; Kägi, J.H.R.; Wüthrich, K. Polypeptide fold in the 2 metal-clusters of metallothionein-2 by nuclear-magnetic-resonance in solution. J. Mol. Biol. 1986, 187, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bofill, R.; Capdevila, M.; Atrian, S. Independent metal-binding features of recombinant metallothioneins convergently draw a step gradation between Zn- and Cu-thioneins. Metallomics 2009, 1, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutherland, D.E.K.; Summers, K.L.; Stillman, M.J. Noncooperative metalation of metallothionein 1A and its isolated domains with zinc. Biochemistry 2012, 51, 6690–6700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutherland, D.E.K.; Stillman, M.J. Challenging conventional wisdom: Single domain Metallothioneins. Metallomics 2014, 6, 702–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blindauer, C.A.; Harrison, M.D.; Robinson, A.K.; Parkinson, J.A.; Bowness, P.W.; Sadler, P.J.; Robinson, N.J. Multiple bacteria encode metallothioneins and SmtA-like zinc fingers. Mol. Microbiol. 2002, 45, 1421–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leszcyszyn, O.I.; Schmid, R.; Blindauer, C.A. Toward a property/function relationship for metallothioneins: Histidine coordination and unusual cluster composition in a zinc-metallothionein from plants. Proteins 2007, 68, 922–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasler, D.W.; Jensen, L.T.; Zerbe, O.; Winge, D.R.; Vašák, M. Effect of the two conserved prolines of human growth inhibitory factor (metallothionein-3) on its biological activity and structure fluctuation: Comparison with a mutant protein. Biochemistry 2000, 39, 14567–14575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leszczyszyn, O.I.; White, C.R.J.; Blindauer, C.A. The isolated Cys(2)His(2) site in EC metallothionein mediates metal-specific protein folding. Mol. BioSyst. 2010, 6, 1592–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palumaa, P.; Njunkova, O.; Pokras, L.; Eriste, E.; Jornvall, H.; Sillard, R. Evidence for non-isostructural replacement of Zn2+ with Cd2+ in the beta-domain of brain-specific metallothionein-3. FEBS Lett. 2002, 527, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leszczyszyn, O.I.; Imam, H.T.; Blindauer, C.A. Diversity and distribution of plant metallothioneins: A review of structure, properties and functions. Metallomics 2013, 5, 1146–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellman, G.L. Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1959, 82, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparky 3. Available online: https://www.cgl.ucsf.edu/home/sparky/ (accessed on 30 November 2015).
- Bogumil, R.; Faller, P.; Pountney, D.L.; Vašák, M. Evidence for Cu(I) clusters and Zn(II) clusters in neuronal growth-inhibitory factor isolated from bovine brain. Eur. J. Biochem. 1996, 238, 698–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Artells, E.; Palacios, O.; Capdevila, M.; Atrian, S. In vivo-folded metal-metallothionein 3 complexes reveal the Cu-thionein rather than Zn-thionein character of this brain-specific mammalian metallothionein. FEBS J. 2014, 281, 1659–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peroza, E.A.; Schmucki, R.; Güntert, P.; Freisinger, E.; Zerbe, O. The β(e)-domain of wheat EC-1 metallothionein: A metal-binding domain with a distinctive structure. J. Mol. Biol. 2009, 387, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Rafael, S.; Monteiro, F.; Dallinger, R.; Atrian, S.; Palacios, O.; Capdevila, M. Cantareus aspersus metallothionein metal binding abilities: The unspecific CaCd/CuMT isoform provides hints about the metal preference determinants in metallothioneins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Proteins Proteom. 2014, 1844, 1694–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Rafael, S.; Mezger, A.; Lieb, B.; Dallinger, R.; Capdevila, M.; Palacios, O.; Atrian, S. The metal binding abilities of Megathura crenulata metallothionein (McMT) in the frame of gastropoda MTs. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2012, 108, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Höckner, M.; Stefanon, K.; de Vaufleury, A.; Monteiro, F.; Perez-Rafael, S.; Palacios, O.; Capdevila, M.; Atrian, S.; Dallinger, R. Physiological relevance and contribution to metal balance of specific and non-specific metallothionein isoforms in the garden snail. Biometals 2011, 24, 1079–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bofill, R.; Orihuela, R.; Romagosa, M.; Domenech, J.; Atrian, S.; Capdevila, M. Caenorhabditis elegans metallothionein isoform specificity—Metal binding abilities and the role of histidine in CeMT1 and CeMT2. FEBS J. 2009, 276, 7040–7069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wickner, S.; Maurizi, M.R.; Gottesman, S. Posttranslational quality control: Folding, refolding, and degrading proteins. Science 1999, 286, 1888–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kowald, G.R.; Stürzenbaum, S.R.; Blindauer, C.A. Earthworm Lumbricus rubellus MT-2: Metal Binding and Protein Folding of a True Cadmium-MT. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17010065
Kowald GR, Stürzenbaum SR, Blindauer CA. Earthworm Lumbricus rubellus MT-2: Metal Binding and Protein Folding of a True Cadmium-MT. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2016; 17(1):65. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17010065
Chicago/Turabian StyleKowald, Gregory R., Stephen R. Stürzenbaum, and Claudia A. Blindauer. 2016. "Earthworm Lumbricus rubellus MT-2: Metal Binding and Protein Folding of a True Cadmium-MT" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 17, no. 1: 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17010065
APA StyleKowald, G. R., Stürzenbaum, S. R., & Blindauer, C. A. (2016). Earthworm Lumbricus rubellus MT-2: Metal Binding and Protein Folding of a True Cadmium-MT. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(1), 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17010065