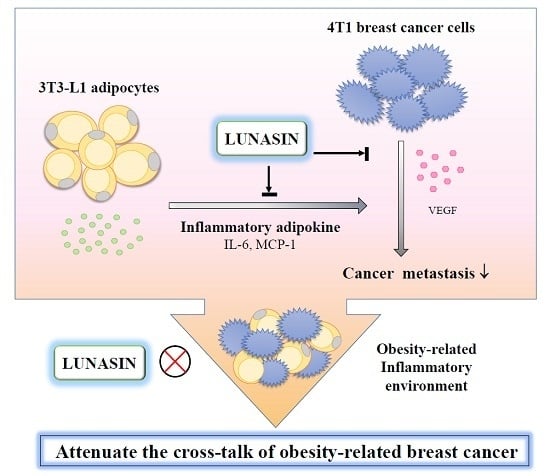
Lunasin Attenuates Obesity-Associated Metastasis of 4T1 Breast Cancer Cell through Anti-Inflammatory Property
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Leptin and Adipocyte-Conditioned Medium (Ad-CM) Stimulated 4T1 Breast Cancer Cell Proliferation
2.2. Lunasin Inhibited 4T1 Cell Metastasis and Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) Production
2.3. Lunasin Did Not Effect 3T3-L1 Adipocytes Differentiation and Lipid Accumulation
2.4. Lunasin Inhibited Pro-Inflammatory Adipokine Secretion in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture and Reagents
4.2. 3T3-L1 Fibroblast Differentiation to Adipocytes
Quantification of 3T3-L1 Lipid Accumulation
4.3. Generation of Conditioned Media
4.4. Cell Metastasis Assay
4.5. Cell Viability Assay
4T1 Cells Cultured in Ad-CM
4.6. Determination of Inflammatory Cytokine Production by Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
4.7. Adipocyte Inflammatory Models
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Ad-CM | adipocyte-conditioned medium |
| TNF-α | tumor necrosis factor |
| RAW-CM | RAW 264.7 cell-conditioned medium |
| VEGF | vascular endothelial growth factor |
| IL-6 | interleukin-6 |
| MCP-1 | macrophage chemoattractant protein |
| LPS | lipopolysaccharide |
| NF-κB | nuclear factor-κB |
| ELISA | enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
| MTT | methylthiazole tetrazolium |
| EGF | epidermal growth factor |
| PPAR-γ | peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ |
| LDL | low density lipoprotein |
| HMG | hepatic 3-hydroxy-3-methyl-glutaryl |
References
- World Health Organization (WHO) Media Center, Geneva. Obesity and Overweight. Facts about Overweight and Obesity. Available online: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs311/en/# (accessed on 5 May 2016).
- Catalan, V.; Gomez-Ambrosi, J.; Rodriguez, A.; Fruhbeck, G. Adipose tissue immunity and cancer. Front. Physiol. 2013, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundaram, S.; Johnson, A.R.; Makowski, L. Obesity, metabolism and the microenvironment: Links to cancer. J. Carcinog. 2013, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mraz, M.; Haluzik, M. The role of adipose tissue immune cells in obesity and low-grade inflammation. J. Endocrinol. 2014, 222, R113–R127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alegre, M.M.; Knowles, M.H.; Robison, R.A.; O'Neill, K.L. Mechanics behind breast cancer prevention—Focus on obesity, exercise and dietary fat. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2013, 14, 2207–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Pergola, G.; Silvestris, F. Obesity as a major risk factor for cancer. J. Obes. 2013, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quail, D.F.; Joyce, J.A. Microenvironmental regulation of tumor progression and metastasis. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 1423–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dushyanthen, S.; Beavis, P.A.; Savas, P.; Teo, Z.L.; Zhou, C.; Mansour, M.; Darcy, P.K.; Loi, S. Relevance of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in breast cancer. BMC Med. 2015, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allavena, P.; Garlanda, C.; Borrello, M.G.; Sica, A.; Mantovani, A. Pathways connecting inflammation and cancer. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2008, 18, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, N.; Afaq, F.; Mukhtar, H. Cancer chemoprevention through dietary antioxidants: Progress and promise. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2008, 10, 475–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korniluk, A.; Koper, O.; Kemona, H.; Dymicka-Piekarska, V. From inflammation to cancer. Ir. J. Med. Sci. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ford, N.A.; Lashinger, L.M.; Allott, E.H.; Hursting, S.D. Mechanistic targets and phytochemical strategies for breaking the obesity-cancer link. Front. Oncol. 2013, 3, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galvez, A.F.; de Lumen, B.O. A soybean cDNA encoding a chromatin-binding peptide inhibits mitosis of mammalian cells. Nat. Biotechnol. 1999, 17, 495–500. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hernandez-Ledesma, B.; Hsieh, C.C.; de Lumen, B.O. Chemopreventive properties of peptide lunasin: A review. Protein Pept. Lett. 2013, 20, 424–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez-Ledesma, B.; Hsieh, C.C.; de Lumen, B.O. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of cancer preventive peptide lunasin in RAW 264.7 macrophages. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 390, 803–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Mejia, E.G.; Dia, V.P. Lunasin and lunasin-like peptides inhibit inflammation through suppression of NF-κB pathway in the macrophage. Peptides 2009, 30, 2388–2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dia, V.P.; Wang, W.; Oh, V.L.; Lumen, B.O.D.; de Mejia, E.G. Isolation, purification and characterisation of lunasin from defatted soybean flour and in vitro evaluation of its anti-inflammatory activity. Food Chem. 2009, 114, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cam, A.; de Mejia, E.G. RGD-peptide lunasin inhibits Akt-mediated NF-κB activation in human macrophages through interaction with the αvβ3 integrin. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2012, 56, 1569–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, G.; Gonzalez-Perez, R.R. Leptin-cytokine crosstalk in breast cancer. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2014, 382, 570–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.T.; Du, Y.; Yamaguchi, H.; Hsu, J.M.; Kuo, H.P.; Hortobagyi, G.N.; Hung, M.C. Targeting the IKKβ/mTOR/VEGF signaling pathway as a potential therapeutic strategy for obesity-related breast cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2012, 11, 2212–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubois, V.; Delort, L.; Billard, H.; Vasson, M.P.; Caldefie-Chezet, F. Breast cancer and obesity: In vitro interferences between adipokines and proangiogenic features and/or antitumor therapies? PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e58541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, F.; Schimming, A.; Jaeger, D.; Podar, K. Targeting the tumor microenvironment: Focus on angiogenesis. J. Oncol. 2012, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kristensen, T.B.; Knutsson, M.L.; Wehland, M.; Laursen, B.E.; Grimm, D.; Warnke, E.; Magnusson, N.E. Anti-vascular endothelial growth factor therapy in breast cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 23024–23041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, C.-C.; Hernández-Ledesma, B.; Jeong, H.J.; Park, J.H.; de Lumen, B.O. Complementary roles in cancer prevention: Protease inhibitor makes the cancer preventive peptide lunasin bioavailable. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e8890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hsieh, C.C.; Hernandez-Ledesma, B.; de Lumen, B.O. Lunasin, a novel seed peptide, sensitizes human breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells to aspirin-arrested cell cycle and induced apoptosis. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 2010, 186, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Q.; Pan, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Li, H.; Liu, D.; Li, H. Lunasin suppresses the migration and invasion of breast cancer cells by inhibiting matrix metalloproteinase-2/-9 via the FAK/AKT/ERK and NF-κB signaling pathways. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 36, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saxena, N.K.; Sharma, D. Multifaceted leptin network: The molecular connection between obesity and breast cancer. J. Mammary Gland Biol. Neoplasia 2013, 18, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues Viana, C.T.; Castro, P.R.; Marques, S.M.; Paz Lopes, M.T.; Goncalves, R.; Campos, P.P.; Andrade, S.P. Differential contribution of acute and chronic inflammation to the development of murine mammary 4T1 tumors. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0130809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarogoulidis, P.; Tsakiridis, K.; Karapantzou, C.; Lampaki, S.; Kioumis, I.; Pitsiou, G.; Papaiwannou, A.; Hohenforst-Schmidt, W.; Huang, H.; Kesisis, G.; et al. Use of proteins as biomarkers and their role in carcinogenesis. J. Cancer 2015, 6, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Liu, B.L.; Liu, K.; Tang, N.; Huang, J.; An, Y.; Li, L. Establishment of the insulin resistance induced by inflammatory response in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes cell line. Inflammation 2008, 31, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allavena, P.; Mantovani, A. Immunology in the clinic review series; focus on cancer: Tumour-associated macrophages: Undisputed stars of the inflammatory tumour microenvironment. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2012, 167, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madera, L.; Greenshields, A.; Coombs, M.R.; Hoskin, D.W. 4T1 murine mammary carcinoma cells enhance macrophage-mediated innate inflammatory responses. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0133385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández-Ledesma, B.; Hsieh, C.C.; de Lumen, B.O. Lunasin and Bowman-Birk protease inhibitor (BBI) in US commercial soy foods. Food Chem. 2009, 115, 574–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.J.; Jeong, J B.; Hsieh, C.C.; Hernandez-Ledesma, B.; de Lumen, B.O. Lunasin is prevalent in barley and is bioavailable and bioactive in in vivo and in vitro studies. Nutr. Cancer 2010, 62, 1113–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dia, V.P.; Torres, S.; de Lumen, B.O.; Erdman, J.W.; de Mejia, E.G. Presence of lunasin in plasma of men after soy protein consumption. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 1260–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galvez, A.F. Abstract 10693: Identification of lunasin as the active component in soy protein responsible for reducing LDL cholesterol and risk of cardiovascular disease. Circulation 2012, 126, A10693. [Google Scholar]
- Galvez, A.F.; Matel, H.H.; Iveya, J.; Bowles, D. Lunasin-Enriched Soy Extract (LunaRich X™), in Combination with the Dietary Supplement Reliv Now, Reduces Free Fatty Acid by Increasing Plasma Leptin and Adiponectin Levels in LDL-Receptor Mutant Pigs. Available online: https://reliv-static.s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/art/FlyersLetters/USCanada/LRXRelivNowStudy-web.pdf (accessed on 19 September 2013).
- Cam, A.; Sivaguru, M.; Gonzalez de Mejia, E. Endocytic mechanism of internalization of dietary peptide lunasin into macrophages in inflammatory condition associated with cardiovascular disease. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e72115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Zhu, J.; Tung, C.-Y.; Gardiner, G.; Wang, Q.; Chang, H.-C.; Zhou, B. Lunasin alleviates allergic airway inflammation while increases antigen-specific tregs. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0115330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jia, S.; Zhang, S.; Yuan, H.; Chen, N. Lunasin inhibits cell proliferation via apoptosis and reduces the production of proinflammatory cytokines in cultured rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, C.C.; Huang, Y.S. Aspirin breaks the crosstalk between 3T3-L1 adipocytes and 4T1 breast cancer cells by regulating cytokine production. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0147161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Lunasin Versus Cytokine | IL-6 | MCP-1 |
|---|---|---|
| Correlation | −0.545 | −0.861 |
| p-Value | 0.029 | 0.006 |
| Lunasin Versus Cytokine | IL-6 | MCP-1 |
|---|---|---|
| Correlation | 0.026 | −0.651 |
| p-Value | 0.926 | 0.006 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hsieh, C.-C.; Wang, C.-H.; Huang, Y.-S. Lunasin Attenuates Obesity-Associated Metastasis of 4T1 Breast Cancer Cell through Anti-Inflammatory Property. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 2109. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17122109
Hsieh C-C, Wang C-H, Huang Y-S. Lunasin Attenuates Obesity-Associated Metastasis of 4T1 Breast Cancer Cell through Anti-Inflammatory Property. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2016; 17(12):2109. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17122109
Chicago/Turabian StyleHsieh, Chia-Chien, Chih-Hsuan Wang, and Yu-Shan Huang. 2016. "Lunasin Attenuates Obesity-Associated Metastasis of 4T1 Breast Cancer Cell through Anti-Inflammatory Property" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 17, no. 12: 2109. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17122109
APA StyleHsieh, C. -C., Wang, C. -H., & Huang, Y. -S. (2016). Lunasin Attenuates Obesity-Associated Metastasis of 4T1 Breast Cancer Cell through Anti-Inflammatory Property. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(12), 2109. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17122109