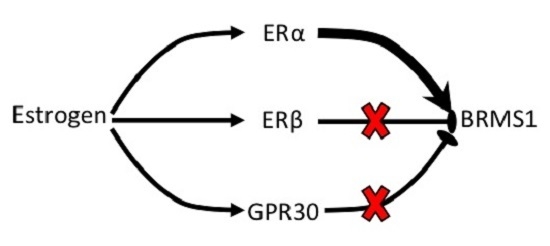
ERα Mediates Estrogen-Induced Expression of the Breast Cancer Metastasis Suppressor Gene BRMS1
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. ER Subtype Expression in MCF-7, TTU-1, MDA-MB-231, and SKBR3 Cell Lines

2.2. E2 and the ERα Agonist PPT Induced BRMS1 Expression in MCF-7 Cells





2.3. E2 and the ERα Agonist PPT Increased BRMS1 Transcription in MCF-7 Cells

2.4. siRNA Inhibition of ERα Expression Decreased E2 and PPT-Induced BRMS1 Expression

3. Discussion

4. Experimental Section
4.1. Cell Culture and Treatment
4.2. Chemical Reagents and Antibodies
4.3. Western Blot Analysis
4.4. RNA Isolation and Quantitative RT-PCR
- BRMS1-V12: Forward-5′-ATTCAGGTGGCAGGGATCTACAAGG-3′
- BRMS1-V12: Reverse-5′-GCAGCAGCTTCTCACTCTCCA-3′
- BRMS1-V1: Forward-5′-CGACATCCTGGAGGACTGGACAGCCA-3′
- BRMS1-V1: Reverse-5′-TGAACAGCAGGGTCAAGGTCCATCCGA-3′
- Forward-5′-CACCACCATGGAGAAGGCTG-3′
- Reverse-5′-GAGGCATTGCTGATGATCTTGAGG-3′
- Step 1: 10 min at 95 °C (enzyme activation)
- Step 2: 40 cycles each of 15 s at 95 °C (denature) and 1 min at 60 °C (anneal/extend).
- 15 s at 95 °C, 1 min at 60 °C, and 15 s at 95 °C.
- Change all Ct values, which were reported as greater than 35 or N/A (undetermined) to 35. Any Ct value equal to 35 was considered a negative call.
- Calculate the average Ct value of each time interval treatment across three replicates.
- Calculate the ΔCt for each time interval treatment in that groupΔCt = average Ct − average of GAPDH (housekeeping gene) for that group
- Calculate ΔΔCtΔΔCt = ΔCt − ΔCt control
- Calculate the fold-change2−ΔΔCt = 2−ΔCt experiment/2−ΔCt control
4.5. siRNA Knockdown
4.6. Data Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BRMS1 | breast cancer metastasis suppressor 1 |
| CRE | cyclic AMP-response element |
| DPN | 2,3-bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)-proprionitrile |
| E2 | estradiol |
| ER | estrogen receptor |
| ERE | estrogen response element |
| G-1 | (±)-1-[(3aR*,4S*,9bS*)-4-(6-Bromo-1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)-3a,4,5,9b-tetrahydro-3H-cyclopenta[c]quinolin-8-yl]-ethanone |
| HDAC | histone deacetylase |
| Hsp | heat shock protein |
| mSin3 | mammalian suppressor of defective silencing 3 |
| PPT | (4,4′,4″-(4-propyl-[1H]-pyrazole-1,3,5-triyl) tris-phenol |
References
- Yamaguchi, Y. Microenvironmental regulation of estrogen signals in breast cancer. Breast Cancer 2007, 14, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furberg, H.; Newman, B.; Moorman, P.; Millikan, R. Lactation and breast cancer risk. Int. J. Epidemiol. 1999, 28, 396–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, M.G. Steroid and related receptors. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 1993, 5, 499–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, K.A.; Korach, K.S. Estrogen receptors and human disease: An update. Arch. Toxicol. 2012, 86, 1491–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Revankar, C.M.; Cimino, D.F.; Sklar, L.A.; Arterburn, J.B.; Prossnitz, E.R. A transmembrane intracellular estrogen receptor mediates rapid cell signaling. Science 2005, 307, 1625–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prossnitz, E.R.; Arterburn, J.B.; Sklar, L.A. GPR30: A G protein-coupled receptor for estrogen. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2007, 265, 138–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rollerova, E.; Urbancikova, M. Intracellular estrogen receptors, their characterization and function (Review). Endocr. Regul. 2000, 34, 203–218. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schiff, R.; Massarweh, S.A.; Shou, J.; Bharwani, L.; Arpino, G.; Rimawi, M.; Osborne, C.K. Advanced concepts in estrogen receptor biology and breast cancer endocrine resistance: Implicated role of growth factor signaling and estrogen receptor coregulators. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2005, 56, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiff, R.; Osborne, C.K. Endocrinology and hormone therapy in breast cancer: New insight into estrogen receptor-α function and its implication for endocrine therapy resistance in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2005, 7, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paech, K.; Webb, P.; Kuiper, G.G.; Nilsson, S.; Gustafsson, J.; Kushner, P.J.; Scanlan, T.S. Differential ligand activation of estrogen receptors ERα and ERβ at AP1 sites. Science 1997, 277, 1508–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webb, P.; Nguyen, P.; Valentine, C.; Lopez, G.N.; Kwok, G.R.; McInerney, E.; Katzenellenbogen, B.S.; Enmark, E.; Gustafsson, J.A.; Nilsson, S.; et al. The estrogen receptor enhances AP-1 activity by two distinct mechanisms with different requirements for receptor transactivation functions. Mol. Endocrinol. 1999, 13, 1672–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kushner, P.J.; Agard, D.A.; Greene, G.L.; Scanlan, T.S.; Shiau, A.K.; Uht, R.M.; Webb, P. Estrogen receptor pathways to AP-1. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2000, 74, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakacka, M.; Ito, M.; Weiss, J.; Chien, P.Y.; Gehm, B.D.; Jameson, J.L. Estrogen receptor binding to DNA is not required for its activity through the nonclassical AP1 pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 13615–13621. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Qin, C.; Singh, P.; Safe, S. Transcriptional activation of insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-4 by 17β-estradiol in MCF-7 cells: Role of estrogen receptor-Sp1 complexes. Endocrinology 1999, 140, 2501–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabbah, M.; Courilleau, D.; Mester, J.; Redeuilh, G. Estrogen induction of the cyclin D1 promoter: Involvement of a cAMP response-like element. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 11217–11222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prossnitz, E.R.; Arterburn, J.B.; Smith, H.O.; Oprea, T.I.; Sklar, L.A.; Hathaway, H.J. Estrogen signaling through the transmembrane G protein-coupled receptor GPR30. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2008, 70, 165–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prossnitz, E.R.; Oprea, T.I.; Sklar, L.A.; Arterburn, J.B. The ins and outs of GPR30: A transmembrane estrogen receptor. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2008, 109, 350–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prossnitz, E.R.; Sklar, L.A.; Oprea, T.I.; Arterburn, J.B. GPR30: A novel therapeutic target in estrogen-related disease. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2008, 29, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osborne, C.K.; Hobbs, K.; Clark, G.M. Effect of estrogens and antiestrogens on growth of human breast cancer cells in athymic nude mice. Cancer Res. 1985, 45, 584–590. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dickson, R.B.; Bates, S.E.; McManaway, M.E.; Lippman, M.E. Characterization of estrogen responsive transforming activity in human breast cancer cell lines. Cancer Res. 1986, 46, 1707–1713. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dubik, D.; Shiu, R.P. Mechanism of estrogen activation of c-myc oncogene expression. Oncogene 1992, 7, 1587–1594. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.M.; Albanese, C.; Anderson, C.M.; Hilty, K.; Webb, P.; Uht, R.M.; Price, R.H., Jr.; Pestell, R.G.; Kushner, P.J. Opposing action of estrogen receptors α and β on cyclin D1 gene expression. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 24353–24360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, G.; Weihua, Z.; Warner, M.; Gustafsson, J.A. Estrogen receptors ER α and ER β in proliferation in the rodent mammary gland. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 3739–3746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.; Lee, E.J.; Madison, L.D.; Lazennec, G. Expression of estrogen receptor β in prostate carcinoma cells inhibits invasion and proliferation and triggers apoptosis. FEBS Lett. 2004, 566, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartusik, D.; Tomanek, B.; Lattova, E.; Perreault, H.; Fallone, G. Combined treatment of human MCF-7 breast carcinoma with antibody, cationic lipid and hyaluronic acid using ex vivo assays. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2010, 51, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rochefort, H.; Platet, N.; Hayashido, Y.; Derocq, D.; Lucas, A.; Cunat, S.; Garcia, M. Estrogen receptor mediated inhibition of cancer cell invasion and motility: An overview. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1998, 65, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platet, N.; Cunat, S.; Chalbos, D.; Rochefort, H.; Garcia, M. Unliganded and liganded estrogen receptors protect against cancer invasion via different mechanisms. Mol. Endocrinol. 2000, 14, 999–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, Y.; Bommer, G.T.; Feng, Y.; Wiese, A.B.; Fearon, E.R.; Cho, K.R. Loss of estrogen receptor 1 enhances cervical cancer invasion. Am. J. Pathol. 2010, 177, 884–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazumdar, A.; Wang, R.A.; Mishra, S.K.; Adam, L.; Bagheri-Yarmand, R.; Mandal, M.; Vadlamudi, R.K.; Kumar, R. Transcriptional repression of oestrogen receptor by metastasis-associated protein 1 corepressor. Nat. Cell Biol. 2001, 3, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lin, K.H.; Wang, W.J.; Wu, Y.H.; Cheng, S.Y. Activation of antimetastatic Nm23-H1 gene expression by estrogen and its α-receptor. Endocrinology 2002, 143, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christgen, M.; Bruchhardt, H.; Ballmaier, M.; Krech, T.; Langer, F.; Kreipe, H.; Lehmann, U. KAI1/CD82 is a novel target of estrogen receptor-mediated gene repression and downregulated in primary human breast cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2008, 123, 2239–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Yu, W.; Liu, M. Regulation of KiSS1 gene expression. Peptides 2009, 30, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, T.; Fukada, H.; Shimizu, M.; Hiramatsu, N.; Hara, A. Quantification of serum levels of precursors to vitelline envelope proteins (choriogenins) and vitellogenin in estrogen treated Masu salmon, Oncorhynchus masou. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2004, 136, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seraj, M.J.; Samant, R.S.; Verderame, M.F.; Welch, D.R. Functional evidence for a novel human breast carcinoma metastasis suppressor, BRMS1, encoded at chromosome 11q13. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 2764–2769. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Seraj, M.J.; Harding, M.A.; Gildea, J.J.; Welch, D.R.; Theodorescu, D. The relationship of BRMS1 and RhoGDI2 gene expression to metastatic potential in lineage related human bladder cancer cell lines. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2000, 18, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shevde, L.A.; Samant, R.S.; Goldberg, S.F.; Sikaneta, T.; Alessandrini, A.; Donahue, H.J.; Mauger, D.T.; Welch, D.R. Suppression of human melanoma metastasis by the metastasis suppressor gene, BRMS1. Exp. Cell Res. 2002, 273, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Lin, Q.D.; Di, W. Suppression of human ovarian carcinoma metastasis by the metastasis-suppressor gene, BRMS1. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2006, 16, 522–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, J.; He, X.; Ding, H.; Zhang, T. BRMS1 regulates apoptosis in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2015, 71, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Yamashita, H.; Toyama, T.; Yamamoto, Y.; Kawasoe, T.; Iwase, H. Reduced expression of the breast cancer metastasis suppressor 1 mRNA is correlated with poor progress in breast cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 6410–6414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hicks, D.G.; Yoder, B.J.; Short, S.; Tarr, S.; Prescott, N.; Crowe, J.P.; Dawson, A.E.; Budd, G.T.; Sizemore, S.; Cicek, M.; et al. Loss of breast cancer metastasis suppressor 1 protein expression predicts reduced disease-free survival in subsets of breast cancer patients. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 6702–6708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frolova, N.; Edmonds, M.D.; Bodenstine, T.M.; Seitz, R.; Johnson, M.R.; Feng, R.; Welch, D.R.; Frost, A.R. A shift from nuclear to cytoplasmic breast cancer metastasis suppressor 1 expression is associated with highly proliferative estrogen receptor-negative breast cancers. Tumour Biol. 2009, 30, 148–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuiper, G.G.; Carlsson, B.; Grandien, K.; Enmark, E.; Haggblad, J.; Nilsson, S.; Gustafsson, J.A. Comparison of the ligand binding specificity and transcript tissue distribution of estrogen receptors α and β. Endocrinology 1997, 138, 863–870. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Thomas, P.; Pang, Y.; Filardo, E.J.; Dong, J. Identity of an estrogen membrane receptor coupled to a G protein in human breast cancer cells. Endocrinology 2005, 146, 624–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrington, W.R.; Sheng, S.; Barnett, D.H.; Petz, L.N.; Katzenellenbogen, J.A.; Katzenellenbogen, B.S. Activities of estrogen receptor α- and β-selective ligands at diverse estrogen responsive gene sites mediating transactivation or transrepression. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2003, 206, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, B.D.; Furneaux, H.; White, B.A. The micro-ribonucleic acid (miRNA) miR-206 targets the human estrogen receptor-α (ERα) and represses ERα messenger RNA and protein expression in breast cancer cell lines. Mol. Endocrinol. 2007, 21, 1132–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Leva, G.; Gasparini, P.; Piovan, C.; Ngankeu, A.; Garofalo, M.; Taccioli, C.; Iorio, M.V.; Li, M.; Volinia, S.; Alder, H.; et al. MicroRNA cluster 221–222 and estrogen receptor α interactions in breast cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2010, 102, 706–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strom, A.; Hartman, J.; Foster, J.S.; Kietz, S.; Wimalasena, J.; Gustafsson, J.A. Estrogen receptor β inhibits 17β-estradiol-stimulated proliferation of the breast cancer cell line T47D. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 1566–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okamura, H. Clock genes in cell clocks: Roles, actions, and mysteries. J. Biol. Rhythm. 2004, 19, 388–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunter, T. The age of crosstalk: Phosphorylation, ubiquitination, and beyond. Mol. Cell 2007, 28, 730–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eide, E.J.; Woolf, M.F.; Kang, H.; Woolf, P.; Hurst, W.; Camacho, F.; Vielhaber, E.L.; Giovanni, A.; Virshup, D.M. Control of mammalian circadian rhythm by CKIepsilon-regulated proteasome-mediated PER2 degradation. Mol. Cell Biol. 2005, 25, 2795–2807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silberstein, G.B.; van Horn, K.; Hraβ-Robinson, E.; Compton, J. Estrogen-triggered delays in mammary gland gene expression during the estrous cycle: Evidence for a novel timing system. J. Endocrinol. 2006, 190, 225–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattingly, K.A.; Ivanova, M.M.; Riggs, K.A.; Wickramasinghe, N.S.; Barch, M.J.; Klinge, C.M. Estradiol stimulates transcription of nuclear respiratory factor-1 and increases mitochondrial biogenesis. Mol. Endocrinol. 2008, 22, 609–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cadenas, C.; van de Sandt, L.; Edlund, K.; Lohr, M.; Hellwig, B.; Marchan, R.; Schmidt, M.; Rahnenfuhrer, J.; Oster, H.; Hengstler, J.G. Loss of circadian clock gene expression is associated with tumor progression in breast cancer. Cell Cycle 2014, 13, 3282–3291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Ferguson, A.T.; Nass, S.J.; Phillips, D.L.; Butash, K.A.; Wang, S.M.; Herman, J.G.; Davidson, N.E. Transcriptional activation of estrogen receptor α in human breast cancer cells by histone deacetylase inhibition. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 6890–6894. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kawai, H.; Li, H.; Avraham, S.; Jiang, S.; Avraham, H.K. Overexpression of histone deacetylase HDAC1 modulates breast cancer progression by negative regulation of estrogen receptor α. Int. J. Cancer 2003, 107, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, H.H.; Bird, A. Histone deacetylases: Silencers for hire. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2000, 25, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurst, D.R. Metastasis suppression by BRMS1 associated with SIN3 chromatin remodeling complexes. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2012, 31, 641–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Smith, P.W.; Jones, D.R. Breast cancer metastasis suppressor 1 functions as a corepressor by enhancing histone deacetylase 1-mediated deacetylation of RelA/p65 and promoting apoptosis. Mol. Cell Biol. 2006, 26, 8683–8696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cicek, M.; Fukuyama, R.; Cicek, M.S.; Sizemore, S.; Welch, D.R.; Sizemore, N.; Casey, G. BRMS1 contributes to the negative regulation of uPA gene expression through recruitment of HDAC1 to the NF-κB binding site of the uPA promoter. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2009, 26, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khotskaya, Y.B.; Beck, B.H.; Hurst, D.R.; Han, Z.; Xia, W.; Hung, M.C.; Welch, D.R. Expression of metastasis suppressor BRMS1 in breast cancer cells results in a marked delay in cellular adhesion to matrix. Mol. Carcinog. 2014, 53, 1011–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, L.M.; Cao, X.; Dowell, A.E.; Debies, M.T.; Edmonds, M.D.; Beck, B.H.; Kesterson, R.A.; Desmond, R.A.; Frost, A.R.; Hurst, D.R.; et al. Ubiquitous BRMS1 expression is critical for mammary carcinoma metastasis suppression via promotion of apoptosis. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2012, 29, 315–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volinia, S.; Galasso, M.; Sana, M.E.; Wise, T.F.; Palatini, J.; Huebner, K.; Croce, C.M. Breast cancer signatures for invasiveness and prognosis defined by deep sequencing of microRNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 3024–3029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Z.; Colls, N.; Cheng, K.H.; Vaughn, M.W.; Gollahon, L. Microfluidic-based diagnostics for cervical cancer cells. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2006, 21, 1991–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Image J. Available online: http://rsbweb.nih.gov/ij/ (accessed on 1 December 2015).
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, H.; Gollahon, L.S. ERα Mediates Estrogen-Induced Expression of the Breast Cancer Metastasis Suppressor Gene BRMS1. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 158. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17020158
Ma H, Gollahon LS. ERα Mediates Estrogen-Induced Expression of the Breast Cancer Metastasis Suppressor Gene BRMS1. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2016; 17(2):158. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17020158
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Hongtao, and Lauren S. Gollahon. 2016. "ERα Mediates Estrogen-Induced Expression of the Breast Cancer Metastasis Suppressor Gene BRMS1" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 17, no. 2: 158. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17020158
APA StyleMa, H., & Gollahon, L. S. (2016). ERα Mediates Estrogen-Induced Expression of the Breast Cancer Metastasis Suppressor Gene BRMS1. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(2), 158. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17020158