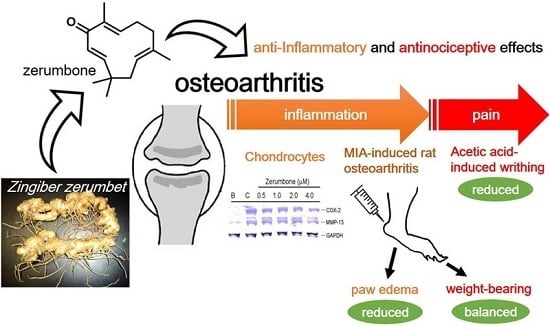
Antinociceptive and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Zerumbone against Mono-Iodoacetate-Induced Arthritis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Zerumbone on LPS-Induced RAW 264.7 Cells
2.2. Inhibition of COX-2 and MMP-13 Expressions by Zerumbone in IL-1β-stimulated PRCs
2.3. Analgesic Effects of Zerumbone on the Acetic-Acid-Induced Writhing Response
2.4. Analgesic and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Zerumbone on MIA-Induced OA
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Zerumbone
4.2. Anti-Inflammatory in Vitro Assay
4.2.1. Cell Cultures
4.2.2. Primary Chondrocyte Culture
4.2.3. Measurement of NO and PGE2 Production
4.2.4. Measurement of iNOS, COX-2, and MMP-13 Protein Expressions
4.3. Anti-Inflammatory and Antinociception in Vivo Assay
4.3.1. Animals
4.3.2. Acetic Acid-Induced Writhing Test
4.3.3. MIA-Induced OA Model
4.4. Statistics
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yob, N.J.; Jofrry, S.M.; Affandi, M.M.; Teh, L.K.; Salleh, M.Z.; Zakaria, Z.A. Zingiber zerumbet (L.) Smith: A review of its ethnomedicinal, chemical, and pharmacological uses. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2011, 2011, 543216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasannan, R.; Kalesh, K.A.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Nachiyappan, A.; Ramachandran, L.; Nguyen, A.H.; Kumar, A.P.; Lakshmanan, M.; Ahn, K.S.; Sethi, G. Key cell signaling pathways modulated by zerumbone: Role in the prevention and treatment of cancer. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2012, 84, 1268–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, H.S.; Rasedee, A.; Yeap, S.K.; Othman, H.H.; Chartrand, M.S.; Namvar, F.; Abdul, A.B.; How, C.W. Biomedical properties of a natural dietary plant metabolite, zerumbone, in cancer therapy and chemoprevention trials. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 920742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chien, T.Y.; Chen, L.G.; Lee, C.J.; Lee, F.Y.; Wang, C.C. Anti-inflammatory constituents of Zingiber zerumbet. Food Chem. 2008, 110, 584–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shieh, Y.H.; Huang, H.M.; Wang, C.C.; Lee, C.C.; Fan, C.K.; Lee, Y.L. Zerumbone enhances the Th1 response and ameliorates ovalbumin-induced Th2 responses and airway inflammation in mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2015, 24, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bijlsma, J.W.J.; Berenbaum, F.; Lafeber, F.P.J.G. Osteoarthritis: An update with relevance for clinical practice. Lancet 2011, 377, 2115–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrage, P.S.; Mix, K.S.; Brinckerhoff, C.E. Matrix metalloproteinases: Role in arthritis. Front. Biosci. 2006, 11, 529–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guingamp, C.; Gegout-Pottie, P.; Philippe, L.; Terlain, B.; Netter, P.; Gillet, P. Mono-iodoacetate-induced experimental osteoarthritis: A dose-response study of loss of mobility, morphology, and biochemistry. Arthritis Rheum. 1997, 40, 1670–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernihough, J.; Gentry, C.; Malcangio, M.; Fox, A.; Rediske, J.; Pellas, T.; Kidd, B.; Bevan, S.; Winter, J. Pain related behaviour in two models of osteoarthritis in the rat knee. Pain 2004, 112, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janusz, M.J.; Hookfin, E.B.; Heitmeyer, S.A.; Woessner, J.F.; Freemont, A.J.; Hoyland, J.A.; Brown, K.K.; Hsieh, L.C.; Almstead, N.G.; De, B.; et al. Moderation of iodoacetate-induced experimental osteoarthritis in rats by matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2001, 9, 751–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bove, S.E.; Calcaterra, S.L.; Brooker, R.M.; Huber, C.M.; Guzman, R.E.; Juneau, P.L.; Schrier, D.J.; Kilgore, K.S. Weight bearing as a measure of disease progression and efficacy of anti-inflammatory compounds in a model of monosodium iodoacetate-induced osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2003, 11, 821–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolf, A.D.; Pfleger, B. Burden of major musculoskeletal conditions. Bull. World Health Organ. 2003, 81, 646–656. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hinton, R.; Moody, R.L.; Davis, A.W.; Thomas, S.F. Osteoarthritis: Diagnosis and therapeutic considerations. Am. Fam. Physician 2002, 65, 841–848. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wieland, H.A.; Michaelis, M.; Kirschbaum, B.J.; Rudolphi, K.A. Osteoarthritis-an untreatable disease? Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2005, 4, 331–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silverstein, F.E.; Faich, G.; Goldstein, J.L.; Simon, L.S.; Pincus, T.; Whelton, A.; Makuch, R.; Eisen, G.; Agrawal, N.M.; Stenson, W.F.; et al. Gastrointestinal toxicity with Celecoxib vs. nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for osteoarthritis and reumatoid arthritis: The CLASS study: A randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2000, 284, 1247–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalid, M.H.; Akhtar, M.N.; Mohamad, A.S.; Perimal, E.K.; Akira, A.; Israf, D.A.; Lajis, N.; Sulaiman, M.R. Antinociceptive effect of the essential oil of Zingiber zerumbet in mice: Possible mechanisms. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 137, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perimal, E.K.; Akhtar, M.N.; Mohamad, A.S.; Khalid, M.H.; Ming, O.H.; Khalid, S.; Tatt, L.M.; Kamaldin, M.N.; Zakaria, Z.A.; Israf, D.A.; et al. Zerumbone-induced antinociception: Involvement of the l-arginine-nitric oxide-cGMP-PKC-K+ATP channel pathways. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2011, 108, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sulaiman, M.R.; Perimal, E.K.; Zakaria, Z.A.; Mokhtar, F.; Akhtar, M.N.; Lajis, N.H.; Israf, D.A. Preliminary analysis of the antinociceptive activity of zerumbone. Fitoterapia 2009, 80, 230–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryter, S.W.; Alam, J.; Choi, A.M.K. Heme oxygenase-1/carbon monoxide: From basic science to therapeutic applications. Physiol. Rev. 2006, 86, 583–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shih, R.H.; Yang, C.M. Induction of heme oxygenase-1 attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced cyclooxygenase-2 expression in mouse brain endothelial cells. J. Neuroinflamm. 2010, 7, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abacioglu, N.; Tunctan, B.; Akbulut, E.; Cakici, I. Participation of the components of l-arginine/nitric oxide/cGMP cascade by chemically-induced abdominal constriction in the mouse. Life Sci. 2000, 67, 1127–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pol, O. The involvement of the nitric oxide in the effects and expression of opioid receptors during peripheral inflammation. Curr. Med. Chem. 2007, 14, 1945–1955. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z.; Wang, Y.; Piao, T.; Liu, J. Echinocystic acid inhibits IL-1β-induced COX-2 and iNOS expression in human osteoarthritis chondrocytes. Inflammation 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, A.R.; Attur, M.; Patel, R.N.; Thakker, G.D.; Marshall, P.J.; Rediske, J.; Stuchin, S.A.; Patel, I.R.; Abramson, S.B. Superinduction of cyclooxygenase-2 activity in human osteoarthritis-affected cartilage. Influence of nitric oxide. J. Clin. Investig. 1997, 99, 1231–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rousset, F.; Nguyen, M.V.C.; Grange, L.; Morel, F.; Lardy, B. Heme oxygenase-1 regulates matrix metalloproteinase MMP-1 secretion and chondrocyte cell death via Nox4 NADPH oxidase activity in chondrocytes. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koster, R.; Anderson, M.; Ej, D.B. Acetic acid for analgesic screening. Fed Proceeds 1959, 18, 412–416. [Google Scholar]
- Berenbaum, F. Osteoarthritis as an inflammatory disease (osteoarthritis is not osteoarthrosis!). Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2013, 21, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, G.C.; Chien, T.Y.; Chen, L.G.; Wang, C.C. Antitumor effects of zerumbone from Zingiber zerumbet in P-388D1 cells in vitro and in vivo. Planta Med. 2005, 71, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Largo, R.; Alvarez-Soria, M.A.; Diez-Ortego, I.; Calvo, E.; Sanchez-Pernaute, O.; Egido, J.; Herrero-Beaumont, G. Glucosamine inhibits IL-1β-induced NFκB activation in human osteoarthritic chondrocytes. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2003, 11, 290–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, S.H.; Lee, H.H.; Chen, L.G.; Wu, C.H.; Wang, C.C. Effects of three purgative decoctions on inflammatory mediators. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2006, 105, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taber, R.I.; Greenhouse, D.D.; Rendell, J.K.; Irwin, S. Agonist and antagonist interactions of opioids on acetic acid-induced abdominal stretching in mice. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1969, 169, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]







© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chien, T.-Y.; Huang, S.K.-H.; Lee, C.-J.; Tsai, P.-W.; Wang, C.-C. Antinociceptive and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Zerumbone against Mono-Iodoacetate-Induced Arthritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 249. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17020249
Chien T-Y, Huang SK-H, Lee C-J, Tsai P-W, Wang C-C. Antinociceptive and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Zerumbone against Mono-Iodoacetate-Induced Arthritis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2016; 17(2):249. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17020249
Chicago/Turabian StyleChien, Ting-Yi, Steven Kuan-Hua Huang, Chia-Jung Lee, Po-Wei Tsai, and Ching-Chiung Wang. 2016. "Antinociceptive and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Zerumbone against Mono-Iodoacetate-Induced Arthritis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 17, no. 2: 249. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17020249
APA StyleChien, T. -Y., Huang, S. K. -H., Lee, C. -J., Tsai, P. -W., & Wang, C. -C. (2016). Antinociceptive and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Zerumbone against Mono-Iodoacetate-Induced Arthritis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(2), 249. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17020249