Proteomic Analysis Reveals the Leaf Color Regulation Mechanism in Chimera Hosta “Gold Standard” Leaves
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Variegated Leaf Color Changes in Different Development Stages
2.2. Chlorophyll Contents in Differrent Regions of Leaves
2.3. Nitrogen Contents and Activities of Nitrogen Metabolism-Related Enzymes
2.4. Identification of Differentially Expressed Proteins (DEPs) in Various Leaf Regions
2.5. Annotation and Functional Categorization of DEPs
2.6. Proteoform Analysis of DEPs
2.7. Subcellular Localization of DEPs
2.8. Hierarchical Cluster Analysis of DEPs
3. Discussion
3.1. Leaf Color Difference of Variegated Leaves Is Determined by the Chlorophyll Contents
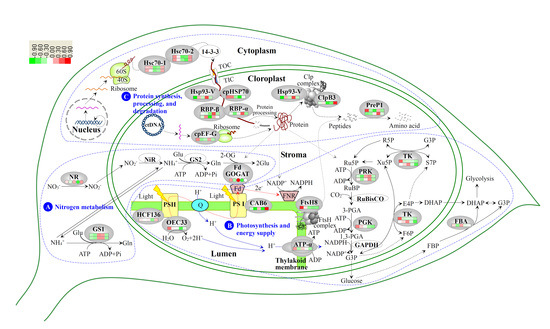
3.2. Nitrogen Metabolism Level Determined the Chlorophyll Synthesis in Variegated Leaves
3.3. Chloroplast Development in Different Stages and Nitrogen Levels
3.4. Photosynthesis and Energy Supply Are Different in Various Regions of Variegated Leaves
3.5. Chloroplast Protein Synthesis, Processing and Degradtaion in Variegated Leaves
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials and Treatment
4.2. Leaf Color Quantification
4.3. Chlorophyll Content Determination
4.4. Leaf Nitrogen Content Determination
4.5. Nitrogen Metabolism-Related Enzymes Activity Assay
4.6. Protein Sample Preparation, 2-DE, and Image Analysis
4.7. Protein Identification and Database Searching
4.8. Protein Classification
4.9. Protein Subcellular Location
4.10. Multiple Sequence Alignment
4.11. Hierarchical Cluster Analysis
4.12. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kumar, A.M.; Söll, D. Antisense HEMA1 RNA expression inhibits heme and chlorophyll biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2000, 122, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Choi, Y.; Voytas, D.F.; Rodermel, S. Mutations in the Arabidopsis VAR2 locus cause leaf variegation due to the loss of a chloroplast FtsH protease. Plant J. 2000, 22, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aluru, M.R.; Bae, H.; Wu, D.; Rodermel, S.R. The Arabidopsis immutans mutation affects plastid differentiation and the morphogenesis of white and green sectors in variegated plants. Plant Physiol. 2001, 127, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Zhang, X.; He, B.; Diao, L.; Sheng, S.; Wang, J.; Guo, X.; Su, N.; Wang, L.; Jiang, L. A chlorophyll-deficient rice mutant with impaired chlorophyllide esterification in chlorophyll biosynthesis. Plant Physiol. 2007, 145, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terry, M. Phytochrome chromophore-deficient mutants. Plant Cell Environ. 1997, 20, 740–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Fu, A.; Aluru, M.; Park, S.; Xu, Y.; Liu, H.; Liu, X.; Foudree, A.; Nambogga, M.; Rodermel, S. Variegation mutants and mechanisms of chloroplast biogenesis. Plant Cell Environ. 2007, 30, 350–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, D.Y.; Xu, H.; Du, G.Y.; Lin, J.T.; Duan, M.; Guo, A.G. Proteome analysis of chloroplast proteins in stage albinism line of winter wheat (triticum aestivum) FA85. BMB Rep. 2009, 42, 450–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Huang, J.; Liu, S.; Li, J.; Yang, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z. Proteomic analysis of young leaves at three developmental stages in an albino tea cultivar. Proteome Sci. 2011, 9, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tcherkez, G.; Guérard, F.; Gilard, F.; Lamothe, M.; Mauve, C.; Gout, E.; Bligny, R. Metabolomic characterisation of the functional division of nitrogen metabolism in variegated leaves. Funct. Plant Biol. 2012, 39, 959–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toshoji, H.; Katsumata, T.; Takusagawa, M.; Yusa, Y.; Sakai, A. Effects of chloroplast dysfunction on mitochondria: White sectors in variegated leaves have higher mitochondrial DNA levels and lower dark respiration rates than green sectors. Protoplasma 2012, 249, 805–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakamoto, W.; Uno, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Miura, E.; Kato, Y. Arrested differentiation of proplastids into chloroplasts in variegated leaves characterized by plastid ultrastructure and nucleoid morphology. Plant Cell Physiol. 2009, 50, 2069–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamasaki, H.; Heshiki, R.; Ikehara, N. Leaf-goldenning induced by high light in Ficus microcarpa L. f., a tropical fig. J. Plant Res. 1995, 108, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, S.; Tamashiro, A.; Sakihama, Y.; Yamamoto, Y.; Kawamitsu, Y.; Yamasaki, H. High-susceptibility of photosynthesis to photoinhibition in the tropical plant Ficus microcarpa L. f. cv. Golden Leaves. BMC Plant Biol. 2002, 2, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Deng, B. Antioxidative response of Golden Agave leaves with different degrees of variegation under high light exposure. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2012, 34, 1925–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, C.; Xie, J. A comparison of plants regenerated from a variegated Epipremnum aureum. Biol. Plant. 2009, 53, 610–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downton, W.; Grant, W. Photosynthetic and growth responses of variegated ornamental species to elevated CO2. Funct. Plant Biol. 1994, 21, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raveh, E.; Wang, N.; Nobel, P.S. Gas exchange and metabolite fluctuations in green and yellow bands of variegated leaves of the monocotyledonous CAM species Agave americana. Physiol. Plant. 1998, 103, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Meng, Y.-L.; Ishikawa, H.; Hibino, T.; Tanaka, Y.; Nii, N.; Takabe, T. Photosynthetic adaptation to salt stress in three-color leaves of a C4 plant Amaranthus tricolor. Plant Cell Physiol. 1999, 40, 668–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Liu, H.; Sun, G. Effects of nitrogen fertilizer rate on leaf color of chimera Hosta “Gold standard”. Acta Prataculturae Sin. 2011, 20, 93–100. [Google Scholar]
- Fulgosi, H.; Ljubešić, N.; Wrischer, M. Regreening of yellow leaves. In Plastid Development in Leaves during Growth and Senescence; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2013; pp. 589–599. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, M.; Xu, M.Y.; Yuan, S.; Chen, Y.E.; Du, J.B.; Xu, F.; Zhang, Z.W.; Guo, Z.C.; Zhao, Z.Y.; Lin, H.H. Light regulation to chlorophyll synthesis and plastid development of the chlorophyll-less golden-leaf privet. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2010, 52, 809–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaughn, K.C.; Wilson, K.G.; Stewart, K.D. Light-harvesting pigment-protein complex deficiency in Hosta (Liliaceae). Planta 1978, 143, 275–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fulgosi, H.; Jurić, S.; Lepeduš, H.; Hazler-Pilepić, K.; Prebeg, T.; Ljubešić, N. Thylakoid system disassembly during bleaching of aurea mutants of maple Acer negundo Hassk. var. Odessanum. Croat. Chem. Acta 2008, 81, 89–95. [Google Scholar]
- Okabe, K.; Schmid, G.H.; Straub, J. Genetic characterization and high efficiency photosynthesis of an aurea mutant of tobacco. Plant Physiol. 1977, 60, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawata, E.E.; Cheung, A.Y. Molecular analysis of an aurea photosynthetic mutant (Su/Su) in tobacco: LHCP depletion leads to pleiotropic mutant phenotypes. EMBO J. 1990, 9, 4197–4203. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Oelmüller, R.; Kendrick, R. Blue light is required for survival of the tomato phytochrome-deficient aurea mutant and the expression of four nuclear genes coding for plastidic proteins. Plant Mol. Biol. 1991, 16, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oelmüller, R.; Kendrick, R.; Briggs, W. Blue-light mediated accumulation of nuclear-encoded transcripts coding for proteins of the thylakoid membrane is absent in the phytochrome-deficient aurea mutant of tomato. Plant Mol. Biol. 1989, 13, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palomares, R.; Herrmann, R.; Oelmüller, R. Different blue-light requirement for the accumulation of transcripts from nuclear genes for thylakoid proteins in Nicotiana tabacum and Lycopersicon esculentum. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 1991, 11, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Hosta Society. Registrations. Hosta J. 2009, 40, 3–70. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, H.; Sun, G.; He, Q. Effects of excessive application of nitrogen fertilizer on leaf color, key enzymes activities of nitrogen metabolism and chloroplast ultrastructure of a chimera Hosta “Gold Standard”. Acta Prataculturae Sin. 2011, 20, 93–101. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Harmon, A.C. Advances in plant proteomics. Proteomics 2006, 6, 5504–5516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Chen, S.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, T.; Yang, C.; Diaz, C.; Sun, G.; Dai, S. Physiological and proteomic analysis of salinity tolerance in Puccinellia tenuiflora. J. Proteome Res. 2011, 10, 3852–3870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suo, J.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, S.; Cao, J.; Liu, G.; Wei, X.; Wang, T.; Yang, C.; Dai, S. Cytological and proteomic analyses of Osmunda cinnamomea germinating spores reveal characteristics of fern spore germination and rhizoid tip-growth. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2015, 14, 2510–2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.; Zhang, H.; Wang, T.; Chen, S.; Dai, S. Proteomics-based investigation of salt-responsive mechanisms in plant roots. J. Proteom. 2013, 82, 230–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Han, B.; Wang, T.; Chen, S.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Dai, S. Mechanisms of plant salt response: Insights from proteomics. J. Proteome Res. 2011, 11, 49–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernard, S.M.; Møller, A.L.B.; Dionisio, G.; Kichey, T.; Jahn, T.P.; Dubois, F.; Baudo, M.; Lopes, M.S.; Tercé-Laforgue, T.; Foyer, C.H. Gene expression, cellular localisation and function of glutamine synthetase isozymes in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Plant Mol. Biol. 2008, 67, 89–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, R.; Karan, R.; Singla-Pareek, S.L.; Pareek, A. Ectopic expression of Pokkali phosphoglycerate kinase-2 (OsPGK2-P) improves yield in tobacco plants under salinity stress. Plant Cell Rep. 2016, 35, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, W.; Tang, X.; Huo, Y.; Xu, R.; Qi, S.; Huang, J.; Zheng, C.; Wu, C.-A. Identification and characterization of fructose 1,6-bisphosphate aldolase genes in Arabidopsis reveal a gene family with diverse responses to abiotic stresses. Gene 2012, 503, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, D.Y.; Vierling, E.; Guy, C.L. Comprehensive expression profile analysis of the Arabidopsis Hsp70 gene family. Plant Physiol. 2001, 126, 789–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weisberg, L.A.; Wimmers, L.E.; Turgeon, R. Photoassimilate-transport characteristics of nonchlorophyllous and green tissue in variegated leaves of Coleus blumei Benth. Planta 1988, 175, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, P.; Nayak, L.; Misra, A.N.; Biswal, B. Response of mature, developing and senescing chloroplasts to environmental stress. In Plastid Development in Leaves during Growth and Senescence; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2013; pp. 641–668. [Google Scholar]
- Tischner, R. Nitrate uptake and reduction in higher and lower plants. Plant Cell Environ. 2000, 23, 1005–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, S.M.; Habash, D.Z. The importance of cytosolic glutamine synthetase in nitrogen assimilation and recycling. New Phytol. 2009, 182, 608–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNally, S.F.; Hirel, B.; Gadal, P.; Mann, A.F.; Stewart, G.R. Glutamine synthetases of higher plants evidence for a specific isoform content related to their possible physiological role and their compartmentation within the leaf. Plant Physiol. 1983, 72, 22–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomsen, H.C.; Eriksson, D.; Møller, I.S.; Schjoerring, J.K. Cytosolic glutamine synthetase: A target for improvement of crop nitrogen use efficiency? Trends Plant Sci. 2014, 19, 656–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-García, A.; de Vicente, A.; Cantón, F.R.; Cazorla, F.M.; Codina, J.C.; García-Gutiérrez, Á.; Cánovas, F.M. Light-dependent changes of tomato glutamine synthetase in response to Pseudomonas syringae infection or phosphinothricin treatment. Physiol. Plant. 1998, 102, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finnemann, J.; Schjoerring, J.K. Post-translational regulation of cytosolic glutamine synthetase by reversible phosphorylation and 14-3-3 protein interaction. Plant J. 2000, 24, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, C.; Pereira, A.; Pereira, S.; Teixeira, J. Regulation of glutamine synthetase expression in sunflower cells exposed to salt and osmotic stress. Sci. Hortic. Amst. 2004, 103, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavernier, V.; Cadiou, S.; Pageau, K.; Laugé, R.; Reisdorf-Cren, M.; Langin, T.; Masclaux-Daubresse, C. The plant nitrogen mobilization promoted by Colletotrichum lindemuthianum in Phaseolus leaves depends on fungus pathogenicity. J. Exp. Bot. 2007, 58, 3351–3360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borner, T.; Mendel, R.; Schiemann, J. Nitrate reductase is not accumulated in chloroplast-ribosome-deficient mutants of higher plants. Planta 1986, 169, 202–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozaki, A.; Sakamoto, A.; Takeba, G. The promoter of the gene for plastidic glutamine synthetase (GS2) from rice is developmentally regulated and exhibits substrate-induced expression in transgenic tobacco plants. Plant Cell Physiol. 1992, 33, 233–238. [Google Scholar]
- Cren, M.; Hirel, B. Glutamine synthetase in higher plants regulation of gene and protein expression from the organ to the cell. Plant Cell Physiol. 1999, 40, 1187–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukanya, R.; Li, M.-G.; Snustad, D.P. Root-and shoot-specific responses of individual glutamine synthetase genes of maize to nitrate and ammonium. Plant Mol. Biol. 1994, 26, 1935–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishiyama, K.; Inoue, E.; Watanabe-Takahashi, A.; Obara, M.; Yamaya, T.; Takahashi, H. Kinetic properties and ammonium-dependent regulation of cytosolic isoenzymes of glutamine synthetase in Arabidopsis. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 16598–16605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishiyama, K.; Inoue, E.; Tabuchi, M.; Yamaya, T.; Takahashi, H. Biochemical background and compartmentalized functions of cytosolic glutamine synthetase for active ammonium assimilation in rice roots. Plant Cell Physiol. 2004, 45, 1640–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bondada, B.R.; Syvertsen, J.P. Leaf chlorophyll, net gas exchange and chloroplast ultrastructure in citrus leaves of different nitrogen status. Tree Physiol. 2003, 23, 553–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Xia, X.; Fang, W.; Fu, Y.; An, M.; Zhou, M. Identification of genes involved in spontaneous leaf color variation in Pseudosasa japonica. Genet. Mol. Res. 2015, 14, 11827–11840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zavaleta-Mancera, H.; Franklin, K.; Ougham, H.; Thomas, H.; Scott, I. Regreening of senescent Nicotiana leaves I. Reappearance of NADPH-protochlorophyllide oxidoreductase and light-harvesting chlorophyll a/b-binding protein. J. Exp. Bot. 1999, 50, 1677–1682. [Google Scholar]
- Plücken, H.; Müller, B.; Grohmann, D.; Westhoff, P.; Eichacker, L.A. The HCF136 protein is essential for assembly of the photosystem II reaction center in Arabidopsis thaliana. FEBS Lett. 2002, 532, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, Y. Quality control of photosystem II. Plant Cell Physiol. 2001, 42, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hemmingsen, S.M. The plastid chaperonin. Semin. Cell Biol. 1990, 1, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gutteridge, S.; Gatenby, A.A. Rubisco synthesis, assembly, mechanism, and regulation. Plant Cell 1995, 7, 809–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, K.; Nakanishi, H.; Bower, J.; Yoder, D.W.; Osteryoung, K.W.; Miyagishima, S.-Y. Plastid chaperonin proteins Cpn60α and Cpn60β are required for plastid division in Arabidopsis thaliana. BMC Plant Biol. 2009, 9, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raines, C.A.; Lloyd, J.C.; Dyer, T.A. Molecular biology of the C3 photosynthetic carbon reduction cycle. Photosynth. Res. 1991, 27, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raines, C.A. The Calvin cycle revisited. Photosynth. Res. 2003, 75, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zhou, M.; Li, X.; Yu, X.; Jiang, C.; Sun, G. The single and interactive effects of nitrogen application rate and light condition on Hosta “Blue Umbrella” growth and photosynthetic characteristics. Acta Hortic. Sin. 2007, 34, 1497. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, M.; Zhang, J.; Li, M.; Wang, Z. The single and interactive effects of nitrogen application rate and light condition on Hosta “Francee” growth and photosynthetic characteristics. J. Hebei For. Sci. Technol. 2007, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Hikosaka, K. Interspecific difference in the photosynthesis-nitrogen relationship: patterns, physiological causes, and ecological importance. J. Plant Res. 2004, 117, 481–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Zhou, J.; Li, H.; Shi, W.; Polle, A.; Lu, M.; Sun, X.; Luo, Z.-B. Global poplar root and leaf transcriptomes reveal links between growth and stress responses under nitrogen starvation and excess. Tree Physiol. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokhele, B.; Zhan, X.; Yang, G.; Zhang, X. Review: Nitrogen assimilation in crop plants and its affecting factors. Can. J. Plant Sci. 2012, 92, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Zhou, Y.; Gao, Y.; Li, Y.; Shen, Q. New insights into the nitrogen form effect on photosynthesis and photorespiration. Pedosphere 2007, 17, 601–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pogson, B.J.; Albrecht, V. Genetic dissection of chloroplast biogenesis and development: An overview. Plant Physiol. 2011, 155, 1545–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albrecht, V.; Ingenfeld, A.; Apel, K. Characterization of the snowy cotyledon 1 mutant of Arabidopsis thaliana: the impact of chloroplast elongation factor G on chloroplast development and plant vitality. Plant Mol. Biol. 2006, 60, 507–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Zhu, Y.; Ma, Z.; Sun, Y.; Quan, Q.; Li, P.; Hu, P.; Shi, T.; Lo, C.; Chu, I.K. Proteomic evidence for genetic epistasis: ClpR4 mutations switch leaf variegation to virescence in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2013, 76, 943–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, Y.; Sakamoto, W. Plastid protein degradation during leaf development and senescence: Role of proteases and chaperones. In Plastid Development in Leaves during Growth and Senescence; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2013; pp. 453–477. [Google Scholar]
- Su, P.-H.; Li, H.-M. Stromal Hsp70 is important for protein translocation into pea and Arabidopsis chloroplasts. Plant Cell 2010, 22, 1516–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latijnhouwers, M.; Xu, X.-M.; Møller, S.G. Arabidopsis stromal 70-kDa heat shock proteins are essential for chloroplast development. Planta 2010, 232, 567–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, U.; Rioflorido, I.; Hong, S.W.; Larkindale, J.; Waters, E.R.; Vierling, E. The Arabidopsis ClpB/Hsp100 family of proteins: chaperones for stress and chloroplast development. Plant J. 2007, 49, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sjögren, L.L.; MacDonald, T.M.; Sutinen, S.; Clarke, A.K. Inactivation of the clpC1 gene encoding a chloroplast Hsp100 molecular chaperone causes growth retardation, leaf chlorosis, lower photosynthetic activity, and a specific reduction in photosystem content. Plant Physiol. 2004, 136, 4114–4126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaltsman, A.; Ori, N.; Adam, Z. Two types of FtsH protease subunits are required for chloroplast biogenesis and photosystem II repair in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2005, 17, 2782–2790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cederholm, S.N.; Bäckman, H.G.; Pesaresi, P.; Leister, D.; Glaser, E. Deletion of an organellar peptidasome PreP affects early development in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Mol. Biol. 2009, 71, 497–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goloubinoff, P.; Mogk, A.; Zvi, A.P.B.; Tomoyasu, T.; Bukau, B. Sequential mechanism of solubilization and refolding of stable protein aggregates by a bichaperone network. PNAS 1999, 96, 13732–13737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke, A.K.; MacDonald, T.M.; Sjögren, L.L. The ATP-dependent Clp protease in chloroplasts of higher plants. Physiol. Plant. 2005, 123, 406–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Maurizi, M.R.; Esser, L.; Xia, D. Crystal structure of ClpA, an Hsp100 chaperone and regulator of ClpAP protease. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 46743–46752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagawara, E.; Sakuraba, Y.; Yamasato, A.; Tanaka, R.; Tanaka, A. Clp protease controls chlorophyll b synthesis by regulating the level of chlorophyllide a oxygenase. Plant J. 2007, 49, 800–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamasato, A.; Nagata, N.; Tanaka, R.; Tanaka, A. The N-terminal domain of chlorophyllide a oxygenase confers protein instability in response to chlorophyll b accumulation in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2005, 17, 1585–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kmiec, B.; Glaser, E. A novel mitochondrial and chloroplast peptidasome, PreP. Physiol. Plant. 2012, 145, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, L.S.M.F. Studies on the stage albescent phenomenon in tea the changes of rubpcase and proteinase. Sci. Agric. Sin. 1999, 32, 33–38. [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan-Wollaston, V.; Earl, S.; Harrison, E.; Mathas, E.; Navabpour, S.; Page, T.; Pink, D. The molecular analysis of leaf senescence—A genomics approach. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2003, 1, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olinares, P.D.B.; Kim, J.; van Wijk, K.J. The Clp protease system: A central component of the chloroplast protease network. BBA Bioenerg. 2011, 1807, 999–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Yu, F.; Rodermel, S. Arabidopsis chloroplast FtsH, var2 and suppressors of var2 leaf variegation: A review. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2010, 52, 750–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, M.; Bukau, B. Hsp70 chaperones: cellular functions and molecular mechanism. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2005, 62, 670–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, Q.; Trösch, R.; Jarvis, P. The ins and outs of chloroplast protein transport. In Plastid Development in Leaves during Growth and Senescence; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2013; pp. 239–280. [Google Scholar]
- Rial, D.V.; Arakaki, A.K.; Ceccarelli, E.A. Interaction of the targeting sequence of chloroplast precursors with Hsp70 molecular chaperones. Eur. J. Biochem. 2000, 267, 6239–6248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waegemann, K.; Paulsen, H.; Soll, J. Translocation of proteins into isolated chloroplasts requires cytosolic factors to obtain import competence. FEBS Lett. 1990, 261, 89–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kourtz, L.; Ko, K. The early stage of chloroplast protein import involves Com70. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 2808–2813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kessler, F.; Blobel, G. Interaction of the protein import and folding machineries of the chloroplast. PNAS 1996, 93, 7684–7689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Shi, L.; Shi, A.; Zhang, Q. Photosynthetic responses of four Hosta cultivars to shade treatments. Photosynthetica 2004, 42, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willis, O.O.; Mouti, M.E.; Sila, D.N.; Mwasaru, M.; Thiongo, G.; Murage, H.; Ojijo, N.O. Physico-chemical properties and antioxidant potential of syrup prepared from “Madhura”sweet sorghum (Sorghum bicolor L. Moench) cultivar grown at different locations in Kenya. Sugar Tech. 2013, 15, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnon, D.I. Copper enzymes in isolated chloroplasts. Polyphenoloxidase in Beta vulgaris. Plant Physiol. 1949, 24, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lichtenthaler, H.; Wellburn, A. Determinations of total carotenoids and chlorophylls a and b of leaf extracts in different solvent. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 1983, 603, 591–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Shi, G.; Dong, X. Experiment Instruction of Plant Physiology; China Agriculture Technology Press: Beijing, China, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, R.P.; Srivastava, H.S. Increase in glutamate synthase (NADH) activity in maize seedlings in response to nitrate and ammonium nitrogen. Physiol. Plant. 1986, 66, 413–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, S.; Zhang, H.; Shi, L.; Cao, F.; Guo, L.; Xie, Y.; Wang, T.; Yan, X.; Dai, S. Desiccation tolerance mechanism in resurrection fern-ally Selaginella tamariscina revealed by physiological and proteomic analysis. J. Proteome Res. 2010, 9, 6561–6577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, S.; Li, L.; Chen, T.; Chong, K.; Xue, Y.; Wang, T. Proteomic analyses of Oryza sativa mature pollen reveal novel proteins associated with pollen germination and tube growth. Proteomics 2006, 6, 2504–2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, Q.; Li, Z.; Hou, L.; Dai, S.; Liu, W. Comparative proteomics of peanut gynophore development under dark and mechanical stimulation. J. Proteome Res. 2013, 12, 5502–5511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information non-redundant (NCBInr) protein databases. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/ (accessed on 20 January 2010).
- Matrix Science. Available online: http://www.matrixscience.com (accessed on 20 January 2010).
- UniProt. Available online: http://www.uniprot.org/ (accessed on 15 August 2015).
- Zhao, Q.; Gao, J.; Suo, J.; Chen, S.; Wang, T.; Dai, S. Cytological and proteomic analyses of horsetail (Equisetum arvense L.) spore germination. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- YLoc: Interpretable Subcellular Localization Prediction. Available online: http://abi.inf.uni-tuebingen.de/Services/YLoc/webloc.cgi (accessed on 27 August 2015).
- LocTree3: Protein Subcellular Localization Prediction System. Available online: https://rostlab.org/services/loctree3/ (accessed on 27 August 2015).
- Plant-mPLoc: Predicting Subcellular Localization of Plant Proteins Including Those with Multiple Sites. Available online: http://www.csbio.sjtu.edu.cn/bioinf/plant-multi/# (accessed on 27 August 2015).
- ngLOC: A Bayesian Method for Predicting Protein Subcellular Localization. Available online: http://genome.unmc.edu/ngLOC/index.html (accessed on 27 August 2015).
- TargetP 1.1 Server. Available online: http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/TargetP/ (accessed on 27 August 2015).
- BoxShade: Pretty Printing and Shading of Multiple-Alignment Files. Available online: http://www.ch.embnet.org/software/BOX_form.html (accessed on 12 October 2015).
- Cluster 3.0 Software. Available online: http://bonsai.hgc.jp/~mdehoon/software/cluster/software.htm (accessed on 20 October 2015).
- Yu, J.; Chen, S.; Wang, T.; Sun, G.; Dai, S. Comparative proteomic analysis of Puccinellia tenuiflora leaves under Na2CO3 stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 1740–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]









| Spot No. a | Protein Name b | SCL c | Plant Species d | gi Number e | Exp. Mw (Da)/pI f | Thr. Mw (Da)/pI g | Sco h | Cov (%) i | QM j | V% ± SE k YLM MLM LENF YLC MLC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nitrogen metabolism (2) | ||||||||||
| 795 | glutamine synthetase isoform GS1c (GS1) | Cyt | Triticum aestivum | 71361904 | 39,676/5.58 | 39,445/5.41 | 89 | 15 | 2 |  |
| 806 | glutamine synthetase isoform GS1c (GS1) | Cyt | T. aestivum | 71361904 | 39,505/5.75 | 39,445/5.41 | 168 | 15 | 3 |  |
| Photosynthesis (11) | ||||||||||
| 1120 | chlorophyll a/b-binding protein type I, chlorophyll a-b binding protein 6 (CAB6) * | Chl | Malus x domestica | 33772151 | 23,327/5.86 | 15,693/5.05 | 101 | 19 | 3 |  |
| 881 | photosystem II stability/assembly factor HCF136, chloroplastic | Chl | Vitis vinifera | 225423755 | 35,844/5.32 | 44,473/6.92 | 575 | 37 | 12 |  |
| 982 | O2 evolving complex 33kD family protein (OEC33) | Chl | Populus trichocarpa | 224084209 | 28,767/5.00 | 35,348/5.89 | 490 | 56 | 12 |  |
| 740 | phosphoglycerate kinase (PGK) | Chl | Ricinus communis | 255544584 | 41,980/5.63 | 50,114/8.74 | 597 | 35 | 11 |  |
| 338 | plastid transketolase (TK) | Chl | Nicotiana tabacum | 194396261 | 78,879/5.95 | 80,451/6.16 | 141 | 17 | 10 |  |
| 346 | transketolase (TK) | Chl | P. trichocarpa | 224063766 | 79,837/5.87 | 81,122/5.97 | 337 | 13 | 9 |  |
| 459 | hypothetical protein SORBIDRAFT_09g014430, RuBisCO large subunit-binding protein subunit alpha (RBP-α) * | Chl | Sorghum bicolor | 242090109 | 66,151/4.84 | 60,914/5.07 | 233 | 31 | 13 |  |
| 476 | RuBisCO large subunit-binding protein subunit beta (RBP-β) | Chl | V. vinifera | 225442531 | 63,140/5.18 | 65,255/5.62 | 474 | 17 | 8 |  |
| 472 | function unknown, RuBisCO large subunit-binding protein subunit beta (RBP-β) * | Chl | Zea mays | 223948025 | 64,795/5.24 | 61,969/5.42 | 524 | 30 | 11 |  |
| 840 | phosphoribulokinase (PRK) | Chl | Pisum sativum | 1885326 | 38,189/4.99 | 39,230/5.41 | 113 | 13 | 3 |  |
| 832 | function unknown, chloroplastic phosphoribulokinase (PRK) * | Chl | Glycine max | 255646270 | 38,858/4.85 | 45,757/5.89 | 277 | 38 | 11 |  |
| Carbohydrate and energy metabolism (5) | ||||||||||
| 847 | fructose-bisphosphate aldolase (FBA) | Cyt | Pandanus amaryllifolius | 40716077 | 37,892/6.55 | 38,642/6.48 | 236 | 26 | 6 |  |
| 497 | glycosyl hydrolase family 1 family protein (GH1) | Chl | P. trichocarpa | 224135485 | 61,209/5.61 | 59,060/9.16 | 79 | 24 | 9 |  |
| 286 | NADH-ubiquinone oxidoreductase (complex I) | Mit | R. communis | 255582280 | 86,431/5.81 | 81,687/6.56 | 630 | 21 | 13 |  |
| 550 | chloroplast ATP synthase alpha chain | Chl | Yucca schidigera | 69214356 | 55,476/5.31 | 55,406/5.35 | 276 | 44 | 18 |  |
| 887 | haloalkane dehalogenase (HLD) | Chl | V. vinifera | 225442892 | 35,349/5.18 | 42,368/6.17 | 99 | 9 | 2 |  |
| Protein synthesis (2) | ||||||||||
| 268 | function unknown, chloroplastic elongation factor G (cpEF-G) * | Chl | Arabidopsis thaliana | 14532624 | 90,396/5.21 | 86,287/5.48 | 585 | 25 | 15 |  |
| 292 | mitochondrial glycyl-tRNA synthetase 1 (GRS) | Mit | V. vinifera | 225456501 | 86,133/6.16 | 79,370/5.98 | 108 | 5 | 3 |  |
| Protein processing and degradation (10) | ||||||||||
| 355 | heat shock cognate 70 kDa protein 1 (Hsc70-1) | Cyt | V. vinifera | 225449497 | 77,129/5.15 | 71,525/5.17 | 1050 | 61 | 26 |  |
| 361 | heat shock cognate 70 kDa protein 1 (Hsc70-1) | Cyt | V. vinifera | 225449497 | 77,663/5.10 | 71,525/5.17 | 959 | 58 | 25 |  |
| 358 | heat shock protein, heat shock cognate 70 kDa protein 2 * (Hsc70-2) | Cyt | R. communis | 255573627 | 78,743/5.06 | 71,276/5.14 | 977 | 53 | 23 |  |
| 367 | heat shock cognate 70 kDa protein 2 (Hsc70-2) | Cyt | V. vinifera | 225434984 | 76,864/5.20 | 71,589/5.17 | 847 | 57 | 25 |  |
| 332 | hypothetical protein VITISV_006707, stromal 70 kDa heat shock-related protein (cpHsp70) * | Chl | V. vinifera | 147805297 | 80,390/4.75 | 69,198/5.11 | 722 | 36 | 16 |  |
| 225 | hypothetical protein VITISV_009951, chloroplastic chaperone protein ClpB3 * | Chl | V. vinifera | 147842424 | 102,884/5.89 | 89,292/5.28 | 324 | 28 | 16 |  |
| 238 | ATP-dependent Clp protease ATP-binding subunit clpA homolog CD4B (ClpA) | Chl | Solanum lycopersicum | 399213 | 98,201/5.59 | 102,463/5.86 | 719 | 34 | 27 |  |
| 170 | zinc metalloprotease (insulinase family), homologous to presequence protease 1 (PreP1) * | Chl/Mit | A. thaliana | 9294618 | 113,711/4.99 | 118,265/5.32 | 346 | 13 | 11 |  |
| 179 | zinc metalloprotease (insulinase family), homologous to presequence protease 1 (PreP1) * | Chl/Mit | A. thaliana | 9294618 | 113,515/5.07 | 118,265/5.32 | 157 | 11 | 9 |  |
| 417 | AC007592_12 F12K11.22, ATP-dependent zinc metalloprotease FtsH8 * | Chl | A. thaliana | 6692685 | 71,862/5.35 | 71,014/5.81 | 144 | 13 | 5 |  |
| Stress and defence (1) | ||||||||||
| 1023 | dehydroascorbate reductase (DHAR) class glutathione transferase DHAR1 | Chl/Cyt | P. trichocarpa | 283135904 | 27,322/6.05 | 24,525/4.93 | 143 | 10 | 2 |  |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, Y.; Chen, S.; Guo, H.; Shi, L.; Dai, S. Proteomic Analysis Reveals the Leaf Color Regulation Mechanism in Chimera Hosta “Gold Standard” Leaves. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 346. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17030346
Yu J, Zhang J, Zhao Q, Liu Y, Chen S, Guo H, Shi L, Dai S. Proteomic Analysis Reveals the Leaf Color Regulation Mechanism in Chimera Hosta “Gold Standard” Leaves. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2016; 17(3):346. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17030346
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Juanjuan, Jinzheng Zhang, Qi Zhao, Yuelu Liu, Sixue Chen, Hongliang Guo, Lei Shi, and Shaojun Dai. 2016. "Proteomic Analysis Reveals the Leaf Color Regulation Mechanism in Chimera Hosta “Gold Standard” Leaves" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 17, no. 3: 346. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17030346
APA StyleYu, J., Zhang, J., Zhao, Q., Liu, Y., Chen, S., Guo, H., Shi, L., & Dai, S. (2016). Proteomic Analysis Reveals the Leaf Color Regulation Mechanism in Chimera Hosta “Gold Standard” Leaves. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(3), 346. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17030346