Arsenite Regulates Prolongation of Glycan Residues of Membrane Glycoprotein: A Pivotal Study via Wax Physisorption Kinetics and FTIR Imaging
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Result
2.1. FTIR Analysis of Skin Cells Exposed to Oligomycin and Sodium Arsenite
2.2. Alteration of Surface Protein-Linked Glycan Residues Induced by Arsenite Exposure
2.3. The Alteration of Surface Protein-Linked Glycan Residues of Skin Cells Treated with Oligomycin and Sodium Arsenite
3. Discussion
4. Methods
4.1. Cell Culture and Cell Sample Preparation
4.2. Integrating Sphere for FTIR Reflectance Spectroscopy and SR- FTIR Microspectroscopy
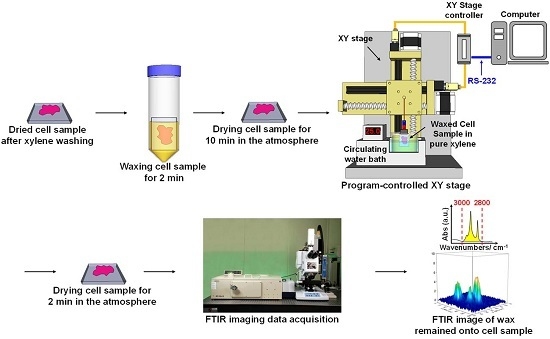
4.3. WPK Procedures and FPA-FTIR Imaging
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mead, M.N. Arsenic: In search of an antidote to a global poison. Environ. Health Perspect. 2005, 113, A378–A386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.J.; Hsu, L.I.; Wang, C.H.; Shih, W.L.; Hsu, Y.H.; Tseng, M.P.; Lin, Y.C.; Chou, W.L.; Chen, C.Y.; Lee, C.Y.; et al. Biomarkers of exposure, effect, and susceptibility of arsenic-induced health hazards in Taiwan. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2005, 206, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.S.; Lee, C.H.; Jee, S.H.; Ho, C.K.; Guo, Y.L. Environmental and occupational skin diseases in Taiwan. J. Dermatol. 2001, 28, 628–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, S.-M.; Wang, T.-N.; Ko, Y.-C. Mortality for certain diseases in areas with high levels of arsenic in drinking water. Arch. Environ. Health Int. J. 1999, 54, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.-H.; Liao, W.-T.; Yu, H.-S. Mechanisms and immune dysregulation in arsenic skin carcinogenesis. J. Cancer Ther. 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitchin, K.T. Recent Advances in arsenic carcinogenesis: Modes of action, animal model systems, and methylated arsenic metabolites. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2001, 172, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kojima, C.; Ramirez, D.C.; Tokar, E.J.; Himeno, S.; Drobná, Z.; Stýblo, M.; Mason, R.P.; Waalkes, M.P. Requirement of arsenic biomethylation for oxidative DNA damage. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2009, 101, 1670–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, A.T.; Li, M.; Xie, R.; He, Q.Y.; Chiu, J.F. Opposed arsenite-induced signaling pathways promote cell proliferation or apoptosis in cultured lung cells. Carcinogenesis 2004, 25, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, G.; Calaf, G.M.; Partridge, M.A.; Echiburu-Chau, C.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, S.; Chai, Y.; Li, B.; Hu, B.; Hei, T.K. Neoplastic transformation of human small airway epithelial cells induced by arsenic. Mol. Med. 2008, 14, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trouba, K.J.; Geisenhoffer, K.M.; Germolec, D.R. Sodium arsenite-induced stress-related gene expression in normal human epidermal, HaCaT, and HEL30 keratinocytes. Environ. Health Perspect. 2002, 110, 761–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, W.; Zhao, L.; Yin, K.; Feng, D.; Yang, F.; Liang, J.; Chen, H.; Bi, C.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; et al. Effects of arsenic trioxide on proliferation, paracrine and migration of cardiac progenitor cells. Int. J. Cardiol. 2015, 179, 393–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, K.P.; Kumari, R.; Treas, J.; DuMond, J.W. Chronic exposure to arsenic causes increased cell survival, DNA damage, and increased expression of mitochondrial transcription factor A (mtTFA) in human prostate epithelial cells. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2011, 24, 340–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.H.; Wu, S.B.; Hong, C.H.; Liao, W.T.; Wu, C.Y.; Chen, G.S.; Wei, Y.H.; Yu, H.S. Aberrant cell proliferation by enhanced mitochondrial biogenesis via mtTFA in arsenical skin cancers. Am. J. Pathol. 2011, 178, 2066–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuccillo, F.M.; de Laurentiis, A.; Palmieri, C.; Fiume, G.; Bonelli, P.; Borrelli, A.; Tassone, P.; Scala, I.; Buonaguro, F.M.; Quinto, I.; et al. Aberrant glycosylation as biomarker for cancer: Focus on CD43. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granovsky, M.; Fata, J.; Pawling, J.; Muller, W.J.; Khokha, R.; Dennis, J.W. Suppression of tumor growth and metastasis in Mgat5-deficient mice. Nat. Med. 2000, 6, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Burchell, J.; Poulsom, R.; Hanby, A.; Whitehouse, C.; Cooper, L.; Clausen, H.; Miles, D.; Taylor-Papadimitriou, J. An α2,3 sialyltransferase (ST3Gal I) is elevated in primary breast carcinomas. Glycobiology 1999, 9, 1307–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiricolo, M.; Malagolini, N.; Bonfiglioli, S.; Dall’Olio, F. Phenotypic changes induced by expression of β-galactoside α2,6 sialyltransferase I in the human colon cancer cell line SW948. Glycobiology 2006, 16, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.Y.; Jan, Y.H.; Juan, Y.H.; Yang, C.J.; Huang, M.S.; Yu, C.J.; Yang, P.C.; Hsiao, M.; Hsu, T.L.; Wong, C.H. Fucosyltransferase 8 as a functional regulator of nonsmall cell lung cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 630–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.; Liu, D.; Ge, Y.; Zhou, F.; Xu, J.; Chen, H.; Yun, X.; Gu, J.; Jiang, J. Down-regulation of β1,4GalT V at protein level contributes to arsenic trioxide-induced glioma cell apoptosis. Cancer Lett. 2008, 267, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petibois, C.; Desbat, B. Clinical application of FTIR imaging: New reasons for hope. Trends Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 495–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, L.M.; Bourassa, M.W.; Smith, R.J. FTIR spectroscopic imaging of protein aggregation in living cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2013, 1828, 2339–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasse, M.J.; Walsh, M.J.; Mattson, E.C.; Reininger, R.; Kajdacsy-Balla, A.; Macias, V.; Bhargava, R.; Hirschmugl, C.J. High-resolution Fourier-transform infrared chemical imaging with multiple synchrotron beams. Nat. Meth. 2011, 8, 413–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noreen, R.; Chien, C.C.; Chen, H.H.; Bobroff, V.; Moenner, M.; Javerzat, S.; Hwu, Y.; Petibois, C. FTIR spectro-imaging of collagen scaffold formation during glioma tumor development. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 8729–8736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krafft, C.; Shapoval, L.; Sobottka, S.B.; Geiger, K.D.; Schackert, G.; Salzer, R. Identification of primary tumors of brain metastases by SIMCA classification of IR spectroscopic images. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2006, 1758, 883–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beljebbar, A.; Dukic, S.; Amharref, N.; Manfait, M. Screening of biochemical/histological changes associated to C6 glioma tumor development by FTIR/PCA imaging. Analyst 2010, 135, 1090–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, L.F.; Huang, P.Y.; Chiang, W.F.; Wong, T.Y.; Lin, S.H.; Lee, Y.C.; Shieh, D.B. Oral cancer diagnostics based on infrared spectral markers and wax physisorption kinetics. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 1995–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, M.M.; Huang, P.Y.; Lee, Y.C.; Fang, Y.C.; Chan, M.W.; Lee, C.I. FT-IR microspectrometry reveals the variation of membrane polarizability due to epigenomic effect on epithelial ovarian cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 17963–17973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munro, K.L.; Bambery, K.R.; Carter, E.A.; Puskar, L.; Tobin, M.J.; Wood, B.R.; Dillon, C.T. Synchrotron radiation infrared microspectroscopy of arsenic-induced changes to intracellular biomolecules in live leukemia cells. Vib. Spectrosc. 2010, 53, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, W.T.; Chang, K.L.; Yu, C.L.; Chen, G.S.; Chang, L.W.; Yu, H.S. Arsenic induces human keratinocyte apoptosis by the FAS/FAS ligand pathway, which correlates with alterations in nuclear factor-kappa B and activator protein-1 activity. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2004, 122, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, P.C.; Chattopadhyay, A.; Manna, A.K.; Dutta, S.K. Skin cancers in chronic arsenic toxicity—A study of predictive value of some proliferative markers. Indian J. Pathol. Microbiol. 2004, 47, 206–209. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Zhang, J.; McHenry, K.T.; Kim, M.M.; Zeng, W.; Lopez-Pajares, V.; Dibble, C.C.; Mizgerd, J.P.; Yuan, Z.M. Induction of cytoplasmic accumulation of p53: A mechanism for low levels of arsenic exposure to predispose cells for malignant transformation. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 9131–9136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Li, B.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Jin, Y.; Piao, F.; Sun, G. Effects of sodium arsenite on catalase activity, gene and protein expression in HaCaT cells. Toxicol. In Vitro 2006, 20, 1139–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, W.T.; Lan, C.C.; Lee, C.H.; Yu, H.S. Concentration-dependent cellular responses of arsenic in keratinocytes. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 2011, 27, 390–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niewiarowska, A.; Caltabiano, M.M.; Bailey, D.S.; Poste, G.; Greig, R.G. Alterations in lipid-linked oligosaccharide metabolism in human melanoma cells concomitant with induction of stress proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 1987, 262, 14815–14820. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shang, J.; Gao, N.; Kaufman, R.J.; Ron, D.; Harding, H.P.; Lehrman, M.A. Translation attenuation by PERK balances ER glycoprotein synthesis with lipid-linked oligosaccharide flux. J. Cell Biol. 2007, 176, 605–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taniguchi, N. A sugar-coated switch for cellular growth and arrest. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2007, 3, 307–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, M.; Qin, C.; Li, W.; Yan, Y.; Zeng, L.; Yang, X. Effect of glucosamine and chitooligomer on the toxicity of arsenite against Escherichia coli. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 91, 390–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, H.; Zhuang, G.; Ma, A.; Jing, C. Arsenic interception by cell wall of bacteria observed with surface-enhanced Raman scattering. J. Microbiol. Methods 2012, 89, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke, B.R.; Greenfield, L.K.; Bouwman, C.; Whitfield, C. Coordination of polymerization, chain termination, and export in assembly of the Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide O9a antigen in an ATP-binding cassette transporter-dependent pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 30662–30672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke, B.R.; Richards, M.R.; Greenfield, L.K.; Hou, D.; Lowary, T.L.; Whitfield, C. In vitro reconstruction of the chain termination reaction in biosynthesis of the Escherichia coli O9a O-polysaccharide: The chain-length regulator, WbdD, catalyzes the addition of methyl phosphate to the non-reducing terminus of the growing glycan. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 41391–41401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujiwara, Y.; Yamamoto, C.; Hirooka, T.; Terada, N.; Satoh, M.; Kaji, T. Arsenite but not arsenate inhibits general proteoglycan synthesis in cultured arterial smooth muscle cells. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2008, 33, 487–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujiwara, Y.; Yamamoto, C.; Inagaki, T.; Satoh, M.; Kaji, T. Bismuth protects against arsenite-induced inhibition of proteoglycan synthesis in cultured vascular endothelial cells. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2012, 37, 837–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.H.; Wu, S.B.; Hong, C.H.; Chen, G.S.; Wei, Y.H.; Yu, H.S. Involvement of mtDNA damage elicited by oxidative stress in the arsenical skin cancers. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2013, 133, 1890–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, M.J.; Trevisan, J.; Bassan, P.; Bhargava, R.; Butler, H.J.; Dorling, K.M.; Fielden, P.R.; Fogarty, S.W.; Fullwood, N.J.; Heys, K.A.; et al. Using Fourier transform IR spectroscopy to analyze biological materials. Nat. Protoc. 2014, 9, 1771–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kalmodia, S.; Parameswaran, S.; Yang, W.; Barrow, C.J.; Krishnakumar, S. Attenuated total reflectance fourier transform infrared spectroscopy: An analytical technique to understand therapeutic responses at the molecular level. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Press, W.H.; Teukolsky, S.A.; Vetterling, W.T.; Flannery, B.P. Numerical Recipes in FORTRAN: The Art of Scientific Computing, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1992; p. 963. [Google Scholar]






| KC | HaCaT | HSC-1 | Assignment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wavenumbers/cm−1 | |||
| 3294 | 3295 | 3295 | Amide A (N-H stretching vibration) |
| 3063 | 3062 | 3064 | Amide B (overtone of amide II) |
| 2958 | 2957 | 2957 | νasCH3 (CH3 antisymmetric stretching vibration, dominant contribution from proteins) |
| 2924 | 2923 | 2923 | νasCH2 (CH2 antisymmetric stretching vibration, dominant contribution from lipids) |
| 2872 | 2873 | 2872 | νsCH3 (CH3 symmetric stretching vibration, dominant contribution from proteins) |
| 2853 | 2853 | 2852 | νsCH2 (CH2 symmetric stretching vibration, dominant contribution from lipids) |
| 1738 | 1738 | 1738 | νsC=O (acid esters) |
| 1650 | 1649 | 1657 | Amide I (C=O stretching vibration, proteins) |
| 1542 | 1542 | 1544 | Amide II (vibration motion coupled C-N stretching vibration and C-N-H bending vibration) |
| 1454 | 1454 | 1452 | δasCH2 (CH2 antisymmetric bending, lipids and proteins) |
| 1390 | 1396 | 1389 | δasCH3 (CH3 antisymmetric bending, lipids and proteins) |
| 1237 | 1238 | 1237 | νasPO2− (PO2− antisymmetric stretching vibration of DNA/RNA) |
| 1080 | 1084 | 1080 | νsPO2− (PO2− symmetric stretching vibration of DNA/RNA) |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, C.-H.; Hsu, C.-Y.; Huang, P.-Y.; Chen, C.-I.; Lee, Y.-C.; Yu, H.-S. Arsenite Regulates Prolongation of Glycan Residues of Membrane Glycoprotein: A Pivotal Study via Wax Physisorption Kinetics and FTIR Imaging. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 427. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17030427
Lee C-H, Hsu C-Y, Huang P-Y, Chen C-I, Lee Y-C, Yu H-S. Arsenite Regulates Prolongation of Glycan Residues of Membrane Glycoprotein: A Pivotal Study via Wax Physisorption Kinetics and FTIR Imaging. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2016; 17(3):427. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17030427
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Chih-Hung, Chia-Yen Hsu, Pei-Yu Huang, Ching-Iue Chen, Yao-Chang Lee, and Hsin-Su Yu. 2016. "Arsenite Regulates Prolongation of Glycan Residues of Membrane Glycoprotein: A Pivotal Study via Wax Physisorption Kinetics and FTIR Imaging" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 17, no. 3: 427. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17030427
APA StyleLee, C.-H., Hsu, C.-Y., Huang, P.-Y., Chen, C.-I., Lee, Y.-C., & Yu, H.-S. (2016). Arsenite Regulates Prolongation of Glycan Residues of Membrane Glycoprotein: A Pivotal Study via Wax Physisorption Kinetics and FTIR Imaging. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(3), 427. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17030427