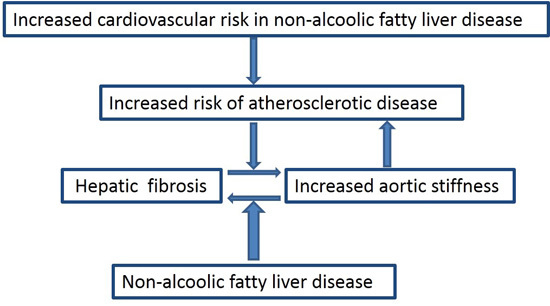
NAFLD and Increased Aortic Stiffness: Parallel or Common Physiopathological Mechanisms?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Cardiovascular Risk and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
3. Prognostic Markers: The Role of Fibrosis
4. Aortic Stiffness and NAFLD
5. NAFLD and Arterial Stiffness: Is There an Interplay?
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Angulo, P. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 346, 1221–1231. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Marchesini, G.; Bugianesi, E.; Forlani, G.; Cerrelli, F.; Lenzi, M.; Manini, R.; Natale, S.; Vanni, E.; Villanova, N.; Melchionda, N.; et al. Nonalcoholic fatty liver, steatohepatitis, and the metabolic syndrome. Hepatology 2003, 37, 917–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bedogni, G.; Miglioli, L.; Masutti, F.; Tiribelli, C.; Marchesini, G.; Bellentani, S. Prevalence of and risk factors for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: The Dionysos nutrition and liver study. Hepatology 2005, 42, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhala, N.; Angulo, P.; van der Poorten, D.; Lee, E.; Hui, J.M.; Saracco, G.; Adams, L.A.; Charatcharoenwitthaya, P.; Topping, J.H.; Bugianesi, E.; et al. The natural history of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease with advanced fibrosis or cirrhosis: An international collaborative study. Hepatology 2011, 54, 1208–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, D.L.; Kanwal, F.; El-Serag, H.B. Association between nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and risk for hepatocellular cancer, based on systematic review. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 10, 1342–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, N.; Afendy, A.; Stepanova, M.; Nader, F.; Srishord, M.; Rafiq, N.; Goodman, Z.; Younossi, Z. Independent predictors of fibrosis in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2009, 7, 1224–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prashanth, M.; Ganesh, H.K.; Vima, M.V.; John, M.; Bandgar, T.; Joshi, S.R.; Shah, S.R.; Rathi, P.M.; Joshi, A.S.; Thakkar, H.; et al. Prevalence of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Assoc. Physicians India 2009, 57, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Leite, N.; Villela-Nogueira, C.; Pannain, V.; Bottino, A.; Rezende, G.; Cardoso, C.; Salles, G. Histopathological stages of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in type 2 diabetes: Prevalences and correlated factors. Liver Int. 2011, 31, 700–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittal, S.; El-Serag, H.B.; Sada, Y.H.; Kanwal, F.; Duan, Z.; Temple, S.; May, S.B.; Kramer, J.R.; Richardson, P.A.; Davila, J.A. Hepatocellular carcinoma in the absence of cirrhosis in United States veterans is associated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 14, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musso, G.; Gambino, R.; Cassader, M.; Pagano, G. Meta-analysis: Natural history of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and diagnostic accuracy of non-invasive tests for liver disease severity. Ann. Med. 2011, 43, 617–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Koenig, A.B.; Abdelatif, D.; Fazel, Y.; Henry, L.; Wymer, M. Global Epidemiology of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease-Meta-Analytic Assessment of Prevalence, Incidence and Outcomes. Hepatology 2015, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morita, S.; Neto, D.D.S.; Morita, F.H.; Morita, N.K.; Lobo, S.M. Prevalence of Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Steatohepatitis Risk Factors in Patients Undergoing Bariatric Surgery. Obes. Surg. 2015, 25, 2335–2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matteoni, C.; Younossi, Z.; Gramlich, T.; Boparai, N.; Liu, Y.; McCullough, A. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A spectrum of clinical and pathological severity. Gastroenterology 1999, 116, 1413–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunt, E.M.; Janney, C.G.; Di Bisceglie, A.M.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; Bacon, B.R. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: A proposal for grading and staging the histological lesions. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 1999, 94, 2467–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben-Shlomo, Y.; Spears, M.; Boustred, C.; May, M.; Anderson, S.G.; Benjamin, E.J.; Boutouyrie, P.; Cameron, J.; Chen, C.H.; Cruickshank, J.K.; et al. Aortic pulse wave velocity improves cardiovascular event prediction: An individual participant meta-analysis of prospective observational data from 17,635 subjects. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2014, 63, 636–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavalcante, J.L.; Lima, J.A.; Redheuil, A.; Al-Mallah, M.H. Aortic stiffness: Current understanding and future directions. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2011, 57, 1511–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Athyros, V.G.; Tziomalos, K.; Katsiki, N.; Doumas, M.; Karagiannis, A.; Mikhailidis, D.P. Cardiovascular risk across the histological spectrum and the clinical manifestations of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: An update. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 6820–6834. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Targher, G.; Bertolini, L.; Rodella, S.; Tessari, R.; Zenari, L.; Lippi, G.; Arcaro, G. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is independently associated with an increased incidence of cardiovascular events in type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Care 2007, 30, 2119–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Targher, G.; Bertolini, L.; Padovani, R.; Rodella, S.; Tessari, R.; Zenari, L.; Day, C.; Arcaro, G. Prevalence of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and its association with cardiovascular disease among type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Care 2007, 30, 1212–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Targher, G.; Day, C.P.; Bonora, E. Risk of cardiovascular disease in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 1341–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anstee, Q.M.; Targher, G.; Day, C.P. Progression of NAFLD to diabetes mellitus, cardiovascular disease or cirrhosis. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 10, 330–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Choi, S.Y.; Park, E.H.; Lee, W.; Kang, J.H.; Kim, W.; Kim, Y.J.; Yoon, J.H.; Jeong, S.H.; Lee, D.H.; et al. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is associated with coronary artery calcification. Hepatology 2012, 56, 605–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oni, E.T.; Agatston, A.S.; Blaha, M.J.; Fialkow, J.; Cury, R.; Sposito, A.; Erbel, R.; Blankstein, R.; Feldman, T.; Al-Mallah, M.; et al. A systematic review: Burden and severity of subclinical cardiovascular disease among those with nonalcoholic fatty liver; should we care? Atherosclerosis 2013, 230, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mellinger, J.L.; Pencina, K.M.; Massaro, J.M.; Hoffmann, U.; Seshadri, S.; Fox, C.S.; O'Donnell, C.J.; Speliotes, E.K. Hepatic steatosis and cardiovascular disease outcomes: An analysis of the Framingham Heart Study. J. Hepatol. 2015, 63, 470–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, S.H.; Noh, T.S.; Cho, Y.S.; Hong, S.P.; Hyun, S.H.; Choi, J.Y.; Kim, B.T.; Lee, K.H. Association between nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and carotid artery inflammation evaluated by 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography. Angiology 2015, 66, 472–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Targher, G.; Zenari, L.; Bertolini, L.; Cigolini, M.; Padovani, R.; Falezza, G.; Rodella, S.; Arcaro, G.; Zoppini, G. Relations between carotid artery wall thickness and liver histology in subjects with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Diabetes Care 2006, 29, 1325–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoneda, M.; Mawatari, H.; Fujita, K.; Iida, H.; Yonemitsu, K.; Kato, S.; Takahashi, H.; Kirikoshi, H.; Inamori, M.; Nozaki, Y.; et al. High-sensitivity C-reactive protein is an independent clinical feature of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) and also of the severity of fibrosis in NASH. J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 42, 573–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wieckowska, A.; Papouchado, B.G.; Li, Z.; Lopez, R.; Zein, N.N.; Feldstein, A.E. Increased hepatic and circulating interleukin-6 levels in human nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 103, 1372–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thuy, S.; Ladurner, R.; Volynets, V.; Wagner, S.; Strahl, S.; Konigsrainer, A.; Maier, K.P.; Bischoff, S.C.; Bergheim, I. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in humans is associated with increased plasma endotoxin and plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 concentrations and with fructose intake. J. Nutr. 2008, 138, 1452–1455. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cigolini, M.; Targher, G.; Agostino, G.; Tonoli, M.; Muggeo, M.; DeSandre, G. Liver steatosis and its relation to plasma haemostatic factors in apparently healthy men—Role of the metabolic syndrome. Thromb. Haemost. 1996, 76, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Targher, G.; Bertolini, L.; Rodella, S.; Lippi, G.; Franchini, M.; Zoppini, G.; Muggeo, M.; Day, C. NASH predicts plasma inflammatory biomarkers independently of visceral fat in men. Obesity 2008, 16, 1394–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, C.; Herath, C.B.; Jia, Z.; Goodwin, M.; Mak, K.Y.; Watt, M.J.; Forbes, J.M.; Angus, P.W. Dietary glycotoxins exacerbate progression of experimental fatty liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2014, 60, 832–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pischon, T.; Girman, C.J.; Hotamisligil, G.S.; Rifai, N.; Hu, F.B.; Rimm, E.B. Plasma adiponectin levels and risk of myocardial infarction in men. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2004, 291, 1730–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leite, N.; Salles, G.; Cardoso, C.; Villela-Nogueira, C. Serum biomarkers in type 2 diabetic patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis and advanced fibrosis. Hepatol. Res. 2013, 43, 508–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekstedt, M.; Franzen, L.; Mathiesen, U.; Thorelius, L.; Holmqvist, M.; Bodemar, G.; Kechagias, S. Long-term follow-up of patients with NAFLD and elevated liver enzymes. Hepatology 2006, 44, 865–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soderberg, C.; Stal, P.; Askling, J.; Glaumann, H.; Lindberg, G.; Marmur, J.; Hultcrantz, R. Decreased Survival of Subjects with Elevated Liver Function Tests During a 28-Year Follow-Up. Hepatology 2010, 51, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Allen, A.M.; Wang, Z.; Prokop, L.J.; Murad, M.H.; Loomba, R. Fibrosis progression in nonalcoholic fatty liver vs. nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis of paired-biopsy studies. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 13, 643–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argo, C.K.; Northup, P.G.; Al-Osaimi, A.M.; Caldwell, S.H. Systematic review of risk factors for fibrosis progression in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. J. Hepatol. 2009, 51, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pais, R.; Charlotte, F.; Fedchuk, L.; Bedossa, P.; Lebray, P.; Poynard, T.; Ratziu, V.; Group, L.S. A systematic review of follow-up biopsies reveals disease progression in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver. J. Hepatol. 2013, 59, 550–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, S.A. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and fibrosis progression: The good, the bad, and the unknown. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 13, 655–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laurent, S.; Cockcroft, J.; van Bortel, L.; Boutouyrie, P.; Giannattasio, C.; Hayoz, D.; Pannier, B.; Vlachopoulos, C.; Wilkinson, I.; Struijker-Boudier, H. European Network for Non-invasive Investigation of Large, A., Expert consensus document on arterial stiffness: Methodological issues and clinical applications. Eur. Heart J. 2006, 27, 2588–2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laurent, S.; Boutouyrie, P. Recent advances in arterial stiffness and wave reflection in human hypertension. Hypertension 2007, 49, 1202–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zieman, S.J.; Melenovsky, V.; Kass, D.A. Mechanisms, pathophysiology, and therapy of arterial stiffness. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2005, 25, 932–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, C.P.; Baugh, R.; Wilson, C.A.; Burns, J. Age related changes in the tunica media of the vertebral artery: Implications for the assessment of vessels injured by trauma. J. Clin. Pathol. 2001, 54, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blacher, J.; Guerin, A.P.; Pannier, B.; Marchais, S.J.; Safar, M.E.; London, G.M. Impact of aortic stiffness on survival in end-stage renal disease. Circulation 1999, 99, 2434–2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laurent, S.; Boutouyrie, P.; Asmar, R.; Gautier, I.; Laloux, B.; Guize, L.; Ducimetiere, P.; Benetos, A. Aortic stiffness is an independent predictor of all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in hypertensive patients. Hypertension 2001, 37, 1236–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardoso, C.R.; Ferreira, M.T.; Leite, N.C.; Salles, G.F. Prognostic impact of aortic stiffness in high-risk type 2 diabetic patients: The Rio deJaneiro Type 2 Diabetes Cohort Study. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 3772–3778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willum-Hansen, T.; Staessen, J.A.; Torp-Pedersen, C.; Rasmussen, S.; Thijs, L.; Ibsen, H.; Jeppesen, J. Prognostic value of aortic pulse wave velocity as index of arterial stiffness in the general population. Circulation 2006, 113, 664–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, G.F.; Hwang, S.J.; Vasan, R.S.; Larson, M.G.; Pencina, M.J.; Hamburg, N.M.; Vita, J.A.; Levy, D.; Benjamin, E.J. Arterial stiffness and cardiovascular events: The Framingham Heart Study. Circulation 2010, 121, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiotani, A.; Motoyama, M.; Matsuda, T.; Miyanishi, T. Brachial-ankle pulse wave velocity in Japanese university students. Intern. Med. 2005, 44, 696–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvi, P.; Ruffini, R.; Agnoletti, D.; Magnani, E.; Pagliarani, G.; Comandini, G.; Pratico, A.; Borghi, C.; Benetos, A.; Pazzi, P. Increased arterial stiffness in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: The Cardio-GOOSE study. J. Hypertens. 2010, 28, 1699–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlachopoulos, C.; Manesis, E.; Baou, K.; Papatheodoridis, G.; Koskinas, J.; Tiniakos, D.; Aznaouridis, K.; Archimandritis, A.; Stefanadis, C. Increased arterial stiffness and impaired endothelial function in nonalcoholic Fatty liver disease: A pilot study. Am. J. Hypertens. 2010, 23, 1183–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.J.; Kim, N.H.; Kim, B.S.; Kang, J.H. The association between nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, metabolic syndrome and arterial stiffness in nondiabetic, nonhypertensive individuals. Cardiology 2012, 123, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Bi, Y.; Xu, M.; Ma, Z.; Xu, Y.; Wang, T.; Li, M.; Liu, Y.; Lu, J.; Chen, Y.; et al. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is associated with atherosclerosis in middle-aged and elderly Chinese. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2012, 32, 2321–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.J.; Shim, J.Y.; Moon, B.S.; Shin, Y.H.; Jung, D.H.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, H.R. The relationship between arterial stiffness and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2012, 57, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, R.C.; Beilin, L.J.; Ayonrinde, O.; Mori, T.A.; Olynyk, J.K.; Burrows, S.; Hands, B.; Adams, L.A. Importance of cardiometabolic risk factors in the association between nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and arterial stiffness in adolescents. Hepatology 2013, 58, 1306–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sunbul, M.; Agirbasli, M.; Durmus, E.; Kivrak, T.; Akin, H.; Aydin, Y.; Ergelen, R.; Yilmaz, Y. Arterial stiffness in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is related to fibrosis stage and epicardial adipose tissue thickness. Atherosclerosis 2014, 237, 490–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omelchenko, E.; Gavish, D.; Shargorodsky, M. Adiponectin is better predictor of subclinical atherosclerosis than liver function tests in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Am. Soc. Hypertens 2014, 8, 376–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.Y.; Zhao, Y.; Song, X.X.; Song, Z.Y. Association between non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and arterial stiffness in the non-obese, non-hypertensive, and non-diabetic young and middle-aged Chinese population. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2014, 15, 879–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Xu, M.; Wang, T.; Sun, J.; Sun, W.; Xu, B.; Huang, X.; Xu, Y.; Lu, J.; Li, X.; et al. Advanced fibrosis associates with atherosclerosis in subjects with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Atherosclerosis 2015, 241, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, C.Y.; Yang, Y.C.; Wu, J.S.; Sun, Z.J.; Lu, F.H.; Chang, C.J. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease associated with increased arterial stiffness in subjects with normal glucose tolerance, but not pre-diabetes and diabetes. Diabetes Vasc. Dis. Res. 2015, 12, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozturk, K.; Uygun, A.; Guler, A.K.; Demirci, H.; Ozdemir, C.; Cakir, M.; Sakin, Y.S.; Turker, T.; Sari, S.; Demirbas, S.; et al. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is an independent risk factor for atherosclerosis in young adult men. Atherosclerosis 2015, 240, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, G.E.; Choi, S.Y.; Kim, D.; Kwak, M.S.; Park, H.E.; Kim, M.K.; Yim, J.Y. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease as a risk factor of arterial stiffness measured by the cardioankle vascular index. Medicine 2015, 94, e654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Zhang, G.W.; Zhang, J.R.; Jin, D.; Li, Y.; Liu, T.; Wang, R.T. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is associated with progression of arterial stiffness. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2015, 25, 218–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leite, N.C.; Villela-Nogueira, C.A.; Fereira, M.T.; Cardoso, C.R.; Salles, G.F. Increasing aortic stiffness is predictive of advanced liver fibrosis in patients with type 2 diabetes: The Rio-T2DM cohort study. Liver. Int. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nickenig, G.; Roling, J.; Strehlow, K.; Schnabel, P.; Bohm, M. Insulin induces upregulation of vascular AT1 receptor gene expression by posttranscriptional mechanisms. Circulation 1998, 98, 2453–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jesmin, S.; Sakuma, I.; Salah-Eldin, A.; Nonomura, K.; Hattori, Y.; Kitabatake, A. Diminished penile expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptors at the insulin-resistant stage of a type II diabetic rat model: A possible cause for erectile dysfunction in diabetes. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2003, 31, 401–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzoni, D.; Porteri, E.; Guelfi, D.; Muiesan, M.L.; Valentini, U.; Cimino, A.; Girelli, A.; Rodella, L.; Bianchi, R.; Sleiman, I.; et al. Structural alterations in subcutaneous small arteries of normotensive and hypertensive patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Circulation 2001, 103, 1238–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cusi, K.; Maezono, K.; Osman, A.; Pendergrass, M.; Patti, M.E.; Pratipanawatr, T.; DeFronzo, R.A.; Kahn, C.R.; Mandarino, L.J. Insulin resistance differentially affects the PI 3-kinase- and MAP kinase-mediated signaling in human muscle. J. Clin. Investig. 2000, 105, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, S.; Khera, R.; Corrales-Medina, V.F.; Townsend, R.R.; Chirinos, J.A. Inflammation and arterial stiffness in humans. Atherosclerosis 2014, 237, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fargion, S.; Porzio, M.; Fracanzani, A.L. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and vascular disease: State-of-the-art. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 13306–13324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Author, Year | Number of Participants and Methods of Liver Investigation | Study Design | Aims | Conclusions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shiotani et al., 2005 [50] | 353 young university Japanese adults, submitted to abdominal ultrasound. | Transversal | To evaluate the validity of noninvasive ba-PWV measurements in overweight young adults. | ba-PWV was increased in males with NAFLD and might conceivably be useful to predict NAFLD. |
| Salvi et al., 2010 [51] | 220 participants (123 women), aged between 30 and 70 years, from the Cardio-gambettola observatory liver steatosis estimation (GOOSE) study, submitted to abdominal ultrasound. | Transversal | To evaluate the relationship between metabolic syndrome, NAFLD and subclinical vascular disease, evaluated by carotid IMT and cf-PWV. | A possible independent role of NAFLD in determining arterial stiffness. |
| Vlachopoulos et al., 2010 [52] | 23 biopsy-proven NAFLD patients and 28 matched controls. | Transversal | To investigate associations between NAFLD and functional arterial changes and early atherosclerosis. | NAFLD was associated with endothelial dysfunction and aortic stiffness (cf-PWV). |
| Kim et al., 2012 [53] | 4467 patients submitted to abdominal ultrasound. | Transversal | To evaluate the association of NAFLD and ba-PWV in patients with and without metabolic syndrome. | NAFLD was independently associated with increased ba-PWV, irrespective of multiple covariates, only in patients without metabolic syndrome. |
| Huang et al., 2012 [54] | 8632 Chinese from a population-based sample; NAFLD detected by ultrasound. | Transversal | To evaluate associations between NAFLD and early atherosclerosis (carotid IMT and ba-PWV). | NAFLD was associated with increased carotid IMT and ba-PWV, independent of traditional CV risk factors and metabolic syndrome. |
| Lee et al., 2012 [55] | 1442 healthy adults; NAFLD detected by ultrasound. | Transversal | To evaluate association between NAFLD and arterial stiffness (ba-PWV). | Arterial stiffness was associated with NAFD, independent of classical CV risk factors. |
| Huang et al., 2013 [56] | 964 adolescents (17-year-olds) from an Australian birth cohort, submitted to abdominal ultrasound. | Transversal | To examine if NAFLD was associated with aortic PWV, independent of cardiometabolic factors. | Aortic PWV was related to the presence of NAFLD that was predicated by the presence of an adverse metabolic profile in adolescents. |
| Sunbul et al., 2014 [57] | 100 patients with biopsy-proven NAFLD and 50 age- and sex-matched controls. | Transversal | To examine the relationship between aortic PWV and AIx, the histological severity of NAFLD and epicardial fat thickness (EFT). | Patients with NAFLD have an increased arterial stiffness, which reflects both the severity of liver fibrosis and increased EFT values. |
| Omelchenko et al., 2014 [58] | 52 NAFLD patients detected by ultrasound. | Transversal | To evaluate associations between adiponectin levels and arterial stiffness parameters (cf-PWV and AIx). | Adiponectin remained a significant predictor of PWV, even after controlling for age and gender, suggesting an active role of adiponectin in the pathophysiology of vascular disease in NAFLD patients. |
| Yu et al., 2014 [59] | 1296 non-obese, non-hypertensive, non-diabetic adults, NAFLD by ultrasound. | Transversal | To evaluate then association between NAFLD and arterial stiffness (ba-PWV). | NAFLD was associated with ba-PWV in Chinese individuals without obesity, hypertension and diabetes. |
| Chen et al., 2015 [60] | 2550 participants with ultrasound-confirmed NAFLD from a community-based sample. | Transversal | To evaluate whether advanced fibrosis assessed by NAFLD fibrosis score was associated with subclinical atherosclerosis in NAFLD patients. | Advanced fibrosis was associated with carotid intima media thickness, the presence of carotid plaques and arterial stiffness, independent of cardiometabolic risk factors and insulin resistance. |
| Chou et al., 2015 [61] | 4860 non-diabetic, pre-diabetic and newly-diagnosed T2DM individuals, evaluated by abdominal ultrasound. | Transversal | To evaluate PWV in patients with NAFLD. | The effect of NAFLD on arterial stiffness was apparent only in subjects with normal glucose tolerance. |
| Ozturk et al., 2015 [62] | 61 biopsy-proven NAFLD patients and 41 controls without NAFLD; adult male patients between 20 and 40 years of age. | Transversal | To evaluate the relationship between NAFLD and subclinical atherosclerosis and to investigate the associations according to the presence or absence of metabolic syndrome. | The presence of NAFLD was associated with endothelial dysfunction and atherosclerosis, independent of metabolic syndrome. |
| Chung et al., 2015 [63] | 2954 healthy individuals; NAFLD detected by ultrasound. | Transversal | To evaluate the association between NAFLD and arterial stiffness (cardio-ankle vascular index). | NAFLD was associated with increased arterial stiffness, independent of cardio-metabolic risk factors. |
| Li et al., 2015 [64] | 728 men and 497 women without hypertension and diabetes; NAFLD detected by ultrasound. | Longitudinal | To evaluate the relationship between the presence of NAFLD at baseline and progression of arterial stiffness (ba-PWV) during follow-up (5 years). | Patients with NAFLD had a faster progression of arterial stiffness, independent of other CV risk factors. |
| Leite et al., 2015 [65] | 291 T2DM patients; NAFLD by abdominal ultrasound or liver biopsy. | Longitudinal | To evaluate the association between progressions of aortic PWV (7 years of follow-up) with advanced liver fibrosis identified by transient elastography. | High or increasing aortic stiffness predicted the development of advanced liver fibrosis on transient elastography. |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Villela-Nogueira, C.A.; Leite, N.C.; Cardoso, C.R.L.; Salles, G.F. NAFLD and Increased Aortic Stiffness: Parallel or Common Physiopathological Mechanisms? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 460. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17040460
Villela-Nogueira CA, Leite NC, Cardoso CRL, Salles GF. NAFLD and Increased Aortic Stiffness: Parallel or Common Physiopathological Mechanisms? International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2016; 17(4):460. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17040460
Chicago/Turabian StyleVillela-Nogueira, Cristiane A., Nathalie C. Leite, Claudia R. L. Cardoso, and Gil F. Salles. 2016. "NAFLD and Increased Aortic Stiffness: Parallel or Common Physiopathological Mechanisms?" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 17, no. 4: 460. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17040460
APA StyleVillela-Nogueira, C. A., Leite, N. C., Cardoso, C. R. L., & Salles, G. F. (2016). NAFLD and Increased Aortic Stiffness: Parallel or Common Physiopathological Mechanisms? International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(4), 460. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17040460