Protective Effect of Salicornia europaea Extracts on High Salt Intake-Induced Vascular Dysfunction and Hypertension
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Composition of Salicornia europaea Extracts (SE)
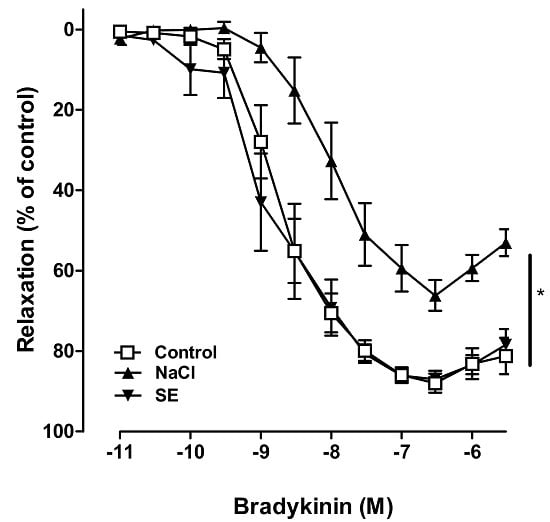
2.2. Effect of SE on High Salt-Induced Vascular Dysfunction in Porcine Coronary Arteries
2.3. Influence of High Salt and SE on Body Weight and Food Consumption
2.4. Effect of SE on Blood Pressure in Normotensive Rat
2.5. Effect of SE on Blood Pressure in Hypertensive Rats
2.6. Kidney Index and Cardiac Index
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Ethics Statement
4.2. Plant Material and Analysis of SE Constituents by HPLC
4.3. Vascular Reactivity Study
4.4. Animals and Experimental Design
4.5. Body Weight and Feed Intake
4.6. Kidney Index (KI) and Cardiac Index (CI) Analysis
4.7. Determination of Tail Arterial Pressure
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SE | Salicornia europaea extracts |
| SBP | Systolic blood pressure |
| DBP | Diastolic blood pressure |
| MAP | Mean arterial pressure |
| CVD | Cardiovascular disease |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| BP | Blood pressure |
| tR | Retention time |
| SHR | Spontaneously hypertensive rat |
| SD | Sprague–Dawley |
| KI | Kidney index |
| CI | Cardiac index |
| HPLC | High-pressure liquid chromatography |
| eNOS | Endothelial nitric oxide synthase |
References
- Kearney, P.M.; Whelton, M.; Reynolds, K.; Muntner, P.; Whelton, P.K.; He, J. Global burden of hypertension: Analysis of worldwide data. Lancet 2005, 365, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. A Global Brief on Hypertension: Silent Killer, Global Public Health Crisis; WHO Press: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Carretero, O.A.; Oparil, S. Essential hypertension. Part I: Definition and etiology. Circulation 2000, 101, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; McDermott, R. Obesity, albuminuria, and γ-glutamyl transferase predict incidence of hypertension in indigenous Australians in rural and remote communities in northern Australia. J. Hypertens. 2015, 33, 704–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.Y.; Park, H.C.; Ha, S.K. Salt Sensitivity and Hypertension: A Paradigm Shift from Kidney Malfunction to Vascular Endothelial Dysfunction. Electrolyte Blood Press 2015, 13, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karppanen, H.; Mervaala, E. Sodium intake and hypertension. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2006, 49, 59–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, F.J.; Burnier, M.; Macgregor, G.A. Nutrition in cardiovascular disease: Salt in hypertension and heart failure. Eur. Heart J. 2011, 32, 3073–3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunt, J.C. Sodium intake and hypertension: A cause for concern. Ann. Intern. Med. 1983, 98, 724–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, L.; Yang, G.; Xu, H.; Liu, J. Chinese Herbal Medicine Combined with Conventional Therapy for Blood Pressure Variability in Hypertension Patients: A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 2015, 582751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Xiong, X. Evidence-based Chinese medicine for hypertension. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013, 978398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, X.; Yang, X.; Liu, W.; Chu, F.; Wang, P.; Wang, J. Trends in the treatment of hypertension from the perspective of traditional Chinese medicine. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013, 275279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isca, V.; Seca, A.M.; Pinto, D.C.; Silva, A. An overview of Salicornia genus: The phytochemical and pharmacological profile. Nat. Prod. Res. Rev. 2014, 2, 145–176. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.H.; Kim, T.H. Salicornia SPP.-derived salt and its production process. Patent US20100304000, 16 April 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Cowan, C.L.; Cohen, R.A. Two mechanisms mediate relaxation by bradykinin of pig coronary artery: NO-dependent and -independent responses. Am. J. Physiol. 1991, 261, H830–H835. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, A.; Yamamoto, M.; Jokura, H.; Fujii, A.; Tokimitsu, I.; Hase, T.; Saito, I. Ferulic acid restores endothelium-dependent vasodilation in aortas of spontaneously hypertensive rats. Am. J. Hypertens. 2007, 20, 508–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kusche-Vihrog, K.; Schmitz, B.; Brand, E. Salt controls endothelial and vascular phenotype. Pflugers Arch. 2015, 467, 499–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bragulat, E.; de la Sierra, A.; Antonio, M.T.; Coca, A. Endothelial dysfunction in salt-sensitive essential hypertension. Hypertension 2001, 37, 444–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oberleithner, H.; Riethmuller, C.; Schillers, H.; MacGregor, G.A.; de Wardener, H.E.; Hausberg, M. Plasma sodium stiffens vascular endothelium and reduces nitric oxide release. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 16281–16286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grootaert, C.; Kamiloglu, S.; Capanoglu, E.; van Camp, J. Cell Systems to Investigate the Impact of Polyphenols on Cardiovascular Health. Nutrients 2015, 7, 9229–9255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sanders, P.W. Vascular consequences of dietary salt intake. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2009, 297, F237–F243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf-Maier, K.; Cooper, R.S.; Banegas, J.R.; Giampaoli, S.; Hense, H.W.; Joffres, M.; Kastarinen, M.; Poulter, N.; Primatesta, P.; Rodríguez-Artalejo, F. Hypertension prevalence and blood pressure levels in 6 European countries, Canada, and the United States. JAMA 2003, 289, 2363–2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mozaffarian, D.; Fahimi, S.; Singh, G. Global Sodium Consumption and Death from Cardiovascular Causes. J. Vasc. Surg. 2015, 2, 567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohta, Y.; Tsuchihashi, T.; Ueno, M.; Kajioka, T.; Onaka, U.; Tominaga, M.; Eto, K. Relationship between the awareness of salt restriction and the actual salt intake in hypertensive patients. Hypertens. Res. 2004, 27, 243–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, C.L.; Henry, J.E. Strategies to Reduce Sodium Intake in the United States; National Academies Press (US): Washington, DC, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Suwanmanon, K.; Hsieh, P.-C. Effect of γ-aminobutyric acid and nattokinase-enriched fermented beans on the blood pressure of spontaneously hypertensive and normotensive Wistar-Kyoto rats. J. Food Drug Anal. 2014, 22, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldo, M.P.; Zaniqueli, D.; Forechi, L.; Machado, R.C.; Rodrigues, S.L.; Mill, J.G. Effects of spironolactone in spontaneously hypertensive adult rats subjected to high salt intake. Clinics 2011, 66, 477–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, H.; Kashimoto, N.; Kajimura, J.; Kamiya, K. A miso (Japanese soybean paste) diet conferred greater protection against hypertension than a sodium chloride diet in Dahl salt-sensitive rats. Hypertens. Res. 2006, 29, 731–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, T.L.; Hutchins, P.M. Central hemodynamics in the developmental stage of spontaneous hypertension in the unanesthetized rat. Hypertension 1979, 1, 508–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.Y.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, K.M.; Oak, M.H. Vasorelaxant prenylated flavonoids from the roots of Sophora flavescens. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2013, 77, 395–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norsidah, K.Z.; Asmadi, A.Y.; Azizi, A.; Faizah, O.; Kamisah, Y. Palm tocotrienol-rich fraction improves vascular proatherosclerotic changes in hyperhomocysteinemic rats. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013, 976967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Groups | KI (mg·g−1) | CI (mg·g−1) |
|---|---|---|
| CTR–SD | 6.23 ± 0.31 | 3.18 ± 0.36 |
| HS–SD | 6.46 ± 0.38 | 2.86 ± 0.15 |
| SE–SD | 6.15 ± 0.43 | 2.72 ± 0.25 |
| CTR–SHR | 5.99 ± 0.31 | 3.62 ± 0.26 * |
| HS–SHR | 6.19 ± 0.20 | 3.67 ± 0.28 * |
| SE–SHR | 6.47 ± 0.43 | 3.96 ± 0.25 * |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Panth, N.; Park, S.-H.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, D.-H.; Oak, M.-H. Protective Effect of Salicornia europaea Extracts on High Salt Intake-Induced Vascular Dysfunction and Hypertension. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1176. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17071176
Panth N, Park S-H, Kim HJ, Kim D-H, Oak M-H. Protective Effect of Salicornia europaea Extracts on High Salt Intake-Induced Vascular Dysfunction and Hypertension. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2016; 17(7):1176. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17071176
Chicago/Turabian StylePanth, Nisha, Sin-Hee Park, Hyun Jung Kim, Deuk-Hoi Kim, and Min-Ho Oak. 2016. "Protective Effect of Salicornia europaea Extracts on High Salt Intake-Induced Vascular Dysfunction and Hypertension" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 17, no. 7: 1176. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17071176
APA StylePanth, N., Park, S. -H., Kim, H. J., Kim, D. -H., & Oak, M. -H. (2016). Protective Effect of Salicornia europaea Extracts on High Salt Intake-Induced Vascular Dysfunction and Hypertension. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(7), 1176. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17071176