Circulating Organ-Specific MicroRNAs Serve as Biomarkers in Organ-Specific Diseases: Implications for Organ Allo- and Xeno-Transplantation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Current Status of Biomarkers in the Detection of Graft Rejection
1.2. Potential of Circulating miRNAs as Biomarkers of Graft Rejection
2. Background
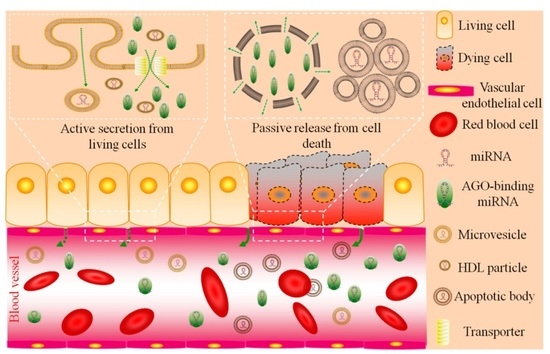
2.1. Circulating miRNA: Sources and Functions
2.2. Circulating Liver-Specific miRNAs Serve as Novel Biomarkers in Liver Disease
2.3. Circulating Cardiac-Specific miRNAs Serve as Novel Biomarkers in Heart Disease
2.4. Circulating Kidney-Specific miRNAs Serve as Novel Biomarkers in Renal Disease
2.5. Circulating Lung-Specific miRNAs Serve as Novel Biomarkers in Lung Disease
3. The Potential Role of Circulating miRNAs to Detect Graft Rejection
3.1. Circulating Organ-Specific miRNAs in Organ Allotransplantation
3.2. Circulating Immune-Associated miRNAs in Organ Allotransplantation
3.3. Circulating Organ-Specific miRNAs in Organ Xenotransplantation
4. Discussion—Challenges and Solutions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AGO | argonaute protein |
| HDL | high density lipoprotein |
| hsa | Homo sapiens |
| miRNA(miR-) | MicroRNA |
| PCR | polymerase chain reaction |
| qPCR | quantitative PCR |
| RNA | ribonucleic acid |
| RISC | RNA-induced silencing complex |
| ssc | Sus scrofa |
| CMV | Cytomegalovirus |
References
- Buchman, T.G. Multiple organ failure. Curr. Opin. Gen. Surg. 1993, 26–31. [Google Scholar]
- Cooper, D.K.; Ekser, B.; Tector, A.J. Immunobiological barriers to xenotransplantation. Int. J. Surg. 2015, 23, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, W.W.; Taheri, D.; Tolkoff-Rubin, N.; Colvin, R.B. Clinical role of the renal transplant biopsy. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2012, 8, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snyder, T.M.; Khush, K.K.; Valantine, H.A.; Quake, S.R. Universal noninvasive detection of solid organ transplant rejection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 6229–6234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sood, S.; Testro, A.G. Immune monitoring post liver transplant. World J. Transplant. 2014, 4, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Townamchai, N.; Eiam-Ong, S. Biomarkers in kidney transplantation: From bench to bedside. World J. Nephrol. 2015, 4, 487–491. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ronco, C. Acute kidney injury: From clinical to molecular diagnosis. Crit. Care 2016, 20, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 2004, 116, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, B.P.; Burge, C.B.; Bartel, D.P. Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell 2005, 120, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croce, C.M.; Calin, G.A. MiRNAs, cancer, and stem cell division. Cell 2005, 122, 6–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambros, V. The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature 2004, 431, 350–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagos-Quintana, M.; Rauhut, R.; Yalcin, A.; Meyer, J.; Lendeckel, W.; Tuschl, T. Identification of tissue-specific microRNAs from mouse. Curr. Biol. 2002, 12, 735–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landgraf, P.; Rusu, M.; Sheridan, R.; Sewer, A.; Iovino, N.; Aravin, A.; Pfeffer, S.; Rice, A.; Kamphorst, A.O.; Landthaler, M.; et al. A mammalian microRNA expression atlas based on small RNA library sequencing. Cell 2007, 129, 1401–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Getz, G.; Miska, E.A.; Alvarez-Saavedra, E.; Lamb, J.; Peck, D.; Sweet-Cordero, A.; Ebert, B.L.; Mak, R.H.; Ferrando, A.A.; et al. MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature 2005, 435, 834–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Ba, Y.; Ma, L.; Cai, X.; Yin, Y.; Wang, K.; Guo, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, J.; Guo, X.; et al. Characterization of microRNA s in serum: A novel class of biomarkers for diagnosis of cancer and other diseases. Cell Res. 2008, 18, 997–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farid, W.R.; Pan, Q.; van der Meer, A.J.; de Ruiter, P.E.; Ramakrishnaiah, V.; de Jonge, J.; Kwekkeboom, J.; Janssen, H.L.; Metselaar, H.J.; Tilanus, H.W.; et al. Hepatocyte-derived microRNAs as serum biomarkers of hepatic injury and rejection after liver transplantation. Liver Transplant. 2012, 18, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miura, K.; Morisaki, S.; Abe, S.; Higashijima, A.; Hasegawa, Y.; Miura, S.; Tateishi, S.; Mishima, H.; Yoshiura, K.; Masuzaki, H. Circulating levels of maternal plasma cell-free pregnancy-associated placenta-specific microRNAs are associated with placental weight. Placenta 2014, 35, 848–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, M.; Ge, Q.; Li, H.; Yang, Q.; Lu, J.; Zhang, D.; Lu, Z. Sequencing the miRNAs in maternal plasma from women before and after parturition. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2012, 12, 4035–4043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarzenbach, H.; Nishida, N.; Calin, G.A.; Pantel, K. Clinical relevance of circulating cell-free microRNA s in cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 11, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sigdel, T.K.; Vitalone, M.J.; Tran, T.Q.; Dai, H.; Hsieh, S.C.; Salvatierra, O.; Sarwal, M.M. A rapid noninvasive assay for the detection of renal transplant injury. Transplantation 2013, 96, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vlaminck, I.; Martin, L.; Kertesz, M.; Patel, K.; Kowarsky, M.; Strehl, C.; Cohen, G.; Luikart, H.; Neff, N.F.; Okamoto, J.; et al. Noninvasive monitoring of infection and rejection after lung transplantation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 13336–13341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, Y.M.; Tein, M.S.; Pang, C.C.; Yeung, C.K.; Tong, K.L.; Hjelm, N.M. Presence of donor-specific DNA in plasma of kidney and liver-transplant recipients. Lancet 1998, 351, 1329–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, D.H.; Mainolfi, E.; Elias, E.; Neuberger, J.M.; Rothlein, R. Detection of circulating intercellular adhesion molecule-1 after liver transplantation—Evidence of local release within the liver during graft rejection. Transplantation 1993, 55, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Z.K.; Tian, P.X.; Wang, X.Z.; Xue, W.J.; Ding, X.M.; Zheng, J.; Ding, C.G.; Mao, T.C.; Duan, W.L.; Xi, M. Kidney injury molecule-1 and osteopontin: New markers for prediction of early kidney transplant rejection. Mol. Immunol. 2013, 54, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pritchard, C.C.; Cheng, H.H.; Tewari, M. MicroRNA profiling: Approaches and considerations. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2012, 13, 358–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendell, J.T.; Olson, E.N. MicroRNA s in stress signaling and human disease. Cell 2012, 148, 1172–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleissner, F.; Goerzig, Y.; Haverich, A.; Thum, T. Microvesicles as novel biomarkers and therapeutic targets in transplantation medicine. Am. J. Transplant. 2012, 12, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, J.A.; Baxter, D.H.; Zhang, S.; Huang, D.Y.; Huang, K.H.; Lee, M.J.; Galas, D.J.; Wang, K. The microRNA spectrum in 12 body fluids. Clin. Chem. 2010, 56, 1733–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chim, S.S.; Shing, T.K.; Hung, E.C.; Leung, T.Y.; Lau, T.K.; Chiu, R.W.; Lo, Y.M. Detection and characterization of placental microRNAs in maternal plasma. Clin. Chem. 2008, 54, 482–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrie, C.H.; Gal, S.; Dunlop, H.M.; Pushkaran, B.; Liggins, A.P.; Pulford, K.; Banham, A.H.; Pezzella, F.; Boultwood, J.; Wainscoat, J.S.; et al. Detection of elevated levels of tumour-associated microRNA s in serum of patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Br. J. Haematol. 2008, 141, 672–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, P.S.; Parkin, R.K.; Kroh, E.M.; Fritz, B.R.; Wyman, S.K.; Pogosova-Agadjanyan, E.L.; Peterson, A.; Noteboom, J.; O’Briant, K.C.; Allen, A.; et al. Circulating microRNAs as stable blood-based markers for cancer detection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 10513–10518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turchinovich, A.; Weiz, L.; Burwinkel, B. Extracellular mirnas: The mystery of their origin and function. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2012, 37, 460–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajit, S.K. Circulating microRNAs as biomarkers, therapeutic targets, and signaling molecules. Sensors 2012, 12, 3359–3369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grasedieck, S.; Sorrentino, A.; Langer, C.; Buske, C.; Dohner, H.; Mertens, D.; Kuchenbauer, F. Circulating microRNAs in hematological diseases: Principles, challenges, and perspectives. Blood 2013, 121, 4977–4984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arroyo, J.D.; Chevillet, J.R.; Kroh, E.M.; Ruf, I.K.; Pritchard, C.C.; Gibson, D.F.; Mitchell, P.S.; Bennett, C.F.; Pogosova-Agadjanyan, E.L.; Stirewalt, D.L.; et al. Argonaute2 complexes carry a population of circulating microRNAs independent of vesicles in human plasma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 5003–5008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turchinovich, A.; Weiz, L.; Langheinz, A.; Burwinkel, B. Characterization of extracellular circulating microRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, 7223–7233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winter, J.; Jung, S.; Keller, S.; Gregory, R.I.; Diederichs, S. Many roads to maturity: MicroRNA biogenesis pathways and their regulation. Nat. Cell Biol. 2009, 11, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pegtel, D.M.; Cosmopoulos, K.; Thorley-Lawson, D.A.; van Eijndhoven, M.A.; Hopmans, E.S.; Lindenberg, J.L.; de Gruijl, T.D.; Wurdinger, T.; Middeldorp, J.M. Functional delivery of viral miRNAs via exosomes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 6328–6333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosaka, N.; Iguchi, H.; Yoshioka, Y.; Takeshita, F.; Matsuki, Y.; Ochiya, T. Secretory mechanisms and intercellular transfer of microRNAs in living cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 17442–17452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittelbrunn, M.; Gutierrez-Vazquez, C.; Villarroya-Beltri, C.; Gonzalez, S.; Sanchez-Cabo, F.; Gonzalez, M.A.; Bernad, A.; Sanchez-Madrid, F. Unidirectional transfer of MicroRNA-loaded exosomes from T cells to antigen-presenting cells. Nat. Commun. 2011, 2, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trajkovic, K.; Hsu, C.; Chiantia, S.; Rajendran, L.; Wenzel, D.; Wieland, F.; Schwille, P.; Brugger, B.; Simons, M. Ceramide triggers budding of exosome vesicles into multivesicular endosomes. Science 2008, 319, 1244–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valadi, H.; Ekstrom, K.; Bossios, A.; Sjostrand, M.; Lee, J.J.; Lotvall, J.O. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007, 9, 654–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunter, M.P.; Ismail, N.; Zhang, X.; Aguda, B.D.; Lee, E.J.; Yu, L.; Xiao, T.; Schafer, J.; Lee, M.L.; Schmittgen, T.D.; et al. Detection of microRNA expression in human peripheral blood microvesicles. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turchinovich, A.; Samatov, T.R.; Tonevitsky, A.G.; Burwinkel, B. Circulating mirnas: Cell-cell communication function? Front. Genet. 2013, 4, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, D.; Chen, X.; Li, J.; Li, L.; Bian, Z.; Sun, F.; Lu, J.; Yin, Y.; Cai, X.; et al. Secreted monocytic mir-150 enhances targeted endothelial cell migration. Mol. Cell 2010, 39, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collino, F.; Deregibus, M.C.; Bruno, S.; Sterpone, L.; Aghemo, G.; Viltono, L.; Tetta, C.; Camussi, G. Microvesicles derived from adult human bone marrow and tissue specific mesenchymal stem cells shuttle selected pattern of miRNAs. PLoS ONE 2009, 5, e11803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robbins, P.D.; Dorronsoro, A.; Booker, C.N. Regulation of chronic inflammatory and immune processes by extracellular vesicles. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 1173–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Candia, P.; De Rosa, V.; Casiraghi, M.; Matarese, G. Extracellular RNAs: A secret arm of immune system regulation. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 7221–7228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathivanan, S.; Hong, J.; Simpson, R.J. Exosomes: Extracellular organelles important in intercellular communication. J. Proteom. 2010, 73, 1907–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clotilde, T.; Matias, O.; Elodie, S. Membrane vesicles as conveyors of immune responses. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 9, 581–593. [Google Scholar]
- Vickers, K.C.; Palmisano, B.T.; Shoucri, B.M.; Shamburek, R.D.; Remaley, A.T. microRNAs are transported in plasma and delivered to recipient cells by high-density lipoproteins. Nat. Cell Biol. 2011, 13, 423–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zernecke, A.; Bidzhekov, K.; Noels, H.; Shagdarsuren, E.; Gan, L.; Denecke, B.; Hristov, M.; Koppel, T.; Jahantigh, M.N.; Lutgens, E.; et al. Delivery of microRNA -126 by apoptotic bodies induces CXCL12-dependent vascular protection. Sci. Signal. 2009, 2, ra81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cocucci, E.; Racchetti, G.; Meldolesi, J. Shedding microvesicles: Artefacts no more. Trends Cell Biol. 2009, 19, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muralidharan-Chari, V.; Clancy, J.W.; Sedgwick, A.; D’Souza-Schorey, C. Microvesicles: Mediators of extracellular communication during cancer progression. J. Cell Sci. 2010, 123, 1603–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iveson-Iveson, J. Anatomy and physiology: The accessory organs of digestion. Nurs. Mirror 1979, 148, 24–25. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.; Nicolas, E.; Marks, D.; Sander, C.; Lerro, A.; Buendia, M.A.; Xu, C.; Mason, W.S.; Moloshok, T.; Bort, R.; et al. MiR-122, a mammalian liver-specific microRNA, is processed from HCR mRNA and may downregulate the high affinity cationic amino acid transporter CAT-1. RNA Biol. 2004, 1, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esau, C.; Davis, S.; Murray, S.F.; Yu, X.X.; Pandey, S.K.; Pear, M.; Watts, L.; Booten, S.L.; Graham, M.; McKay, R.; et al. MiR-122 regulation of lipid metabolism revealed by in vivo antisense targeting. Cell Metab. 2006, 3, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marsit, C.J.; Eddy, K.; Kelsey, K.T. microRNA responses to cellular stress. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 10843–10848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, X.G.; Qiu, R.L.; Wu, Y.H.; Li, Z.X.; Xie, P.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, J.J.; Zeng, L.X.; Tang, J.; Maharjan, A.; et al. Overexpression of miR-122 promotes the hepatic differentiation and maturation of mouse ESCs through a miR-122/FOXA1/HNF4A-positive feedback loop. Liver Int. 2014, 34, 281–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enache, L.S.; Enache, E.L.; Ramiere, C.; Diaz, O.; Bancu, L.; Sin, A.; Andre, P. Circulating RNA molecules as biomarkers in liver disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 17644–17666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.H.; Jiang, D.; Rao, H.Y.; Zhao, J.M.; Wang, Y.; Wei, L. Absolute quantification of serum microRNA -122 and its correlation with liver inflammation grade and serum alanine aminotransferase in chronic hepatitis C patients. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2015, 30, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cermelli, S.; Ruggieri, A.; Marrero, J.A.; Ioannou, G.N.; Beretta, L. Circulating microRNA s in patients with chronic hepatitis C and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e23937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Ouyang, X.; Jiang, X.; Gu, D.; Lin, Y.; Kong, S.K.; Xie, W. Dysregulated serum microRNA expression profile and potential biomarkers in hepatitis C virus-infected patients. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2015, 12, 590–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bala, S.; Tilahun, Y.; Taha, O.; Alao, H.; Kodys, K.; Catalano, D.; Szabo, G. Increased microRNA -155 expression in the serum and peripheral monocytes in chronic HCV infection. J. Transl. Med. 2012, 10, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.M.; Hu, Z.B.; Zhou, Z.X.; Chen, X.; Liu, F.Y.; Zhang, J.F.; Shen, H.B.; Zhang, C.Y.; Zen, K. Serum microRNA profiles serve as novel biomarkers for HBV infection and diagnosis of HBV-positive hepatocarcinoma. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 9798–9807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bihrer, V.; Friedrich-Rust, M.; Kronenberger, B.; Forestier, N.; Haupenthal, J.; Shi, Y.; Peveling-Oberhag, J.; Radeke, H.H.; Sarrazin, C.; Herrmann, E.; et al. Serum miR-122 as a biomarker of necroinflammation in patients with chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 106, 1663–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Li, Q.Y.; Guo, Z.Z.; Guan, Y.; Du, J.; Lu, Y.Y.; Hu, Y.Y.; Liu, P.; Huang, S.; Su, S.B. Serum levels of microRNAs can specifically predict liver injury of chronic hepatitis B. World J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 18, 5188–5196. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Winther, T.N.; Bang-Berthelsen, C.H.; Heiberg, I.L.; Pociot, F.; Hogh, B. Differential plasma microRNA profiles in HBEAG positive and hbeag negative children with chronic hepatitis B. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e58236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Wu, C.; Che, X.; Wang, L.; Yu, D.; Zhang, T.; Huang, L.; Li, H.; Tan, W.; Wang, C.; et al. Circulating MicroRNAs, miR-21, miR-122, and miR-223, in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma or chronic hepatitis. Mol. Carcinog. 2011, 50, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, P.; Cheng, S.Q.; Wang, H.; Li, N.; Chen, Y.F.; Gao, C.F. Serum microRNA s as biomarkers for hepatocellular carcinoma in chinese patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e28486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anadol, E.; Schierwagen, R.; Elfimova, N.; Tack, K.; Schwarze-Zander, C.; Eischeid, H.; Noetel, A.; Boesecke, C.; Jansen, C.; Dold, L.; et al. Circulating microRNA S as a marker for liver injury in human immunodeficiency virus patients. Hepatology 2015, 61, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Zhang, S.; Marzolf, B.; Troisch, P.; Brightman, A.; Hu, Z.; Hood, L.E.; Galas, D.J. Circulating microRNAs, potential biomarkers for drug-induced liver injury. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 4402–4407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Starkey Lewis, P.J.; Dear, J.; Platt, V.; Simpson, K.J.; Craig, D.G.; Antoine, D.J.; French, N.S.; Dhaun, N.; Webb, D.J.; Costello, E.M.; et al. Circulating microRNAs as potential markers of human drug-induced liver injury. Hepatology 2011, 54, 1767–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koberle, V.; Waidmann, O.; Kronenberger, B.; Andrei, A.; Susser, S.; Fuller, C.; Perner, D.; Zeuzem, S.; Sarrazin, C.; Piiper, A. Serum MicroRNA-122 kinetics in patients with chronic hepatitis C virus infection during antiviral therapy. J. Viral Hepat. 2013, 20, 530–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trebicka, J.; Anadol, E.; Elfimova, N.; Strack, I.; Roggendorf, M.; Viazov, S.; Wedemeyer, I.; Drebber, U.; Rockstroh, J.; Sauerbruch, T.; et al. Hepatic and serum levels of miR-122 after chronic HCV-induced fibrosis. J. Hepatol. 2013, 58, 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Y.; Ge, G.; Pan, T.; Wen, D.; Chen, L.; Yu, X.; Zhou, X.; Gan, J. A serum microRNA panel as potential biomarkers for hepatocellular carcinoma related with hepatitis B virus. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Yu, L.; Gao, X.; Hu, J.; Wang, J.; Dai, Z.; Wang, J.F.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, S.; Huang, X.; et al. Plasma microRNA panel to diagnose hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 4781–4788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arataki, K.; Hayes, C.N.; Akamatsu, S.; Akiyama, R.; Abe, H.; Tsuge, M.; Miki, D.; Ochi, H.; Hiraga, N.; Imamura, M.; et al. Circulating microRNA-22 correlates with microRNA-122 and represents viral replication and liver injury in patients with chronic hepatitis B. J. Med.Virol. 2013, 85, 789–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giray, B.G.; Emekdas, G.; Tezcan, S.; Ulger, M.; Serin, M.S.; Sezgin, O.; Altintas, E.; Tiftik, E.N. Profiles of serum microRNAs; miR-125b-5p and miR223–3p serve as novel biomarkers for hbv-positive hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2014, 41, 4513–4519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Y.; Ge, G.; Pan, T.; Wen, D.; Gan, J. A pilot study of serum microRNAs panel as potential biomarkers for diagnosis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e105192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kent, A.F. Researches on the structure and function of the mammalian heart. J. Physiol. 1893, 14, 233–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pleister, A.; Selemon, H.; Elton, S.M.; Elton, T.S. Circulating miRNAs: Novel biomarkers of acute coronary syndrome? Biomark. Med. 2013, 7, 287–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.K.; Zhu, J.Q.; Zhang, J.T.; Li, Q.; Li, Y.; He, J.; Qin, Y.W.; Jing, Q. Circulating microRNA: A novel potential biomarker for early diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction in humans. Eur. Heart J. 2010, 31, 659–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimmeler, S.; Zeiher, A.M. Circulating microRNAs: Novel biomarkers for cardiovascular diseases? Eur. Heart J. 2010, 31, 2705–2707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Alessandra, Y.; Devanna, P.; Limana, F.; Straino, S.; Di Carlo, A.; Brambilla, P.G.; Rubino, M.; Carena, M.C.; Spazzafumo, L.; De Simone, M.; et al. Circulating microRNAs are new and sensitive biomarkers of myocardial infarction. Eur. Heart J. 2010, 31, 2765–2773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corsten, M.F.; Dennert, R.; Jochems, S.; Kuznetsova, T.; Devaux, Y.; Hofstra, L.; Wagner, D.R.; Staessen, J.A.; Heymans, S.; Schroen, B. Circulating microRNA-208b and microRNA-499 reflect myocardial damage in cardiovascular disease. Circ. Cardiovasc. Genet. 2010, 3, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Tan, N.; Yang, J.; Liu, X.; Cao, X.; He, P.; Dong, X.; Qin, S.; Zhang, C. A translational study of circulating cell-free microRNA-1 in acute myocardial infarction. Clin. Sci. 2010, 119, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ai, J.; Zhang, R.; Li, Y.; Pu, J.; Lu, Y.; Jiao, J.; Li, K.; Yu, B.; Li, Z.; Wang, R.; et al. Circulating microRNA-1 as a potential novel biomarker for acute myocardial infarction. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 391, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adachi, T.; Nakanishi, M.; Otsuka, Y.; Nishimura, K.; Hirokawa, G.; Goto, Y.; Nonogi, H.; Iwai, N. Plasma microRNA 499 as a biomarker of acute myocardial infarction. Clin. Chem. 2010, 56, 1183–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lippi, G.; Mattiuzzi, C.; Cervellin, G. Circulating microRNAs (miRs) for diagnosing acute myocardial infarction: Meta-analysis of available studies. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 167, 277–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olivieri, F.; Antonicelli, R.; Lorenzi, M.; D’Alessandra, Y.; Lazzarini, R.; Santini, G.; Spazzafumo, L.; Lisa, R.; La Sala, L.; Galeazzi, R.; et al. Diagnostic potential of circulating miR-122-499–5p in elderly patients with acute non ST-elevation myocardial infarction. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 167, 531–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Pei, F.; Zhu, X.; Duan, D.D.; Zeng, C. Circulating microRNAs as novel and sensitive biomarkers of acute myocardial infarction. Clin. Biochem. 2012, 45, 727–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fichtlscherer, S.; Zeiher, A.M.; Dimmeler, S. Circulating microRNAs: Biomarkers or mediators of cardiovascular diseases? Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2011, 31, 2383–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, X.; Takahashi, R.; Hiura, Y.; Hirokawa, G.; Fukushima, Y.; Iwai, N. Plasma miR-122-208 as a biomarker of myocardial injury. Clin. Chem. 2009, 55, 1944–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zampetaki, A.; Willeit, P.; Drozdov, I.; Kiechl, S.; Mayr, M. Profiling of circulating microRNAs: From single biomarkers to re-wired networks. Cardiovasc. Res. 2012, 93, 555–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nassirpour, R.; Ramaiah, S.K.; Whiteley, L.O. Nephron segment specific microRNA biomarkers of pre-clinical drug-induced renal toxicity: Opportunities and challenges. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2016, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willeit, P.; Zampetaki, A.; Dudek, K.; Kaudewitz, D.; King, A.; Kirkby, N.S.; Crosby-Nwaobi, R.; Prokopi, M.; Drozdov, I.; Langley, S.R.; et al. Circulating microRNAs as novel biomarkers for platelet activation. Circ. Res. 2013, 112, 595–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, G.; Wang, F.; Duan, Q.; Chen, F.; Yang, S.; Gong, W.; Wang, Y.; Chen, C.; Wang, D.W. Human circulating microRNA-1 and microRNA-126 as potential novel indicators for acute myocardial infarction. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2012, 8, 811–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukushima, Y.; Nakanishi, M.; Nonogi, H.; Goto, Y.; Iwai, N. Assessment of plasma miRNAs in congestive heart failure. Circ. J. 2011, 75, 336–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, M.A. Anatomy and physiology of the kidney. AORN J. 1998, 68, 799–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Koo, S.; White, N.; Peralta, E.; Esau, C.; Dean, N.M.; Perera, R.J. Development of a micro-array to detect human and mouse microRNAs and characterization of expression in human organs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, e188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, M.; Liu, Y.; Mladinov, D.; Cowley, A.W., Jr.; Trivedi, H.; Fang, Y.; Xu, X.; Ding, X.; Tian, Z. microRNA: A new frontier in kidney and blood pressure research. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2009, 297, F553–F558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Z.; Greene, A.S.; Pietrusz, J.L.; Matus, I.R.; Liang, M. MicroRNA-target pairs in the rat kidney identified by microRNA microarray, proteomic, and bioinformatic analysis. Genome Res. 2008, 18, 404–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenzen, J.M.; Kielstein, J.T.; Hafer, C.; Gupta, S.K.; Kumpers, P.; Faulhaber-Walter, R.; Haller, H.; Fliser, D.; Thum, T. Circulating miR-122-210 predicts survival in critically ill patients with acute kidney injury. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. CJASN 2011, 6, 1540–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.F.; Zha, Y.F.; Li, H.W.; Wang, F.; Bian, Q.; Lai, X.L.; Yu, G. Screening plasma miRNAs as biomarkers for renal ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. Med. Sci. Monit. Int. Med. J. Exp. Clin. Res. 2014, 20, 283–289. [Google Scholar]
- Schena, F.P.; Serino, G.; Sallustio, F. MicroRNAs in kidney diseases: New promising biomarkers for diagnosis and monitoring. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2014, 29, 755–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kito, N.; Endo, K.; Ikesue, M.; Weng, H.; Iwai, N. MiRNA profiles of tubular cells: Diagnosis of kidney injury. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 465479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, Y.F.; Chen, H.H.; Lai, P.F.; Cheng, C.F.; Huang, Y.T.; Lee, Y.C.; Chen, T.W.; Lin, H. MicroRNA-494 reduces ATF3 expression and promotes AKI. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. JASN 2012, 23, 2012–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanke, M.; Hoefig, K.; Merz, H.; Feller, A.C.; Kausch, I.; Jocham, D.; Warnecke, J.M.; Sczakiel, G. A robust methodology to study urine microRNA as tumor marker: MicroRNA-126 and microRNA-182 are related to urinary bladder cancer. Urol. Oncol. 2010, 28, 655–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, A.E.; Larner-Svensson, H.; Perry, M.M.; Campbell, G.A.; Herrick, S.E.; Adcock, I.M.; Erjefalt, J.S.; Chung, K.F.; Lindsay, M.A. microRNA expression profiling in mild asthmatic human airways and effect of corticosteroid therapy. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e5889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Weng, T.; Gou, D.; Chen, Z.; Chintagari, N.R.; Liu, L. Identification of rat lung-specific microRNAs by micoRNA microarray: Valuable discoveries for the facilitation of lung research. BMC Genom. 2007, 8, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.; Yang, L.; Wang, W.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Xu, Z. Discovery and validation of extracellular/circulating microRNAs during idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis disease progression. Gene 2015, 562, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.; Cao, J.; Wu, Y.C.; Liu, X.; Han, J.; Huang, X.C.; Jiang, L.H.; Hou, X.X.; Mao, W.M.; Ling, Z.Q. Circulating miRNAs is a potential marker for Gefitinib sensitivity and correlation with EGFR mutational status in human lung cancers. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2015, 5, 1692–1705. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Verhoeven, C.J.; Farid, W.R.R.; Ruiter, P.E.E.D.; Jonge, J.D.; Kwekkeboom, J.; Metselaar, H.J.; Tilanus, H.W.; Laan, L.J.W.V.D.; Kazemier, G. MicroRNAs in preservation solution are more predictive of graft quality than their expression in liver tissue. Liver Transplant. 2012, 18, S116. [Google Scholar]
- Verhoeven, C.J.; Farid, W.R.; de Ruiter, P.E.; Hansen, B.E.; Roest, H.P.; de Jonge, J.; Kwekkeboom, J.; Metselaar, H.J.; Tilanus, H.W.; Kazemier, G.; et al. MicroRNA profiles in graft preservation solution are predictive of ischemic-type biliary lesions after liver transplantation. J. Hepatol. 2013, 59, 1231–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapiro, M.D.; Bagley, J.; Latz, J.; Godwin, J.G.; Ge, X.; Tullius, S.G.; Iacomini, J. MicroRNA expression data reveals a signature of kidney damage following ischemia reperfusion injury. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e23011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godwin, J.G.; Ge, X.; Stephan, K.; Jurisch, A.; Tullius, S.G.; Iacomini, J. Identification of a microRNA signature of renal ischemia reperfusion injury. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 14339–14344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanak, M.A.; Takita, M.; Shahbazov, R.; Lawrence, M.C.; Chung, W.Y.; Dennison, A.R.; Levy, M.F.; Naziruddin, B. Evaluation of microRNA375 as a novel biomarker for graft damage in clinical islet transplantation. Transplantation 2015, 99, 1568–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poy, M.N.; Eliasson, L.; Krutzfeldt, J.; Kuwajima, S.; Ma, X.; Macdonald, P.E.; Pfeffer, S.; Tuschl, T.; Rajewsky, N.; Rorsman, P.; et al. A pancreatic islet-specific microRNA regulates insulin secretion. Nature 2004, 432, 226–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duong Van Huyen, J.P.; Tible, M.; Gay, A.; Guillemain, R.; Aubert, O.; Varnous, S.; Iserin, F.; Rouvier, P.; Francois, A.; Vernerey, D.; et al. MicroRNAs as non-invasive biomarkers of heart transplant rejection. Eur. Heart J. 2014, 35, 3194–3202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Y.; Shi, C.; Manduchi, E.; Civelek, M.; Davies, P.F. MicroRNA-10a regulation of proinflammatory phenotype in athero-susceptible endothelium in vivo and in vitro. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 13450–13455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lind, E.F.; Ohashi, P.S. Mir-155, a central modulator of t-cell responses. Eur. J. Immunol. 2014, 44, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suarez, Y.; Wang, C.; Manes, T.D.; Pober, J.S. Cutting edge: Tnf-induced microRNAs regulate tnf-induced expression of e-selectin and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 on human endothelial cells: Feedback control of inflammation. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Zhou, M.; Wang, Y.; Huang, W.; Qin, G.; Weintraub, N.L.; Tang, Y. MiR-122-92a inhibits vascular smooth muscle cell apoptosis: Role of the mkk4-jnk pathway. Apoptosis Int. J. Programm. Cell Death 2014, 19, 975–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenzen, J.M.; Volkmann, I.; Fiedler, J.; Schmidt, M.; Scheffner, I.; Haller, H.; Gwinner, W.; Thum, T. Urinary miR-210 as a mediator of acute t-cell mediated rejection in renal allograft recipients. Am. J. Transplant. 2011, 11, 2221–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danger, R.; Pallier, A.; Giral, M.; Martinez-Llordella, M.; Lozano, J.J.; Degauque, N.; Sanchez-Fueyo, A.; Soulillou, J.P.; Brouard, S. Upregulation of miR-122-142–3p in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of operationally tolerant patients with a renal transplant. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. JASN 2012, 23, 597–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Fraga, M.; Dominguez-Gil, B.; Capron, A.M.; Van Assche, K.; Martin, D.; Cozzi, E.; Delmonico, F.L. A needed convention against trafficking in human organs. Lancet 2014, 383, 2187–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reardon, S. New life for pig-to-human transplants. Nature 2015, 527, 152–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekser, B.; Ezzelarab, M.; Hara, H.; van der Windt, D.J.; Wijkstrom, M.; Bottino, R.; Trucco, M.; Cooper, D.K. Clinical xenotransplantation: The next medical revolution? Lancet 2012, 379, 672–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Vaught, T.D.; Boone, J.; Chen, S.H.; Phelps, C.J.; Ball, S.; Monahan, J.A.; Jobst, P.M.; McCreath, K.J.; Lamborn, A.E.; et al. Targeted disruption of the α1,3-galactosyltransferase gene in cloned pigs. Nat. Biotechnol. 2002, 20, 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phelps, C.J.; Koike, C.; Vaught, T.D.; Boone, J.; Wells, K.D.; Chen, S.H.; Ball, S.; Specht, S.M.; Polejaeva, I.A.; Monahan, J.A.; et al. Production of alpha 1,3-galactosyltransferase-deficient pigs. Science 2003, 299, 411–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, L.; Guell, M.; Niu, D.; George, H.; Lesha, E.; Grishin, D.; Aach, J.; Shrock, E.; Xu, W.; Poci, J.; et al. Genome-wide inactivation of porcine endogenous retroviruses (PERVS). Science 2015, 350, 1101–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salomon, D.R. A crispr way to block pervs—Engineering organs for transplantation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 1089–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarchum, I. Getting rid of pervs. Nat. Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, L.A.; Lee, K.C.; Palacios Jimenez, C.; Alibhai, H.; Chang, Y.M.; Leckie, P.J.; Mookerjee, R.P.; Davies, N.A.; Andreola, F.; Jalan, R. Circulating microRNAs reveal time course of organ injury in a porcine model of acetaminophen-induced acute liver failure. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0128076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, A.M.; Zheng, Y.; Jagadeeswaran, G.; Macmil, S.L.; Graham, W.B.; Roe, B.A.; Desilva, U.; Zhang, W.; Sunkar, R. Cloning, characterization and expression analysis of porcine microRNAs. BMC Genom. 2009, 10, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Li, X.; Sun, W.K.; Cheng, C.; Chen, Y.H.; Zeng, K.; Chen, X.; Gu, Y.; Gao, R.; Liu, R.; et al. Comparison of liver microRNA transcriptomes of tibetan and yorkshire pigs by deep sequencing. Gene 2016, 577, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, J.; Fang, L.; Fang, R.; Xiao, J.; Chen, X.; Zhou, A.; Zhang, Y.; Ren, L.; et al. Difference in microRNA expression and editing profile of lung tissues from different pig breeds related to immune responses to hp-prrsv. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, S.S.; Li, X.Y.; Liu, T.; Cao, J.H.; Zhong, Q.; Zhao, S.H. Discovery of porcine microRNAs in multiple tissues by a solexa deep sequencing approach. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, I.S.; Kim, J.; Seo, H.Y.; Lim do, H.; Hong, J.S.; Park, Y.H.; Park, D.C.; Hong, K.C.; Whang, K.Y.; Lee, Y.S. Cloning and characterization of microRNAs from porcine skeletal muscle and adipose tissue. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2010, 37, 3567–3574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mai, M.; Jin, L.; Tian, S.; Liu, R.; Huang, W.; Tang, Q.; Ma, J.; Jiang, A.; Wang, X.; Hu, Y.; et al. Deciphering the microRNA transcriptome of skeletal muscle during porcine development. PeerJ 2016, 4, e1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mentzel, C.M.; Anthon, C.; Jacobsen, M.J.; Karlskov-Mortensen, P.; Bruun, C.S.; Jorgensen, C.B.; Gorodkin, J.; Cirera, S.; Fredholm, M. Gender and obesity specific microRNA expression in adipose tissue from lean and obese pigs. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0131650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glazov, E.A.; Cottee, P.A.; Barris, W.C.; Moore, R.J.; Dalrymple, B.P.; Tizard, M.L. A microRNA catalog of the developing chicken embryo identified by a deep sequencing approach. Genome Res. 2008, 18, 957–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berezikov, E.; Thuemmler, F.; van Laake, L.W.; Kondova, I.; Bontrop, R.; Cuppen, E.; Plasterk, R.H. Diversity of microRNAs in human and chimpanzee brain. Nat. Genet. 2006, 38, 1375–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burnside, J.; Ouyang, M.; Anderson, A.; Bernberg, E.; Lu, C.; Meyers, B.C.; Green, P.J.; Markis, M.; Isaacs, G.; Huang, E.; et al. Deep sequencing of chicken microRNAs. BMC Genom. 2008, 9, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Cho, I.S.; Hong, J.S.; Choi, Y.K.; Kim, H.; Lee, Y.S. Identification and characterization of new microRNAs from pig. Mamm. Genome 2008, 19, 570–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timoneda, O.; Balcells, I.; Nunez, J.I.; Egea, R.; Vera, G.; Castello, A.; Tomas, A.; Sanchez, A. MiRNA expression profile analysis in kidney of different porcine breeds. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e55402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mas, V.R.; Dumur, C.I.; Scian, M.J.; Gehrau, R.C.; Maluf, D.G. MicroRNAs as biomarkers in solid organ transplantation. Am. J. Transplant. 2013, 13, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haider, B.A.; Baras, A.S.; McCall, M.N.; Hertel, J.A.; Cornish, T.C.; Halushka, M.K. A critical evaluation of microRNA biomarkers in non-neoplastic disease. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e89565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Types | Sources | Functions | Content | Size | Citation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AGO-binding | mainly necrotic cells a | byproducts | 90%–99% | unknown | [35,36] |
| exosomes | living cells | cell-to-cell communication | minority | 30–100 nm | [39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46] |
| shedding vesicles | living cells | cell-to-cell communication | minority | 0.1–1 μm | [32,53,54] |
| HDL particles | living cells | cell-to-cell communication | minority | 8–12 nm | [51] |
| apoptotic bodies | apoptotic cells | byproducts | minority b | 1–4 μm | [52] |
| Organ/Tissue | Specific/Enriched miRNAs a | Citation |
|---|---|---|
| Liver | miR-122, miR-125b, miR-16, miR-99a | [12,56] |
| Heart | miR-1, miR-126, miR-133a, miR-208, miR-296, miR-499 | [82,83,84,85,86,87,88,89,90,91] |
| Kidney | miR-192, miR-194, miR-204, miR-215, miR-216 | [101] |
| Lung | let-7b, miR-125a, miR-125b, miR-16, miR-195, miR-200c, miR-26a, miR-92 | [110,111] |
| Pancreas/Islet | miR-375 | [13,119] |
| Organ/Tissue | Specific/Enriched miRNAs a | Xeno-miRNAs | Citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Liver | miR-122, miR-153-3p, miR-194 | miR-199b* | [136,137,146] |
| Heart | miR-1, miR-133, miR-208, miR-499 | miR-199b* | [136,146] |
| Kidney | miR-125b, miR-192, miR-200a, miR-23b | unknown | [139,147] |
| Lung | let-7i, miR-143-3p, miR-145, miR-320 | miR-199b* | [138,139,146] |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, M.; Hara, H.; Dai, Y.; Mou, L.; Cooper, D.K.C.; Wu, C.; Cai, Z. Circulating Organ-Specific MicroRNAs Serve as Biomarkers in Organ-Specific Diseases: Implications for Organ Allo- and Xeno-Transplantation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1232. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17081232
Zhou M, Hara H, Dai Y, Mou L, Cooper DKC, Wu C, Cai Z. Circulating Organ-Specific MicroRNAs Serve as Biomarkers in Organ-Specific Diseases: Implications for Organ Allo- and Xeno-Transplantation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2016; 17(8):1232. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17081232
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Ming, Hidetaka Hara, Yifan Dai, Lisha Mou, David K. C. Cooper, Changyou Wu, and Zhiming Cai. 2016. "Circulating Organ-Specific MicroRNAs Serve as Biomarkers in Organ-Specific Diseases: Implications for Organ Allo- and Xeno-Transplantation" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 17, no. 8: 1232. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17081232
APA StyleZhou, M., Hara, H., Dai, Y., Mou, L., Cooper, D. K. C., Wu, C., & Cai, Z. (2016). Circulating Organ-Specific MicroRNAs Serve as Biomarkers in Organ-Specific Diseases: Implications for Organ Allo- and Xeno-Transplantation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(8), 1232. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17081232