Coordination Environment of Cu(II) Ions Bound to N-Terminal Peptide Fragments of Angiogenin Protein
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Conformational Features of Ang(1–17) and AcAng(1–17) Peptides
2.2. Far ultraviolet-Circular Dichroism (Far-UV CD) Study of Copper Complexes with Ang(1–17) and AcAng(1–17) Peptides
2.3. Speciation and Characterization of Copper Complexes with Ang(1–17) and AcAng(1–17) Peptides
2.4. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Study of Peptide-Copper Complexes
2.5. Neuroblastoma Cells Experiments
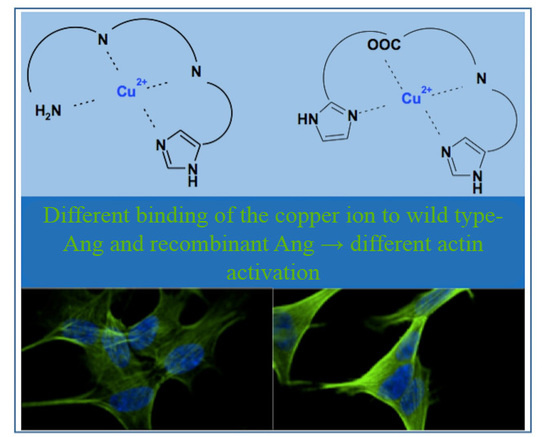
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals
4.2. Potentiometric Titrations
4.3. Ultraviolet-Visible (UV-vis) Measurements
4.4. Circular Dichroism (CD) Measurements
4.5. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy
4.6. Cellular Experiments
4.6.1. Cell Viability Assay
4.6.2. Confocal Microscopy Imaging
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Strydom, D.J.; Fett, J.W.; Lobb, R.R.; Alderman, E.M.; Bethune, J.L.; Riordan, J.F.; Vallee, B.L. Amino acid sequence of human tumor derived angiogenin. Biochemistry 1985, 24, 5486–5494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fett, J.W.; Strydom, D.J.; Lobb, R.R.; Alderman, E.M.; Bethune, J.L.; Riordan, J.F.; Vallee, B.L. Isolation and characterization of angiogenin, an angiogenic protein from human carcinoma cells. Biochemistry 1985, 24, 5480–5486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strydom, D.J. The angiogenesis. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 1998, 54, 811–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, S.A.; Subramanian, V. The angiogenins: An emerging family of ribonuclease related proteins with diverse cellular functions. Angiogenesis 1999, 3, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tello-Montoliu, A.; Patel, J.V.; Lip, G.Y. Angiogenin: A review of the pathophysiology and potential clinical applications. Thromb. Haemost. 2006, 4, 1864–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badet, J.; Soncin, F.; N’Guyen, T.; Barritault, D. In vivo and in vitro studies of angiogenin a potent angiogenic factor. Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis 1990, 1, 721–724. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sheng, J.; Xu, Z. Three decades of research on angiogenin: A review and perspective. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2016, 48, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, G.; Xu, C.; Riordan, J.F. Human angiogenin is rapidly translocated to the nucleus of human umbilical vein endothelial cells and binds to DNA. J. Cell. Biochem. 2000, 76, 452–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.P.; Tsuji, T.; Riordan, J.F.; Hu, G.F. The nuclear function of angiogenin in endothelial cells is related to rRNA production. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2002, 294, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.P.; Tsuji, T.; Riordan, J.F.; Hu, G.F. Identification and characterization of an angiogenin-binding DNA sequence that stimulates luciferase reporter gene expression. Biochemistry 2003, 42, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kishimoto, K.; Liu, S.; Tsuji, T.; Olson, A.K.; Hu, G.F. Emerging role of angiogenin in stress response and cell survival under adverse conditions. Oncogene 2005, 24, 445–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Hu, G.-F. Angiogenin-mediated rRNA transcription in cancer and neurodegeneration. Int. J. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2010, 1, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vallee, B.L.; Riordan, J.F. Organogenesis and angiogenin. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 1997, 53, 803–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Xu, Z. Mechanism of action of angiogenin. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2008, 40, 619–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Yu, D.; Xu, Z.P.; Riordan, J.F.; Hu, G.F. Angiogenin activates Erk1/2 in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001, 287, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Monti, D.M.; Hu, G. Angiogenin activates human umbilical artery smooth muscle cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001, 285, 909–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, G.F.; Riordan, J.F.; Vallee, B.L. A putative angiogenin receptor in angiogenin-responsive human endothelial cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 2204–2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.; Gao, X.; Sun, Y.; Zhou, J.; Yang, M.; Xu, Z. α-Actinin-2, a cytoskeletal protein, binds to angiogenin. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 329, 661–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Hu, H.; Zhu, J.; Xu, Z. Identification and characterization of follistatin as a novel angiogenin-binding protein. FEBS Lett. 2007, 581, 5505–5510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Gao, X.; Weng, C.; Xu, Z. Interaction between angiogenin and fibulin 1: Evidence and implication. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2008, 40, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, G.F.; Strydom, D.J.; Fett, J.W.; Riordan, J.F.; Vallee, B.L. Actin is a binding protein for angiogenin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 1217–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pyatibratov, M.G.; Tolkatchev, D.; Plamondon, J.; Xu, P.; Ni, F.; Kostyukova, A.S. Binding of human angiogenin inhibits actin polymerization. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2010, 495, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pyatibratov, M.G.; Kostyukova, A.S. New insigthts into the role of angiogenin in actin polymerization. Int. Rev. Cell Mol. Biol. 2012, 295, 175–198. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Greenway, M.J.; Andersen, P.M.; Russ, C.; Ennis, S.; Cashman, S.; Donaghy, C.; Patterson, V.; Swingler, R.; Kieran, D.; Prehn, J.; et al. ANG mutations segregate with familial and “sporadic” amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Nat. Genet. 2006, 38, 411–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Sheng, J.; Hu, J.K.; Yu, W.; Kishikawa, H.; Hu, M.G.; Shima, K.; Wu, D.; Xu, Z.; Xin, W.; et al. Ribonuclease 4 protects neuron degeneration by promoting angiogenesis, neurogenesis, and neuronal survival under stress. Angiogenesis 2013, 16, 387–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.N.; Kim, H. Decreased serum angiogenin level in Alzheimer’s disease. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2012, 38, 116–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steidinger, U.; Slone, S.R.; Ding, H.; Standaert, D.G.; Yacoubian, T.A. Angiogenin in Parkinson disease models: Role of Akt phosphorylation and evaluation of AAV-mediated angiogenin expression in MPTP treated mice. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McAuslan, B.R.; Reilly, W.G.; Hannan, G.N.; Gole, G.A. Angiogenic factors and their assay: Activity of formyl methionyl leucyl phenylalanine, adenosine diphosphate, heparin, copper, and bovine endothelium stimulating factor. Microvasc. Res. 1983, 26, 323–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, J.H.; Lutsenko, S. Copper transport in mammalian cells: Special care for a metal with special needs. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 25461–25465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, W.; James Kang, Y. Ischemia-induced copper loss and suppression of angiogenesis in the pathogenesis of myocardial infarction. Cardiovasc. Toxicol. 2013, 13, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finney, L.; Vogt, S.; Fukai, T.; Glesne, D. Copper and angiogenesis: Unravelling a relationship key to cancer progression. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2009, 36, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, K.M.; Mercer, J.F.; Chen, N.; Double, K.L. Copper dyshomeostasis in Parkinson’s disease: Implications for pathogenesis and indications for novel therapeutics. Clin. Sci. 2016, 130, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovejoy, D.B.; Guillemin, G.J. The potential for transition metal-mediated neurodegeneration in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2014, 6, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayton, S.; Lei, P.; Bush, A.I. Metallostasis in Alzheimer’s disease. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2013, 62, 76–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finney, L.; Mandava, S.; Ursos, L.; Zhang, W.; Rodi, D.; Vogt, S.; Legnini, D.; Maser, J.; Ikpatt, F.; Olopade, O.I.; et al. X-ray fluorescence microscopy reveals large-scale relocalization and extracellular translocation of cellular copper during angiogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 2247–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badet, J.; Soncin, F.; Guitton, J.D.; Lamare, O.; Cartwright, T.; Barritault, D. Specific binding of angiogenin to calf pulmonary artery endothelial cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 8427–8431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soncin, F.; Guitton, J.D.; Cartwrigh, T.; Badet, J. Interaction of human angiogenin with copper modulates angiogenin binding to endothelial cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1997, 236, 604–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Mendola, D.; Magrì, A.; Vagliasindi, L.I.; Hansson, Ö.; Bonomo, R.P.; Rizzarelli, E. Copper(II) complex formation with a linear peptide encompassing the putative cell binding site of angiogenin. Dalton Trans. 2010, 10678–10684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Mendola, D.; Farkas, D.; Bellia, F.; Magrì, A.; Travaglia, A.; Hansson, Ö.; Rizzarelli, E. Probing the copper(II) binding features of angiogenin. Similarities and differences between a N-terminus peptide fragment and the recombinant human protein. Inorg. Chem. 2012, 51, 128–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, G.F. Copper stimulates proliferation of human endothelial cells under culture. J. Cell. Biochem. 1998, 69, 326–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacomelli, C.; Trincavelli, M.L.; Satriano, C.; Hansson, Ö.; La Mendola, D.; Rizzarelli, E.; Martini, C. Copper (II) ions modulate Angiogenin activity in human endothelial cells. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2015, 60, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Mendola, D.; Arnesano, F.; Hansson, Ö.; Giacomelli, C.; Calò, V.; Mangini, V.; Magrì, A.; Bellia, F.; Trincavelli, M.L.; Martini, C.; et al. Copper binding to naturally occurring, lactam form of angiogenin differs from that to recombinant protein, affecting their activity. Metallomics 2016, 8, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kallay, C.; Varnagy, K.; Micera, G.; Sanna, D.; Sovago, I.J. Copper(II) complexes of oligopeptides containing aspartyl and glutamyl residues. Potentiometric and spectroscopic studies. Inorg. Biochem. 2005, 99, 1514–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Mendola, D.; Bonomo, R.P.; Caminati, S.; Di Natale, G.; Emmi, S.; Hansson, Ö.; Maccarrone, G.; Pappalardo, G.; Pietropaolo, A.; Rizzarelli, E. Copper(II) complexes with an avian prion N-terminal region and their potential SOD-like activity. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2009, 103, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiskoot, W.; Crommelin, D.J.A. Methods for Structural Analysis of Protein Pharmaceuticals; AAPS Press: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- La Mendola, D.; Magrì, A.; Hansson, Ö.; Bonomo, R.P.; Rizzarelli, E. Copper(II) complexes with peptide fragments encompassing the sequence 122–130 of human doppel protein. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2009, 103, 758–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pietropaolo, A.; Muccioli, L.; Zannoni, C.; La Mendola, D.; Maccarrone, G.; Pappalardo, G.; Rizzarelli, E. Unveiling the role of histidine and tyrosine residues on the conformation of the avian prion hexarepeat domain. J. Phys. Chem. B 2008, 112, 5182–5188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowalik-Jankowska, T.; Ruta-Dolejsz, M.; Wiśniewska, K.; Łankiewicz, L.; Kozłowski, H. Copper(II) complexation by human and mouse fragments (11–16) of β-amyloid peptide. J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. 2000, 4511–4519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalik-Jankowska, T.; Ruta, M.; Wiśniewska, K.; Lankiewicz, L. Coordination abilities of the 1–16 and 1–28 fragments of β-amyloid peptide towards copper(II) ions: A combined potentiometric and spectroscopic study. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2003, 95, 270–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalik-Jankowska, T.; Rajewska, A.; Wiśniewska, K.; Grzonka, Z.; Jezierska, J. Coordination abilities of N-terminal fragments of α-synuclein towards copper(II) ions: A combined potentiometric and spectroscopic study. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2005, 99, 2282–2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Mendola, D.; Magrì, A.; Campagna, T.; Campitiello, M.A.; Raiola, L.; Isernia, C.; Hansson, O.; Bonomo, R.P.; Rizzarelli, E. A doppel α-helix peptide fragment mimics the copper(II) interactions with the whole protein. Chemistry 2010, 16, 6212–6223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertini, I.; Luchinat, C.; Parigi, G.; Pierattelli, R. NMR spectroscopy of paramagnetic metalloproteins. Chembiochem 2005, 6, 1536–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Travaglia, A.; Arena, G.; Fattorusso, R.; Isernia, C.; La Mendola, D.; Malgieri, G.; Nicoletti, V.G.; Rizzarelli, E. The inorganic perspective of nerve growth factor: Interactions of Cu2+ and Zn2+ with the N-terminus fragment of nerve growth factor encompassing the recognition domain of the TrkA receptor. Chemistry 2011, 17, 3726–3738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pietropaolo, A.; Satriano, C.; Strano, G.; La Mendola, D.; Rizzarelli, E. Different zinc(II) complex species and binding modes at Aβ N-terminus drive distinct long range cross-talks in the Aβ monomers. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2015, 153, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amorini, A.M.; Bellia, F.; Di Pietro, V.; Giardina, B.; La Mendola, D.; Lazzarino, G.; Sortino, S.; Tavazzi, B.; Rizzarelli, E.; Vecchio, G. Synthesis and antioxidant activity of new homocarnosine β-cyclodextrin conjugates. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 42, 910–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gans, P.; Sabatini, A.; Vacca, A. Investigation of equilibria in solution. Determination of equilibrium constants with the HYPERQUAD suite of programs. Talanta 1996, 43, 1739–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alderighi, L.; Gans, P.; Ienco, A.; Peters, D.; Sabatini, A.; Vacca, A. Hyperquad simulation and speciation (HySS): A utility program for the investigation of equilibria involving soluble and partially soluble species. Coord. Chem. Rev. 1999, 184, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remelli, M.; Peana, M.; Medici, S.; Ostrowska, M.; Gumienna-Kontecka, E.; Zoroddu, M.A. Manganism and Parkinson’s disease: Mn(II) and Zn(II) interaction with a 30-amino acid fragment. Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 5151–5161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoroddu, M.A.; Peana, M.; Medici, S.; Anedda, R. An NMR study on nickel binding sites in Cap43 protein fragments. Dalton Trans. 2009, 28, 5523–5534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satriano, C.; Carnazza, S.; Licciardello, A.; Guglielmino, S.; Marletta, G. Cell adhesion and spreading on polymer surfaces micropatterned by ion beams. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 2003, 21, 1145–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Speciesqr | logβqr b | logβqr b |
|---|---|---|
| L = Ang(1–17) | L = AcAng(1–17) | |
| HL | 7.18 (2) | 10.89 (1) |
| H2L | 13.60 (2) | 20.90 (1) |
| H3L | 19.45 (2) | 29.87 (3) |
| H4L | 23.28 (3) | 36.39 (5) |
| H5L | 26.55 (2) | 42.34 (4) |
| H6L | - | 46.24 (5) |
| H7L | - | 49.63 (4) |
| pK COO− | 3.27 | 3.39 |
| pK COO− | 3.83 | 3.90 |
| pK His | 5.84 | 5.95 |
| pK His | 6.42 | 6.52 |
| pK NH2 | 7.18 | - |
| pK Tyr or Lys | - | 8.97 |
| pK Tyr or Lys | - | 10.01 |
| pK Tyr or Lys | - | 10.89 |
| Species (pqr) | logβpqr b L = Cu–Ang(1–17) | pK(n/m) | Species (pqr) | logβpqr b L = Cu–AcAng(1–17) | pK(n/m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CuLH | 13.23 (1) | - | CuLH4 | 40.38 (3) | - |
| CuL | 6.80 (2) | (1/0) = 6.43 | CuLH3 | 35.82 (1) | (4/3) = 4.56 |
| CuLH−1 | −1.34 (2) | (0/−1) = 8.14 | CuLH2 | 29.52 (3) | (3/2) = 6.30 |
| CuLH−2 | −10.39 (2) | (−1/−2) = 9.04 | CuLH | 23.73 (1) | (2/1) = 5.79 |
| CuLH−3 | −19.85 (2) | (−2/−3) = 9.46 | CuL | 16.35 (2) | (1/0) = 7.38 |
| CuLH−4 | −30.12 (2) | (−3/−4) = 10.25 | CuLH−1 | 7.66 (2) | (−1/0) = 8.69 |
| CuLH−5 | −40.04 (2) | (−4/−5) = 9.94 | CuLH−2 | −2.16 (2) | (−2/−1) = 9.82 |
| CuLH−3 | −12.36 (2) | (−3/−2) = 10.20 |
| L | pH | Species (CuLH) | UV-vis λ (nm) (ε, M−1·cm−1) a | CD λ (nm) (Δε, M−1·cm−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ang(1–17) | 5.5 | CuLH | 628 (90) | 265 (1.171); 298 (−1.224); 620 (−0.223) |
| 7 | CuL | 605 (95) | 264 (3.28); 299 (−1.318); 336 (0.456); 597 (−0.456) | |
| 8.5 | CuLH−1 | 574 (106) | 265 (3.847); 297 (0.305) 322 (1.051); 574 (−0.704) | |
| 9 | CuLH−1 CuLH−2 CuLH-3 | - | 263 (3.805); 315 (1.409); 563 (−0.875) | |
| 10 | CuLH−3 CuLH−3 CuLH−4 | - | 263 (3.225); 309 (1.675); 363 (−0.221); 555 (−1.023) | |
| 11 | CuLH−5 | 525 (130) | 262 (3.051); 308 (1.454); 352 (−0.314); 555 (−1.056) | |
| AcAng(1–17) | 5 | Cu (40%), CuLH4 (20%), CuLH3 (40%) | - | 619 (0.163) |
| 5.9 | CuLH3 | 650 (60) | 258 (2.518); 331 (0.304); 598 (−0.236) | |
| 6.5 | CuLH3; CuLH2; CuLH | - | 256 (7.449); 330 (0.602); 526 (0.203); 594 (−0.403) | |
| 7.5 | CuLH | 585 (105) | 262 (8.525); 323 (1.031); 365 (−0.127); 502 (−0.745); 678 (0.621) | |
| 8.3 | CuL | 540 (125) | 263 (7.999); 318 (1.143); 359 (-0.524); 500 (−1.127); 648 (0.989) | |
| 9.5 | CuLH-1; | 540 (135) | 264 (7.812); 310 (1.360); 352 (−0.791); 501 (−1.216); 641 (1.276) | |
| 10.2 | CuLH-2 | 540 (128) | 264 (7.622); 312 (1.252); 351 (−0.789); 502 (−1.192); 648 (1.262) | |
| 11 | CuLH−2; CuLH−3 | 540 (135) | 264 (7.115); 312 (1.181); 350 (−0.825); 501 (−1.161); 641 (1.269) |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Magrì, A.; Munzone, A.; Peana, M.; Medici, S.; Zoroddu, M.A.; Hansson, O.; Satriano, C.; Rizzarelli, E.; La Mendola, D. Coordination Environment of Cu(II) Ions Bound to N-Terminal Peptide Fragments of Angiogenin Protein. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1240. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17081240
Magrì A, Munzone A, Peana M, Medici S, Zoroddu MA, Hansson O, Satriano C, Rizzarelli E, La Mendola D. Coordination Environment of Cu(II) Ions Bound to N-Terminal Peptide Fragments of Angiogenin Protein. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2016; 17(8):1240. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17081240
Chicago/Turabian StyleMagrì, Antonio, Alessia Munzone, Massimiliano Peana, Serenella Medici, Maria Antonietta Zoroddu, Orjan Hansson, Cristina Satriano, Enrico Rizzarelli, and Diego La Mendola. 2016. "Coordination Environment of Cu(II) Ions Bound to N-Terminal Peptide Fragments of Angiogenin Protein" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 17, no. 8: 1240. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17081240
APA StyleMagrì, A., Munzone, A., Peana, M., Medici, S., Zoroddu, M. A., Hansson, O., Satriano, C., Rizzarelli, E., & La Mendola, D. (2016). Coordination Environment of Cu(II) Ions Bound to N-Terminal Peptide Fragments of Angiogenin Protein. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(8), 1240. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17081240